The ear is an organ of hearing that performs very important functions in the human body. It provides the perception of sounds and their conduction, as well as orientation in space. Ripple or noise in the ear are symptoms of pathological changes in the auditory analyzer, the causes of which must be urgently determined in order to begin treatment in a timely manner. When there is a constant pulsation in the ear, a person becomes irritated and nervous, sleeps and eats poorly, and becomes depressed. These signs ultimately lead to even greater health problems: hearing impairment, mental disorders.
It can pulsate in both ears simultaneously or separately in each. The pulsation in the ear can be ringing, reminiscent of clicking, or dull, almost imperceptible. It is often accompanied by a feeling of congestion. In healthy people, the cause of painless pulsation in the ears, which occurs periodically, is stressful and conflict situations, physical and psycho-emotional stress, fluctuations in pressure and body temperature. In such cases, pulsating tinnitus is not a pathology and does not require special treatment. If it is heard constantly and is accompanied by pain, incoordination of movements, and the appearance of “spots before the eyes,” you should immediately visit a doctor. Such pulsation is a manifestation of a disease, the cause of which must be determined and eliminated.
Etiology
The causes of pulsation in the ear are very diverse. These include:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the auditory analyzer,
- Closed and open head injuries,
- Vascular diseases - atherosclerosis, hypertension, various vascular malformations,
- Stress,
- Neoplasms of the head and neck,
- Wax plugs in the ears,
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics, especially ototoxic ones,
- Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,
- Hormonal surge during pregnancy, menopause,
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine,
- Daily use of headphones
- Pressure surges during air travel, diving, mountain climbing,
- The natural process of aging of the body.
Inflammatory processes and pathologies of the hearing organs
The occurrence of a pounding pulse in the ears can be provoked by disturbances in one or another part of the sound analyzer, which receives and transmits the sound signal to the brain. The following inflammatory processes and pathologies of the hearing organs can cause the appearance of such a symptom:
- sulfur plug;
- developmental anomalies;
- inflammation of the tympanic membrane and eustachian tube;
- purulent inflammation (otitis);
- disturbances in the outflow of fluid, causing an echo effect that increases pulsation.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
Persons suffering from cardiac pathology quite often experience tinnitus, reminiscent of a heartbeat. The pulsation is especially acute when the patient climbs stairs or bends forward. He feels pressure in his head, lack of air, and noise in both ears.
- With hypertension , vascular tone is disrupted, capillaries become overfilled with blood, and systemic blood flow becomes difficult. The sound of blood “friction” through the vessels is perceived by a person as a pulsating noise. “It’s as if the heart is pulsating in the ears” - this is how patients characterize this phenomenon. If a hypertensive crisis develops, the flow of blood into the vessels of the inner ear becomes uneven. This stimulates the nerve endings, which also results in pulsation in the ears.
- Atherosclerotic processes lead to loss of elasticity of the vascular wall, which ceases to contract in the same rhythm as the heart. Such pathological pulsation becomes audible. If the ear is pressed against the pillow, it becomes especially noticeable. Patients with atherosclerosis complain of regular dizziness, noise and pulsation in the head, easy fatigue, poor memory, and hypertension.
- Violation of the structure and functioning of large arteries and veins , their narrowing or stratification changes the speed and direction of blood flow, which hits the walls of blood vessels. Patients claim that their ear throbs, but it does not hurt. Small aneurysms manifest themselves as pulsations in the head. The larger the size of the protrusion, the more pronounced these unpleasant sensations are.
What preventive measures will be required?
In some cases, the following simple recommendations can prevent pulsation in the ears:
- Use headphones correctly.
- Follow the rules of hearing hygiene.
- Prevent the occurrence of inflammatory diseases of the ears (wear a scarf and hat in cold weather, avoid drafts, do not dive in dirty water, etc.).
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Correctly plan your daily diet.
- Consult a doctor in a timely manner for treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system, hearing organs, throat, nose, injuries, etc.
Diseases of the ENT organs
Pulsation in the ear can occur with diseases of the ENT organs:
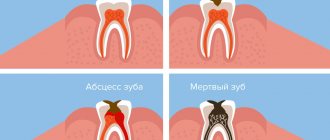
- Any part of the ear can become inflamed, as well as the Eustachian tube connecting it to the nasopharynx. Pathological changes in the auditory analyzer distort sound waves and reduce their perception. With otitis, the outflow of serous-purulent exudate is disrupted, an “echo effect” is created, internal noise increases, and blood pulsates. The patient has throbbing in the left ear due to left-sided inflammation of the auditory analyzer. If otosclerosis develops, in which the mobility of the auditory ossicles in the middle ear is impaired, then patients experience decreased hearing, dizziness and tinnitus.
- Labyrinthitis is an inflammation of the inner ear caused by the penetration of infection from chronic foci in the body. The main manifestations of labyrinthitis are vestibular disorders. In patients, coordination of movements is impaired, everything floats before the eyes, ataxia, nystagmus, and autonomic disorders occur: pallor, hyperhidrosis and dizziness. Irritation and death of sound receptors leads to pulsation in the ears, reversible hearing loss and even deafness.
- Hypersecretion of earwax often results in the formation of cerumen plugs, which must be removed promptly. Earwax blocks the ear canals, which causes hearing loss, inflammation and the appearance of pathological pulsation.
Possible complications
Pulsation in the ears and the inability to suppress it cause severe discomfort to a person. Prolonged stay in this state can cause mental disorders and lead to changes in feelings, perceptions, thinking and behavior. Complications that arise from auditory hallucinations may be the following:
- increased irritability;
- insomnia;
- memory impairment;
- impaired concentration;
- chronic fatigue;
- rarefied breathing;
- depressive state.
If the cause of noise effects in one ear is pathological processes, then the consequences of such a condition can be much more serious, even fatal. The presence of a tumor or neuroma of the auditory nerve can lead to complete or partial hearing loss. Infection of the middle ear threatens to spread the infection to other organs and systems, which is fraught with pulmonary edema and hypoxia. In the absence of timely medical assistance, complications that arise may be irreversible, so it is important to go to the hospital in time.
- Chicken liver in sour cream: recipes
- INR blood test - what is it. Norm and interpretation of INR blood test in adults and children
- Haircut with hot scissors: pros, cons, before and after photos of hair
Traumatic injuries
Brain injuries are a dangerous condition that threatens human health and life. With TBI, the blood supply to the auditory organ is disrupted, swelling and other signs of inflammation occur. This leads to dysfunction of auditory cells, disruption of sound transmission and sound perception. The throbbing and pressing headache intensifies when the victim begins to move his head.
If there is a fall or blow to the head, it is necessary to conduct a tomographic examination to rule out a concussion. This is extremely important for patients who experience increased pulsation and loudness of noise, drumming, dyspeptic symptoms, and dizziness. TBI has a severe course and serious consequences. After discharge, patients continue to complain of dizziness, pulsation in the head, and headache for a long time.
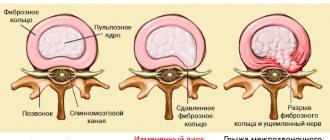
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the spine, in which deformation of the vertebrae develops. Gradually, the distance between them decreases, the nerve roots and blood vessels of the neck are compressed by osteophytes. Blood stops circulating normally, nutrition, innervation of the brain and sensory organs are disrupted.
Immediately after an exacerbation, patients complain of congestion and constant tinnitus, reminiscent of a painless pulsation. It can be sharply expressed or, conversely, practically unnoticeable. In some cases it is tolerable, and in others it is acute, preventing a person from turning his head. Constant pounding in the ear makes patients feel stiff and immobile. Light pulsation causes minor discomfort in patients and does not cause any particular problems. Such symptoms are ignored by patients and remain unnoticed until a certain moment when it is impossible to turn the head. The pulsation may subside in an advantageous position of the head and appear again during active movements.
In addition to tinnitus, patients experience pain in the back of the head and temples, insomnia, ringing, whistling, clicking and crackling in the ears, visual acuity decreases, memory deteriorates, hands become numb, and blood pressure increases.
Overwork
In healthy people, pulsating tinnitus is a sign of fatigue, exhaustion of the nervous system and chronic stress. At the end of a busy day of work, spent in a noisy and uncomfortable environment, your ears begin to throb. Intrusive noise at night prevents a person from falling asleep, relaxing and resting. Even basic sounds: the ticking of a clock, raindrops, breathing begin to irritate and seem loud. In this state, the movement of blood through the vessels is perceived as a pulsating noise. Tired people listen to everything, become depressed and begin to invent non-existent illnesses. If drug therapy does not help to cope with the problem, the help of a psychotherapist is necessary.
Other reasons
- Throbbing pain in the ears appears in patients suffering from cancer. Brain tumors and acoustic neuromas grow rapidly and compress the main neurovascular bundles of the neck. This leads to painless pulsation in the ears, unilateral hearing loss, and impaired facial expressions and speech.
- Hormonal changes occurring in the body of a pregnant woman lead to disruption of the water-electrolyte balance and swelling of the mucous membrane of the hearing organ.
- With age, atherosclerotic and degenerative processes develop in the body, the functions of auditory cells are disrupted, acoustic signals are distorted, and a constant background noise appears.
- Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease characterized by destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers and slow transmission of nerve impulses. Patients develop paralysis and paresis, breathing problems, and tinnitus.
- Depression and neuroses are manifested by psychogenic noise and pulsation in the ears. Stress, nervous tension, lack of sleep deplete the central nervous system, neurasthenia develops, which is manifested by increased fatigue, insomnia, irritability, depressive mood, pulsation and noise in the head, and headache.
- Long-term use of Gentamicin, Streptomycin, Haloperidol, Furosemide or Aspirin can cause damage to the structures of the inner ear and hearing impairment.
- Occupational hazards resulting in the development of hearing loss - increased noise levels at work, at the airfield.
- Persons with chronic sinusitis often complain that their ear is blocked and throbbing, pressing sensations appear in the head, sound perception worsens, autophony and monotonous noise appear. If the stuffy ear throbs and hurts a lot, you need to visit an ENT doctor. Since such symptoms are characteristic of otitis media, which has become a complication of inflammation of the maxillary sinus. And this is not surprising, because there is a close connection between the organs, facilitating the migration of infection.
- Poisoning with poor quality food, narcotic and sleeping pills is manifested by vomiting and diarrhea, fever, noise and pulsation in the ears, chills, lightheadedness, weakness, and convulsions.
- Alcohol abuse.
If the cause of pulsating tinnitus cannot be determined, it is called idiopathic.
What is pulsating noise in the right ear?
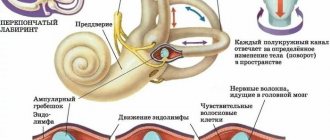
A complex paired organ located in the temporal bones of the bony part of the head is the ear. In addition to its main function (perception of sound vibrations), this organ provides balance and is responsible for the position of the body in space. Anatomically, the ear consists of three parts (outer, middle, inner), the most complex of which is the inner ear, where the receptors of the vestibular apparatus are located. The structural basis of the apparatus is a cluster of ciliated cells, the sensitive hairs of which react to changes in the position of the body in space.
Pulsating noise in the ears or in one right ear is a consequence of irritation of the hairs of the ciliated cells, as a result of which the order of nerve impulses entering the brain is disrupted and the person hears sound in the absence of an external source. This condition may indicate either short-term disorientation in space due to nervous strain or stress, or a serious pathological process occurring in the body.
In order to determine the pathogenicity of the appearance of noises, it is necessary to identify accompanying symptoms (dizziness, loss of coordination, pain) and determine the nature of the sound (dull, clicking, ringing, monophonic). This disorder cannot be ignored due to the fact that it can lead to negative health consequences, such as sleep disturbances, depression, and mental disorders.
Treatment
Pulsation in the ear is not the main disease, but just a symptom. To get rid of pulsating tinnitus, you need to find out its cause. Treatment of pathologies manifested by pathological pulsation is carried out by otolaryngologists, neurologists, angiosurgeons, and oncologists.
Experts recommend that patients follow these rules:
- Keep your ears clean, remove wax plugs,
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking tobacco,
- Massage the neck and head to quickly relieve pulsation in the ear,
- Listen to music without headphones and at low volume,
- Take sedatives and psychotropic drugs if necessary,
- Take long walks in the fresh air
- Eat more fruits and vegetables
- Exercise,
- Carry out neck exercises
- Wear hats in the cold season,
- Normalize blood pressure levels,
- Avoid colds, get treatment on time,
- Always have a good mood.
These general recommendations, together with drug therapy, will alleviate the condition of patients and help prevent the recurrence of pulsation in the ears.
General restorative therapy
- Drugs that improve microcirculation of cerebral vessels - Vinpocetine, Cerebrolysin, Piracetam,
- Medicines that normalize heart function - “Korglikon”, “Strofanthin”, “Digoxin”,
- Sedatives – “Novopassit”, “Persen”, “Tenoten”,
- Physiotherapeutic procedures - magnetic therapy, ultrasound, solux, UHF heating, microcurrent therapy, intra-ear laser treatment.
Treatment of otitis media
- Ear drops containing NSAIDs – “Otipax”, “Otinum”; containing glucocorticoids - Anauran, Polidexa; containing antibiotic – “Normax”, “Otofa”; containing an antifungal agent - “Candibiotic”.
- Antibacterial therapy is carried out after receiving the results of a microbiological study of ear discharge and determining the sensitivity of the isolated pathogen to antibiotics. Patients are usually prescribed Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Ciprofloxacin, and Cefolexin.
- Antibacterial therapy should be accompanied by the intake of probiotics - “Linex”, “Acipol”, “Bifidumbacterin”.
- Painkillers and antipyretics to reduce symptoms - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen.
- Antihistamines for relieving edema - Suprastin, Claritin, Zirtec.
- Vasoconstrictor nasal drops to facilitate nasal breathing - “Vibrocil”, “Tizin”, “Nazivin”.
- Immunomodulators – “Immunorix”, “Licopid”, “Polyoxidonium”.
This is a comprehensive treatment for otitis of various localizations, allowing you to completely get rid of this pathology, and along with it, pulsation in the ear.
Removing wax plugs
You can remove wax plugs yourself at home. First, the cork needs to be soaked. This is done by instilling a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution into the ear. After some time, they move on to removing it. A warm decoction of medicinal herbs is taken into a large syringe without a needle, which is poured into the ear canal. At the same time, the head is tilted to the side of the sore ear so that the water pours back out. For three days after washing out the plugs, anti-inflammatory drops should be dripped into the ear to prevent the development of inflammation. If the plug is loose, it can be removed using A-Cerumen ear drops. They are instilled into the ear and waited for 3-5 minutes, then placed on the affected side. Dissolved sulfur flows out on its own.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
To treat osteochondrosis, patients are prescribed NSAIDs that reduce pain and other signs of inflammation - Voltaren, Nise, Ortofen. This is the basis of therapy, which is supplemented with effective pain relief, muscle relaxation, and vitamin therapy. Patients with osteochondrosis are recommended to exercise therapy, spinal traction, massage, acupuncture, and manual therapy.
Diagnostics
A symptom alone is not able to tell the doctor what exactly is bothering his patient. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient will have to undergo examination in a clinic. Its results help the specialist identify the factor that provokes discomfort in the ear.
In case of unreasonable pulsation in the hearing organ, it is necessary to undergo the following diagnostic procedures:
- CT.
- MRI.
- Ultrasound of cerebral vessels.
- Pneumootoscopy.
- Audiometry.