The risk of this disease increases in people over 45 - 50 years of age. Moreover, up to 40% of hemorrhages can be fatal. How to recognize the problem and what to do? Let's find out with the expert ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member of the St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists POLINA PETROSYAN Neurologist at SM-Clinic, specialist in cerebrovascular diseases and headaches
The second name for this pathology is hemorrhagic stroke. It occurs at any age, but most often mature and elderly people suffer - approximately 15 - 20% of all serious cerebrovascular accidents are caused by cerebral hemorrhage.
What is a cerebral hemorrhage
A cerebral hemorrhage is a life-threatening condition that occurs when one of the brain's arteries ruptures, causing blood to leak into the brain tissue.
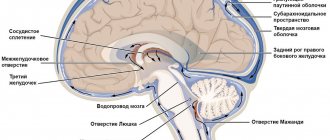
The brain tissue becomes saturated with blood or a hematoma forms (an accumulation of blood that puts pressure on surrounding tissues); blood may leak into the ventricle of the brain, which disrupts the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and increases intracranial pressure. The part of the brain that has lost blood due to rupture of blood vessels and those tissues that are saturated with blood stop working, the cells die. Accordingly, the larger the vessel that ruptures, the more dangerous the consequences will be for life and health.
Therapeutic measures
Since this condition usually develops quickly, the presence of the first suspicious symptoms should be a reason to urgently go to the hospital. If the doctor says that you need to go to the hospital, you should under no circumstances refuse. In any case, timely treatment of vascular pathologies can prevent the development of a dangerous condition.
It should be borne in mind that intraventricular hemorrhages quickly lead to death. Sometimes a patient's death occurs shortly after his or her admission to a medical facility. The danger of the pathology lies in the fact that the outpouring of blood affects the vital brain centers located at the bottom of the rhomboid fossa.
If the victim is diagnosed with hemorrhage, then therapy for the hemorrhage is aimed at its rapid elimination. To save the patient’s life and provide effective treatment, specialists resort to surgery. This takes into account the presence of diseases in the anamnesis and possible contraindications. If the victim falls into a coma and remains in this state for more than 12 hours, then the operation no longer makes sense, since serious complications will arise.
Surgical treatment consists of puncture suction of blood from the brain cavities with special instruments and removal of formed hematomas, which allows normalizing intracranial pressure and stopping compression of adjacent tissues and structures of the brain.
Causes of cerebral hemorrhage in adults
There are many reasons why blood vessels rupture and blood spills into the brain tissue. Among the most common are:
- arterial aneurysms (thinning of the wall, the formation of a sac with blood that overflows and bursts);
- vascular malformations (birth defects, thinning, tortuosity of the walls);
- ruptures of blood vessels during a hypertensive crisis due to the prohibitive load on the walls;
- head injuries with vascular ruptures;
- tumors that grow and damage arteries;
- taking blood thinning medications (if dosages are not followed);
- the development of certain systemic diseases in which the walls of the arteries are affected (for example, amyloidosis).
At a young age, the leading causes of hemorrhage are injuries and congenital vascular anomalies. In the elderly – damage to blood vessels by atherosclerosis and their rupture due to hypertension, tumor processes.
Recovery time after hemorrhagic stroke
The rehabilitation performed after such a brain injury consists of several stages:
- early period, lasting about six months after the attack;
- later recovery, lasting from six months to 1 year;
- the stage of final recovery, which in its duration occupies the entire subsequent time.
A year after the attack, residual effects begin. The best results during rehabilitation can be obtained in the first year; for this reason, recovery should not be delayed.
Effective results are obtained by strictly observing the following important principles:
- taking action at an early stage of ongoing treatment in a hospital;
- daily implementation by the patient of appropriate recommendations without any delays;
- prescribing special physical activity with appropriate intensity and gradual complication of exercises.
In addition, it is very important to take comprehensive measures: prescribing physiotherapy, drug treatment and the necessary correction of the patient’s psychological state. During this period, a recovering person must protect himself from unnecessary stressful situations, and also be surrounded by the care and love of family and friends.
Symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage in adults
The key symptoms that occur during a cerebral hemorrhage were given to us by neurologist Polina Petrosyan. According to her, intracerebral hemorrhage is characterized by an acute onset, with a rapid development of the clinical picture:
- sudden severe headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness.
Depending on the volume and location of the hemorrhage, the following may occur:
- one-sided weakness in the limbs (hemiparesis) up to a complete lack of movement in them (hemiplegia);
- restriction of eyeball movement;
- speech impairment - both its reproduction and understanding;
- difficulty swallowing and breathing;
- disturbance of consciousness up to coma.
Much of the severity of symptoms depends on what part of the brain is damaged, how much blood leaks out, and how large the vessel is.
Subdural hematoma.
This type of brain hematoma means the outpouring and accumulation of blood in the space between the membranes of the brain. The most common cause is traumatic brain injury of varying severity. However, a subdural hematoma can also be caused by vascular damage due to hypertension, arteriovenous malformations (pathologies of the connection between veins and arteries) or aneurysms.
There are such forms of subdural hematoma as:
- acute (the first manifestations occur within 72 hours after injury);
- subacute (manifests symptomatically from 72 hours to 21 days after injury);
- chronic (manifests within 3 weeks after injury).
The symptomatic manifestation of a subdural hematoma is extremely variable and in most cases begins after the so-called “light” interval, which means some time after the injury (from several minutes to several days and even up to several months or years in the chronic form), when there are no manifestations of the hematoma. This type of cerebral hematoma is also characterized by an undulating progression of the disease with the risk of sudden loss of consciousness.
Diagnostics
A doctor may suspect a brain hemorrhage based on typical symptoms, especially if they are associated with injury or other risk factors.
But the gold standard for diagnosis is brain CT. On the first day after the onset of hemorrhage, the data will be most accurate, even more significant than with MRI. On tomograms, fresh hematomas are clearly visible; the doctor can determine their exact location, size and shape. In addition, he immediately assesses how damaged the brain structures, membranes and cerebrospinal fluid circulation system are. If hemorrhage is detected after 3 days or more, an MRI will be more accurate. It will better identify a hematoma in which the blood already has oxidized, partially disintegrating hemoglobin.
If these are young people without hypertension, they may be prescribed angiography of cerebral vessels. Additionally, an ECG, chest X-ray, blood tests for electrolyte levels, PTT with APTT (coagulation indices) are performed.
Recovery points after hemorrhagic stroke
Complications for the patient mainly depend on the location of the hemorrhage that occurs, as well as its volume. Today there are the following groups of possible threatening consequences:
- Motor disorders. The appearance of severe weakness and paresis in a person, the patient’s inability to accept and maintain a sitting position. This may be paralysis of one side of the body, high muscle tone or spasms that occur, which seriously complicates self-care, requires mandatory assistance and causes a lot of inconvenience to the person.
- Impaired sensitivity is, for example, numbness of the limbs, a feeling of “insects under the skin” and burning, the inability to control the hands, leading to various everyday problems.
- The appearance of speech pathologies after a stroke is confusion of speech and the inability to correctly pronounce individual sounds or loss of the ability to maintain a conversation. There may be loss of skills such as recognizing the meaning of words, counting, reading, telling time by a clock, and understanding calendar periodicity.
- Problems with swallowing when eating food and various liquids, and in some cases, complete loss of the ability to eat independently.
- Disorders of the excretory system: the appearance of urinary and stool incontinence, problems with the intestines and urinary system that arise on an ongoing basis.
The patient often develops acute and chronic psychological and mental disorders in the form of depression, excessive emotional temper or apathy. Sometimes partial amnesia occurs: the inability to recognize familiar people or objects, the understanding of performing simple everyday actions disappears.
Consequences of cerebral hemorrhage in adults
The most dangerous thing with a cerebral hemorrhage is the consequences that can develop.
Among them, Polina Petrosyan notes: “The consequences can lead to disability, but may not affect a normal lifestyle and ability to work,” says Dr. Polina Petrosyan. – After hemorrhage, one-sided weakness in the limbs, decreased sensitivity in them, and various speech disorders may persist. Full recovery is possible if rehabilitation measures are taken in a timely manner and if the patient independently puts effort into rehabilitation measures.
Prevention
Intraventricular hemorrhage can be prevented by adhering to the following rules:
- Monitor blood pressure. If the levels are consistently high, be sure to undergo the necessary treatment.
- Do not take medications that affect blood composition without your doctor’s knowledge.
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
After a stroke, life goes on, but not everyone manages to survive it. Much depends on the location of the lesion and the true causes of bleeding. If the pathological process is caused by vascular disease, then the respiratory and cardiac systems suffer. Oncological pathologies and skull injuries often lead to severe consequences, including cerebral edema and coma. A timely operation and competent treatment tactics during the rehabilitation period help to avoid a sad outcome.
Surgical treatment of ependymoma
The only correct treatment is to remove the brain ependymoma. The neurosurgeon performs the operation after simple preparation and a comprehensive examination. Diagnosis primarily involves performing a computed tomography scan. Experts also prescribe magnetic resonance imaging. Differential diagnosis involves determining the exact type of tumor and comparing it with other gliomas.
After surgical treatment of brain ependymoma, the cerebrospinal fluid is subjected to additional cytological diagnostics. The study allows you to determine the number of tumor cells and make an appropriate prognosis for the future.
Before the operation, the patient undergoes installation of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid. It is extremely important to seek help from experienced and qualified professionals. Similar operations are carried out at the expert level at the Burdenko Research Institute. If the neurosurgeon does not have the necessary skills and knowledge, damage to the cranial nerves and other complications, including speech problems, may occur. Temporary disturbances usually disappear in the first months after surgery.
Radiation therapy is an adjunct to surgery. It is also used when it is impossible to completely remove brain ependymoma in patients in an advanced stage of the disease.
Types of rehabilitation after hemorrhagic stroke
The necessary medicinal and motor rehabilitation is carried out for the following purposes:
- significant reduction in the risk of recurrence of hemorrhagic stroke;
- gradual return to normal lifestyle;
- return of lost ability to work;
- the patient performs basic skills and actions;
- preserving the patient’s identity through the provision of social and psychological assistance.
Drug treatment
In the human brain, dead neurons are replaced with elements with high activity. But due to the increasing load, additional energy is necessarily required. Neurons that remain alive after damage restore lost functions over time.
Prescribed medications provide additional nutrition and significantly improve recovery processes in the brain. Additional courses of essential drug therapy are recommended once every three months throughout the year.
Drugs that are administered to the patient by injection during treatment:
- nootropics, which include piracetam, Actovegin and other drugs;
- medications to stimulate the necessary impulses in brain cells, for example, proserin or neuromidin;
- selected B vitamins that improve cell metabolism.
Taking the prescribed medications should continue even after completion of the prescribed treatment in the hospital. At home, tablets are taken with food.
Chronically high blood pressure is corrected with medication. If necessary, the doctor prescribes suitable medications for blood pressure, calcium channel blockers in vascular cells, or drugs to lower blood sugar levels.
Motor recovery
It is necessary to restore lost movement already at the stage of inpatient treatment after primary care has been provided. It is imperative to provide physical activity to the limbs to improve blood circulation, which helps in reducing tone and prevents the appearance of congestion in the blood vessels, and also protects the patient from the occurrence of pneumonia due to a recumbent lifestyle.
The position of the limbs in a supine state, if necessary, is corrected using a splint or special weights. Such patients must turn over every 2 hours to prevent the appearance of bedsores on the skin; in addition, this is recommended to stabilize blood pressure.
A few days after the attack, passive gymnastics begins, during which the person is assisted in smooth movement of various parts of the body. Procedures are carried out only if the person does not experience pain. If the condition improves, you should help the patient learn to take a sitting position, and then help him restore an upright position. Before walking, leg training is performed in order to regain the lost sense of position in space. Then the patient needs to begin to move around using supports, walkers and canes.
Movement restoration techniques
Physical therapy plays a significant role in the rehabilitation of lost motor ability. In this case, suitable exercises are developed for different muscle groups, classes are conducted using special simulators, and a device is used to reduce high muscle tone.
Prescribing a special massage is very useful. First, the limbs are stroked with a sufficiently high muscle tone, and then other muscle groups are rubbed. The use of a warm heating pad before the session significantly improves the effect. The massage procedure can take 20 minutes and mainly depends on the current condition of the patient.
Effective methods of physiotherapy include oxygen baths, electrophoresis of blood vessels in the neck, and electrical stimulation of muscles that have lost their functions as a result of a stroke.
Speech restoration
The return of speech is possible even after an attack that occurred more than a year ago. Conversation after a stroke should be slow and words pronounced clearly. At the same time, there is no need to rush to answer and ask difficult questions.
Working with a speech therapist helps a lot in restoring muscle functionality. Practicing in front of a mirror can also be very useful. In the process of noticeable improvements, it is possible to complicate tasks and stimulate a person to pronounce more complex spoken phrases.
Restoring breathing and swallowing
Nutrition of patients in a hospital is most often performed using a special feeding tube. Then comes the time to independently master the skill of eating food. Proper preparation of foods greatly simplifies the rehabilitation of a patient seriously affected by a stroke. Cooked food should be warm, not hard and have a soft texture. Flavorful foods trigger saliva production.
Patients should absolutely not be rushed during the process of eating; this process can take half an hour or more. You may need help holding a utensil or spoon. Restoration of the functions of the swallowing muscles occurs with regular repetition of the nutritional process.
Psychological recovery
Many patients develop depression and serious behavioral problems after a severe hemorrhagic stroke. Properly selected drug therapy helps in restoring thinking: courses of nootropic drugs that stimulate neurometabolic functions
Correcting the current state of the psyche is possible with regular work with a psychologist and psychotherapist. A good effect is achieved in group and individual psychotherapy sessions with an appropriate specialist. In this case, support from relatives and friends is of great importance, restoring a person’s joy of life and self-confidence.
Typically, the prognosis after this disease is unfavorable due to severe damage to brain function and its gradual progressive swelling, often leading to death. In some cases, death may occur due to another hemorrhage that occurs in another part of the brain. Even if the patient survives, the consequences often lead to disability, and recovery from a hemorrhagic stroke becomes an extremely difficult and lengthy process.
Full recovery after a stroke is almost impossible, but still, partial return of lost functions with due persistence, good care and the necessary care becomes possible.
For this purpose, doctors, nurses, physical therapy instructors, caregivers and nannies take part in the rehabilitation process. This often takes months and years. Rehabilitation procedures are carried out in special departments of hospitals and sanatoriums, where highly qualified specialists closely monitor the patient’s recovery.