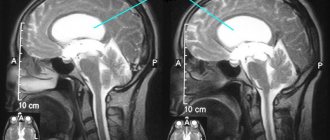
The ventricles of the brain are a collection of cavities of the nervous system filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The ventricles perform several functions:
- protection of brain tissue from mechanical damage (impacts, shocks);
- liquid environment surrounding soft tissues; cerebrospinal fluid contains ions and nutrients that provide trophism to the brain;
- utilization of metabolic products - the ventricles remove “waste” from the brain;
- a single organized system - the ventricles communicate with parts of the brain, delivering mediators from one part to another.
In the brain are located:
- Lateral ventricles;
- Third ventricle
- Fourth ventricle.
Structure and functions of the ventricles of the brain
The brain has four chambers. They produce and circulate in the cerebrospinal fluid. Its main job is to transport nutrients to brain cells, remove waste products from the brain, and absorb head impacts.
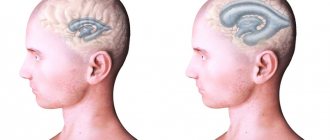
Two lateral ventricles (ventriculi lateralis) are located in the cerebral hemispheres - the first on the left, the second on the right. The normal depth of the sinuses is from 1 to 4 mm. An increase in the capacity of the organ to 5 mm leads to a noticeable change in shape: the lateral C-shaped curvature disappears, the defect acquires a rounded shape.
In this case we are talking about the initial stage of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles. Many people wonder what it is and how dangerous is this pathology?
Causes of enlargement of the cerebral ventricles
Throughout life, there is a gradual increase in the spaces containing cerebrospinal fluid. Some pathological conditions lead to compression of the ventricular structures:
- Hydrocephalus - accumulation of fluid inside the brain with the development of dropsy;
- Birth injury;
- Long-term inflammation of the meninges with the formation of adhesions;
- Hemorrhagic hemorrhages;
- Strokes, hemorrhages.
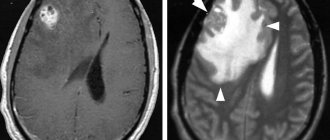
There is a fundamental difference between the concepts of asymmetry and ventricular dilatation. The second nosology is an independent disease. It is formed under the influence of intrauterine infections and acquired pathology. Asymmetry is caused by additional cerebral formations (tumors, limited accumulation of blood). Immediately after birth, the condition is detected by ultrasound through open fontanelles. After healing of the cranial sutures, soft tissue components are shown by MRI.
The clinical picture of the asymmetrical arrangement of cerebral structures depends on the location and degree of compression. Small imbalances in the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid are compensated by the reverse absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
The cause of dilation may be overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid. In most cases, the etiological factor of the nosology is a violation of oxygen supply (hypoxia). The condition provokes increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid in order to improve the supply of nutrients and vitamins to the brain formations.
Causes of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles
The expansion (expansion) of caverns is associated with the accumulation of liquors in them. There may be two reasons for this: excessive production of fluid or disruption of its outflow.
The following diseases can provoke an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid:
- Hydrocephalus, in which the absorption of cerebral fluid is impaired.
- Changes in the central nervous system - schizophrenia, bipolar disorder.
Inadequate circulation of cerebrospinal fluid occurs when mechanical compression of the exit ducts occurs.
This phenomenon is most often caused by damaging factors:
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Malformation of the Sylvian canal (a narrow canal connecting the third and fourth ventricles);
- Brain hemorrhages;
- Intracranial tumors, cysts, papillomas, hematomas;
- Meningitis;
- Thrombosis of cerebral veins.
Lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain often occurs in newborns, more often in premature infants.
Benign intracranial hypertension syndrome in children: diagnosis and treatment
A lot of controversy arises around the so-called intracranial hypertension syndrome.
Someone says that such a condition does not exist and doctors are allegedly engaged in pseudo-treatment, deceiving parents. Most often, this misinformation is carried out by doctors of related specialties themselves, and sometimes even directly by some pediatric neurologists. The purpose of this short article is to explain in an accessible form what this mysterious, ambiguous condition is - intracranial hypertension syndrome? To do this, I will rely primarily on scientific articles, the results of various studies, as well as my personal experience as a practicing neurologist at a medical center with almost 10 years of medical experience.
Symptoms of pathology
We often have to listen to parents complain that their child has such unhealthy signs as:
- tearfulness;
- restless sleep;
- decreased appetite;
- irritability.
Of course, these manifestations are not characteristic only of intracranial hypertension syndrome (ICH). Almost any illness can cause these symptoms. One can say even more, it is impossible to reliably diagnose ICH syndrome only on the basis of patient complaints. Any pain syndromes in children tend to generalize. Also, headaches in children, especially in the first years of life, are manifested by general reactions similar to the complaints described above, which complicates topical diagnosis.
Examination of the child is very important for a high-quality diagnosis of pathology. First of all, you should pay attention to such additional signs as:
- Enlarged, rounded head shape.
- Swelling and pulsation of the large fontanelle.
- Expansion of the vascular network at the temples, bridge of the nose, and around the eyes.
- Neck muscle tension.
- Graefe's symptom (manifestation of sclera between the upper eyelid and the iris of the eye, exophthalmos).
The baby's behavior also changes. He has a desire to lie on a cold surface, putting his head against it, he can touch, hit his head with his hand or a toy, both his own and someone else’s, hit his head on the floor or wall, or simply scratch behind the ear. Often, intracranial hypertension syndrome can be accompanied by nosebleeds.
Features of the disease
Information about the child’s life history, illness, and heredity is important for a specialist. The main cause of the development of ICH syndrome is perinatal hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system (CNS). Children with a burdened obstetric history are at risk for the development of intracranial hypertension. The course of ICH syndrome is chronic, with periods of exacerbation followed by periods of remission. Like any chronic disease, there is no point in trying to cure it completely. The main task of the doctor is to transfer the course of the disease to the stage of remission.
It should be understood that in the remission stage such a child is no different from a healthy peer. He is also well developed in psycho-speech and motor development. If this is not the case, then it is a different condition, but it is important to know that ICH syndrome does not cause delays in the development of the child. In medical practice, there are cases of the spread of ICH syndrome in one family (among siblings and cousins).
Diagnosis of the disease
In terms of instrumental confirmation of ICH in children, nowadays there are many neuroimaging methods, in particular:
- neurosonography (number 1 for children of the first year of life);
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
It is worth noting that none of these methods can directly determine the amount of intracranial pressure, but they can show indirect signs (expansion of the liquor spaces, dilation of the veins and venous sinuses of the brain). Most authors agree that for a reliable diagnosis of benign intracranial hypertension, a child needs a combination of three of the following four criteria:
- Increase in head circumference.
- The presence of ventriculomegaly (enlargement of the ventricles of the brain).
- Headaches or their equivalent in children under 3 years of age.
- Complicated obstetric history.
There are other syndromes with similar manifestations that require a different approach in terms of treatment and diagnosis. These include: the consequences of traumatic brain injury or neuroinfections, intracranial tumors and hematomas, the initial stage of occlusive hydrocephalus, which we will not dwell on in this article.
Treatment methods
So we found out that the child has ICH syndrome. What to do? First of all, don't panic! As noted above, developmental delays do not develop in children with this syndrome. The main problem is pain. To eliminate it, you should not use painkillers. It is necessary to dehydrate the body with diuretics. In particular, the drug Diacarb, by inhibiting the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, not only accelerates the excretion of cerebrospinal fluid, but also reduces its production. Do not try to prescribe medications to your child yourself! This should only be done by a qualified doctor. The inclusion of nootropic and vasoactive drugs in therapy increased the percentage of positive treatment outcomes in various studies.
Preventive measures
In addition to drug treatment, it is necessary to follow certain rules necessary to prevent exacerbation of ICH syndrome:
- Any blows, even minor ones, to the child’s head are undesirable.
- Correct sleep and wakefulness patterns.
- Do not allow your child to stay in noisy rooms for a long time.
- Limit water load in the evening.
- Do not walk for a long time in the sun, especially without a hat.
And, perhaps, the best information: the manifestations of ICH syndrome become less frequent with age and can often gradually disappear forever. That is why the incidence of benign intracranial hypertension in adults is extremely low.
Kabardiev Alimkhan Arslanovich, pediatric neurologist.
Works in a clinic of a medical network in the city. Khasavyurt at the address: st. Abubakarova, 9a.
Opening hours: daily, Monday to Saturday - from 13.00 to 17.00.
Phone numbers for inquiries and appointments: +7
Symptoms of enlarged ventricles
The mechanism of development of pathology has common features, regardless of the reasons. Fluid accumulates in the ventricles, which expand and contract brain tissue. The pressure in the cavities themselves also increases.
Patients may complain of sudden headaches, nausea and vomiting, a feeling of distraction in the eyeballs, hearing and vision problems. Performance gradually decreases, memory impairment, apathy, and drowsiness appear.
All these are symptoms of pathology of the spinal system. If the abnormality is not detected and treated early, it becomes a chronic condition.
Symptoms and signs
Ventricular asymmetry does not have a specific clinical picture. All symptoms of the pathology are common and are characteristic of many infectious diseases of the nervous system. In terms of symptoms, asymmetry can imitate, for example, intoxication syndrome.
Symptoms of pathology in adults:
- Dizziness and headaches.
- Nausea and urge to vomit.
- Feeling of fullness in the head.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Visual impairment, slower reaction of the eyes to a visual stimulus.
- Diplopia is double vision.
- Hearing impairment, possibly tinnitus.
- Unpleasant sensations in the head when turning the head sharply, sneezing and coughing.
- Mental symptoms: irritability, emotional lability.
- Autonomic symptoms: hyperhidrosis - increased sweating, hot flashes to the extremities.
It is important to remember that the presence of these symptoms does not determine that the lateral ventricles of the brain are asymmetrical and the final diagnosis is made only after instrumental research methods.
Signs of pathology in children:
- Constant crying, anxiety.
- Lack of appetite.
- Throwing the head back.
- Frequent regurgitation immediately after eating, as a result of which the child does not gain weight well.
Diagnostics
Lateral ventricular asymmetry is detected using the following procedures:
- Ultrasound of the brain is the most informative examination;
- Examination of the fundus, detection of swelling of the eye disc, spasms, hemorrhages;
- Neurosonography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography of the brain.
If the above methods give conflicting results, lumbar puncture is recommended. Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid reveals the cause of the curvature of the lateral sinuses.
Neurosonography technique and its results
Signs of a concussion in a child: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Neurosonography can be carried out both within the walls of a medical institution (maternity hospital, for example), and on an outpatient basis - in a children's clinic or private medical center. It takes about a quarter of an hour. During this procedure, the baby is picked up and the head is exposed. When studying babies in the first months of life, it is desirable that they are well-fed and calm, since strong crying can complicate the study and even distort its results.
Ultrasound of a child’s brain does not require any specific preparation. The most important condition for success is calm, so about half an hour before neurosonography, the baby needs to be fed. The ideal examination option is for the child to be asleep, but if the baby is not going to sleep, then you can distract him with an interesting toy, a pacifier or a drinking bottle.
Before starting the diagnosis, the doctor assesses the child’s height, weight and clarifies his age, then applies a special neutral gel to the child’s scalp in the area of the large fontanelle, which helps in conducting the wave to the soft tissues. It is advisable that the gel is not cold, as cold may cause anxiety in the subject. After applying the gel, using a sensor that moves directly over the skin, intracranial structures are examined, and the image is transmitted to the screen.
After examining the brain and its structures on the monitor screen, measuring their sizes, determining the nature of the blood flow, identifying possible foci of pathology, the skin of the baby’s head is wiped with a clean towel or diaper, and the parent receives a specialist’s opinion.
It is important to note that the conclusion does not indicate a diagnosis, but only the identified anatomical and functional features. The diagnosis will be made by a neurologist or pediatrician if any abnormalities are detected during neurosonography
Repeated study
Most often, parents prefer to perform an ultrasound when the child grows up a little. 1 month is the most optimal age. But in cases where the above-described alarming symptoms are observed, the procedure is performed in the maternity hospital for newborn babies.
However, parents should be prepared for the fact that several such studies will be required. If a deviation is detected in the baby, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. Such a child must receive the therapy prescribed by the doctor. Treatment is carried out for 1 month or 2. Then the baby is sent for re-examination. Ultrasound is necessary to monitor the dynamics of the disease. The doctor must make sure that the prescribed therapy is effective and that the pathology identified in the baby is treatable.
For children in critical condition, such research is a real salvation. These babies undergo ultrasound almost every day. Moreover, unlike x-rays, it does not cause harm to health.
Pathologies
By refusing an examination, parents risk not being seen in time, and, therefore, not starting timely treatment in the case of tumors of the type. Cysts can be different - some, for example, arachnoid ones, are quite dangerous for the baby and definitely need treatment.
An increased volume of cerebral fluid inside the skull may indicate the presence of dropsy of the brain, and darkening and vascular pathologies may indicate ischemia, cerebral palsy, and hematomas. The appearance of such terms in an ultrasound report is not yet a diagnosis, since additional diagnostics are required to make a diagnosis; neurosonography alone is not enough.
Quite often, such examinations reveal physiological and functional disorders that do not require any therapy and go away on their own over time. They are caused by neurophysiological immaturity of the brain - a condition quite natural for newborns.
Some formations have a favorable prognosis, but require regular monitoring, and some conditions, for example, require treatment as soon as possible.
You should not assume that a child who visually appears completely healthy cannot have abnormalities in brain development. They are quite insidious and it is almost impossible to see them with the naked eye, unless, of course, the pathologies are of a total nature. We say this not to scare parents, but so that they think carefully before abandoning neurosonography, considering it unnecessary and even harmful.
Consequences
Lateroventriculoasymmetry of the ventricles in a child can have various consequences.
With slight asymmetry, there may be a disturbance in the development of mental and motor functions, which will correct and return to normal over time.
The severe form is the most dangerous, as there is a risk of cerebral palsy, serious mental and nervous disorders, deformation of the skull bones with brain damage.
Detection of asymmetry in a newborn signals the need for comprehensive diagnostics and specialist consultation.
Up to three months, neurological disorders are difficult to identify, so the child must be constantly under the supervision of a neurologist.
If you ignore pathology in an adult, the following manifestations are possible:
- development of chronic cephalgia;
- intellectual impairment;
- the appearance of cognitive disorders;
- dementia (brain cell atrophy);
- impaired coordination of movements.
Timely diagnosis and well-chosen therapy are the key to the health of an adult and the normal development of a child.
For newborns (infants)
Ventriculomegaly is dilatation of the lateral ventricles in a fetus, newborn, or infant in the first year of life.
The first signs of pathology can be detected exactly at the 17th week of pregnancy.
Most often, the pathology manifests itself in premature infants; the asymmetry of the ventricles can be seen in the photo.
Typically, such babies at birth have formed ventricles, while the skull has not yet reached the required size.
If this deviation is not caused by a specific reason, then this may mean that after some time the proportions will level out to normal.
The main causes of ventriculomegaly in newborns:
- intrauterine infections in the mother (syphilis, toxoplasmosis, rubella, mumps, etc.);
- asphyxia of the newborn;
- birth injuries;
- hydrocephalus, which is determined before birth;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus;
- heredity;
- The age of a pregnant woman over 35 years increases the risk of pathology.
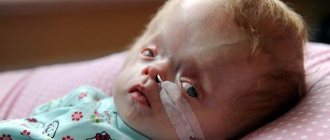
Manifestations of ventriculomegaly in children depend on the age of the baby. A small child with a pathology is often capricious, inhibited, may refuse to breastfeed, and his gaze is usually directed downwards.
If a child has an isolated pathology and no other abnormalities or genetic disorders, the prognosis is usually favorable.
But this only happens if the child receives a month-long course of competent treatment immediately after birth.
In adults
Ventricular dilatation in an adult is usually a secondary symptom, which is caused by the presence of a specific pathology.
For example, dysfunction of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation occurred after a head injury, stroke or infectious disease.
Ventriculoasymmetry of the brain in an adult cannot be ignored. To cure the disease it is necessary to undergo a full medical examination.