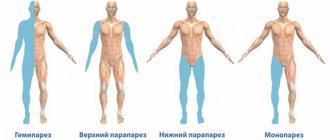
A cramp is a painful tonic spasm that is sometimes mistakenly called a cramp. Part of the muscle or the entire muscle can contract. The duration of contraction ranges from several seconds to several minutes. The syndrome develops more often at night in rest and warmth, when the opposing muscles - antagonists - are relaxed. Quite often, muscle spasms are preceded by fasciculations, clearly visible to the eye in the daytime. The attack passes with clear consciousness, there are no associated disorders. Crumpy practically does not occur in children under 8 years of age, but after 65 years of age the frequency increases sharply. In older people, tonic muscle contractions impair the quality of sleep or cause insomnia.
The frequency of muscle involvement is distributed as follows:
- muscles of the leg and foot;
- biceps brachii;
- extensors of the fingers;
- muscles of the trunk and diaphragm;
- submandibular
A distinctive feature of crampy is severe pain that occurs at the moment of muscle spasm, which stops when it ends. During spasm, the muscle becomes dense and sharply painful when touched. Every 10th person suffers from crampy on a regular basis.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,500
Make an appointment
Why does a cramp occur?
The causes are physiological (primary) and pathological (secondary). Relatively safe physiological causes are muscle strain, as well as temporary metabolic disorders.
In a healthy person, muscle cramps are provoked by the following factors:
- unusual long-term, high-intensity exercise;
- non-physiological muscle tension caused by diseases of the spine and joints of the limbs;
- alcohol abuse;
- insufficient sleep;
- smoking;
- violation of the temperature regime - overheating or hypothermia;
- water and electrolyte disturbances (excessive sweating in the heat, insufficient fluid intake, use of diuretics and medications);
Pathological causes of crampy are various diseases and conditions of the organs and nervous system. These include:
- diseases of peripheral nerves – radiculo- and polyneuropathy;
- Parkinson's disease;
- diseases of the central nervous system - spinal amyotrophy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, consequences of poliomyelitis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- liver diseases, especially chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis;
- intestinal diseases, especially viral enteritis;
- kidney disease, especially chronic renal failure with uremia;
- muscle diseases – muscular dystrophies, metabolic myopathies;
- endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, decreased function of the parathyroid glands;
- growth and development of tumors, benign and malignant;
- iron deficiency in the body;
- obliterating diseases of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- heart failure accompanied by edema;
- pregnancy.
Cramps can develop after blood purification operations - hemodialysis and plasmapheresis. In some cases, the cause of convulsive contractions cannot be detected; such conditions are called idiopathic.
There are familial forms when cramps occur in adolescence or old age for no apparent reason. Such forms have a wave-like course and spread to the muscles of the thighs and anterior abdominal wall. A spasm of the mylohyoid muscle is characteristic when, after yawning, its unilateral contraction develops. Researchers believe that the mechanism of hereditary transmission of this form is autosomal dominant. Many people associate cramps with a deficiency of vitamins B and D, as well as electrolytes.
What are the types of fascicular twitches?
There are several types of fascicular twitches:
- Ballism . Characterized by sweeping and wide movements. This form develops due to damage to the globus pallidus, striatum or subthalamic Lewis nucleus. Ballism may also be based on vascular disorders of the brain.
- Progressive hemiballismus . Appears when a volumetric intracranial formation occurs. In case of circulatory failure in the basilar artery system, transit episodes of hemiballismus are observed.
- Myorhythmias . This is the name given to the rhythmic twitching of individual muscle groups that have a permanent localization. Myorhythmias are observed in the facial area. They may indicate disinhibited or damaged reflex activity of central structures in the brain stem. An example of myorhythmias is nystagmus (tremor) of the soft palate, which occurs with multiple sclerosis or after abdominal surgery.
- Myoclonus . They are characterized by short-term, irregular twitching of individual muscles and occur suddenly. There are 3 types of myoclonus: generalized, multifocal and focal. Myoclonus can develop as a result of metabolic disorders in the body. Possible combination with epileptic seizures. Seizures are observed in degenerative, infectious and inflammatory diseases, and in postanoxic brain damage. If attacks of myoclonus are accompanied by increased sweating, we are talking about cholinergic hyperactivity. In addition, muscle contractions are observed during the transition from the waking state to the sleep state. These are so-called benign myoclonus, which should not be considered as pathology or evidence of the presence of any diseases.
- Multiple paramyoclonus . This term refers to irregular, spontaneously occurring twitching of the muscles of the shoulder girdle.
- Myokymia . May develop after treatment with certain drugs. These are contractions passing through individual muscle groups and individual muscle fibers.
- Infantile polymyoclonus . It got its name because it occurs in childhood. Infantile polymyoclonus in a child can be determined by “dancing” eye movements. Over time it tends to progress.
- Fibrillary chorea (otherwise known as multiple fibrillary myoclonus). The probable cause is exposure to mercury salts. Fibrillary chorea is characterized by chaotic and irregular contractions of individual muscle areas. It can be distinguished from other forms by the appearance of drowsiness, hallucinations and mental disorders in the patient.
- Iatrogenic fasciculations . Caused by the bites of some poisonous insects. They have been described with overdoses of anticholinergics and the use of Penicillin.
The already mentioned benign muscle fasciculations are classified as a separate group. They are characteristic of the orbicularis oculi muscle and the muscles of the leg. They can occur in a completely healthy person. Benign fasciculations can last from several minutes to several years.
In the latter case, involuntary contractions may appear at regular intervals, for example, three to four times a day. With benign fasciculations, the EMG (electromyogram) does not record excessive deviations, sensitivity is not impaired, there is no decrease in the speed of excitation along the nerve, and no changes in reflexes are observed.
Diagnostic principles
Only a doctor can distinguish a physiological reaction from a pathological condition; it is impossible to do this on your own.
You should not worry only if cramps occur rarely, no more than once a month, and the cause “lies on the surface”, there is a clear connection with physical overload, profuse sweating or other “natural” reasons mentioned above. In all other cases, you need to see a doctor as early as possible to rule out diseases or adjust your medication intake. Particularly noteworthy are long, protracted convulsive contractions that are repeated.
Sometimes muscle tightness and soreness last for several days. An indirect confirmation of long-term cramps is an increase in the level of creatine phosphokinase. Tonic spasm of the muscles of the chest or diaphragm is rare, but can create a picture of a heart or lung infarction.
Careful diagnosis is the basis for successful treatment. Due to the variety of reasons, the examination may take about a week. The diagnostic equipment of the CELT clinic allows us to identify hidden diseases that a person did not know about. An important aspect is the determination of homeostasis indicators and their possible deviations from the norm. The identified changes in water-electrolyte metabolism make it possible to quickly correct the condition.
A set of diagnostic procedures may include, if necessary, not only general clinical tests, but also electroneuromyography, studies of the function of the heart, thyroid gland, kidneys and other organs. ENMG outside an attack can reveal signs of primary muscle pathology and disruption of muscle innervation; high-frequency and amplitude potentials are recorded during muscle contraction.
It is known that cramps occur more often in people with “thick” calves or some hypertrophy of these muscles. Researchers attribute this to the large amount of myoglobin in them (the so-called “red muscles”). It is interesting that among peoples who spend a lot of time squatting and thus constantly straining their calf muscles, cramps are observed much less frequently. However, prolonged stay in this position can lead to pinching of the peroneal nerve.
Diagnostic criteria
A neurologist treats fasciculations and accompanying pathologies. If a person constantly feels muscle spasms and twitching, he should consult a doctor to determine the cause of their occurrence.
The specialist will usually ask a series of questions that will help determine whether the patient is suffering from a serious medical condition or whether the muscle twitching is benign. First of all, the doctor must know how long ago the patient started having involuntary contractions, and how long the twitching usually lasts.
The patient must also tell the doctor exactly which muscles are contracting. The doctor should also know about the nature of these contractions: rhythmic, non-rhythmic, etc. You need to tell the specialist about the presence of other symptoms and diseases, if any. If a woman knows she is pregnant, she needs to notify her doctor.
Depending on the symptoms, the doctor may prescribe one or another type of examination. In most cases, the patient undergoes an electromyogram, a nerve conduction study, and a blood test.
Our doctors
Novikova Larisa Vaganovna
Neuropathologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Pankov Alexander Rostislavovich
Neurologist
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Fasciculations: causes in polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy is characterized by multiple lesions of the peripheral nerves, in which continuous fasciculations, muscle weakness, trembling of the fingers, and impaired respiratory function occur.
Fasciculations can be caused by increased excitability of nerve endings. During fasciculation, ion channels can regulate the intensity of the manifestations of involuntary twitching. As sodium channels are blocked, fasciculations decrease with medication.
Neurologists, when treating patients with induced fasciculations, use drugs registered in the Russian Federation. A complement to drug therapy for neurological diseases is physical therapy, physiotherapy and massages performed by specialists at the Yusupov Hospital Rehabilitation Clinic.
Treatment rules
Crumpies themselves do not pose a threat to life or health. However, they are extremely painful and cause a lot of trouble. The symptoms accompanying cramps are varied, so the efforts of the doctors at the CELT clinic are aimed at identifying the underlying disease. Treatment of this disease, as well as the abolition of excess medications, can quickly improve health outcomes.
Emergency relief for pain relief consists of passive stretching of the contracted muscle or voluntary active contraction of the antagonist muscle. So, when there is a cramp in the calf muscle, you need to stand up, leaning on the irritated leg, and when the muscles of the fingers contract, straighten them with your hand.
To prevent cramps after physical activity, you need to raise your legs high from a lying position. In this position, venous outflow improves and the likelihood of convulsive contraction decreases. If electrolytes are lost through sweat or diarrhea, potassium and magnesium supplements are recommended.
Physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary method, in particular the following methods:
- physical therapy aimed at general strengthening of muscles;
- contrast water procedures, massage and hardware types of physiotherapy.
If the effect of physiotherapeutic procedures is insignificant, the doctor may prescribe medication.
Fasciculations in ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is an incurable disease, with the progression of which the patient develops muscle atrophy and weakness. Fasciculations in ALS are manifested by spontaneous, rapid and irregular muscle contractions. Fasciculations in this disease occur at the initial stage due to damage to central or peripheral motor neurons. In different forms of ALS, the frequency of fasciculations is different, but their development is accompanied by muscle weakness.
Patients who develop tongue fasciculation in ALS experience difficulty swallowing, increased salivation, and voice changes. When assessing the degree of muscle damage using electromyography, specialists identify positive fasciculations potentials, indicating chronic denervation.
Specialists at the diagnostic center of the Yusupov Hospital have the necessary skills and equipment to identify neurological diseases and their signs. Thus, during the examination, the frequency of fasciculations in ALS is determined.
Prevention
Giving up bad habits, streamlining your lifestyle and nutrition are the basic principles of prevention. Along with this, moderate physical activity is useful - walking or exercising on an exercise bike. It’s good to do simple muscle stretching exercises in your free time. At any time of the year you need to drink a sufficient amount of clean water - 30 ml per kilogram of weight in the cool season and 50 ml in the hot season.
For those who experience frequent cramps, it is advisable to reduce the consumption of drinks containing a lot of caffeine and stop smoking. When sleeping, you need to cover yourself warmly, especially keep your feet warm.
The best prevention of cramps, as well as other disorders, is an examination that can be completed at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic at any time.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions