Pinchuk Elena Anatolyevna
Deputy chief physician for medical work, kmn, neurologist, doctor of physical and rehabilitation medicine
Lipovka Nadezhda Sergeevna
Head of the Department of Medical Rehabilitation, Physician of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Neurologist
Sobolev Arkady Igorevich
Doctor of physical and rehabilitation medicine, neurologist
As women age, the likelihood of having a stroke increases significantly. So, if in women over 60 years of age the incidence rate is 2-3%, then at the age of 75 to 80 this percentage increases to 11%. At this age, both men and women are equally at risk of stroke. Due to age-related disorders in brain tissue, cerebral infarctions and spontaneous hemorrhages develop more often. At this age, symptoms are not as pronounced as at a younger age. Symptoms may be flickering or wave-like. The lesions may be small and therefore may go unnoticed. Accordingly, prolonged treatment time will not give the expected positive effect.
It is known that during a stroke, brain cells (neurons) die. The more neurons died, the worse the consequences of the disease. Diagnosis is also complicated by the fact that it is very difficult to obtain a clinical picture in an elderly patient. Therefore, doctors use instrumental diagnostic methods - CT and MRI. Computer diagnostics will help to accurately determine the location of the lesion, its size, and whether there were other undetected microstrokes and in what quantity.
Types of stroke
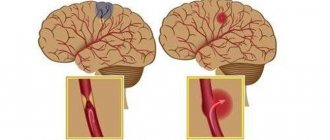
Clinicians distinguish two types of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic. The ischemic type accounts for more than 80% of all cases of the disease. It occurs due to narrowing or blockage of blood arteries, which impedes the flow of oxygen to the brain. Typically, this type of stroke occurs after age 60.
Hemorrhagic occurs when blood vessels rupture as a result of high blood pressure and bleeding in the brain. In this case, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable and the survival rate is quite low.
It is also worth highlighting transient ischemic attack (ministroke). An acute transient circulatory disorder lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, but if this is not given due importance, the consequences can be quite serious.
Differential diagnosis of different types of stroke
This type of diagnosis is performed to distinguish ischemic stroke (left hemisphere) from hemorrhagic stroke. Most often this is possible through CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Diagnostics will also make it possible to distinguish a stroke from a number of other diseases (tumors, hypertension and others). If a hemorrhagic stroke is suspected, fluid is often removed from the spinal cord. Sometimes a picture of the eyeball is taken to see if there is blood or vascular changes on the retina.
Signs of a stroke
Most often, cerebrovascular accident occurs suddenly. Symptoms include:
- Increased blood pressure.
- Strong headache.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of balance.
- Noise in ears.
- Visual impairment (loss of fields).
- Numbness of the facial muscles and limbs.
- Articulation impairment.
In addition, older women may have atypical symptoms: hiccups, fever, attacks of fear.
A stroke can develop from several hours to days. You can understand that changes in blood circulation are occurring by the occurrence of tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), attacks of fear, decreased attention, and loss of orientation.
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to seek emergency medical help. Taking timely measures will help stop cell death and avoid serious complications.
Causes of left hemisphere stroke
- Obesity. If a person is not physically active, they are at risk of stroke. In order to protect yourself from this, you should lead a healthy lifestyle: eat right, exercise regularly.
- Too much physical activity. The other side of physical activity - overexertion - can also lead to a stroke, therefore, you need to correctly calculate your strength, you cannot use up your entire energy reserve, it is important to take long breaks between workouts, and then put a sharp load on the body.
- Excessive use of medications. Oversaturation with drugs can lead not only to stroke, but also to a number of other diseases. Therefore, you should always monitor this and consult a doctor before taking medications.
- Violation of body functions that arise due to a person’s lack of physical activity (this is called physical inactivity).
- Vascular diseases and heart diseases. Normal pain can lead to a stroke if you do not see a doctor and do not follow the right treatment.
- Autoimmune diseases are pathologies that appear due to a failure of the body’s defenses.
- Diabetes.
- Vein thrombosis is a venous disease in which a blood clot (i.e. thrombus) forms in the lumen of a vessel, which leads to impaired blood circulation in this perimeter of the skin.
- Arterial hypertension is a prolonged excess of blood pressure in a calm, peaceful state.
- Age characteristics of the body. Even natural aging can cause disruption of certain functions in the body.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Smoking.
- Regular or long-term use of contraceptives.
- The appearance of vasculitis - diseases affecting the capillaries of the skin, joints, intestinal tract and kidneys.
Symptoms of a left hemisphere stroke:
- Insensitivity. Numbness in the arms and legs can be the cause of a person’s pre-stroke condition;
- Poor spatial orientation, loss of control over one’s own body;
- Unnatural facial expression. For example, the corners of the lips may be raised, which creates the feeling that the face is skewed, and the lower eyelid, on the contrary, is drooping;
- Convulsions and vomiting;
- Pain in the head that increases, prolonged dizziness;
- Blurred vision, vision deteriorates significantly;
- Speech apparatus disorder;
- Severe, prolonged pain in the chest area;
- Clouding of consciousness;
- Photophobia and sound sensitivity;
- Unjustified surges in blood pressure in the body;
- Restriction of movements.
Symptoms can also be divided into three groups:
- General symptoms. They appear due to increased pressure and disruption of the meninges. It is quite difficult to immediately understand that this is a pre-stroke condition. Only if the stroke is extensive, the signs are obvious.
- Vegetative symptoms. They occur as a result of pressure fluctuations and heartbeat disturbances. It is easier to track these symptoms because the patient’s skin color changes, panic grows, and he begins to fear death.
- Symptoms of the neurological picture of the disease. They appear due to the focus of the disease. They are accompanied by impaired sensitivity, numbness of the limbs, convulsions, loss of hearing, vision and sometimes even memory.
A stroke does not last long, only a few minutes, but sometimes, if care is not taken to treat the patient, it can be fatal. A left hemisphere stroke is accompanied by:
- paralysis of the right side of the body;
- unintelligible speech;
- short-term amnesia.
Stroke in older women
According to statistical studies, stroke occurs in 1.5-2% of the population every year, while timely medical care is provided only in 50% of cases. It is for this reason that this pathology often causes disability and death.
As a rule, women are susceptible to stroke after 60 years of age, while in men this risk occurs much earlier - after 40 years of age. This is largely due to hormonal disorders that occur in the body of women during menopause. Smoking, alcohol, long-term use of hormonal drugs, and blood clotting disorders also contribute to the development of stroke in women.
Women suffer the pathology more severely than men and only a small percentage of patients return to a normal lifestyle. The reason for this is untimely provision of medical care.
Prognosis for treatment of left hemisphere stroke
The further prognosis of a person’s life after a stroke of the left hemisphere is very individual. Much depends on age, what treatment was prescribed to the patient, whether he was given first aid, procedures during rehabilitation, adherence to the diet recommended by the doctor and sessions with a psychotherapist.
It should be noted that patients who were treated at home rather than in hospital fared significantly worse. The vast majority (about 95%) will die. Also at risk are people who faint frequently, or have problems with their mental health, muscles and joints. To prevent death due to these diseases, they also need to be given proper attention and treatment.
Five years later, many patients have a second left hemisphere stroke. If not, then the chances of a long life increase. However, this is only possible in 11% of all patients. This is why first aid, seeing a doctor, quickly taking action and rehabilitation are so important - if all these points are observed, the likelihood that the patient will fall into these 11% increases.
How to recognize a stroke
You can determine the development of a stroke by doing the following:
- Try to quickly repeat the phrase.
- Smile widely (if a stroke develops, the immobility of part of the face will be noticeable).
- Raise your arms up (if cerebral circulation is impaired, this will not be possible).
- Ask the person to show their tongue (in the case of a stroke, its tip will be deviated towards the brain lesion).
If the patient cannot pass this test, you must immediately call an ambulance, and during this time provide first aid:
- Lay the patient down, raising his head above body level.
- Provide air flow (open a window, balcony).
- Free yourself from tight clothing (unfasten your bra, belt, belt, tie, etc.).
- When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
- Measure blood pressure, pulse, record all readings.
When signs of a stroke appear, it is important to behave calmly and reassure the person, since excessive emotionality contributes to increased blood pressure.
Diagnosis of left hemisphere stroke
In order to diagnose a left hemisphere stroke before hospitalization, an experienced specialist only needs to visually assess the patient’s condition. Thanks to certain factors, he is able to notice and diagnose the disease.
List of these factors:
- Smile of a patient. The doctor should ask the patient to smile, and if one side of the mouth is higher or lower than the other, that is, the smile is skewed, this means the first sign of a left hemisphere stroke.
- Incoherent slow speech. If the patient speaks unintelligibly, illogically, with long pauses, this is also one of the signs of a left hemisphere stroke.
- Impairment of the musculoskeletal system. In the case of a stroke, the patient has poor control of his body, he has problems with movement and coordination. Often he cannot stand firmly on his feet and maintain balance, which provokes a fall.
- Semi-fainting and impaired consciousness of the patient.
- The patient complains of headache, blurred vision, double vision.
Differential diagnosis can be divided into two criteria:
- Criterion for thrombosis of a cerebral vessel. The age most often exceeds 50 years. Focal neurological symptoms often occur. Pallor is characteristic. Appears gradually. Most often occurs at night or early in the morning.
- A criterion for embolism (a process during which particles that should not occur there under normal conditions circulate in the blood and lymph) of the brain. Absolutely any age with the presence of embolism. No previous symptoms. Pallor also appears on the patient’s face. The onset of the disease occurs suddenly.
During instrumental diagnosis of a stroke in the left hemisphere, a slowdown in blood supply to brain tissue is detected, which causes poor functioning and destruction of neurons. In most cases, this occurs due to blockage of blood vessels by a blood clot.
General diagnosis of left hemisphere stroke:
- Taking an anamnesis is collecting facts about the patient’s condition from people close to him.
- Visit to a neurologist.
- Blood tests as part of laboratory diagnostics.
- Complete examination of the human body.
- Examination using computed tomography of the brain or MRI.
- ECG (electrocardiogram).
- Blood pressure measurement.
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
Risk factors
- Severe arterial hypertension. This also includes persistently high blood pressure. Pathologies are observed in 70% of elderly people. Over the course of a year, 3–4 hypertensive crises occur, which after 80 years of age often provoke a stroke.
- Atrial fibrillation (another name is atrial fibrillation). It is a heart rhythm disorder that causes uneven blood flow and blood clots in the heart. When blood clots enter the brain, they cause a stroke.
- Increased blood cholesterol levels. In older people, lipid metabolism is disrupted, as a result of which excess cholesterol begins to settle on the walls of blood vessels. Over time, blood flow becomes more difficult and, in severe cases, stops completely.
- Obesity in combination with the metabolic syndrome characteristic of the elderly (metabolic disorders, production of vital hormones and other processes). Increases the load on the heart.
- Myocardial infarction. Heart failure in people over 85 years of age. They are signs of the development of atherosclerotic processes that affect all vessels, including cerebral ones.
- Floor. There is a predisposition in females up to 80 years of age, and in males after 82 years of age.
- Alcoholism and smoking. They worsen the condition of the cardiovascular system and provoke obesity.
- Uncontrolled use of medications that affect blood circulation and the functioning of the heart muscle. For example, taking estrogen-containing contraceptives by women who smoke and have hypertension increases the risk of stroke.
- Diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle with little physical activity. Provokes slow blood circulation and obesity.
- Constant stress, increased mental stress, nervous exhaustion. Contraindicated for older people who have already had a stroke before.
Important! The presence of two or more factors in an elderly person increases the risk of a fatal stroke.
Also at risk are older people who have:
- congenital defects in the structure of the myocardium and valve apparatus;
- chronic diseases that provoke an increase in blood pressure, but are not pathologies;
- acquired defects of the cardiac folds, leading to disruption of blood flow;
- narrowing of the paired artery;
- damage to the cranial bones and soft tissues of the head;
- IHD;
- inflammatory process in the arterial vessels of the legs;
- holding your breath during sleep;
- inflammatory process of an autoimmune nature of the walls of blood vessels;
- muscle and joint diseases affecting the cardiovascular system.
The causes of a spinal stroke can be:
- injuries, surgeries and other physical impacts;
- atherosclerotic pathological processes;
- embolism.
Rehabilitation
Elderly people who have suffered a stroke must undergo a long course of rehabilitation. This period is very important, since rehabilitation will help minimize the consequences of circulatory disorders and significantly improve your overall condition.
The list of actions to restore the patient includes both physical and psychological assistance. A person must feel important and supported; only in this case will he be able to overcome the psychological discomfort associated with the partial loss of cognitive functions.
Even if the patient’s motor function is normal, it is necessary to purchase an orthopedic mattress. When a disruption in activity does occur and a person has limited physical capabilities, it is necessary to regularly change his position (to avoid bedsores).
Often, a person who has suffered a stroke is prescribed medications to normalize blood circulation. They must be taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician. If signs of apathy or aggression appear, the help of a psychologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, is necessary.
Which stroke is more dangerous: right-sided or left-sided?
When comparing right-sided and left-sided strokes, it is impossible to say for sure which one is more dangerous because each has its own consequences, but some believe that right-sided stroke entails more difficulties. When the right hemisphere is damaged, patients are unable to perform usual actions again; they have to learn walking, writing, literacy, and speech, which greatly affects social adaptation. They are also forced to relearn tactile sensations and control of their own actions and body. This takes a lot of time and effort, so some patients may give up at this stage. But people with a right-sided hemisphere stroke are less susceptible to depression and mental disorders, and this speeds up their recovery process.
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help prevent a stroke:
- Annual medical examination (cholesterol control, blood glucose levels).
- Regular blood pressure monitoring.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Sleep at least 7 hours.
- Daily walking.
- Proper nutrition (the diet should include a lot of protein, vegetables, fruits).
- Active lifestyle (exercise, yoga, swimming).
Stroke is a disease that leads to disability. To avoid it, you need to be careful about your health and lead a healthy lifestyle.