A sudden panic attack can occur at night - before bed, during, and also in the early morning after sleep. Panic attacks during sleep are accompanied by the same symptoms as daytime vegetative crises: in addition to a strong feeling of fear, a person experiences suffocation, as if he does not have enough air, his heartbeat quickens, trembling appears in the limbs, less often - numbness, chills run through the body, and cold sweat, often during an attack there is an upset stomach, and the feeling of anxiety increases. A person has a desire to go out into the air to “breathe,” call an ambulance, or remain completely motionless under the blanket, waiting out an attack of “horror.”
Panic attacks during night sleep are often confused with a heart attack, with a normal reaction to a nightmare, or even with mild mental confusion. However, the fact that a person cannot fully rest and get enough sleep during a night’s sleep is clear evidence that the balance between the mechanisms of excitation and inhibition, for which the autonomic part of the nervous system is responsible in our body, is disturbed. At the chemical level, this process in the human body is manifested by an imbalance between the production of adrenaline, norepinephrine and acetylcholine. The production of the latter becomes insufficient to “extinguish” the stimulating effect of adrenaline on the body, which is why the above-described condition occurs.
It should be noted separately that caffeine-containing drinks consumed late in the evening or early in the morning also often cause a panic attack in patients with impaired functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
Panic attack before bed
A panic attack at night often results in insomnia. The patient cannot sleep for hours, experiencing increasing anxiety. This state develops into a feeling of extreme fear, up to the fear of going crazy and even dying.
Anxiety can arise without obvious reasons, but more often it is caused by important events of the upcoming day: a significant meeting, speech, exam, trip, etc. The attack is accompanied by obsessive thoughts: what if something doesn’t work out? What if I find myself in an awkward situation? what if I feel bad?
Any stress factors can serve as an additional catalyst that triggers the development of a panic attack at night. Thus, an unstable psycho-emotional state caused by problems in the family, at work, with money or health also creates favorable conditions for the development of night attacks. In this case, the patient is visited by obsessive thoughts related to the current state of affairs.
The patient himself may associate his “nervousness” and irrational behavior with increased emotionality and anxiety characteristic of him “in life”, and for a long time ignore his painful condition or alleviate it with the help of sleeping pills or antidepressants.
Undoubtedly, a person’s personal qualities, such as increased anxiety or emotional sensitivity, become the basis on which a disorder of the autonomic nervous system can develop. However, this is not a reason to ignore such manifestations of this disorder as panic attacks, since by letting the disease take its course, we aggravate its harmful effect on our entire body.
Thus, with a milder form of autonomic disorder, the patient may experience stomach problems only directly during his nightly “experiences.” However, in a patient whose disease is already at a more advanced stage, gastrointestinal distress is observed constantly, including during the daytime, even with the slightest mental, emotional or physical stress. That is, the body cannot withstand the systematic load at night and the lack of proper rest during night sleep, the “spring” of the ANS, which is responsible for excitation and inhibition in our nervous system, eventually completely fails and the autonomic nervous disorder progresses. Therefore, it is important to prevent the development of a disorder of the autonomic nervous system as early as possible.
Treatment
Symptoms of narcolepsy can usually be controlled or alleviated so that those with the condition experience symptoms less frequently and can lead fairly normal lives. If you are diagnosed with narcolepsy, your treatment plan will include several components: medications, behavioral therapy and the organization of certain activities in the patient's environment.
Medications.
The types, number, and severity of symptoms determine which medications need to be used to treat narcolepsy. Only a doctor can prescribe medications that can effectively control excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, hallucinations and sleep disorders.
Behavioral therapy.
Treatment for narcolepsy will likely require not only the use of medications, but also the organization of activities that will help significantly improve your feelings of well-being.
- Maintain a regular sleep and wake schedule. Go to bed and wake up at approximately the same time every day.
- Regular short periods of napping during the day may be helpful.
- Be careful when performing activities that may be dangerous, such as driving or cooking; Try to plan your schedule so that you are alert during this time.
- Carefully follow your doctor's recommendations for taking medications. Tell him or her right away about any changes or problems with your medications.
It is difficult to control narcolepsy if your family, friends and colleagues do not understand the essence of the disease. Daytime sleepiness may be mistaken for laziness, depression, or loss of ability. Signs of cataplexy or dreaming while awake may be mistakenly considered a psychiatric problem. Understanding the symptoms of narcolepsy can relieve fears, shame, anger, and depression.
Therefore, if you suffer from narcolepsy, your doctor or you yourself should talk to your family members and reassure them that your behavior is not intentional or mentally abnormal. Family support is an important step in coping with the disease.
Tell your employers about the disease. Providing certain conditions at work will allow you to remain a profitable employee. If narcolepsy is interfering with your job, consider other available sources of income. If your child has narcolepsy, make sure their teachers are aware of the condition. Small adjustments in the classroom can have a huge impact on your child's self-esteem and ability to receive a good education.
Panic attack in a dream
In the middle of the night, people with a disorder of the autonomic nervous system are often disturbed by sudden awakenings, which seem to “throw out” a person from sleep – “like a jolt.” Sudden awakenings can be accompanied by so-called “nightmarish” dreams, which are often perceived by the patient as the main cause of fear, rapid pulse, chills, sweating and other symptoms, which are actually direct symptoms of a panic attack at night.
“Nightmares” often accompany a panic attack during sleep and are direct evidence of an autonomic nervous system disorder. This phenomenon is also associated with the excessive production of adrenaline in the blood even at a time when our body is trying to tune in to rest: the harmonious unity of the chemical processes occurring in our body is disrupted, and sleep is abruptly interrupted.
Causes
The exact causes of narcolepsy are not well understood. According to a number of experts, they are based on a lack of a biologically active substance in the brain, which regulates the processes of falling asleep and waking up. Factors that contribute to the development of this disease are often skull trauma, severe debilitating infections, and severe fatigue. Sometimes the disease is associated with the function of the endocrine glands, especially with a disorder of the pituitary gland. In some cases, narcolepsy runs in families. Psychiatric and psychological problems are not the cause of narcolepsy.
Panic attack after sleep
A panic attack may occur in the early morning. Long before the alarm clock is supposed to ring, a person suddenly wakes up from a strong feeling of causeless anxiety and can no longer fall asleep. The attack is accompanied by obsessive thoughts and feelings of “being overwhelmed” and tired. A person does not feel rested, but can no longer fall asleep. Symptoms of a panic attack after sleep: a person suddenly wakes up in strong anxiety, reaching the fear of death, feels chills or, conversely, a rush of heat, the heartbeat is rapid, there is trembling in the body, a headache, nausea or diarrhea are possible.
A person who has had a panic attack before, during or after a night's sleep experiences a loss of strength in the morning and throughout the day, loses interest in life, and has a fear of leaving the house, going to work or school, that is, new panic attacks occur. attacks. At the same time, an additional burden is placed on the entire body, the psycho-emotional background worsens, and, as a result, the disease progresses. Subsequently, the patient is afraid to go to bed again, since the fear of fear itself arises, which becomes a faithful companion of night sleep. Thus, the person’s condition only worsens. Therefore, it is very important to identify and diagnose a disorder of the autonomic nervous system, manifested by a panic attack during night sleep, at an early stage of development and put your nervous system in order.
The Clinical Center for Autonomic Neurology offers innovative methods for diagnosing and treating panic attacks at night using direct physical influence on the autonomic nerve nodes using various physiotherapeutic methods. The effectiveness of this treatment has been tested over the years and with positive results from the treatment of our patients.
Treatment of panic attacks in Moscow
What's happening?
Why does the disease develop? The patency of the upper respiratory tract depends on its internal diameter, the tone of the pharyngeal muscles and the amount of negative pressure during inspiration. During sleep, when there is a significant decrease in the tone of the pharyngeal muscles, conditions are created for complete collapse of the airways. This usually occurs during inhalation, when negative pressure is formed and a force arises that helps bring the walls of the airways closer together.
When a person falls asleep, the muscles of the pharynx gradually relax. One of the next breaths leads to a complete collapse of the airways and breathing stops. To restore patency of the airways, activation of the brain is required, which must send an impulse to the pharyngeal muscles and open the airways. After breathing resumes, normal oxygen levels in the body are restored, the brain calms down and falls asleep again... the cycle repeats again.
Frequent, prolonged stops in breathing cause a sharp decrease in blood oxygen saturation. In this case, first of all, the organs that consume large amounts of oxygen are affected: the brain and heart. Constant morning headaches are a manifestation of nocturnal brain hypoxia. In the case of coronary heart disease, disturbances in blood oxygen saturation can provoke the development of dangerous arrhythmias and myocardial infarction. In addition, hypoxia disrupts the action of insulin, which can aggravate the course of diabetes mellitus.
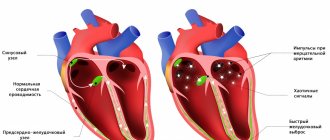
Each cessation of breathing is stress for the body, accompanied by a short-term increase in blood pressure to 200-250 mm Hg. Art. Constant nighttime episodes of increased pressure lead to chronic arterial hypertension, which often has a crisis course. This may explain the increased likelihood of developing a stroke in this category of patients. Moreover, in such cases, blood pressure is difficult to treat with conventional antihypertensive drugs.
Hypoxia and the absence of deep stages of sleep cause a decrease in the production of growth hormone, which is responsible for fat metabolism in the adult body. As you know, the food eaten is partially processed into energy, and partially stored as fat. When there is a lack of food, fat is converted into energy and consumed by the body. Growth hormone ensures the process of converting fat into energy. What happens when the secretion of this hormone is disrupted? Fat cannot be converted into energy despite its lack in the body. Thus, a person almost constantly must consume food to replenish energy expenditure. At the same time, all the resulting surplus becomes a “dead weight” that cannot be claimed. A person begins to quickly gain weight, and any efforts, dietary or medicinal, aimed at losing weight are unsuccessful.
Moreover, fat deposits at the neck level lead to further narrowing of the airways and the progression of sleep apnea disease, which in turn aggravates the lack of growth hormone. Thus, a vicious circle is created, which is almost impossible to break without special treatment. In severe forms of the disease, there is also a decrease in testosterone production, which leads to decreased libido and impotence in men.
Which doctor should I contact if I have sleep disturbances?
If self-help does not bring sufficient results or if you want to get a faster effect, then you should seek the help of a doctor. You should not delay contacting a specialist, as the sleep disorder will progress and lead to exhaustion of the body.
If you are concerned about sleep disorders, which doctor should you contact? First of all, you need the help of a psychiatrist-psychotherapist, but you may need to consult related specialists - a neurologist or psychologist. It is better to go to places that can provide the views of doctors of different specialties and a specific examination. A clinic where sleep disorders are treated must have a license and a staff of highly qualified specialists who have experience in sleep medicine. Only in this case will the patient receive a thorough and up-to-date diagnosis and different treatment options depending on the situation.
If you are looking for a clinic that deals with the problems of sleep disorders, the best person to contact will be the availability of experienced specialists with appropriate qualifications and the possibility of conducting a full examination. Diagnostics should include:
- Collecting anamnesis and clarifying habits: the doctor will identify and study the probable causes of your problem, perhaps recommend keeping a sleep diary with subsequent analysis
- Laboratory and instrumental examination: it is necessary to understand whether insomnia is a consequence of somatic problems. For example, you may need a blood test for hormones or instrumental methods for examining the brain
- Competent analysis of medications and procedures that were prescribed for other diseases
- Conducting polysomnography: this is a modern method of studying the parameters and functions of the body during sleep with subsequent analysis
If you have poor sleep, you should choose which doctor you see responsibly. Sleep disorders are a separate area of medicine that requires special knowledge and knowledge of different approaches: from behavioral therapy to a combination of different medications. Specialists without experience in caring for patients with such disorders may not be up to date with modern approaches and may not be familiar with effective treatment techniques.
Sources
- Kongsong W., Rochanavibhata S. Reoperative genioplasty: a 10-year retrospective study. // Oral Maxillofac Surg - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33905017
- Schar MS., Omari TI., Woods CM., Ferris LF., Doeltgen SH., Lushington K., Kontos A., Athanasiadis T., Cock C., Chai Coetzer CL., Eckert DJ., Ooi EH. Altered swallowing biomechanics in people with moderate-severe obstructive sleep apnea. // J Clin Sleep Med - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33904392
- Matsuzaki S., Shimada A., Tanaka J., Kothari M., Castrillon E., Iida T., Svensson P. Effect of mandibular advancement device on plasticity in corticomotor control of tongue and jaw muscles. // J Clin Sleep Med - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33904391
- Strollo PJ., Soose RJ. Personalized care of obstructive sleep apnea with hypoglossal nerve stimulation. // Sleep - 2021 - Vol44 - NSupplement_1 - p.S1-S3; PMID:33903912
- Del Brutto OH., Mera RM., Castillo PR., Recalde BY., Costa AF. Previously diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea is not associated with increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in community-dwelling older adults living in a highly endemic setting. // Clin Neurol Neurosurg - 2021 - Vol205 - NNULL - p.106639; PMID:33901750
- You A.H., Kang HY., Kim Y. The 95% effective target concentration of propofol for drug-induced sleep endoscopy in males with obstructive sleep apnea. // J Clin Anesth - 2021 - Vol72 - NNULL - p.110312; PMID:33901742
- Niroshana SMI., Zhu X., Nakamura K., Chen W. A fused-image-based approach to detect obstructive sleep apnea using a single-lead ECG and a 2D convolutional neural network. // PLoS One - 2021 - Vol16 - N4 - p.e0250618; PMID:33901251
- Alshhrani WM., Kohzuka Y., Okuno K., Hamoda MM., Fleetham JA., Almeida FR. Compliance and side effects of tongue stabilizing device in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. // Cranio - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.1-14; PMID:33899699
- Chen J., Lin S., Zeng Y. An Update on Obstructive Sleep Apnea for Atherosclerosis: Mechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment. // Front Cardiovasc Med - 2021 - Vol8 - NNULL - p.647071; PMID:33898538
- Li W., Huang K., Wen F., Cui G., Guo H., He Z., Zhao S. Intermittent hypoxia-induced downregulation of microRNA-320b promotes lung cancer tumorigenesis by increasing CDT1 via USP37. // Mol Ther Nucleic Acids - 2021 - Vol24 - NNULL - p.528-541; PMID:33898105