Clinical manifestations
Regardless of the nature of its occurrence, the clinical picture of meningitis has a set of common symptoms:
- General infectious symptoms - the most serious symptom is the occurrence of intoxication, which leads to the development of various disorders in the body (for example, hormonal disorders, water-salt disorders, etc.).
- Meningeal syndrome - this process is caused by the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the meninges. Conventionally, it is divided into general cerebral symptoms (photophobia, dizziness, headache) and meningeal symptoms (Kernig's, Brudzinski's symptoms, etc.).
- Changes in the cerebrospinal fluid (for example, with purulent meningitis, turbidity of the cerebrospinal fluid is observed, the amount of protein increases, etc.).
The essence of the problem
The inflammatory process in children is severe, affecting the central nervous system and some internal organs.
This disease occurs most often in childhood and adolescence, and failure to take timely measures can lead to death.
The disease can have a primary and secondary mechanism of infection.
In the first case, direct infection occurs through contact with a carrier of the infection, and in the second, brain damage occurs as a result of complications of diseases of other organs, when the infection is transmitted hematogenously.
Why do spots appear?
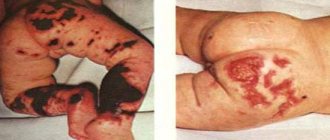
The appearance of spots on a child's skin is a very dangerous symptom of meningitis .
This phenomenon is called meningeal rash, and, as a rule, begins from the legs, gradually rising higher and higher. The main reason for the appearance of spots lies in the harmful effects of meningococci on the child’s body. As a rule, the appearance of a rash is characteristic of purulent meningitis, so it is necessary to begin treatment urgently, otherwise the consequences can be very dire.
Does it happen without fever?
It should be noted that often not always a child may experience a full set of symptoms characteristic of meningitis . In particular, an increase in body temperature is not necessary. It may remain at the same level.
IMPORTANT : However, in any case, at the slightest suspicion that a child has this disease, it is necessary to urgently contact a medical institution, since sometimes the count may not be days, but hours.
You should especially carefully monitor the condition of infants, since they cannot express in words what exactly is bothering them.
How to recognize at home?
There are several of the most striking childhood symptoms of meningitis, the appearance of which directly signals a developing disease. As mentioned above, these symptoms are called meningeal. Thus, knowing the meningeal symptoms, you can check for meningitis in your child at home . So, let's look at them in detail.
Kernig's symptom - is expressed in the fact that the patient, lying on his back with his leg bent at the knee and also at the hip joint, cannot straighten it due to the fact that the muscles of the back of the thigh are in severe spasm. At the same time, trying to bend one leg, the second also begins to reflexively bend.
Brudzinski's symptoms contain a set of signs indicating damage to the membranes of the brain.
So, there are the following 4 symptoms that can be used to identify meningitis in a child, even at home:
The upper Brudzinski symptom is expressed in the fact that when trying to bring the patient’s chin closer to the chest, there is strong resistance from the neck muscles, as well as flexion of both legs at the knee and hip joint.- The average Brudzinski symptom is when light pressure is applied to the patient’s pubic bone, and the leg is pulled toward the abdomen. This is a positive sign.
- The lower Brudzinski symptom is a kind of Kering symptom. If, when trying to bend the patient’s leg at a right angle at the knee and hip joints, the second leg involuntarily begins to be pulled towards the stomach, then, accordingly, the lower sign can be considered positive.
- Brudzinski's buccal symptom - if, when pressing on a point located just below the zygomatic arch, the patient bends the arm at the elbow joint and raises the wrist, then accordingly this sign can be considered positive.
Brudzinski's symptoms in children at an early age are usually very mild.
Ankylosing spondylitis's symptom is called the zygomatic symptom , and is expressed in the fact that when lightly tapping the cheekbones with a hammer, the patient experiences a severe headache, and a painful grimace appears on the face. This indicates pathological processes occurring in the brain.
Expert opinion
Zemlyanukhina Tatyana Vyacheslavovna
Ambulance and emergency paramedic at the Clinical Emergency Hospital #7 in Volgograd.
Ask an expert
Meningitis has its own set of symptoms by which you can determine the presence of the disease at home. But most often, especially in children, the disease begins asymptomatically or is accompanied by such nonspecific manifestations as irritability or drowsiness.
Diagnostics
To diagnose viral meningitis, a spinal tap is performed to examine the cerebrospinal fluid. During the procedure, a clear liquid flows out under pressure. Immediately after the cerebrospinal fluid is removed, the patient feels better. The punctate contains a large number of lymphocyte cells, as well as an increased protein content against the background of a normal amount of sugar. The virus cannot be detected in the cerebrospinal fluid; it is contained only in the serous membranes. An indirect sign of viral meningitis with a characteristic clinical picture will be the absence of bacteria in the cerebrospinal fluid, the appearance of which indicates bacterial meningitis.
Besides:
- A clinical blood test reveals leukocytes. In a biochemical blood test, as a rule, there is a high content of proteins, namely the globulin fraction.
- It is possible to isolate a culture of enteroviruses from feces, nasopharyngeal washings, by sowing.
To determine the specific causative agent of the disease, a serological analysis is performed, which will reveal the genus and class of the virus based on RNA components (polymerase chain reaction). This is important to exclude specific meningitis.
Symptoms in infants
REFERENCE! Meningitis in infants occurs in 1 child out of 100; children under one year of age are most often affected. Half of the sick die.
It's also worth reading about the MSD Handbook.
The first signs in children under one year old
During the incubation period of meningitis, infants develop symptoms:
- headache, bursting pain;
- body temperature rises;
- the child feels sick and vomits;
- the baby is weak, lethargic;
- drowsiness;
- the skin is unnaturally pale;
- body aches;
- bright light and loud sounds are poorly tolerated;
- constant, high-pitched crying.
When the disease begins to develop, the temperature of the infant rises quickly. In 3-4 hours it rises to 40 degrees. With timely measures taken, the temperature subsides on the third day.
Headache in the forehead, eyes, nose. At elevated temperatures, nausea and vomiting begin. The cause of vomiting is that the vomiting center of the brain swells. Vomiting is not associated with food; the child begins to vomit when he is turned over or the headaches intensify.
Main manifestations
The child refuses to eat, the respiratory rhythm is changed, and he suffers from convulsions. Consciousness is lost, the fontanel thickens. Fever, poor appetite and vomiting do not indicate that it is meningitis. Such signs are also characteristic of other diseases. An accurate diagnosis is made if there are the following symptoms of meningitis in infants:
- The neck muscles become numb.
- Buccal symptom.
- Muscles are tense.
- The baby lies on its side, head thrown back and knees bent to the stomach.
What to do if warning signs of the disease appear?
If a child under one year of age develops symptoms of meningitis, an ambulance is quickly called. Only the doctor knows what measures to take for treatment. You cannot act independently.
Why is self-medication dangerous?
Traditional methods of treatment are unacceptable. The disease is acute and passes with lightning speed. The baby’s immune system is not able to cope with the pathology on its own; self-medication methods will not bring a positive effect.
Self-medication with medications is also dangerous. There are medications that are incompatible with other medications. The dosage of the drug depends on the weight of the child; only the pediatrician can determine this accurately. The duration of taking medications is determined by the doctor.
IMPORTANT: incorrectly chosen medications lead to gastrointestinal disorders. The child feels nauseous, has problems with bowel movements, and has a bloated stomach.
If traditional treatment is not started in a timely manner, consequences and complications arise:
- excess fluid accumulates in the brain;
- intoxication of the body leads to toxic shock;
- the brain swells;
- hearing deteriorates.
In a hospital, “establishing the exact nature of the illness may take several days. This is a necessary delay, so the doctor usually prescribes an antibiotic immediately, without waiting for diagnostic results.” EMC (European Medical Center)
Prevention
Viral meningitis can be effectively prevented by observing hygiene measures, refusing to swim in a body of water, and using boiled or bottled water for drinking. To prevent infectious diseases in Russia, according to the calendar, mandatory vaccination of children against polio, measles and mumps is carried out. Vaccinations simultaneously protect children from complications of infections in the form of viral meningitis. Annual seasonal influenza vaccination is a means of preventing infection and complications of the disease.
The best method of preventing bacterial meningitis is vaccination. According to WHO guidelines, all people from 1 to 29 years of age in the African meningitis belt are immunized against meningococcus with the MenA vaccine.
As a result, we recall that the causative agent of viral meningitis is often identified as enterovirus. If neurological symptoms are positive, confirmation is made by lumbar puncture. The course and prognosis of the infection is favorable. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to follow hygiene rules and make mandatory vaccinations for children against common infections according to the Russian Calendar. Vaccination simultaneously prevents complications of viral meningitis infections.
Up to a year
First signs
The first signs of meningitis in children under one year of age are the same as in other neonatal infections:
- lethargy, weakness, passivity;
- frequent regurgitation and vomiting;
- difficulty breathing;
- breast refusal, loss of appetite;
- fluctuations in body temperature.
Infants weighing more than two kilograms may develop a sudden rise in temperature.
In premature babies, the first symptoms may not be so obvious. These are the symptoms of meningitis in children under one year of age:
- fever;
- monotonous crying;
- swelling of the fontanel.
Now you know about the signs of the disease in newborns and infants.
How to recognize houses?
Note! If there is a suspicion of meningitis, then the fontanel should be examined. When meningitis occurs, it becomes inflamed and pulsates.
You can also check for Lesage's sign. To do this, you need to grab the baby by the armpit area. If there is meningitis, the baby involuntarily pulls his legs towards his stomach and throws his head back.
Differences from ARVI
Meningitis is very dangerous because its initial symptoms also occur in less dangerous diseases. However, in the following cases, you should immediately seek professional help, because: there is a possibility that the baby fell ill with meningitis:
- prolonged headache due to a current infectious disease;
- at high temperatures, pain appears in the back and neck, which will intensify when moving the head;
- nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, confusion;
- cramps, no matter how long they lasted or how severe they were;
- a rash that appears at high temperatures.
Causes and routes of infection
The most common route of infection in children is airborne .
When communicating with an infected person, droplets of saliva can enter the respiratory organs of the child’s weakened body and begin their progressive work.
Infection through the oral-fecal route is possible when eating poorly washed vegetables and fruits, as well as when swimming in polluted water bodies.
Most often, children are susceptible to illness on warm summer days, when raw foods appear in large quantities and the swimming season begins. However, an outbreak of meningitis occurs in the spring and winter.
The infection can also be transmitted intrauterinely or transmissibly, that is, through insect bites.
The main carriers of infection are mosquitoes and ticks. The infection, settling on the walls of the intestine or on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, is sent after a certain period of time (incubation period) directly into the circulatory system. It reaches the meninges through the blood vessels and forms a focus of infection in its membrane, directly in the soft tissues. At an advanced stage of the disease, the virus reaches the cerebrospinal fluid.
Signs in children 1-2 years old
How to recognize at the initial stage?
The danger of meningitis lies in the fact that at the initial stage its manifestations are not typical and resemble the symptoms of colds. However, attentive parents can consider the disease at an early stage.
First signs
Let's talk about the signs of meningitis in children 2 years of age and under 1 year of age.
There are manifestations by which the parents of the baby may suspect the development of this infectious disease. These include:
Increased body temperature up to 40 degrees: the baby’s body reacts to the introduction of the microorganism with fever. In this case, antipyretic drugs have no effect.- Lethargy, drowsiness, loss of strength of the child.
- Pale skin and bluish nasolabial triangle.
- Development of sound and photophobia: a small patient tries to close himself off from the light source and turns away from loud sounds.
- Confused consciousness: the baby does not respond to the parents’ appeal.
- The appearance of vomiting.
- If the baby's condition worsens, seizures and spasms are likely to occur.
Basic
Inflammation of the meninges is complicated by the fact that children 1-2 years old are not able to explain their complaints to an adult. For this reason, diagnosing the disease requires extreme care so as not to miss a single sign.
General infectious syndrome
Such manifestations do not indicate the appearance of meningitis, but indicate the presence of an infectious disease in the child. These include:
- Fever with high body temperature.
- Loss of strength, lethargy.
- Extreme thirst: the baby greedily drinks large quantities of water.
- The appearance of a runny nose, redness of the throat.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
General cerebral
These symptoms in 1-year-old children are characteristic of the development of a pathological process in the brain and spinal cord . These include:
- The appearance of vomiting in the baby.
- Confusion: the child does not respond to the words of an adult.
- Headaches with the appearance of fear of light and sound: the baby covers himself with a blanket and turns to the wall.
- The occurrence of seizures associated with increased intracranial pressure.
Meningeal
To identify inflammation of the meninges, the specialist uses specific techniques that confirm meningitis. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Kernig's symptom is considered the most famous test for diagnosing the disease in children and adults. It is carried out by passive flexion of the lower limb at the hip and knee joints with the patient lying on his back. The doctor cannot straighten the leg due to excessive tension in the muscles.- Stiff neck – the doctor tries to press the chin to the chest, but instead there is resistance in the back of the head, leading to limited movement.
- Brudzinski's sign - the baby lies on his back, and the specialist flexes the knee joint of 1 lower limb. Together with it, the other leg reflexively tightens.
- Ankylosing spondylitis symptom - the doctor taps on the cheekbone of a small patient, and the facial muscles contract to form a kind of grimace. This is explained by the appearance of severe pain even with the slightest tapping.
- Mendel's sign - a specialist inserts a finger into the external auditory canal and then presses on the ear. This is accompanied by a sharp increase in headache, causing the patient to grimace in pain. The technique is especially useful in cases where classical tests raise doubts among the doctor.
- Hermann's sign: the child lies on his back with his limbs straightened. The doctor performs a passive tilt of the head, and at this time the baby’s first toe spontaneously extends.
- Flatau's symptom - in a patient with meningitis, dilated pupils are detected when the head is tilted.
For children 4 years old
In childhood, the disease manifests itself as a respiratory disease. The baby has a fever, a sore throat and a headache. The nature and strength of symptoms depends on the type of infection.
A child who is about 4 years old can tell what is bothering him, which will allow him to recognize the disease based on a number of symptoms. The first signs of meningitis are fever and headache. Other symptoms include:
- Hallucinations, confusion, delirium.
- Cramping in the abdomen, similar to an intestinal infection.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- Yellow tint to the whites and swelling of the face.
- Sore throat, redness and looseness of the palate.
- Spasms and cramps, numbness of the skin.
Principles of treatment
Treatment of the disease should begin when the first signs appear. In this case, symptomatic manifestations disappear after 4-5 days, and the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid stabilizes after 7-10 days. Self-medication is extremely dangerous, because... leads to serious complications.
Treatment should be carried out by a pediatrician with the participation of a neurologist and an infectious disease specialist. The basis of treatment is antibiotic therapy, which depends on the type of pathogen. In particular, for the bacterial form of the disease, Ceftriaxone and Meronem are prescribed. In case of viral infection, dehydration therapy is of primary importance.
We diagnose at home
The main task of parents is to promptly recognize the appearance of meningitis in a child 1-2 years old by signs and symptoms and seek qualified help from a medical institution.
We recommend using the step-by-step steps below.
Take the baby's temperature: with meningitis it is high and is accompanied by the child's lethargy and weakness.- Pay attention to the baby’s consciousness: when inflammation of the meninges develops, it is confused, and he does not make contact with an adult.
- See if there is any strange position of the baby's body. Meningitis is characterized by a peculiar position when he lies on his side for a long time, bending his knees and pressing them to his body, while his head is thrown back.
- If convulsions occur , they may indicate a serious condition.
Important! Don't wait for your child to get worse. At the slightest suspicion of the development of meningitis, consult a specialist immediately!
Differences from ARVI
Serous and meningococcal forms at an early stage often resemble colds. They are accompanied by elevated body temperature and the appearance of weakness, as with ARVI.
However, parents should be wary if the disease develops rapidly. The baby is capricious and refuses to eat. Loud noises and bright lights irritate him.
When a child has a cold, he takes a characteristic position : on his side in a lying position, he brings his legs to his stomach and throws his head back. Any change in posture is accompanied by the appearance of wild pain.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor performs tests to confirm inflammation of the meninges. The most common test for neck stiffness is that the doctor places one hand on the upper chest and the other on the back of the baby's head. Then the specialist presses on the back of the head, bending the neck, and the chin reaches the palm that lies on the chest. If a baby develops meningitis, such a test cannot be performed.
Providing first aid to a child
The first thing the baby’s parents must do is call an ambulance. There is no need to put off calling, much less try to treat your child on your own!
Remember: the faster quality, qualified assistance is provided, the greater the child’s chances of recovery.
Before the arrival of specialists, it is necessary to provide the little patient with peace, silence and darkness. You should not let your child get up.
If he needs to go to the toilet, provide a bedpan or put on a diaper. The baby should be given drinks more often. If vomiting occurs, it is necessary to turn the child's head to the side to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
The same technique should be carried out in the case when a small patient experiences convulsions. This will protect the baby during an attack from the tongue retracting and blocking the respiratory tract.