Author Rina Miro
08/26/2019 18:07 (Updated: 05/21/2021 12:40)
Health
There are different types of headaches, but perhaps the most merciless and debilitating are migraines.
Is it possible to beat migraines?
Migraine is a disease whose main symptom is severe attack-like headaches.
Table of contents
Relieve tension Change contraceptive method Check your vision Primary or secondary headache? Sources
Headache can be caused by stress, fatigue, taking oral contraceptives, overstrain of the eye muscles with incorrectly selected glasses or lenses, a jump in blood pressure, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, which in turn leads to secondary tension in the cervical-occipital muscles, causing tension in the aponeurosis, and many other reasons.
One of the common triggers of headaches can be anemia, leading to chronic pain syndrome.
It happens that there is no painkiller at hand or it is impossible to use: the pain is caused by a side effect of another drug, the patient fundamentally avoids taking pills, the medicine cannot be taken due to pregnancy or lactation. How to relieve a headache in this case?
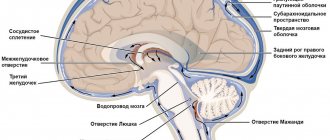
Causes of migraine
Migraines can be caused by many factors or combinations of factors. First of all, this is due to the condition of the blood vessels. If they are not able to contract and expand in a timely manner, any temperature change can trigger an attack. If a vessel needs to expand in response to increased temperature or some other factor, but it remains in its previous state, aneurysms occur.
In addition, migraines are often triggered by hunger. When the brain does not receive glucose for a long time, it signals danger through a headache. Before you swallow the pills, you need to eat well. If a person is in conditions where there is nothing to snack on, a glucose solution or some kind of sweet placed on the tongue will help. The brain, having received glucose, will begin to reduce the severity of headaches.
Another cause of migraines is hormonal imbalance. It can occur during pregnancy. Many expectant mothers suffer from unbearable headaches, for which it is impossible to take a pill - an interesting situation is a contraindication for taking most effective painkillers. Hormones, due to pregnancy, are produced in different volumes. Obstetricians note that expectant mothers expecting boys are more likely to suffer from migraines than those expecting girls, which is directly related to the balance of female and male hormones.
Nervous stress also often causes migraines. If work activity forces you to constantly be in a state of stress, and the situation requires you to quickly make serious and responsible decisions, nervous exhaustion may occur. It leads to changes in blood pressure and increased heart rate. If the vessels do not have time to react to this by expanding, migraines occur.
Relieve tension
Tension headaches are a common problem for people whose jobs involve high levels of concentration, responsibility, and stress.
The prevalence of this type of pain in the world ranges from 46 to 78%. Statistically, tension headaches lead to more missed work days than migraines. There are three categories of tension headaches: infrequent episodic, frequent episodic and chronic. Doctors usually advise treating headaches with over-the-counter analgesics. However, with frequent and chronic pain, medications soon stop helping.
Massage helps treat headaches. Scientists conducted an experiment: over the course of 4 weeks, they conducted four treatment sessions for participants in two groups. For the first group, therapy included massage and manipulation of the cervical spine, for the second group - only massage. 8 weeks after the experiment, participants in both groups showed significant improvement in performance.
A course of relaxing massage, gentle manual practices, and osteopathic techniques can be an effective method of reducing the frequency and intensity of headaches. But if this is not possible, then an independent head massage will help relieve the spasm that is causing the problem.
Cervical exercises can also help situationally: bending and turning the neck will improve blood circulation and reduce the intensity of pain.
But you should be careful with circular movements, they can provoke spinal tension.
If the pain is caused by mild stress or fatigue, you can use breathing practices, meditation and other methods that reduce arousal.
Prevention of migraines
When there is a predisposition to such a serious condition as migraine, you need to be able to prevent such attacks.
First of all, this is the sleep and wakefulness pattern. When a person is exhausted at work and no more than 4-6 hours are allocated for sleep, the body weakens, including the blood vessels losing their elasticity. It is important to accustom yourself, regardless of any difficulties and responsibilities, to go to bed at the same time and get up at a certain hour. The correct time to go to bed is considered to be 22:00, then you can get up at 7:00 fully rested.
Regular self-massage of the cervical spine with menovazine will help get rid of stagnation of blood flow, which is very important for the prevention of migraines.
Timely nutrition is another important condition that will protect against migraines that occur due to hunger. If a patient often experiences darkening of the eyes during a sudden change in body position, for example, when getting up from a lying position, you should try to do this smoothly, without rushing.
Vascular training is a prerequisite for migraine prevention. Every day you need to stand under a contrast shower. You can start with washing your face. First with warm water until a blush appears, and then with cold water. When home training becomes a habit, you can fit into your schedule a weekly visit to the bathhouse or sauna and subsequent immersion in an ice bath.
Change your contraceptive method
In some cases, if you have a headache, it should be treated not by prescribing medications, but, on the contrary, by stopping taking them.
For example, patients suffering from migraine with aura should avoid taking combined oral contraceptives due to the high risk of ischemic stroke due to their ability to provoke thrombogenesis. For women suffering from severe headaches and migraines without aura, the risks are lower, but for them exogenous hormones and estrogen withdrawal may also be triggers.
Therefore, if you notice that after starting to take oral contraception, headaches have become more frequent and intense, this is a reason to think about changing your method of preventing pregnancy.
Migraine symptoms
Typically, migraines do not come on suddenly. First, the patient experiences some oddities of the condition, called migraine precursors. Most often it is mild confusion and blurred vision. Segmental loss of visual angle is noted. Patients who complain of regular migraine attacks report that they first gradually lose peripheral vision. Instead of a clear picture, they see a rattling spot spreading across the entire focus area. After 20 minutes, this symptom disappears on its own, vision returns to normal, but a pressing headache comes, which turns into a throbbing headache.
Migraines are often accompanied by nausea and severe photophobia. When trying to stand up, the patient experiences dizziness. And every movement gives off a strong pulsation in the head.
Primary or secondary headache?
Headaches are divided into primary and secondary.
Primary headaches have no structural or metabolic cause. It is mild pain of this type that can be relieved with relaxation, massage, walking in the fresh air, and so on. These also include tension headaches, migraines, cluster headaches, and analgesic rebound headaches. Secondary headaches are caused by conditions such as increased intracranial pressure, pseudotumor cerebri, subdural or intracerebral hematomas, hypertension, meningitis, temporal arteritis, Lyme disease, and brain tumors.
An accurate diagnosis and identification of the causes of headache largely determine the success of its treatment.
Therefore, if you experience frequent, intense or chronic headaches, you need to be examined by a specialist. In this case, it is better to start with a visit to a neurologist and ophthalmologist.
How to get rid of migraines at home
Due to the characteristics of the symptoms, it is important to reduce the level of irritating factors:
- Place the patient in a dark room without bright light sources. If it is daytime, the windows need to be curtained.
- Eliminates all noise, especially loud ones (turn off the TV, mute the volume on the phone).
- Provide fresh air breathing. To do this, you can open the window if it is not hot outside. Otherwise, it is better to use conditioner if possible. You need to set the temperature to +16˚C.
- Massage the cervical and collar areas. By accelerating the blood in this area, it will be possible to remove excess pressure from the brain.
- Hot ginger tea is an excellent pain reliever. Capsaicin, which is part of the root, has a pronounced analgesic effect.
- Put something sweet on your tongue.
- The popular “Star” balm can be rubbed onto your temples, forehead and neck along the hairline. During severe attacks, the bridge of the nose is also rubbed.
- Cold compresses on the forehead will narrow some of the blood vessels, the expansion of which caused the attack.
To completely get rid of pain, you need to try to sleep. As a rule, sleeping for 8-10 hours saves you from a migraine attack, allowing you to wake up as a healthy person.
Sources:
- Scripter C. Headache: Tension-Type Headache. FP Essent. 2018 Oct;473:17-20. PMID: 30346680.
- Espí-López GV, Zurriaga-Llorens R, Monzani L, Falla D. The effect of manipulation plus massage therapy versus massage therapy alone in people with tension-type headache. A randomized controlled clinical trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021 Oct;52(5):606-617. Epub 2021 Mar 18. PMID: 26989818.
- Marks DR, Rapoport AM. Practical evaluation and diagnosis of headache. Semin Neurol. 1997;17(4):307-12. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040943. PMID: 9474710.
- MacGregor E.A. Contraception and headache. Headache. 2013 Feb;53(2):247-76. doi: 10.1111/head.12035. PMID: 23432442.
- Allais G, Gabellari IC, De Lorenzo C, Mana O, Benedetto C. Oral contraceptives in migraine. Expert Rev Neurother. 2009 Mar;9(3):381-93. doi: 10.1586/14737175.9.3.381. PMID: 19271947.
- Friedman DI. Headache and the eye. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2008 Aug;12(4):296-304. doi:10.1007/s11916-008-0050-1. PMID: 18625108.
Published on the portal health.mail.ru
Current issues in the treatment of migraine
Migraine is a chronic disease that disrupts the usual pattern of life and affects performance and family relationships.
In most cases, migraine attacks occur spontaneously and their occurrence is unpredictable. This creates a feeling of fear and apprehension in many patients and, accordingly, disrupts daily functioning. That is why WHO included migraine in the list of 19 chronic diseases that most disrupt the social adaptation of patients. At least a third of humanity suffers from migraines, with women suffering 2-3 times more often than men. A characteristic symptom of migraine headache is its onset before the age of 20 years. The essence of the disease is the periodic appearance of stereotypical attacks of throbbing pain, usually one-sided, which is accompanied by nausea, sometimes vomiting, poor tolerance of bright light, loud sounds, drowsiness, and lethargy after the attack is over. Characterized by recurrence of attacks and hereditary predisposition.
A migraine attack occurs in several phases: prodromal, aura, headache with associated symptoms, and postdromal. The prodromal period occurs before a migraine attack, ranging from a few hours to 2 days. Its typical symptoms include irritability, physical and mental hyperactivity, increased sensitivity to light, sounds, irresistible food cravings, increased bowel and bladder function, thirst, a feeling of detachment, lethargy, feeling tired, difficulty focusing vision, yawning or excessive sleepiness, slurred speech, impaired concentration, general weakness, anorexia.
The Aypa or pain phase of the attack begins after the prodromal period ends. Characterized by a gradual increase in pain and its one-sided nature. In this case, the side of pain can change even during one attack. Pain occurs in the area of the inner eye, postorbital or frontotemporal zone, is initially dull, then can become throbbing (increasing with each pulse beat). In most cases, migraine pain is very severe, lasting from 4 to 72 hours. There is historical evidence of severe intensity of migraine pain.
There are ancient legends about migraines. Even the almighty Zeus, according to one of them, had to turn to Hephaestus, the god of blacksmithing, so that he would smash his head, which was splitting from unbearable pain, with a hammer and relieve him of the monstrous migraine torment. There is also a literary example indicating a significant intensity of migraine pain. Mikhail Bulgakov in “The Master and Margarita” gave an accurate description of “a terrible, invincible disease - hemicrania, in which half the head hurts.” The procurator of Judea, Pontius Pilate, overcome by a migraine attack, saw salvation only in a portion of poison. Over the millennia, humanity has invented other ways to relieve pain, but the symptoms of the disease remain the same. Many patients in the pain phase experience a variety of symptoms such as increased sensitivity to bright light, loud sounds, and various odors.
As the migraine attack subsides, many patients experience a postdromal period, during which they experience difficulty concentrating, weakness, depression, loss of energy, poor coordination of movements, and drowsiness. The duration of this period is from several hours to two days. Migraine attacks are very diverse in severity, duration, and severity of accompanying symptoms both in different patients and in one patient. The disease is divided into two main forms: migraine without aura (MWA) and migraine with aura (MA). MBA is observed in 80% of all migraine cases. MA occurs much less frequently, in 5-10% of patients. Aura is a disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of reversible focal neurological symptoms that worsen over 5 to 20 minutes and last no more than 60 minutes. Frequent types of aura (visual, sensitive and speech) are defined as its typical forms. Visual disturbances are the most common symptom of aura, occurring in 99% of patients with MA in most attacks. Sensitive aura is observed in 30-54% of patients with MA, speech aura - in 20-32% of patients. The most typical manifestation of a visual aura is a flickering scotoma, when the image in some parts of the visual field periodically disappears, creating a sensation of flickering. A scintillating scotoma usually begins as a small blind spot in the center of the visual field that enlarges and moves. The patient may also see flashes of lightning and flickering, some see castles in the air and other interesting objects. Usually such symptoms last 20-30 minutes. Rare types of aura include olfactory, auditory, motor, aura in the form of systemic dizziness, as well as an aura with impaired neuropsychic functions. The differential diagnosis takes into account the characteristic signs of migraine. In addition to the above, there may also be: increased pain from ordinary physical activity, for example, when walking, climbing stairs; typical provoking factors: stress, weather changes, hunger, excess or insufficient sleep, alcohol intake (red wine, beer, champagne), stuffiness and menstruation; cessation of attacks in the third trimester of pregnancy. The treatment of migraine is guided by the following basic principles: 1. depending on the frequency of paroxysms - stopping attacks or preventing them; 2. taking into account the important importance of hypoxia and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of the disease, periodic courses of antihypoxants and antioxidants. Treatment of attacks can be divided into nonspecific and specific. Nonspecific treatment involves the use of drugs that are used to treat pain of any origin and location. Specific are drugs aimed against purely migraine pain. How to relieve a painful migraine attack? Previously, people tightly bandaged their heads with a piece of linen with the names of the gods, since the disease was considered “heavenly punishment.” But the alleviating effect was most likely due to the tight bandage compressing the brain vessels. We find a similar “recipe” in Shakespeare: Desdemona eases Othello’s headache by bandaging his head with her handkerchief.
To relieve migraine attacks, drugs with a nonspecific mechanism of action are used:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- triptans are selective agonists (stimulants) of serotonin receptors;
- antiemetics (metoclopramide, domperidone, etc.).
The choice of a specific drug is the doctor’s task, taking into account previous treatment experience and patient preferences.
It is recommended to take painkillers simultaneously, or even better, 20 minutes after using antiemetics, which improve intestinal motility, accelerate gastric emptying and absorption of the analgesic. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) traditionally occupy a significant place in the treatment and prevention of most pain syndromes. The strategy for a migraine attack is based on the choice of an effective and fast-acting NSAID. Unfortunately, preventive treatment for migraine is rarely used in everyday clinical practice. At the same time, it has been proven that success in the fight against the disease is largely determined by early and active prevention of attacks. Antidepressants may be used to treat migraines. Considering the important role of hypoxia and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of migraine, periodic courses of antihypoxants and antioxidants are recommended according to the generally accepted scheme. Carnitines are of particular interest in this regard. Drug treatment of migraine may not be enough, therefore, in the inter-attack period, non-drug therapy is offered (mountain climate, acupuncture, transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation, hypnosis, relaxation techniques of behavioral psychotherapy, autogenic training, phototherapy, dosed hypobaric hypoxia, ozone therapy, etc.). With concomitant tension in the pericranial muscles, soft manual techniques, massage of the collar area, and reflexology are relevant.
HOW TO EAT WITH A MIGRAINE
Scientists have concluded that dietary factors may be key in the development of migraines in children and adolescents. In adults, avoiding trigger foods reduces the frequency and severity of attacks by 20-50%.
What foods are the most dangerous for migraines?
These are primarily products containing nitrates, the amino acid tyramine, the food additive monosodium glutamate, histamine, caffeine, and simple caxapa. Nitrites are a common component in sausages; it gives them a delicate pink color, and in people with migraines it causes a sharp constriction of blood vessels in the brain. Tyramine, which gives expensive cheeses a deep aroma and special taste, quickly constricts and dilates blood vessels, and also causes a deficiency of serotonin in the body, and the lack of this hormone provokes migraine attacks. Tyramine is found in large quantities in beer, pickled herring, chicken liver, yeast, and citrus fruits. Drinking red wines containing ethanol, sulfites and tyramine also leads to vasospasm and dehydration. While serotonin is often deficient in migraine sufferers, the hormone histamine is found in excess and worsens headache attacks. Therefore, you should avoid eggplants, tomatoes, avocados, cheeses, sausages, beer, red wine and sauerkraut. Monosodium glutamate (E621) causes increased activity in certain areas of the brain, which also provokes an attack. Chocolate, beloved by many, is also unsafe. It contains three migraine provoking substances - phenylethylamine, caffeine and theobromine. Prohibited foods for migraines: aged cheeses (brie, Roquefort, cheddar), cream, sour cream; chocolate, cocoa; meat and fish (smoked, dried, fatty), red caviar; offal; apples, bananas, citrus fruits, pineapples; corn, garlic, onion, sauerkraut, horseradish, radish; caffeinated drinks (coffee, tea, cola); alcohol (red wine, beer). After a diagnosis of migraine is established, the patient should determine his own list of foods that cause headaches. To do this, it is important to completely exclude foods from the “black” list from your diet for two weeks. Then enter them into the menu one at a time and observe your condition. Typically, junk food causes headaches 3-6 hours after consumption. The list of individual dietary triggers may change several times throughout life. But women should be especially attentive to their diet - their personal triggers often vary even within a month. People with migraines should not skip meals, eat dry snacks, or even go hungry. During attacks, it is necessary to limit the consumption of starchy foods (semolina, pasta, white bread), which cause the release of insulin, which provokes a migraine attack. And one more important rule: people suffering from migraines should not eat ice cream or drink cold drinks in hot weather, as the brain reacts painfully to temperature changes.
What should you eat if you have a migraine?
Scientists have discovered that foods rich in magnesium, calcium, vitamins A, B, C, and fiber for migraines are considered not just healthy, but healing.
Fish containing omega-3 fatty acids (cod, salmon, mackerel, etc.) helps prevent attacks. Of vegetable fats, unrefined flaxseed, olive and soybean oils are preferred. The spice ginger is known as a natural remedy for migraines. It has been proven that even slight dehydration provokes migraine attacks. The optimal amount of fluid consumed is at least 2 liters per day. So, foods that are good for migraines: rice (especially brown), oatmeal, buckwheat, poultry, sea fish, bran bread, wholemeal bread, feta cheese, cream cheese, sweet cottage cheese, low-fat milk, pear, cherry, cranberry, broccoli, spinach, chard, cauliflower, cucumbers, sweet potatoes, carrots, zucchini, beets, pumpkin, turnips, dried fruits, walnuts, vegetable oils (corn, olive, flaxseed, soybean). How to quickly relieve migraine pain with medications? All adult patients with migraine should be given recommendations for medication management of the attack. All patients with migraine should be treated with a stepwise approach, which involves managing three attacks at each stage before the patient moves on to the next stage. In the first stage, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) is used, plus, if necessary, an antiemetic. The drug of choice, especially in children, is ibuprofen. Ibuprofen is included in the international recommendations of the European Federation of Neurological Societies (EFNS) for the relief of migraine attacks (evidence level A). At the second stage, if possible and there are no contraindications, then triptans are recommended for patients who failed to help at the first stage. NSAIDs may be an effective alternative to triptans when migraine relapses. In addition to traditional tablets, which begin to act after 40 minutes, and the maximum effect occurs after 2 hours, pharmacies offer Ibuprofen CAPS
, an ultra-fast-acting drug in capsule form.
Ibuprofen CAPS, soft gelatin capsules, contain a solution of ibuprofen in polyethylene glycol. One capsule of the drug contains 200 mg of ibuprofen. One of the main advantages of Ibuprofen CAPS is the rapid onset of pain relief, which begins 15 minutes after administration. And with migraines, it is especially important to quickly relieve pain. Ibuprofen CAPS is used for headaches, toothaches, migraines, painful menstruation, neuralgia, back pain, muscle and rheumatic pain. Ibuprofen CAPS also has an antipyretic effect; a decrease in temperature during fever begins 30 minutes after administration. It also relieves cold and flu symptoms. Ibuprofen CAPS is taken in adults and children over 12 years of age, 1 or 2 capsules up to three times a day as needed, maintaining an interval of at least 4 hours between doses. If you need to take the drug for more than 10 days, or if symptoms persist or worsen, you should stop treatment and consult a doctor. Ibuprofen CAPS is completely equivalent and interchangeable with the capsules of the original drug BEFORE USING THE MEDICINE, READ THE INSTRUCTIONS Apr 21, 2021
Previous News Feed Next
What kind of disease is this?
The first mention of migraine dates back to 1500-3000 BC. Information about it is contained in ancient Egyptian papyri and on Sumerian clay tablets. The disease was described by Hippocrates, Celsus, and Arsenius of Cappadocia. She was treated with bloodletting, herbal decoctions, and sometimes craniotomy.
Migraine is a periodically occurring illness that is accompanied by severe throbbing headache, weakness, nausea, and vomiting.
Visual impairment and the appearance of a “veil before the eyes” are often observed. Duration - from several hours to three days. A person experiences increased sensitivity to sound, light, and touch. Each attack goes through several stages.
| stage | Start | attack | ending |
| duration | 1 day -5 minutes . | 4-72 hours | 1-2 days |
| well-being | malaise | bad | weakness |
| pain | increases | strong | subsides |
| appetite | absent | food aversion | weak |
| nausea | is growing | Possible vomiting | absent |
| vessels | narrowed | expanded | are being restored |
The given classification is conditional. Each case is individual; when compiling the table, I relied on my experience.
Peppermint tea is a delicious remedy for migraines.
The subsidence of pain does not indicate complete recovery. Recovery takes up to three days. The timing depends on the body's reserves. I recovered from the hospital for 2 months.
Home healer
Massage, breathing exercises, and contrast showers are used as aids. Traditional medicine usually recommends herbal remedies, especially relying on soothing decoctions and infusions. >> Pour a tablespoon of St. John's wort herb with a glass of boiling water, boil for 15 minutes. After straining, drink half a glass three times a day. >> Infusion of lemon balm relieves tension well, reduces pain and nervousness. Half 1 tbsp. spoons of lemon balm are poured into a glass of boiling water and left for 30 minutes. Take 1-2 tbsp. spoons 5-6 times a day. >> A tablespoon of crushed valerian root is poured into a glass of boiling water, boiled for 15 minutes in a water bath, left for 10 minutes. Take 1 tbsp. spoon three times a day. Traditional healers and some adherents of official medicine suggest using physical exercise as a preventative measure. >> Clasp your hands behind your head and press on your neck, trying to resist this pressure. >> While sitting on a chair, grab the seat with both hands and pull up forcefully. Count to six, lower your arms and relax. >> Sit on the edge of the chair. Lower your arms freely. Look at the ceiling, count to 10. Inhale deeply and, exhaling, bend down to your knees. Looking at the floor, inhale; exhaling, slowly straighten up. By using all of the above remedies, readers will be able to prevent the onset of a migraine attack, when the head suddenly appears as if in a vice.
Emergency measures
To quickly relieve pain, you need to know what to do for migraines at home. Therefore, among the many folk remedies, it is important to choose the one that suits a particular person.
During an attack, the patient needs a quiet, darkened, ventilated room, a horizontal position, an analgesic and a cold bandage on the head.
Traditional medicine knows a lot of methods and home recipes for quickly getting rid of migraines.
• First aid: stand in a hot shower, direct the stream to the back of your head, or hold your hands and feet in hot water.
• Apply onion halves or onion pulp to your temples and secure with a tight bandage. An alternative to onions is cabbage or lilac leaves.
• At the initial stage of an acute attack, drink a quarter glass of freshly squeezed potato juice;
• Inhale the vapors of a mixture of ammonia and camphor alcohol (take in a 1:1 ratio).
Children can also be treated for migraines at home. The child should be placed in a quiet, darkened room, a cold bandage should be applied to the forehead, and a sweet drink should be offered. Milk with a spoon of honey, berry juice or sweet lemon tea will do. If there is no improvement, use drug treatment.
Pregnant women should be careful when choosing folk remedies to combat migraines, since many herbs help increase the tone of the uterus, causing miscarriage. Mistletoe and horsetail have these properties.
To relieve migraine attacks in pregnant women, the following remedies are used:
• Contrast warm shower. • Cold compresses. • Light exercise, swimming. • Head massage. • Regular walks. • Herbal tea based on lemon balm, rose hips or chamomile, if there is no individual intolerance.
herbal tea helps fight migraines
How to stop a migraine attack if it has already begun?
My problems usually start in the morning. I wake up and understand: something is wrong. Previously, I hoped that it would “go away on its own” if I lay down some more, but that was not the case... The sad experience taught me to be more attentive to my well-being.
I noticed that the condition is preceded by some little things. The day before, you develop a strong appetite or crave junk food. One day, an attack occurred after I had eaten a lot of halva. Another time the “trigger” was cold beer and a late dinner. Now I limit myself by drinking tea instead of evening snacks.
You may have other warning signs and your own triggers. Monitor your health carefully. If the attack escalates, do the following:
- Take time off from work, return home.
- Take a warm shower, drink coffee. I add a tablet of no-shpa and analgin.
- Turn off the lights, close the curtains, get into bed, relax.
- Try to calm down.
- Place a cloth soaked in cool water on your forehead.
- Ask your loved ones to do acupressure.
- If the pain intensifies, vomiting appears or blood pressure rises, call an ambulance.
If your head is in a vice
To interrupt a painful attack, it is often enough to select the appropriate medications. The range of medications for the treatment and prevention of migraines is very wide. But only a specialist can select the necessary medicine and its dosage. You just need to know the diagnosis, clarify the causes of the disease and basic treatment methods in order to prevent the threat of attacks. If you know the factors that provoke an attack, you should get rid of them or at least weaken their influence. You will have to give up habits, for example, a nocturnal lifestyle, adjust your diet, stop worrying about trifles, etc. The best remedies during an attack are sleep, bed rest, peace and quiet in a room where all sounds and lights are muted. Sometimes a glass of hot tea, a heating pad, or, conversely, cold applied to the sore side of the head in the form of a compress helps.