The drug Mexidol has a wide spectrum of biological activity. It is effective for various types of hypoxia (with insufficient oxygen supply to the tissue or impaired absorption). The drug increases the body's resistance to oxygen-dependent pathological conditions (shock, cerebrovascular accidents, etc.), improves mnestic functions (memory processes), reduces the toxic effects (damaging effects) of alcohol, etc.
Mexidol (2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate) is an antioxidant agent, an inhibitor of free radical processes - a membrane protector, which also has antihypoxic, stress-protective, nootropic, antiepileptic and anxiolytic effects.
Mexidol mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of Mexidol is due to its antioxidant and membrane protective properties.
The drug reduces the formation of peroxide substances that destroy cell membranes, which leads to increased oxygen delivery to tissues and preservation of tissue structures.
Mexidol activates the following enzymes: superoxide dismutase, calcium independent phosphodiesterase, acetylcholinesterase. This improves the transmission of nerve impulses at synapses and binding to ligands. Mexidol increases the formation of neurotransmitters, in particular dopamine.
The drug triggers glycolytic reactions and ensures the oxidative processes of the Krebs cycle during tissue hypoxia, which supports the formation of ATP and creatine phosphate at the required level.
Mexidol effect
The main therapeutic effect of Mexidol is the protection of tissues from toxic forms of oxygen. Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate stabilizes cell membranes by suppressing oxidative processes. As a result, cells retain their structure under conditions of prolonged pathological exposure. Improving membrane transport allows normalizing the functions of brain neurons.
All neurons are isolated by a special membrane that protects the internal structures of the cell from negative external factors.
The result of treatment with the drug is the following effects:
- increasing the body's resistance to stress;
- improvement of memory, attentiveness;
- reduction in the number and severity of seizures;
- normalization of cholesterol levels in the blood;
- increasing resistance to aggressive factors;
- improving metabolism in brain cells;
- normalization of cerebral circulation;
- optimization of blood properties, blood thinning;
- reduction of the phenomena of general poisoning.
"Mexidol" in complex therapy for myocardial infarction improved its collateral circulation in the ischemic zone and increased the resistance of myocardial cells to hypoxia. This multifaceted action of the drug has allowed it to be prescribed for a variety of indications in the clinic of internal medicine.
Recommendations during the recovery period
Of course, it is not enough to undergo medical treatment for a concussion and forget about the injury.
During the treatment process and for a long time after, you need to take care and follow simple rules:
- Full sleep. The first month after injury – at least 8-10 hours a day.
- High-quality and varied food.
- Eliminate coffee, chocolate, alcohol, nicotine, drugs.
- Ventilate the living space.
- Avoid reading, watching TV, playing games on the computer or phone, and even listening to music.
- Engage in light exercise with your doctor's permission.
- Regularly take medications prescribed by your doctor for a concussion. Strict adherence to doses and time of administration guarantees a quick recovery and no complications.
If a doctor diagnoses a patient with a mild stage of gray matter damage, after observation for 24 hours, the person is sent home. For a quick recovery at home, treatment of a concussion involves following a special regimen:
- Bed rest: from two days or more.
- Darkening the room from sunlight - with thick curtains.
- Elimination of loud and harsh sounds.
- It is strictly prohibited to watch TV, play games on a mobile phone, work on a computer, or read.
- You can listen to soft music, but not through headphones.
- It is forbidden to be nervous or get into scandals.
- You cannot smoke or drink alcohol.
Medicines for concussion are prescribed if moderate or severe damage to the gray matter is diagnosed. The victims are being treated in a hospital setting.
You should also take pills for a concussion after discharge from the hospital, at home. In addition, to eliminate possible complications, the patient must follow the following regimen:
- Sleep at least 8-10 hours a day.
- Ventilate the sleeping area, maintain the temperature in the room at 18-20 degrees.
- Avoid heavy foods, lemonade, coffee, chocolate.
- Do not drink alcohol, do not smoke.
- Allow feasible physical activity: walking, cycling, swimming.
- Perform physical therapy exercises.
If necessary, after a head injury and long-term treatment of the victim in a hospital, the neurologist may recommend continuing to take medications at home. And also prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures, pressure chambers, massage sessions, manual therapy, acupuncture, etc.
Treatment will be successful if the person suffering from a concussion carefully follows the doctor’s recommendations and adheres to a gentle regimen
It is also important to maintain psycho-emotional balance, avoid stressful situations, reduce physical and mental stress
Dosage, release forms and manufacturers
The drug is produced in two dosage forms: tablets and injections for intramuscular or intravenous administration. Highlight:
- packs of 5 ampoules with 5 ml of the drug;
- packs of 5 ampoules with 10 ml of product;
- tablets of 125 mg, produced either in blisters of 10 pieces, or in plastic jars of 90 pieces.
Several pharmaceutical companies are involved in the release of Mexidol on the domestic market: Pharmasoft, ASI-pharma, Ellara, etc. The medication is also separately produced for use in veterinary practice, but it is absolutely not suitable for people!
List of drugs
In addition to the degree of concussion, when prescribing medications, the patient’s age, physiological characteristics of the body, and the severity of symptoms are taken into account. In accordance with the clinical picture, drugs from several pharmacological groups are used in complex therapy of the disease.
Painkillers
Tablets for concussions are mainly used to relieve pain and relieve cephalalgia. The essence is blocking pain receptors and relieving vascular spasm to expand the lumen of the capillaries. The drugs in this group are toxic, so they should not be taken for a long time. Tablets are prescribed only after diagnosis; pain is not relieved immediately after injury due to the diagnostic importance of the symptom. Despite the different points of application, all medications for concussions have common characteristics:
- quickly relieve pain;
- eliminate spasm of smooth muscles;
- lower the temperature.
The most commonly used analgesic tablets or NSAIDs are:
| Drug name | Cost in rubles |
| Baralgin | 165 |
| Analgin | 12 |
| Sedalgin | 149 |
| Maxigan | 125 |
| Diclofenac | 14 |
| Ketorol | 45 |
| Ketorolac | 27 |
| Pentalgin | 58 |
| Citramon | 10 |
Instructions for use
Instructions for use of Mexidol tablets:
- The drug is taken orally, 3 times every 24 hours, 125-250 mg.
- The maximum daily dose is 800 mg (that is, 6 tablets).
- Duration of treatment with Mexidol: from two to six weeks.
- When relieving alcohol withdrawal, treatment lasts from five to seven days. When stopping treatment, the dose of the drug is gradually reduced over 2-3 days.
- The initial dose of Mexidol: 125-250 mg (that is, 1-2 tablets) 1, 2 times a day, during treatment the dose is gradually increased until the therapeutic effect is fully sufficient.
- For coronary heart disease, the indications for a course of treatment range from one and a half to two months.
For a second course of treatment with Mexidol, the best time is spring and autumn.
Vitamins
A lack of vitamins and microelements will only aggravate the symptoms of injury. Therefore, complex therapy includes vitamin complexes. Both specialized drugs are indicated - most often these are injectable forms of vitamin B, and multicomponent products.
What the doctor will suggest:
- Neurovitan;
- Neovitam;
- Neurobion;
- Magnicum;
- Vitrum;
- Superia.
Injectable forms of drugs are used in the initial post-traumatic period. Tablets – for daily outpatient treatment. The course of treatment with vitamins is long and can be carried out over several months.
Indications for use
- Mexidol is proposed for the treatment of acute cerebrovascular accidents;
- discirculatory encephalopathy (brain disease caused by chronic cerebrovascular accident);
- vegetative-vascular dystonia (impaired vascular tone due to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system);
- atherosclerotic disorders of brain function;
- to relieve withdrawal symptoms (to relieve a condition resulting from a sudden cessation of taking drugs or alcohol) in alcoholism and drug addiction;
- in other conditions accompanied by tissue hypoxia.
- With a concussion.
The drug is used for both therapeutic and prophylactic purposes.
Brain concussion
Vomit
3101 05 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Concussion: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
A concussion is a functionally reversible form of closed craniocerebral injury without organic damage to the brain, resulting from a bruise, blow, and in rare cases as a result of a sudden movement of the head.
Causes of concussion
A concussion can result from a traffic accident, a fall, domestic, sports and work-related injuries, as well as injuries received as a result of street fights and collisions during public events, or exposure to a blast wave. Even a seemingly minor head injury can lead to a concussion. Thus, the fact of an injury may already indicate a possible concussion.
The mechanism of concussion is not precisely known. Most likely, the injury causes some problems with the functioning of the brain's nerve cells (neurons). It is assumed that there is a functional disconnection between the brain stem and hemispheres of the brain. It is believed that due to concussion, a temporary disruption of interneuronal connections occurs. A slight displacement of the layers of brain tissue may appear, their nutrition may deteriorate and the connection between some brain centers may be disrupted, which contributes to the development of functional disorders. In this case, macroscopic and histological changes in brain tissue are not detected.
Among all brain injuries, concussion ranks first in frequency. In most patients, recovery occurs within 1-2 weeks.
If the patient's condition continues to deteriorate over time, and more severe forms of traumatic brain injury have been ruled out, then it is necessary to look for other causes of the existing symptoms - psychological problems, mental illness, side effects of medications or other concomitant diseases.
Classification of the disease
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), concussion is coded S06.0. This nosology is one of the clinical forms of traumatic brain injury.
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and clinical symptoms, three degrees of concussion are distinguished.
Mild concussion. The victim does not have any impairment of consciousness, but disorientation, headache, dizziness, and nausea may occur during the first 20 minutes after the injury. Then general health returns to normal. A short-term increase in body temperature (37.1-38°C) is possible.
Moderate concussion. Although the victim does not lose consciousness, pathological symptoms such as headache, nausea, dizziness, and disorientation may be observed. All of them last more than twenty minutes. Short-term memory loss (amnesia) may occur, most often retrograde amnesia with the loss of several minutes of memories preceding the injury.
Severe concussion. It is necessarily accompanied by loss of consciousness for a short period of time, usually from several minutes to several hours. The victim does not remember what happened - retrograde amnesia develops. Pathological symptoms bother a person for 1-2 weeks after the injury (headache, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, disorientation, loss of appetite and sleep).
Symptoms of a concussion
Physical (somatic) symptoms:
- dizziness at rest, which intensifies when changing body position, turning or tilting the head - this is explained by impaired blood circulation in the vestibular apparatus;
- throbbing headache;
- nausea;
- one-time vomiting;
- rapid breathing, tachycardia;
- blurred vision or double vision;
- flashing of flies or stars before the eyes;
- imbalance;
- increased sensitivity to light or noise;
- ringing, noise in the ears.
Behavioral, emotional symptoms:
- drowsiness;
- increased fatigue or general weakness;
- irritability;
- depression;
- anxiety;
- excessive hours of sleep;
- difficulty falling asleep.
Cognitive symptoms:
- lethargy and impaired coordination of movements;
- short-term confusion;
- slow, incoherent speech;
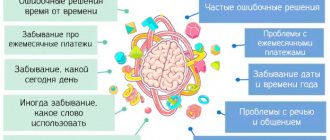
- difficulty concentrating;
- difficulties remembering.
Diagnosis of a concussion
The diagnosis of a concussion is established on the basis of anamnesis, examination and the exclusion of more severe traumatic brain injury.
The doctor examines the patient's entire body for abrasions, bruises, joint deformities, changes in the shape of the chest and abdomen, and bleeding.
In the first hours after a concussion, the victim’s pupils are dilated or constricted - a traumatic brain injury of any severity leads to disruption of the nerve pathways responsible for the functioning of the eyes. The reaction of the pupils to light is normal. The victim complains of pain when moving the eyes to the sides; fine horizontal nystagmus (involuntary trembling movements of the eyeballs) is observed if the eyes are moved to the most extreme positions. Slight asymmetry of tendon reflexes and unsteadiness in the Romberg position (legs together, straight arms extended forward to a horizontal level, eyes closed) may be detected. The level of consciousness is assessed using the Glasgow Coma Scale and is 14-15 points.
The list of laboratory tests includes:
- general blood analysis;
Contraindications and side effects
Like many domestic “broad-acting” drugs, contraindications exist because the drug has simply not been studied in certain situations, and this is written directly in the instructions. In relation to Mexidol, these are conditions such as:
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period;
- childhood.
Also, the drug cannot be used for various “acute failures” of organs associated with the metabolism and excretion of the drug (renal, liver).
Side effects are rare. This may be nausea, headache, dry mouth, drowsiness or, conversely, insomnia. Even more rarely, an allergic reaction occurs.
The best drugs depending on the severity of the concussion
With a mild concussion the following is observed:
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- blurred vision.
What to take for a mild concussion:
- analgin;
- maxilag;
- pentalgin;
- glycine;
- Stugeron.
With moderate severity, the following is observed:
- loss of consciousness;
- nausea;
- noise in ears.
What to take if you have a moderate concussion:
- piracetam;
- theonicol;
- analgin;
- phenazepam.
In cases of severe concussion:
- loss of consciousness;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- short-term memory loss.
What medications are prescribed for severe concussion:
- Corvalol;
- piracetam;
- rudotel;
- tanakan.
For children
The most necessary thing at the beginning of treatment is to ensure complete rest for the child and call an ambulance. They usually prescribe furosemide, piracetam, valerian infusion, and bellaspon as drug treatment.
Mexidol for concussion
Concussions are usually caused by falls, sports, or traffic accidents. A sudden shift in the brain can lead to loss of consciousness. Typically, the longer a person remained unconscious, the more severe the concussion.
Symptoms of a concussion:
- It’s impossible to concentrate and think normally;
- Drowsiness;
- Headache;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Memory loss for a short period of time before or after injury;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Flashes and spots before the eyes;
- Sleep disturbance.
Drug therapy is not mandatory, however, to quickly restore working capacity, victims are recommended to take diacarb with asparkam, Mexidol, vascular, mild painkillers and sedatives.
When treating a concussion, the general condition of victims usually quickly normalizes during the first, less often the second, week after the injury.
There are contraindications, consultation with a specialist is necessary!
Related posts:
- Antibiotics: what they are and why they are needed Antibiotics are medications used to prevent and treat bacterial…
- What is an antiseptic Antiseptic (lat. anti - against, septicus - rotting) is...
- Valerian as a cure for stress Many people from time to time face various stressful situations,…
- Phenibut - a sedative for normal life Insomnia, constant tension, a state of heightened restlessness, affective instability and irritability...
Possible complications
Everything you need to know about the first symptoms and signs of a concussion
Unfortunately, in some cases, a concussion, even with treatment, can lead to certain complications. In particular, vasomotor disorders often occur, which include general constant fatigue, problems with concentration, headaches and dizziness, which worsen with physical activity. As well as frequent and strong rushes of blood to the head, abruptly giving way to general pallor of the skin.
Moreover, a concussion can also affect the psychological state. Often injuries lead to emotional lability, increased irritability, sudden changes in emotions, clouding of consciousness, and neuroses. Much less common are psychoses, which are accompanied by hallucinations and delusions. At risk in this case are professional athletes, especially boxers, who receive blows to the head and, accordingly, concussions of varying severity almost constantly. Often in such cases, dementia and other disorders develop.
If left untreated, post-concussion syndrome develops in case of injury. This is a set of symptoms for a mild concussion that occurs several months after a blow or bruise. Among the complications are:
- Migraine-like headache.
- Dizziness.
- Sensitivity to light and loud, sudden sounds.
- Tinnitus.
- Double or blurred vision.
- Sleep disorders.
- Unstable psycho-emotional state.
- Impaired concentration.
- Difficulties in learning new information.
- Forgetfulness.
There is no special treatment in this case, but based on many years of research, the effectiveness of anti-migraine medications has been proven. Antidepressants and psychotherapy are also used.
When diagnosing a mild concussion, the attending physician will decide what to take based on the condition and individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Self-medication can cause serious complications in the future. That is why, if you suspect an injury, you should contact a specialist.