Hypochondria is a human psychopathological condition that manifests itself in constant and continuous concern and worry about one’s health. A person is afraid of getting sick with some disease, perceives his sensations as unpleasant or threatening his normal functioning.
Often hypochondriacs diagnose themselves and believe that they suffer from some incurable pathology. In other words, a person with hypochondria turns into a kind of machine that records all his sensations and interprets them into diseases and symptoms.
Causes of hypochondria
There are many hypotheses and assumptions about the causes of hypochondria. But researchers are unanimous on one thing: hypochondria occurs against the background of a depressive disorder. Scientists have shown that patients suffering from depression experience a significant increase in any complaints for which there is no physical reason.
Hypochondria also contributes to:
- disturbances in the functioning of the cerebral cortex; - distorted perception by the cortex of impulses from internal organs; — initial manifestations of delusional disorders; - a disturbance between the work of the autonomic nervous system (responsible for the autonomous functioning of organs) and the cortex.
Ministry of Health warns: fear is harmful to your health
It turns out that by worrying about our health, we only worsen our already poor health.
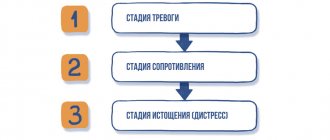
However, this is not a reason to relax and give up on your condition. On the contrary, short-term fear is even useful: fear keeps us from taking unnecessary risks and facing danger. In a state of stress, human memory works better, the sense of smell, vision and hearing become more acute, and all the forces of the body are mobilized. Only a long stay in a depressed state is harmful to our body.
The reaction to danger occurs instantly. Neural detectors sense danger and transmit a signal to the brain. The hypothalamus processes information, and the brain quickly gives the command: fight, run, pull your hand away from the fire, etc. In a state of stress, our body releases adrenaline, which is converted by muscles into energy. If it is not used up, tremor of the limbs and lips begins, and then it spreads to the whole body. Fear has a bad effect on all organs of our body and even contributes to the appearance of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels.
Fear is a disease that relaxes the soul, just as a physical illness relaxes the body. (c) Daniel Defoe
Fear, stress and depression contribute to the development of various diseases: ulcers, cancer, and the formation of metastases. Fear suppresses the immune system; a person who is constantly afraid often gets sick: either a cold, or flu, or ARVI.
Symptoms, complaints and course of the disease
Every practicing doctor has encountered hypochondriacs in his practice. People with this pathology often present all sorts of complaints, look for many diseases, and do many additional examinations. However, their results are usually absolutely normal.
Hypochondria is divided into 3 types:
1. Obsessive. 2. Super valuable. 3. Delusional.
Patients with the obsessive form are anxious and suspicious, overly concerned about the state of their health, and constantly analyze all the processes occurring in the body. An attack of hypochondria can be triggered by viewing medical advertisements or an ambiguous phrase from a doctor. Patients with the overvalued form have similar symptoms, but they are characterized by an acute psycho-emotional reaction to the slightest physical discomfort (for example, a runny nose). The most complex and severe form of hypochondria is delusional.
It is characterized by: confidence in the presence of an incurable disease, attempts to dissuade are interpreted as “even the doctors have given up on me,” there are attempts to commit suicide, as well as depression, delusions and hallucinations.
Fear has big eyes
A person, like any living creature, is afraid of pain, but this is not the only aspect of the biological fear of illness. When we think about getting seriously ill, the negative consequences of serious illnesses immediately come to mind: disability, new diseases, etc. The social aspect of the fear of getting sick is also understandable to everyone. One has only to imagine oneself bedridden, and anyone is immediately overcome by the reluctance to be a burden to others, to force loved ones to waste energy and precious time on themselves.
As biosocial creatures, people fear alienation, and serious illnesses can lead to long-term or even lifelong isolation from society. Someone is groundlessly afraid of a variety of different and unpredictable things: germs, bacteria, viruses, cancer, HIV, infection. It also comes to paradoxical situations: the fear of a heart attack provokes a rapid heartbeat and thereby increases the risk of this very attack.
The most harmful book in the house is the medical encyclopedia. Whatever disease you read about, you immediately find its symptoms in yourself (c) Jerome K. Jerome
Sometimes even a specialist cannot convince people who are confident in their illness. He conscientiously examines patients and does not find any diseases in them, while the symptoms of patients who come to him are purely somatic in nature: they are caused by imagination and self-hypnosis. Of course, such symptoms do not go away when the doctor tells the patient about his actual health, and he is left alone with thoughts about his unique and incurable disease.
Plunging into the abyss of fear does not give us any relief and only burdens our psyche with negative emotions.
Treatment of hypochondria
The tactics for correcting disorders are determined by the type of hypochondria. As a rule, treatment begins with various types of psychotherapy (Gestalt therapy, art therapy, psychoanalysis).
Medications are also used - antidepressants, tranquilizers, antipsychotics. If the patient’s symptoms are manifestations of schizophrenia, powerful antipsychotics should be used. In severe cases, hospitalization is required. Sometimes the use of alternative medicine is justified. Most often it acts as a “placebo” effect. However, if decoctions and infusions of herbs help the patient, they can and even should be included in the treatment regimen for hypochondria.
We also recommend reading the article about Haloperidol.
Don't be afraid, just do it
If, having discovered alarming symptoms, a person refuses to seek medical help, we are dealing with a mechanism of psychological defense against the troubles that the disease causes. However, refusing treatment does not solve the problem.
Another obstacle to treatment is mistrust of doctors, which provokes all sorts of wrong decisions. Which? Someone refuses a consultation, but does not refuse to purchase drugs for various purposes without having a doctor’s opinion in hand. Some people opt for healers and psychics, who allegedly find diseases in people and even treat them without medications or special equipment.
No one will give you such a detailed opinion about the state of your health except a doctor. Make an appointment. Go to several specialists in different clinics to be sure of the diagnosis and no longer doubt. If all the doctors agree, you will finally have certainty.
When you fear for your health or the health of your loved ones, go to the hospital. Let them check you there, examine you, take tests. Even cancer is curable if detected at an early stage. If you continue to be afraid and inactive, fear will accelerate the flywheel further and further. The longer we are afraid, the more difficult it is for us to overcome our fear and begin to solve the problem.
How to get rid of the fear of getting sick
Treatment of any phobia, including nosophobia, must be comprehensive and include medication, psychotherapy and independent fight against the disease.
Drug therapy
Usually the doctor prescribes 2 groups of drugs:
- Tranquilizers. Take them no longer than 2 weeks. Helps cope with mental stress.
- Sedatives. They soothe, eliminate sleep problems, relieve stress in the nervous system and help cope with irritability.
It is worth remembering that only the attending physician can choose the medicine, dosage and duration of treatment. Self-medication is dangerous.
Psychotherapy
Cognitive-behavioral methods have proven themselves to be the best. Their essence is as follows:
- The patient needs to realize the very fact of the problem and accept nosophobia as a real disease.
- A psychotherapist helps to identify the reasons for the development of fear of getting sick, works with them so that they can no longer have a traumatic effect on the psyche.
- The doctor forms positive attitudes in the patient’s mind, and also changes his attitude towards illness and his health.
During psychotherapy sessions, a person learns to control negative emotions and somatic manifestations of nosophobia.
Independent work
What is nosophobia? These are obsessive thoughts, fear of becoming infected with something. It turns out that in the fight against it, first of all, you need to learn to get rid of these thoughts. How to do it?
- Focus on recovery. Pay attention to improving your well-being, and not to the appearance of imaginary symptoms of the disease.
- Turn on your imagination and imagine complete cleansing and restoration of the body.
- Imagine how the body is saturated with oxygen.
In addition, you need to do everything to improve your health day by day. We are talking about proper nutrition, exercise, and regular walks in the fresh air. It is important to praise yourself for following such recommendations.
What else will help in the fight against nosophobia?
- As soon as you feel panic and growing anxiety, do breathing exercises. Take a deep breath, hold your breath and exhale sharply. Perform several repetitions.
- Relax while tense. This exercise also helps cope with panic. Tighten your entire body, hold your breath for a couple of seconds and relax.
- Talk to your inner self. Carry on a dialogue for at least 5 minutes. Tell us about your emotions, fears, bodily sensations. Try to calm yourself down as if you were doing it with a stranger.
And remember the most important thing - awareness significantly speeds up recovery. So don't try to make excuses for yourself. Follow your doctor's instructions exactly.
Cancer and cancerophobia
Cancer
- one of the severe forms of cancer. It has a malignant course and a poor prognosis if the disease is detected late. One of the leading causes of death in old age. According to statistics, the incidence of oncological diseases and cancer in particular in people suffering from cancerophobia is several times lower than in the general population.
This can be explained by several reasons
Firstly, people prone to phobias are usually physically healthy people and therefore diseases of internal organs are observed less frequently in them.
Secondly, due to fear for their health, they are distinguished by frequent (more than necessary) visits to doctors, examinations and tests, and therefore all their existing diseases are detected at an early stage, which allows for timely application of medical measures.
Thirdly, carcinophobes, due to their tendency to causeless anxiety, have well-developed vegetative centers that promote good capillary blood flow and, accordingly, high endurance of the body, which also determines good physical health.
How to protect yourself from cancer?
The most universal and proven method is medical examination. Regular and preventive observation by a doctor allows you to identify any disease in the early stages, cancer - at the stage of a precancerous condition. When the disease is just beginning, it is easier to cope with it.
For cancer patients, this rule becomes an obsession. They are ready, on their own initiative, to take tests for tumor markers (blood indicators indicating cancer) an infinite number of times, undergo examinations and consultations with oncologists.
How to get rid of the fear of getting cancer?
In mild cases, a consultation with a doctor is sufficient, at which it is enough to convince the patient that he does not have cancer or even a predisposition to it. It is very important if the doctor points out high anxiety and teaches how to cope with this anxiety.
Pathogenesis
The fear of death is present in the life of any person as a manifestation of the instinct of self-preservation. Everyone sooner or later thinks about death and its probable causes. Of course, the possibility of getting cancer does not make anyone happy, but still, cancerophobia as a disorder does not develop in everyone, but only in individuals with certain psychological characteristics. Natalya Ermakova in her article “In the grip of cancerophobia”* describes several types of people at risk of developing this type of fear.
- The person feels unwell, and numerous examinations do not reveal any diseases that could explain his poor health. There are indeed many cases of cancer, the media constantly report that one or another famous person (or an ordinary person) died from this disease, and everyone is always surrounded by cancer patients. Therefore, a person develops and gradually strengthens the idea that he has cancer.
- Those who have a family history of cancer are also susceptible to cancerophobia. Their risk of developing cancer is indeed higher than that of everyone else, but the likelihood of developing the disease is by no means one hundred percent.
- Another option is a personal history of cancer. The treatment was once successfully carried out, but the person continues to live with the thought that something was missed, abandoned, or not completed.
To this list I would also add the fears of doctors, whose cancer phobia illustrates the truth “Many knowledge - many sorrows.”
According to my observations, people aged 30-40 years who have not achieved great success in professional and family life are more often susceptible to cancerophobia. Cancerophobes are characterized by a high level of anxiety, usually in combination with hidden depression. The latter does not manifest itself as a clear decrease in mood; its symptoms look like somatic problems - various dysfunctions and vague pain. Since such symptoms cannot be treated with traditional means, patients begin to abuse analgesics, which do not solve the problem of chronic pain, but cause addiction. The symptoms that persist, despite all the tricks, ultimately form in the patient the idea that he has a serious incurable disease.
Those suffering from chronic pain syndrome due to degenerative and chronic diseases, the consequences of trauma, also often experience depressive disorders, and may develop a pathological fear of cancer.
Many people suffering from cancerophobia are aware of their disorder, but cannot cope with it. Very often they need professional psychological and even psychiatric help.
In addition to anxiety, cancerophobes have one more common feature: they are all suggestible and leader-dependent, therefore they often unconditionally believe various charlatan gurus and are consumers of dietary supplements advertised as means of preventing and treating cancer, and frankly dangerous drugs like vituride - a mixture of sublimate with grape wine.
According to the results of a study by the RBC agency. research, the volume of the Russian market of dietary supplements in 2011 was about $1.5-2.3 billion. And if the love for dietary supplements mainly harms the wallet and does not have a significant impact on health, then the passion for urine therapy or ingesting hydrogen peroxide clearly benefits the body doesn't bring. Recovery using such methods, as a rule, does not eliminate cancerophobia. On the contrary, people become dependent on alternative medicine and real health problems that arise are treated using their favorite methods with predictable results.
Clinic
The symptoms of cancerophobia are extremely varied. It can look like a reactive state (the easiest option), persistent neurosis and even psychosis with hallucinatory-delusional disorders.
Cancerophobia neurosis can be expressed to varying degrees (according to an interview with Alexander Methodovsky, deputy chief physician for medical work at the St. Petersburg City Clinical Oncology Center; AiF, 2010):
- A person is afraid of cancer, but does not take any action. Although the thought of a possible illness often arises in him, he is able to pull himself together and not subject his entire life to diagnostic searches.
- The person is afraid of cancer and is constantly being examined. Although he understands that his suspicions are not supported by anything, he cannot cope with them. He constantly imagines what will happen when he dies, feels sorry for his children and other relatives, is anxious, and suffers from insomnia.
- A person is afraid of cancer, is constantly examined, takes “preventive” medications, eats kilograms of cauliflower and pineapples, because he read that they prevent the occurrence of malignant diseases, and generally adheres fanatically to a healthy lifestyle.
- A man is sure that he has cancer, which doctors simply cannot detect, and no one understands his torment and suffering. People often hate them because they don't have cancer and don't know what it's like. Perhaps he is convinced that his tumor was found a long time ago, but is being hidden.
- There is another option. A person is so afraid of discovering a tumor that he deliberately avoids going to the doctor and undergoing examinations aimed at identifying the tumor. Essentially, this is an animal reaction at the level of instinct - to hide or run away when danger arises. Sometimes the fear of cancer is so great that people do not go to the doctor even if they observe frightening symptoms.
Phobia of getting sick
The term "phobia" means a strong obsessive experience and is directed towards a person, an object that may or may not be dangerous. A phobia does not depend on real danger. This word comes from the Greek word Phobos, which means panic. In Greek mythology, Phobos, who was the son of Aphrodite (goddess of love) and Ares (god of war), personified fear. Alexander the Great always prayed to Phobos before battle to get rid of his horrors.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V) lists nosophobia under phobias.
DSM-V diagnostic criteria for defining a phobia
- Intense anxiety about a specific object (eg, flying, heights, animals, injections, the sight of blood). Note: In children, the experience is expressed by crying, hysterics, catatonic manifestations or clinging.
- The phobic object almost always causes immediate suffering.
- The phobic object or situation is actively avoided or experienced with intense distress.
- Signs of suffering are not commensurate with the real danger posed by the object or situation and with the sociocultural context.
- Persistent anxiety, fear, or avoidance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. For example, a person refuses a job that involves constant flying due to fears of flying, or cannot undergo a medical examination using MRI due to claustrophobia.
- Avoidance is persistent, usually lasting for 6 months or more.
Main forms of nosophobia
There are several forms of nosophobia. Their name depends on what disease the patient fears:
- Cardiophobia - heart disease;
- heart attack phobia - heart attack;
- anginophobia - angina attacks;
- cancerophobia/oncophobia - fear of encountering cancer;
- Diabetophobia - disorders associated with diabetes mellitus;
- speedophobia - AIDS;
- syphilophobia - syphilis;
- Dementophobia - dementia.
According to psychologists, the most common are cardiophobia and cancerophobia.