© Author: Ilya Vitalievich Soldatenkov, general practitioner, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Problems with blood vessels are one of the main reasons for the development of serious diseases, often leading to death. Vascular pathology begins to form after 40 years, causing dysfunction of internal organs and posing a danger to human health. That is why problems with blood vessels must be identified and eliminated in a timely manner.
The circulatory system is a unique structure of the human body. Its basis is the heart, which continuously pumps blood. Blood vessels form a network of hollow tubes that envelop the entire body. Due to the contraction of the vascular walls, pressure is created in the system, ensuring blood circulation. A healthy vascular system works smoothly and helps the body cope with any stress and stress. If there are disturbances in the system, the blood supply to organs and tissues deteriorates, which leads to numerous problems. In young people, the vessels are elastic, strong and smooth from the inside. With age they change and become fragile and brittle. Microcracks appear on the loose inner shell, cholesterol plaques are deposited, and blood clots form.
In terms of mortality, vascular pathology occupies one of the leading places
. Its symptoms are polymorphic and often nonspecific. The causes of vascular problems are: excess weight, poor diet and physical inactivity. Treatment of vascular diseases is complex. It is selected individually for each patient. For some people, it is enough to adjust their diet and lifestyle, while for others, surgical intervention is necessary. Vascular problems need to be addressed as soon as their first signs appear. Mild initial manifestations of pathology at first glance seem harmless. If left untreated, they can lead to a vascular accident - stroke or heart attack.
Causes
The etiopathogenetic factors of vascular problems are very diverse. The most common causes of vascular pathologies include the following six.
- Physical inactivity and weak physical activity - the myocardium and muscles of the vascular wall without stress sag, weaken, lose shape, lose elasticity and strength. When their tone decreases, blood circulation slows down.
- Poor nutrition - the predominance of unhealthy foods in the diet, as well as excess daily caloric intake leads to obesity and atherosclerosis. The lumen of blood vessels affected by cholesterol gradually narrows, and they cease to function fully. Blood flow slows down and blood clots form. Internal organs do not receive nutrition and oxygen.
- Alcohol abuse is the cause of serious problems with blood vessels and health in general. The breakdown products of alcoholic beverages poison the body and damage blood vessels, causing atrophic processes in their walls. Alcoholics are more likely to form blood clots, which stretch the vascular cavity and reduce their patency.
- Mental tension, stress, outbursts of emotions are very harmful. They create additional stress on the heart, provoking the development of tachycardia and forcing it to transport blood more intensively. Often the vessels do not cope with the task. Clinically, this is manifested by cephalgia, dizziness, paresthesia, and confusion.
- Lack of adequate sleep is a pressing problem. The body does not have enough time to fully recover and rest. The energy wasted during the day is not replenished, which leads to severe vascular dysfunction.
- Hereditary predisposition - the formation of structural or functional vascular disorders in the prenatal period. Connective tissue dysplasia and adrenal insufficiency are inherited. These processes contribute to the development of varicose veins. Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease that provokes a tendency to thrombosis. Vasculitis, endarteritis and many hereditary pathologies are manifested by vascular damage.
Diseases manifested by dysfunction of arteries and veins:
- Atherosclerosis is a metabolic disorder in which low-density cholesterol accumulates on the endothelium of the arteries and forms a plaque, causing vessel occlusion and tissue ischemia;
development of atherosclerosis and artery blockage
- Arterial hypertension is a pathological change in vascular tone associated with a violation of its neurohumoral regulation and leading to arterial spasm;
- Osteochondrosis causes compression of the arteries by overgrown osteophytes and a slowdown in blood flow;
- Vein dysfunction occurs with varicose veins and thrombophlebitis;
- Coronary insufficiency is the cause of systemic circulatory disorders;
- Intoxication due to alcoholism, drug addiction, acute infection, food poisoning;
- ARVI and infectious diseases of the ENT organs - nose, throat, ear;
- Endocrinopathies;
- TBI.
Factors predisposing to circulatory problems include:
- Staying in a stuffy room for a long time,
- Unfavorable working conditions – long periods of standing or sitting, severe physical strain,
- Living in poor environmental conditions with high air pollution leading to hypoxia,
- Very hot or cold climate.
Under the influence of these factors, self-regulation of the walls of blood vessels is disrupted, and they cease to adequately respond to changes in environmental conditions.
Symptoms and signs of vascular problems
All symptoms of vascular problems are conventionally divided into two large groups - general and local.
Weak vessels react in a special way to endogenous and exogenous stimuli. They cannot raise their tone or relax in time. This inadequate vascular response to changing environmental conditions is manifested by general, nonspecific symptoms:
- Weakness, fatigue, irritability,
- Migraines and frequent dizziness,
- Drowsiness,
- Problems with concentration,
- Weather sensitivity - a feeling of discomfort and poor health when the weather changes,
- Fluctuations in blood pressure
- Tachy or bradycardia,
- Prolonged depression
- Mnestic phenomena.
Local manifestations of vascular disorders depend on the cause and location of the lesion. Signs of problems with blood vessels in the presence of a specific pathology occur regularly and for no reason.
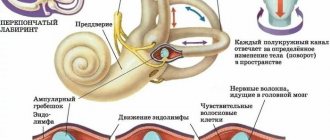
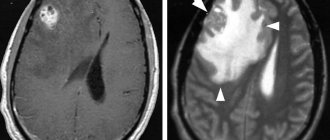
- Problems with the vessels of the neck and head are caused by their atherosclerosis, occlusion or spasm, which reduces blood flow to various brain structures. Insufficient blood supply to the central nervous system leads to the development of numerous disorders, which are manifested by general symptoms of asthenia, as well as insomnia, frequent and abrupt awakenings at night, fatigue and weakness in the morning, irritability and emotional lability, increased cravings for sweets. Patients experience white spots flashing before their eyes, noise in their ears, and nausea and vomiting. In severe cases, speech disorders occur, coordination of movements worsens, disorientation in space occurs, and fainting is possible. Dyscirculatory changes in cerebral structures are characterized by cephalalgia, memory impairment, hearing loss, weakness in the limbs, dizziness, confusion and loss of consciousness. Problems with cerebral vessels as the process progresses lead to decreased ability to work, ataxia, disruption of thinking processes, dysfunction of the pelvic organs, and in advanced cases – to paresis and paralysis.
- The coronary arteries supply blood to the myocardium. With hypoxia and ischemia of the heart muscle, the clinical picture of exertional angina occurs. Patients complain of weakness and fatigue, rapid heartbeat, irregular heart rhythm, pressing or aching chest pain, constant shortness of breath at rest and with exertion. The death of myocardial cells leads to a fatal disease - a heart attack.
- Damage to the vessels of the extremities has an equally striking clinical picture. Problems appear quickly because when the blood flow slows down, there is virtually no blood flow to the distal parts of the arms and legs. A deficiency of oxygen and nutrients in tissues leads to their severe dysfunction. Symptoms of varicose veins in the legs are: rapid fatigue when walking, pain in the limbs that increases with movement, swelling of the ankle, the inability to perform primitive physical exercises, the appearance of dilated and tortuous veins on the skin. With arterial diseases, patients experience numbness and coldness in the extremities, a tingling sensation in the fingers and toes, and pale skin with a bluish tint. Gradually, the condition of the skin on the legs worsens, it becomes dry and thin.
- A less common but more serious sign of damage to the arteries of the legs is intermittent claudication.
- Problems with the vessels of the nose, eyes and ears are manifested by dysfunction of the diseased organ, an increase in the diameter of the vessels, their rupture and signs of bleeding.
- Damage to the smallest blood vessels - capillaries - occurs with diabetic microangiopathy and diapedetic hemorrhage. The disease is accompanied by chills, chills, numbness of the arms and legs, cramps, hyperhidrosis, itching, pale skin, early gray hair.
Some vascular diseases can be asymptomatic for a long time or have a blurred clinical picture. Often patients consult a doctor when the pathology becomes severe, becomes complicated and makes them disabled. That is why it is necessary to listen to your own feelings and not start the process. You should not self-medicate. It is impossible to determine the type of disease by symptoms alone. After a thorough, comprehensive diagnosis, specialists in the field of cardiology or neurology will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy.
Treatment and prevention of thrombosis
Treatment of thrombosis includes anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy, thrombolytic therapy, installation of an inferior vena cava cava filter, and surgical removal of the thrombus [5].
Complications of anticoagulant therapy must be kept in mind: major bleeding, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and warfarin-induced skin necrosis [5]. To reduce the risk of continued thrombus formation, NSAIDs are used [2]. For the purpose of secondary prevention, small doses of heparin are prescribed. Non-drug treatment methods are also prescribed - elastic bandaging, compression hosiery, local hypothermia and exercise therapy [2, 4].
Prevention of thrombosis includes a number of measures used in situations of increased risk of thrombosis.
Primary prevention of atherothrombosis:
- systematic physical activity in the form of walking or morning exercises;
- blood pressure control, maintaining working blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg;
- control of blood sugar levels (less than 6 Mmol/l), early detection and treatment of diabetes mellitus;
- weight loss, body mass index less than 25 kg per m2;
- a diet limited in cholesterol and high-density fat (total cholesterol less than 5 mmol/l), fruits and vegetables;
- smoking cessation [3,7].
Primary prevention of venous thrombosis:
- compression underwear;
- bandaging with elastic bandages;
- drinking plenty of fluids, especially after surgery;
- regular exercise, walking, especially when traveling;
- prohibition of taking alcohol and sleeping pills in large doses;
- prohibition of the use of compressive shoes and clothing [2,5,6].
Sometimes, during periods of particular risk, anticoagulants are prescribed several days before the flight. There is no point in taking aspirin in such cases [5].
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnosis of vascular pathologies is carried out according to a standard scheme, including a conversation with the patient, study of the clinical picture, collection of anamnestic data, general examination and physical examination. These techniques provide only a general idea of the existing pathology. To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment, the results of laboratory and hardware tests are required.
Comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination of the patient:
- General clinical and biochemical blood tests - detection of anemia and inflammatory changes,
- Lipidogram - the ratio of lipid complexes in the blood,
- Coagulogram - determination of blood clotting indicators, tendency to thrombosis or bleeding,
- Determination of hormonal status,
- ECG and EchoCG - identifying the structural and functional state of the heart muscle,
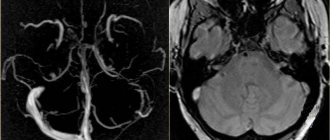
- Contrast angiography, cardiac coronography - assessment of the performance of blood vessels, their location, affected areas, developmental anomalies,
- Duplex scanning includes ultrasound and Dopplerography of blood vessels. Ultrasound visualizes veins and arteries, reflecting the anatomy and existing disorders. Doppler determines the speed and intensity of blood flow.
- Tomography – obtaining a three-dimensional, layer-by-layer image in several projections of any vein or artery.
The results of such an examination make it possible to accurately determine the cause of vascular dysfunction and select a treatment regimen for the patient. To avoid various problems with blood vessels, they need to be strengthened, cleaned and hardened.
Tests for thrombosis
Laboratory indicators play a significant role in the timely diagnosis of thrombosis.
Thus, guidelines for the management of patients with a new coronavirus infection provide for stratification of the risk of coagulopathy in patients with COVID-19 based on simple laboratory tests: D-dimer, prothrombin time, platelet count, fibrinogen level [1,9]. A clinical blood test can detect inflammation. It also determines the level of platelets, that is, the very substrate of thrombosis.
Additionally, the level of inflammation in the blood and the risk of thrombosis is indicated by an increased level of C-reactive protein.
Biochemical analysis primarily demonstrates blood glucose levels. It can be used to judge the presence of diabetes, one of the most serious risk factors for thrombosis.
Also, a biochemical analysis can determine the level of protein C, which also characterizes the severity of the risk of thrombosis.
Elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood are also a currently proven risk of thrombosis, leading to miscarriage and cardiovascular events (heart attacks and strokes).
D-dimer is a laboratory marker of fibrin formation [8]. It also indicates the presence of inflammation, just like C-reactive protein. The level of D-dimer is a control indicator of COVID-19 and its complications, including those associated with thrombosis.
You can take tests under the comprehensive Thrombosis program, which includes determining the levels of Antithrombin-III, D-dimer and genetic factors of cardiac diseases and platelet levels. This program allows you to determine the fact of thrombosis occurring somewhere in the body, as well as determine the genetic predisposition to it. This program, like other tests, is offered by the CITILAB network of clinics.
Additional determination of homocysteine and C-reactive protein levels will help determine the biochemical risk of thrombosis.
Treatment process
Treatment of vascular problems is etiotropic, aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology. Specialists prescribe medications to patients depending on the specific case of the disease. They select the treatment regimen and dosage of drugs individually for each patient.
The treatment process includes normalization of lifestyle, diet therapy, medication, surgery and traditional medicine.
Experts recommend first of all changing your lifestyle: eliminating bad habits, playing sports, walking in the fresh air, getting enough sleep, getting proper rest, avoiding stress and nervous shock, controlling your body weight, and moving more.
Proper nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of vascular problems. Patients need to include fresh vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, cereals, seafood, beans, and lactic acid products in their daily diet. You should limit your intake of animal fats and reduce the amount of easily digestible carbohydrates.
Medicines prescribed to patients:
- If the cause of vascular disorders is atherosclerosis, drugs that normalize lipid metabolism are used - fibrates Bezafibrate, Fenofibrate, statins Atorvastatin, Lovastatin.
- For the treatment of affected coronary vessels, antihypertensive drugs “Enalapril”, “Bisoprolol”, antiplatelet agents “Aspirin Cardio”, “Cardiomagnyl”, antianginal drugs “Nitroglycerin”, “Nitromint” are used.
- Problems with cerebral vessels are relieved with the help of general strengthening, nootropic and vascular tonic drugs “Piracetam”, “Vinpocetine”, “Cavinton”, vasodilators of various groups - calcium channel blockers “Nifedipine”, “Verapamil”, myotropic antispasmodics “Drotaverine”, “Papaverine” . Patients are prescribed diuretics “Lasix”, “Mannitol”, “Veroshpiron”, antihypoxants “Actovegin”, “Mexidol”, metabolic drugs “Riboxin”, “Cinnarizine”.
- For varicose veins, angioprotectors and venotonics are indicated - Detralex, Venarus.
- To treat thromboembolism and thrombosis, enzyme preparations that break down clots are used - “Streptokinase”, “Urokinase”, anticoagulants - “Warfarin”, “Heparin”.
- To strengthen the vascular wall, use “Ascorutin”, “Troxerutin”, multivitamins “Duovit”, “Complivit”.
- To eliminate headaches, analgesics from the NSAID group are prescribed - Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen.
- Sedative and psychotropic drugs – “Amitriptyline”, “Afobazol” - will help you calm down and relieve tension.
One of the invasive methods of treating vein pathologies is sclerotherapy. A special substance is injected into the overstretched vessel, affecting the smooth muscle fibers of the vascular wall and causing its spontaneous narrowing.
Surgical intervention is indicated in severe cases when conservative therapy does not help and complete vascular incapacity occurs. During the operation, the affected area of the vessel is excised, the healthy walls are sutured, normalizing blood flow.
Currently, minimally invasive operations on the arteries are common - stenting of the heart vessels or carotid arteries. They allow you to restore the patency of blood vessels clogged with plaques and blood clots.
Traditional medicine includes various herbal mixtures, decoctions and infusions:
- Lemon juice with honey and mint,
- Yarrow decoction
- Tincture of red pine cones,
- Eating fresh garlic daily
- Turpentine baths,
- Cold and hot shower,
- Freshly squeezed beet and carrot juices,
- Juice mixtures of cucumber, spinach, kiwi, celery, parsley.
Problems with blood vessels will sooner or later lead to impaired circulation and blood supply to internal organs. Timely consultation with a doctor significantly increases the patient’s chances of recovery. In mild cases, normalizing lifestyle and nutrition will help cope with the disease. If the patient has severe dystonia and serious pathology, long-term drug therapy or surgical intervention is required.