Useful articles
Stress, as a complex of psychophysical reactions to strong irritation, is considered the norm. One speaks of pathology if stress reactions occur frequently, and not to excessive stimuli, but to quite ordinary ones. Over time, the process becomes chronic. A person begins to live constantly under conditions of severe mental overstrain. As a result, severe psychopathology develops. In this case, treatment for prolonged stress is required. A stressful chronic condition can result in the development of neuroses, depression and more severe mental ailments.
What is stress and where does it come from?
We are accustomed to perceiving stress as something negative, but in fact it is simply a reaction of the body, a response to overstrain, strong emotions, both positive and with a negative connotation. In this condition, the hormone adrenaline is actively produced, forcing a person to think about the situation and look for a way out of it. Causes of stress can be :
- conflicts with colleagues, relatives, friends;
- dissatisfaction with yourself, your achievements or appearance;
- constant lack of money, debts;
- routine lifestyle without vacation, proper rest;
- illness or death of a loved one;
- job loss;
- loneliness.
Recently, stressful conditions have often developed against the backdrop of the coronavirus pandemic. This is caused by a constant fear of getting sick, a strong concern for loved ones, and the inability to maintain the usual way of life.
How does stress develop?
But when stress occurs too often or exceeds the body’s capabilities, it begins to weaken and lose strength.
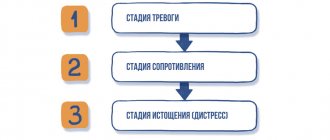
It can even lead to serious illness. three phases in the development of stress :
- mobilization of the body's defenses and resources to combat the stress factor. At this stage, hormones are released that give a boost of energy;
- confrontation - searching for a way out of the situation. The body tries to return to normal functioning due to hormonal changes;
- exhaustion – with prolonged exposure to traumatic circumstances, the body loses the ability to resist, adapt and becomes vulnerable to all kinds of diseases.
The severity of each stage depends on the individual characteristics of the person, his state of health, type of temperament, character.
Factors contributing to the development of chronic stress
Among the reasons it should be noted:
- intense and long-lasting emotions (fears, loss of loved ones, problems at work, in the family, etc.), psychophysical overloads that the psyche of a particular person is not able to cope with;
- impasse (eg serious financial problems);
- passion for some activity that, unnoticed by the patient, takes all his strength and creates insomnia and health problems;
- psychasthenic structure of the psyche and body, in which stimuli that are adequate for other people create pronounced stress in the psychasthenic;
- borderline mental pathologies (neuroses), which are both the outcome of chronic stress and its causes;
- long-term chronic diseases of the body leading to mental exhaustion.
Symptoms and signs of stress
There are a number of symptoms that
appear in most people who find themselves in a state of stress. Physiologically this manifests itself in:
- a sharp drop or, conversely, an increase in pressure;
- attacks of chills or fever;
- increased sweating;
- dizziness;
- digestive disorders;
- significant weight gain or loss;
- muscle hypertonicity and tremor (shaking).
Headaches, pain in the stomach and back often occur, and rashes similar to allergic ones may appear. Stress is accompanied by loss of sleep and appetite .
Doctors identify 7 physiological symptoms
Official medicine associates stress with a long list of physiological symptoms. Let us dwell on the most important of them, which cannot be ignored.
Headache
When we have a headache, we usually think it is a reaction to the weather or overwork. More medically advanced people blame bad blood vessels or high blood pressure. However, they forget that vasospasm and surges in blood pressure can also be triggered by stress.
Chronic pain
The mechanism of long-lasting pain may be of a stressful nature. The brain seems to “remember” that it is necessary to send pain impulses to a specific place. The stress hormone cortisol is to blame for this, which prevents you from being distracted and “forgetting” about the pain. If a person is calm, he relaxes, experiences pleasant emotions and pain subsides, but in a state of prolonged stress this does not happen.
Frequent illnesses
If colds are frequent in your home, perhaps it is not the bad climate that is to blame, but prolonged stress. Excessive emotional stress damages our immune system and makes us more susceptible to infections. In one medical study, subjects were divided into groups with high or low stress levels. Over six months, people with increased stress had 70% more respiratory infections. This topic is covered in detail in the book “Stress and acute respiratory infections” by N. Graham, R. Douglas.
Sleep disorders
Stress affects sleep patterns depending on the individual characteristics of the body. Some suffer from insomnia, while others, on the contrary, are overcome by excessive drowsiness. Due to shallow sleep, there is no feeling of complete rest when waking up. The most typical situation is early awakening, when a person cannot fall asleep due to anxious thoughts about the situation that worries him. You can learn more about the causes of insomnia and ways to combat it here
Changing eating habits
Stress also affects appetite in different ways. Some people experience emotional hunger; they literally “eat up” problems. Nervous overload and negative mood cause a passionate desire to eat “something tasty”: fast food, sweets, exotic dishes. As a result, extra pounds are not long in coming. The opposite case also occurs when, under stress, a person loses his appetite and suddenly loses weight.
Digestive problems
Against the background of nervous tension, the digestive system is one of the first to suffer. Trouble is indicated by a feeling of heaviness and pain in the abdomen, heartburn, and abnormal bowel movements. The most common diagnoses that doctors associate with uncontrolled stress: gastritis, irritable bowel syndrome, peptic ulcer.
Decreased libido
Many people experience decreased sexual desire during stressful periods. This is especially true for the fair half of humanity. The study “Chronic Stress and Sexual Function in Women” by American psychologists L. Hamilton and S. Meston draws a connection between high levels of stress and decreased sexual arousal.
Other signs
In addition to physiological changes, doctors identify emotional symptoms. Nervousness, irritability, anxiety for no apparent reason, attacks of melancholy and apathy, feelings of guilt and dissatisfaction with oneself are just the tip of the “stress” iceberg. Our physiology and psyche are inextricably linked; it is not without reason that people say that “all diseases come from nerves.”
A person exhausted by unpleasant symptoms changes his behavior. When emotional resources are depleted, this inevitably leads to increased conflict with others, absent-mindedness at work, and the emergence of bad habits. Stress also affects the intellectual area, causing loss of concentration, forgetfulness, and difficulty making responsible decisions.
How does stress affect the body?
Severe or prolonged stress may well cause the development of diseases.
In this case, the most weakened systems of the body suffer, so the consequences vary from person to person. Against the background of a stressful state, the following may develop :
- bronchial asthma due to constant tension of the muscles involved in the respiratory system;
- hypertension, heart and vascular diseases due to constantly high blood pressure and rapid heartbeat;
- peptic ulcer;
- neurotic and depressive disorders;
- damage to the gastric mucosa due to increased production of gastric juice;
- diabetes – due to the liver releasing an additional portion of glucose and increasing its concentration in the blood;
- gynecological problems up to infertility.
It is impossible to predict exactly what problems stress will provoke. Moreover, they can appear individually or in groups, or all at once, in a complex.
What signs indicate chronic stress?
Signs of Chronic Stress
Symptoms of stress fall into four categories:
Physiological symptoms
They manifest themselves in increased blood pressure, chest pain, migraines, insomnia, decreased appetite or, conversely, its excessive increase. The person feels apathy, fatigue and weakness. He loses interest in the opposite sex.
Social symptoms
They are expressed in increased conflict, sometimes out of nowhere. Often the “victims” become close and dear people, upon whom accumulated tension and anger fall.
Emotional symptoms
They manifest themselves in aggression or tearfulness, irritability. A person experiences sudden outbursts of anger, and his or her mood may change dramatically.
Cognitive signs
This is a decrease in concentration, memory impairment. At the same time, the criticality of thinking and the perception of new information changes. A person copes worse with problems and tasks, loses professional skills.
Stress has a destructive effect on the entire body, not just on the emotional state and cognitive functions. Our entire body is permeated with nerve endings. If it begins to affect the nervous system, chaotic signals can go throughout the body, all depending on what is actually happening in the body. For example, your shoulder may hurt even though there is no damage to it.
Nerve endings are our only way of communicating with the world. Thanks to them, we feel touch, the temperature of objects, even sound and image enter our brain through nerve fibers
That is why any disorder of the nervous system affects our communication with the outside world. Our body needs stress, but its excess must be kept under control.
How to avoid stress?
The effect of serious stress on the body is clearly negative. But doctors and psychologists have perfectly studied the mechanism of development of such conditions and have found many ways to prevent and combat them. The most interesting thing is that there is nothing complicated about preventive measures. For example, the following help prevent stress :
- morning exercises, regular sports training, especially those related to water (swimming, water aerobics);
- regular rest, preferably in nature;
- reasonable planning of the working day - alternating periods of intense work and proper rest;
- healthy sleep - at least 7-8 hours a day, not once a week, but every day;
- complete nutrition.
As you can see, these are typical tips for those who want to lead a healthy lifestyle
. Hence the conclusion: it is he who is the most terrible enemy of stress.
What to do if you are under extreme stress?
Do not bring yourself to a state of severe exhaustion, be sure to monitor your condition and try to minimize the consequences. Even if it seems to you that nothing is happening to you, it is possible, and even most likely, happening.
People can fall into a state of severe emotional stress under different circumstances, it could be some kind of personal difficult problem or an unpleasant situation in life, or general panic against the backdrop of world cataclysms, and no matter how hard we try to avoid stress in such a situation, we still social creatures and even if it seems to you that there is nothing terrible, and the epidemic is not the first and the financial crisis, especially for us Russians, is already like family, the influence of the group is very strong and difficult to ignore, and the group is in severe panic. Moreover, the whole group is called Earthlings. Here's what you can do so that, on the one hand, you don't get stuck in your individual stress, or minimize its consequences, and on the other hand, you don't succumb to the strong influence of the crowd in cases where the source of your stress is a common problem:
- Turn off all news, leave one source of information that you trust. If among your friends there are those who panic a lot, overthink and escalate (this is their way of coping with the situation), turn them off too - this affects you, whether you like it or not, now there is somewhere to put psychic energy, besides consoling panickers and cleansing your own thoughts from their fears.
- Calculate all the situations that you can influence and those that you cannot. Do everything in your power; whatever you can’t influence, forget about it.
- Physical activity is just like medicine: it utilizes cortisol and promotes the production of endorphins - they are very needed now.
- Food. You ate dumplings and buns in the first days of your stress and that’s enough, go back to proper nutrition, reduce your intake of simple carbohydrates first.
- Dream. It is very important. We did such a funny study. 150 volunteers had the influenza virus injected into their noses. Then, as usual, they began to monitor them, namely how much each one slept. The analysis showed that of those who slept 5 hours or less, 50% got sick; Of those who slept 7 or more -18%, these are the consequences of lack of sleep:
- Meditation, we talk about it all the time, but it really works, just 10 minutes a day will allow you to significantly reduce stress, calm your mind, and in the future perceive information more calmly, without allowing other people’s emotions and panic to drag you into the funnel of anxiety.
- If the above does not help you get rid of the symptoms of stress, then in order to avoid the consequences, it is recommended to talk to a psychologist; as a rule, in such a situation, 1-2 sessions calm the person down, and he learns to cope with his emotions. If necessary, on our website you can do this online from the comfort of your home, through correspondence in an online chat or using an online video session.
Author: Editorial staff of the Help-Point.net portal
Start working with a psychologist right now
Start a consultation
Tags: anxiety consultation with a psychologist cost of consultation with a psychologist psychologist online test stress level test anxiety level
Share
Comments
- Comments
Loading comments...
Previous article
Psychologist online
Next article
How to help yourself?
But if you constantly worry about one thing or another, neither 8 hours of sleep nor proper nutrition will help protect you from stress.
This means you need to pay attention to your mental health. First, you need to determine exactly what exactly worries and excites you, i.e. find the cause of stress. Having identified the source of the problem for yourself, look for ways to distract yourself, switch to pleasant activities, for example, meeting with friends, reading, going to the theater or concert. It also happens that the source of stress is part of your life, and there is no way to change it. But even in such a situation, no one bothers you to change your own attitude towards circumstances. It wouldn’t hurt to analyze your experiences, but do it as if from the outside. It is quite possible that it will turn out that the events that took place are not at all worth such strong emotions. Try to focus on the positive
,
because when we are upset, life situations seem much worse than they really are.
Symptoms
Symptoms of nervous stress are as follows:
- Uncontrollable panic;
- Increased heart rate;
- Increased sweating;
- Unreasonable anxiety;
- Anxiety;
- Increased muscle tension;
- General fatigue;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Irritability;
- Loss of concentration.
Symptoms can increase gradually or suddenly fill the consciousness. Panic attacks most often do not last long. Psychologically, they are expressed by uncontrollable and inexplicable horror. Physiologically, panic is manifested by increased heart rate and sweating, chest compression, and suffocation. Nausea appears, breathing becomes shallow, and the body begins to tremble. A rise in temperature can also be a sign of a panic attack. The most obvious signs of this are anxiety and restlessness.
If all else fails
But what to do if you signed up for fitness, walk the dog for a long time every evening, go to bed no later than 23.00 and are seriously interested in knitting, but you still can’t cope with stress? First of all, don’t despair
and don’t get depressed.
If you don't know how to change a faucet, you call a plumber, right? It’s the same with stress: if you couldn’t resolve the issue on your own, contact a psychotherapy specialist .
psychotherapeutic techniques are used to combat stress ,
so you will have the opportunity to choose what suits you:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy – psychological training that allows you to identify negative thoughts, analyze them, change your behavior pattern, attitude towards a specific situation;
- art therapy – the so-called “art treatment”, which allows you to throw out emotions and understand yourself;
- auto-training – training in methods of controlling breathing and muscle tone, changing internal attitudes.
There are a lot of such methods; an experienced specialist will definitely help you choose the most suitable and effective option.