Why is pressure inside the skull needed, why can it be elevated, and how does this indicator relate to blood pressure? What are the norms and when is blood pressure dangerous to health and life, how to feel it and how to reduce it, let's talk with an expert ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, WHO expert POLINA PETROSYAN Neurologist at SM-Clinic, specialist in cerebrovascular diseases and headaches
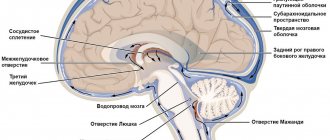
What is intracranial pressure
The brain is surrounded by a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid, which nourishes and protects nerve cells.
Cerebrospinal fluid is continuously produced and flows away from the skull, thereby maintaining a constant pressure. This is intracranial pressure - a certain force that puts pressure on the brain and the walls of the skull. This pressure is changed in mmHg. Art., and normally it is from 10 to 15 mm. If it is higher, this is a reason to be wary, and if the pressure exceeds 25 mm Hg. Art., this can be dangerous for brain function. If the value is more than 35 mmHg. Art. Severe and irreversible changes in the brain are possible - such situations are considered critical.
Clover and mulberry
It turns out that you can lower intracranial pressure using folk remedies using ordinary clover. The clover heads are plucked off, placed in a jar and infused with vodka. The infusion period is two weeks. The patient should take this tincture one tablespoon three times a day. In this case, the tincture is dissolved in a glass of water. After a week of such therapy, intracranial pressure decreases and the headache disappears.
Another treatment option is regular butter. It is enough to melt it and drop it into your nose five times a day or more. Alternatively, use rosehip oil or melted honey from honeycombs.
Mulberry (another name is mulberry) will also help relieve intracranial pressure. This tree, five to ten meters high, grows in the Russian south. First, the young branches of the tree are cut, then they are chopped into pieces of about 2-3 cm. If the branches are large, they are split along the width. The decoction is prepared from approximately 10-15 grams of branches. Just fill them with 1 liter of water, bring to a boil and boil for 20 minutes. The broth is wrapped, for example, in a blanket.
Typically, people suffering from ICP take the decoction three times a day before meals. The duration of therapy is from one to three months, depending on the severity of the disease. Mulberry is also an excellent diaphoretic and antiseptic.
Causes of intracranial pressure in adults
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is not an independent disease, but a syndrome.
Doctors sometimes call it intracranial hypertension. Pressure inside the brain (similar to arterial pressure) fluctuates when the head is tilted back and forth or to the sides, during physical activity or sneezing. But it can increase to serious numbers in case of pathologies, and there are many of them. “ICP (intracranial pressure) occurs as a result of an increase in the volume of intracranial contents (cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid), tissue fluid, or the appearance of foreign tissue (tumors, cysts, brain abscess), says neurologist Polina Petrosyan.
In addition, the causes of increased ICP may be:
- traumatic brain injury;
- tumor;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- neuroinfections (encephalitis, meningitis).
“The cause may also be long-term use of drugs from the group of hormonal contraceptives, corticosteroids or antibiotics,” adds Dr. Polina Petrosyan.
Pressure increases because fluid is either produced in excess (for example, due to an infection that has spread to the brain or its membranes), or because fluid flows out of the skull through special pathways less easily. If volumetric processes develop in the cranial cavity (for example, a tumor grows or hemorrhage occurs), there will be less space for fluid, and its pressure will also increase.
Prognosis and prevention
When driving at high speed, wearing a helmet is mandatory.
Photo: Paha_L / Depositphotos Increased intracranial pressure is most often associated with head injuries. To prevent them, you need to take precautions: wear a seat belt in a car, use a helmet when riding a bicycle, and reduce the risk of falls.
If there are signs of hypertension, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. The earlier treatment is started, the lower the risk of serious health consequences.
Symptoms of intracranial pressure in adults
In many cases, a slight increase in ICP may not manifest itself for a long time. If the pressure rises sharply or high enough, the following symptoms may occur:
- headache - it can be pressing or bursting, usually occurs in the morning, this pain has no clear localization, it can be felt in different parts of the skull;
- nausea and vomiting - they usually occur at the peak of the headache;
- drowsiness, malaise, general poor health;
- memory impairment (forgetfulness), attention disorders, problems with thinking;
- changes in the autonomic nervous system – surges in blood pressure, slow pulse, increased sweating;
- visual impairment up to complete blindness.
Symptoms may come on suddenly or develop gradually over weeks or months.
Symptoms and treatment of ICP
In a good way, if a person experiences any kind of malaise, he or she should consult a doctor. Instead, we self-diagnose and self-medicate on a daily basis. The real world is designed in such a way that people don’t have time to sit in hospital queues. It is easier to find information on the Internet and carry out therapeutic measures to improve health here and now. The main symptoms of ICP are:
- back pain syndrome,
- headache,
- blurred vision,
- vomit,
- nausea,
- swelling,
- increased fatigue,
- lethargy,
- irritability.
If you feel an increase in intracranial pressure, do not rush to self-medicate. Of course, ICP is a fairly common phenomenon among people, but still very dangerous. It is better to seek advice from a professional.
Diagnostics
It is extremely difficult to suspect an increase in ICP based on external signs.
The doctor must know all the complaints and those facts from life that preceded the symptoms. This could be a hypertensive crisis, head injury, severe infection, kidney or liver problems. In order to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a number of studies to the patient: CT or MRI of the brain to evaluate the structure of all tissues of the skull, note the condition of the ventricles of the brain where cerebrospinal fluid accumulates;
- echoencephaloscopy to determine brain function;
- Ultrasound of the brain (mainly in children through the fontanelle);
- examination of the condition of the fundus by an ophthalmologist;
- spinal cord puncture with measurement of the pressure of the escaping cerebrospinal fluid (the cerebrospinal fluid itself is taken for analysis).
Facts and myths about increased intracranial pressure
There are several misconceptions about intracranial hypertension:
- It does not need to be treated; the condition will go away on its own with age. In fact, both children and adults need treatment to avoid serious complications.
- The condition cannot be treated. False: Treatment results depend on the cause and severity of hypertension. Even if it cannot be completely cured, therapy greatly improves the condition and reduces the risk of health consequences.
- High intracranial pressure always causes developmental delays in children. This is a myth: with timely treatment, such consequences can be avoided.
It is important to know that:
- High intracranial pressure in children most often occurs due to hydrocephalus and birth injuries.
- Homeopathic or herbal preparations do not affect blood pressure in any way and do not help normalize it.
- If a person already has intracranial hypertension, he needs to be examined by a neurologist at least once every two years.
Modern methods of treatment
In some cases, the patient does not require treatment; he is observed and treated for the underlying disease, which caused the increase in ICP.
If it is necessary to treat pathology, two approaches are used - conservative and surgical.
Conservative interventions are carried out for those patients whose ICP elevation is chronic and there is no significant deterioration of the condition over time. The basis of treatment is drugs that have a diuretic effect, which reduce the volume of fluid in the head. The specific medicine is determined by the level of pressure and the situation. In severe and acute processes, osmotic diuretics (mannitol) are used, in chronic cases - furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide, spironalactone. While taking them, you need to drink a potassium preparation - Asparkam, Potassium orotate, Panangin.
Surgical methods for treating increased ICP depend on the stage and severity of the disease. In acute situations, craniotomy is performed to reduce fluid pressure on the brain and drain excess fluid. Special shunts (tubes) are installed as planned, which drain fluid from the brain into the abdominal cavity.
Treatment with tinctures and compresses
ICP can also be treated at home. The advantages of this method:
- no surgical intervention;
- non-use of chemicals;
- harmless to other organs.
A compress will help reduce the pressure inside the skull. Its main components are camphor oil and alcohol. Typically, those who are faced with the problem of increasing ICP recommend a one to one ratio, in other words, fifty to fifty. All components can be found freely available at the pharmacy. Usually the solution is applied to the head, then covered with a plastic bag and cloth. The best way to achieve reduced pressure inside the skull is to apply such a compress at night or before bedtime. The compress is easily washed off with shampoo. Don't limit yourself to one session. The optimal option is eight to ten such manipulations. Those who have already dealt with ICP claim that camphor and alcohol can also overcome dandruff.
The second option for treating pressure inside the skull is tinctures. Preparing them at home is quite simple. The basic recipe consists of the following components:
- hawthorn;
- valerian;
- motherwort.
People experiencing ICP are advised to also add eucalyptus and mint to the tincture. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed, placed in a glass bottle (preferably dark) and closed. The tincture takes about two weeks to prepare. Then the finished tincture is consumed orally with a piece of sugar. Experts in the treatment of ICP claim that when using this tincture, the headache caused by the pressure inside the skull will go away and optimal blood stimulation will begin. Among other things, this method is an excellent (though only local) therapy for brain tumors. The tincture is a good treatment for colds, flu and any other infectious diseases.
Prevention of intracranial pressure in adults at home
Prevention of increased ICP is the prevention of various diseases affecting the cranial cavity.
This includes protection against infections that can affect the brain - vaccination against meningococcal and hemophilus influenzae infections, influenza vaccination. It is also necessary to treat various pathologies that can affect brain function. General recommendations are simple:
- follow a daily routine and lead the healthiest lifestyle possible;
- avoid head injuries;
- protect yourself from stress and nervous overload;
- Get enough sleep.
standard treatment
To reduce intracranial pressure, drug therapy is prescribed: diuretics, vasodilators and sedatives; drugs to improve the tone of the vascular wall of veins and stimulate brain activity; vitamin complexes and homeopathic preparations.
For some types of pathology, physiotherapy, acupuncture, massage, and special gymnastic exercises are indicated.
If drug treatment is ineffective and ICP levels are high, surgical treatment is prescribed.
Treatment of floaters before the eyes
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is used as a means to objectively and qualitatively assess the visual impact of opacities. Ultrasound provides quantitative measurements of echo density. This is useful in assessing the severity of the disease and response to therapy. Indirect ophthalmoscopy is designed to identify possible micro-tears, timely correction and prevent detachment.
Considering the fact that artifacts can be a dangerous symptom of various somatic ailments, it is very important to conduct a thorough diagnosis and identify the underlying etiology. The next stage will be treatment of the diagnosed nosology.
Very rarely, unpleasant flickering stops on its own. Most often, the turbidity shifts and leaves the visible zone, but does not completely disappear.
At the current level of development of medicine, there are no sufficiently effective drugs that would help remove circulating bodies. However, there are medications that help activate local metabolism in the optical apparatus and promote the gradual dissolution of particles and inclusions.
If the situation is caused by damage to the retina, then surgical repair of the tears is indicated. Microsurgery is performed on an outpatient basis at the Fedorov Clinic under local anesthesia. This significantly shortens the rehabilitation period.
Floaterectomy:
Laser vitreolysis technology
— surgical correction is carried out with a neodymium laser. The surgeon, using special equipment, targets microinclusions and eliminates them. By focusing short, intense pulses of laser energy into opaque areas, the temperature of these limited spots can be raised to several thousand degrees Kelvin. At this temperature, plasma is formed and the accumulations are destroyed, and in some cases the symptoms can be successfully eliminated. This technique is unsafe, has not been fully studied and causes a large number of side effects. The effectiveness of a YAG laser session can be improved if performed by an experienced surgeon;
Vitrectomy
is a medical intervention that involves extracting the entire vitreous. A sterile saline solution will be placed in its place. This manipulation is not harmless, controversial and sometimes leads to cataracts, hemorrhages, and retinal detachment. The most serious risk of intraocular surgery is endophthalmitis, and in the context of vitrectomy it has become of paramount importance.
Modern instruments and microsurgical techniques have led to shorter operating times and faster recovery.
If the standard technology of ophthalmic surgery is not violated, then patients are satisfied with the final result.
start of treatment
Treatment of intracranial pressure in our center begins with an appointment with a vertebroneurologist. The initial appointment is conducted by the candidate of medical sciences, chief medical doctor Lyudmila Ivanovna Mazheiko.
At the appointment, the vertebroneurologist will examine the cervical spine and determine the tone of the cervical muscles, and, if necessary, prescribe additional examinations (ultrasound, TCD, MRI, CT, EEG, M-Echo, in children under 1 year of age, NSG, fundus examination).
Based on the examination results, the doctor will develop an individual treatment plan.
Appointments with a vertebroneurologist are carried out by appointment. To begin treatment, make an appointment.
Preventive actions
The presence of structural elements of the light-optical apparatus depends on general well-being. Prevention of myodesopsia involves a healthy lifestyle. The neuropsychological state, a balanced diet and regular physical activity are of great importance. It is advisable to give up smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, and promptly cure ophthalmological pathology.
A person should be extremely careful about his health and wear sunglasses. If cloudiness appears or the image is blurry, immediately contact an experienced ophthalmologist in a specialized clinic.
To exclude vegetative crises and pathological symptoms, doctors recommend walking more and taking walks in the fresh air.
Ophthalmologists have developed simple gymnastics that help fight flying objects and stimulate tissue nutrition.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of the disease depend on the type of Arnold-Chiari malformation. A neurologist or neurosurgeon can qualify the pathology. In the clinical practice of neurosurgeons, grade 1 Arnold-Chiari malformation is often encountered. The disease develops after the end of puberty or in adult patients.
The main signs of pathology in adults:
- headache in the neck and back of the head, which tends to get worse with muscle tension, coughing and sneezing;
- vomiting that does not depend on food intake;
- increased muscle tone;
- cerebellar ataxia;
- tendency to nystagmus and speech disorders;
- decreased visual and hearing acuity.
Other symptoms may also appear, including short-term loss of consciousness. Patients with this disease complain of dizziness whenever they turn their head. In some cases, fainting may even occur. A common symptom is atrophic changes in the tongue and larynx. They are accompanied by breathing problems and chronic hoarseness. Similar consequences arise in the absence of effective medical care for a long time.
Arnold-Chiari malformation type 2 causes noisy breathing, combined with laryngeal paresis and reflux of food into the nose. An accurate diagnosis can be made based on examination and diagnostic data. A neurological examination in combination with magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine can reveal characteristic abnormalities. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate treatment should be started as soon as possible.
Magnetic resonance imaging is the most widely used diagnostic method for this disease. During the study, it is possible to detect dislocation of the tonsils and obtain information about the composition of brain tissue. To study the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, phase-contrast MRI is necessary.
Arnold-Chiari malformation grade 1
The cerebellar tonsils are located below the foramen magnum. Arnold-Chiari malformation grade 1 is more common in adults. As the disease progresses, cerebrospinal fluid begins to accumulate in the central canal of the spinal cord. When the disease is combined with syringomyelia, sensitivity is impaired, signs of numbness and atrophic processes in the muscles appear. Peritoneal reflexes may disappear.
Arnold-Chiari malformation grade 2
With this disease, not only the tonsils, but also the cerebellum itself, the fourth ventricle, and the medulla oblongata begin to emerge through the foramen magnum. The disease is associated with congenital spina bifida. The pathology is accompanied by myelomeningocele and spina bifida.
Arnold-Chiari malformation grades 3 and 4
Arnold-Chiari malformation of 3-4 degrees is accompanied by the transition of descended brain formations into meningocele of the back of the head and neck. With stage 4 disease, hypoplastic processes in the cerebellum are often combined with signs of hydrocephalus.
The development of combined pathology is possible. The disease can occur against the background of dysplastic processes in the nervous system, including disturbances in the functionality of the corpus callosum and underdevelopment of subcortical structures.