If you suspect a concussion or the diagnosis has already been established, you will need to be examined by a neurologist. If any studies have been previously performed, be sure to take their results for consultation, incl. the pictures themselves. If studies have not been performed, they will be recommended and performed based on the results of the examination.
- Symptoms of a concussion
- What to do if you have a head injury
- Concussion Screening
- Trauma to the cervical vertebrae due to concussion
- Nose injury due to head injury
- What happens if a concussion is left untreated?
- Treatment of concussion at the Echinacea Clinic
Symptoms of a concussion
Symptoms of a concussion (one or more of the following):
- Headache;
- agitation or drowsiness;
- Poor tolerance to bright light and loud sounds;
- Confusion;
- Dizziness and coordination problems;
- Loss of consciousness - from a few seconds to hours;
- Memory impairment (events immediately before the injury and/or immediately after the injury are usually lost from memory);
- Slurred speech;
- Noise in the ears, double vision;
- Convulsions;
- Different pupil sizes
- Disorientation in time, space, self, etc.
A poorly treated concussion is dangerous, first of all, because of its long-term consequences , which occur 6-18 months after the traumatic brain injury. If you doubt the presence/absence of a concussion, it is better to play it safe and clarify the situation with the help of a neurologist. In doubtful cases, we will clarify the patient’s condition using magnetic resonance imaging , brain evoked potential studies and other highly sensitive diagnostic methods.
Consequences of a concussion
Consequences of a concussion
may appear after a few years, significantly complicating normal life. The hardest thing is for those who, for one reason or another, did not seek medical help in time for a timely diagnosis of the problems that arose.
Short-term disorders
In most cases, after a concussion, a person is bothered by certain symptoms, which most often disappear within a month after a head injury, subject to adequate treatment and compliance with the recommended regimen. Such consequences that occur in the near future after injury include:
- Intense headaches of a migraine or liquorodynamic nature. In most cases, cephalalgia persists during the first two weeks after injury, in case of severe injuries - a little longer.
Headache after a concussion in those who also suffer from hypertension is particularly intense
- Difficulty concentrating, absent-mindedness, memory impairment.
- Attacks of dizziness, often interfering with the patient’s normal movement.
- Nausea; sometimes – vomiting, which does not bring relief.
- Difficulty with reading and writing.
- Drowsiness, general weakness, fatigue.
All of these symptoms are characteristic of the recovery period and are associated with pathological changes resulting from the blow - swelling of brain tissue, destruction of neural connections and asthenia.
If unpleasant symptoms have not disappeared after 3 weeks, you should re-visit a neurologist to determine the cause of this disorder, since it is possible that long-term consequences of a concussion have developed that require special treatment.
Long-term consequences of TBILong-term consequences of TBI
The set of symptoms that occur several weeks, months or even years later and are associated with a concussion is usually called the long-term consequences of the injury. Common consequences are:
- Post-concussion syndrome.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Cognitive disorders.
- Personality changes.
Post-commotion syndromePost-commotion syndrome
Post-concussion syndrome (from the Latin “commotio” - concussion) is considered a common pathology after traumatic brain injury. Most often it occurs in the absence of diagnosis and adequate treatment of concussion.
The first unpleasant symptoms develop after several months, sometimes years, and it is always very difficult to get rid of them.
The main manifestations of post-concussion syndrome:
- Frequent, pronounced headaches of the migraine type, with various variants possible in the form of ophthalmoplegic or basilar migraine.
- Frequent attacks of dizziness.
- Sleep disorders including insomnia.
- Anxiety, excessive worry for no apparent reason.
- Decreased performance.
- Problems concentrating.
- High fatigue with usual loads.
Basilar migraine gets its name from the basilar artery, which supplies the brain stem, cerebellum, and occipital lobe of the brain.
Ostcommotion syndrome can significantly worsen the quality of life, and a complete cure is very difficult to achieve - simple symptomatic therapy is most often used.
Post-traumatic epilepsy Post-traumatic epilepsy
Sometimes a mild blow is enough to cause an epileptic focus in the brain, if a person has a genetic predisposition to the development of epilepsy. In this case, trauma acts as a provoking factor. The first seizures can occur several months or years after a concussion, causing difficulties in diagnosing and identifying the cause-and-effect relationship of the disease.
Personality and Behavioral ChangesPersonality and Behavioral Changes
Head trauma is often the cause of behavioral changes. A person may become irritable, aggressive, and touchy. A bad mood with depressive pessimistic thoughts predominates. The slightest irritating factors put a person into a state of passion and cause outbursts of anger. Such people just as easily enter a state of euphoria, often without reason.
A concussion aggravates all negative character traits, and it has been proven that with a blow to the frontal part, changes appear earlier.
Cognitive disordersCognitive disorders
Cognitive disorders include weakening of memory, high fatigue during mental activity, difficulties in perceiving and remembering new information.
Often after a head injury with a concussion, memory impairment is observed.
Often, after a concussion, a person loses part of his knowledge, his vocabulary becomes smaller.
VSD vegetative-vascular dystoniaVSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia)
Sometimes head trauma acts as a provoking factor in the occurrence of autonomic disorders. A person begins to feel attacks of headache, shortness of breath, tachycardia, and a feeling of suffocation. During an attack, sweating increases, the stomach hurts, nausea, dizziness are noted, and blood pressure often drops or, on the contrary, increases.
Other consequencesOther consequences
In addition to those listed, other unpleasant long-term consequences of a concussion are possible, but they develop much less frequently than others. It can be:
- Psychoses, neuroses, paranoid states.
- Inadequate perception by the body of alcoholic beverages, in which poisoning, intoxication and alcoholic delirium more often occur after previously habitual doses.
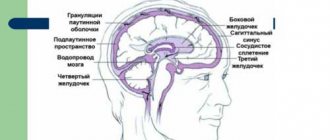
- Increased production of cerebrospinal fluid, which entails an increase in the level of intracranial pressure and the occurrence of corresponding unpleasant symptoms.
- Reduced cerebrospinal fluid production - in this case, on the contrary, cerebrospinal fluid is produced in insufficient quantities, which entails the development of chronic fatigue, dizziness, apathy and headaches.
To summarize, we can conclude that concussion should not be neglected. Even a mild degree of the disease requires compliance with a special regime, since it is possible that unpleasant symptoms will develop, which are very difficult to get rid of in the future. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment will help avoid consequences and allow the patient to get back on his feet faster.
« Back to previous page
What to do if you have a head injury
Immediately after an injury? If one or more of the listed symptoms appear after an injury, you must call an ambulance. If there are no strict indications for hospitalization or if you refuse hospitalization, you can get the necessary help in our clinic.
What help can you provide yourself?
- Lay the victim on his side; this will prevent inhalation of vomit even during loss of consciousness;
- Apply cold to the head to reduce the increase in brain swelling;
- Unfasten clothing that is blocking breathing, belt, trouser waistband;
- Stay close to the victim, because Possible vomiting, psychomotor agitation, and falling when trying to stand up.
After being discharged from the hospital.
If the patient remains unwell after discharge from the hospital, there is usually a persistent increase in intracranial pressure and/or damage to the joints and ligaments connecting the skull to the cervical spine. This is easy to establish using magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and x-ray examination of the cervical vertebrae. This will require a slight correction of the course of treatment (special exercises and medications), which usually leads to improvement within 1-2 weeks. The total planned course of medication after a concussion is at least two months.
First aid for TBI
If you receive a TBI, you should consult a doctor . The danger of self-medication is that the clinical picture is often blurry; a concussion in children is confused with an ordinary bruise, especially considering the length of time the child has been compensating for the pathology. Adults may also have no symptoms. With an increase in temperature, during or after a brain injury, as noted above, swelling of the hypothalamus is possible, and due to the lack of adequate diuretic therapy, severe complications can occur.
Immediately after receiving an injury, you need to call an ambulance, and the victim must be laid on his side, taking into account the side of the injury. If this is not possible, place it on a horizontal surface with the head end raised.- If the patient is conscious, this must be supported by conversation. If a child is injured, he should also not be allowed to sleep.
- Open lesions of the skin and tendon helmet are treated with hydrogen peroxide, but a cold compress is applied to the forehead.
- The victim is transported only on a stretcher. Hospitalization is carried out in a traumatology, neurological or surgical department.
We invite you to watch a video about first aid for a concussion:
The temperature that appears after a concussion cannot be brought down with pills!
- This is a diagnostic criterion.
- Allergies are possible, which will only worsen vascular reactions and the general condition of the patient.
- If the victim vomits, a drop in temperature can cause a new attack and asphyxia is possible.
It is not recommended to give any medications before consultation with medical professionals.
Concussion Screening
Why do you need a concussion evaluation? To promptly notice and treat possible dangerous conditions that often accompany a concussion:
- The release of blood into the membranes and substance of the brain;
- Fractures of the bones of the skull, orbits, face, cervical vertebrae;
- Hemorrhage in the orbital tissue and eyeball;
- Inner ear injury;
- Foci of death of brain matter.
MRI and X-ray computed tomography of the brain will show brain swelling, hemorrhage, traumatic changes in the brain, damage to the bones of the brain and facial skull.
To assess the mobility of the vertebrae after injury, an x-ray of the cervical spine with the head tilted forward and backward (fractures, dislocations and subluxations of the vertebrae are clearly visible).
Evoked potentials of the brain are the most accurate research method today, providing information about disturbances in the conduction of impulses in various parts of the brain (visual, auditory, sensory, motor pathways of the nervous system).
Treatment of concussion with fever
There is a general set of therapeutic measures that are used regardless of the presence of fever. If the condition is mild, the patient is sent home. You need to put it in a dark, regularly ventilated room, and also:
- protect from watching TV, computer and reading books;
- allow you to get out of bed only when necessary;
- do not give junk food - spicy, fried, pickled, sweet;
- avoid irritants such as loud music;
- relieve stress.
A complex of medications is used to treat concussion:
- diuretics to avoid tissue swelling and for better circulation of fluids;
- medicines containing potassium to maintain normal functioning of the heart muscle;
- sedatives to relieve anxiety and tension;
- nootropic drugs strengthen blood vessels and restore neural connections;
- non-steroidal medications relieve headaches and prevent general malaise;
- antiemetic tablets eliminate nausea, improve the functioning of the stomach and intestines;
- anti-inflammatory medications are used in case of a significant increase in temperature;
- vitamins and minerals accelerate the processes of regeneration and rehabilitation.
In the event of a sudden increase in temperature due to a concussion, you should inform your doctor about this change, who will adjust the treatment regimen.
Trauma to the cervical vertebrae due to concussion
Injuries to the cervical vertebrae often go unrecognized because their symptoms are similar to those of a concussion.
The skull is firmly fixed to the first cervical vertebra by joints and ligaments. Therefore, the impact force acting on the skull is necessarily transmitted to the cervical vertebrae . Most often, with a concussion, the ligaments and joints connecting the cervical vertebrae are affected (traumatic subluxations). Fractures and dislocations of the cervical vertebrae are less common.
If, after hitting your head, you continue to experience dizziness, unsteadiness, pain in the back of your head or underneath it, pain in the eyes, visual disturbances, or pain when moving your neck for a long time, we will definitely perform an X-ray or MRI scan of the cervical vertebrae. Traumatic subluxations of the cervical vertebrae are usually easily removable ; their symptoms resolve within a few hours after reduction.
Is it necessary to reduce the temperature during a concussion?
If the temperature does not exceed 37.5 degrees, then there is no need to bring it down. Provide the patient with bed rest and complete rest. If, during a concussion, the temperature rises above 37.5 degrees, and there are concomitant inflammatory diseases (ARVI, colds, etc.) in the background, then they need to be treated. But in the case of fever during a concussion in adults and children, it is strictly forbidden to take any measures on your own. You need to call a doctor at home or arrive at the hospital with an ambulance, after which it is the doctor who, after all the tests, will decide on hospitalization or home treatment, and also prescribe a course of therapy.
Read also
Encopresis
Encopresis is a condition in which a person does not control or feel the urge to defecate, and also cannot control the act of defecation itself;
Fecal incontinence significantly worsens the patient’s quality of life,… Read more
Sudden memory loss/transient global ischemia
Transient, that is, temporary memory loss occurs in elderly patients and people suffering from migraines. At the same time, memory for past and present events disappears. But the person is conscious, accessible...
More details
Pinched nerve
This morning you arrived at your country house. While taking out a heavy and large bag of tools from the trunk of your car, you suddenly felt a very strong, shooting pain in your lower back on the right side. Raise...
More details
Gliomas
What is a glioma? Glioma is a neuroepithelial tumor, a type of tumor of the central nervous system, the source of growth of which is glial tissue. In turn, glial tissue (glia) ...
More details
Aphasia
Aphasias are speech defects that appear with minor brain damage, most often affecting the left hemisphere in right-handed people, and consisting of various forms of speech changes. Location and size...
More details
Diagnostics
After the examination, the doctor may prescribe additional tests, namely: x-rays, MRI, neurosonography, computed tomography or electroencephalography.
X-rays help reveal the integrity of the skull bones.
Neurosonography is prescribed for children under 2 years of age. Using this procedure, the doctor will be able to identify this or that brain pathology.
Electroencephalography will allow you to study the bioelectrical activity of the brain and assess the severity of the injury.
Computed tomography is an effective method for detecting brain damage.