Vascular diseases of the brain
The brain (cerebrum)
is an organ of the central nervous system, consisting of many interconnected nerve cells and their processes.
Vascular diseases of the brain are recognized in medicine as one of the most dangerous groups of diseases, as they have quite serious consequences for the body. Each cerebral vascular disease has characteristic features that depend on which specific vessels are affected by the pathological process. But in any case, doctors at OKB No. 1 warn that diseases in this group can provoke a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, after which the patient either becomes disabled or dies.
Clinical manifestations of vascular diseases of the brain can be divided into the following forms:
- chronic cerebral ischemia stage I-II;
- cerebral circulatory disorder of a transient nature;
- cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke);
- bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke).
Causes of cerebrovascular diseases:
The occurrence of cerebrovascular diseases occurs as follows: insufficient blood supply limits the access of oxygen and glucose, resulting in a cerebral infarction, the results of which are unpredictable. In adulthood, vascular atherosclerosis and hypertension can negatively affect blood supply.
Treatment of vascular diseases of the brain:
Among the many diseases of the cerebral vessels, coronary disease and discirculatory encephalopathy deserve special attention.
Treatment of ischemic disease involves:
- work on restoring impaired physiological and behavioral functions, for which restorative therapy, magnetic and electrophoresis, physical therapy, and massage are used;
- stabilization of blood pressure and prevention of strokes with the help of anticoagulant and vasodilator drugs;
- normalization of metabolism and proper blood circulation. The best results are ensured by taking medications according to medical prescriptions.
Vegetative vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a disturbance in the functioning of the body’s vascular system, leading to insufficient oxygen supply to tissues and organs. Otherwise, this disease is called neurocirculatory dystonia, or cardiac neurosis.
Causes of VSD:
- Exhaustion of the body due to acute or chronic infectious diseases or intoxications.
- Sleep disturbances such as insomnia, early awakening or difficulty falling asleep.
- Chronic fatigue, depressed mood, depression.
- Irregular unbalanced diet.
- Excessive physical activity or physical inactivity.
- Hormonal changes in the body during puberty in adolescents, pregnancy or menopause in women.
- Change of climate or time zone.
Types of vegetative vascular dystonia:
With a more accurate diagnosis, three types of vegetative-vascular dystonia are distinguished:
- if, with general signs of fatigue, you sometimes have a feeling of lack of air, you complain of irregular heartbeats, then this is vegetative-vascular dystonia of the cardiac type;
- The hypotensive form of vegetative vascular dystonia is characterized by low blood pressure, general weakness, headaches, coldness of the fingers and toes, and a tendency to faint;
- periodic surges in blood pressure indicate hypertensive vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Diagnosis of VSD:
The diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia is made only after a comprehensive examination of the patient and the exclusion of other pathologies that have similar manifestations to VSD.
The list of diagnostic measures includes:
- Laboratory research of general blood test, biochemical composition of plasma, coagulation indicators, hormone levels. If necessary, urine tests are performed. Most often, the indicators of these studies do not go beyond normal values.
- Functional techniques, including ultrasound examination of internal organs and blood vessels of the head and neck, ECG, monitoring of blood pressure levels.
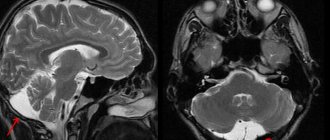
- X-ray of the spinal column, tomography of the brain and spinal cord.
- Consultations with specialists in related specialties.
Only after confirming the absence of other diseases can a diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia be made.
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia:
The majority of patients with VSD do not require drug therapy. The basis of treatment for them is methods aimed at changing the patient’s lifestyle and normalizing the functioning of the nervous system. Physiotherapeutic methods are mainly used to treat the disease. This could be hydromassage, physical therapy. If the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are serious, acupuncture, manual therapy, and herbal medicine give good results. Vegetative-vascular dystonia responds well to treatment. The main thing is not to self-medicate. The choice of methods by which to treat vegetative vascular dystonia should be determined only by a doctor after conducting the necessary research. Often, VSD “masks” another disease, so its treatment should be aimed primarily at eliminating the underlying disease. And, of course, first of all, don’t bring yourself to the point of needing to see a doctor: try to avoid stressful situations and emotional breakdowns, and, if possible, take a few days of rest and spend them as you would like for a long time. Thus, treatment of vegetative vascular dystonia should be based on both drug therapy and regulation of the mental state.
Vascular neurology: consultation of professionals
Most people do not consider migraine a serious symptom, and yet it is at the initial stage that it is worth contacting the neurology center in Moscow.
Therefore, as soon as you note:
- frequent headaches, especially paroxysmal ones, making it difficult to concentrate;
- increase or sharp decrease in pressure;
- tinnitus, hearing impairment;
- dizziness, nausea that occurs when turning the head;
- “butterflies” before the eyes and other visual disturbances;
- fatigue, insomnia, nervousness, -
Make an appointment for diagnostics at the State Research Center for Pregnancy and Pregnancy as soon as possible. One of our main specializations is neurology, consultation is provided to all applicants without any restrictions.
Vascular neurology in our center is studied at a very high level, our doctors never stop improving their qualifications, raise their level, participate in seminars and exchange experiences with foreign colleagues. Only the latest equipment is used, which makes it possible to make the most accurate diagnosis and begin treatment immediately. Paid neurology in our center is a modern approach to the treatment of many diseases. Our doctors do not make “vague” diagnoses and do not try to treat non-existent diseases. We work honestly, professionally and efficiently.
Vascular diseases of the spinal cord
The spinal cord (Medulla spinalis)
is an organ of the central nervous system, consisting of nerve cells and fibers and located in the spinal canal. It starts from the brain and ends in the vertebrae of the lumbar spine and is a long cord, shaped like a cylinder.
It consists of gray matter, which is surrounded on all sides by white matter. The gray matter is predominantly nerve cells, and the white matter is the processes of nerve cells. Spinal cord damage can be caused by various factors. Diseases of the brain and spinal cord, as well as other lesions of its various parts can cause sensory, motor and autonomic disorders. The length of the adult spinal cord ranges from 41 to 45 cm. The spinal cord regulates the functions of the entire body by transmitting nerve impulses to all internal organs.
The human spinal cord can be divided into 5 sections:
-cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal. Syndromes of spinal cord lesions differ at different levels, and also depending on which substance is affected, gray or white.
Myelitis
Myelitis
is an inflammation of the spinal cord. The sooner we stop the inflammation, the less the loss of spinal cord substance, the faster the recovery.
Causes and symptoms of myelitis:
Inflammation and destruction of spinal cord tissue leads to a disconnection of communication between the brain and the body, and therefore to:
- sensitivity disorders;
- paresis (paralysis).
Myelitis usually responds well to treatment, you just need to clarify the cause of its occurrence. Therefore, we suggest you conduct research on the following:
- neuroinfections;
- multiple sclerosis;
- disseminated encephalomyelitis.
Diagnosis of myelitis:
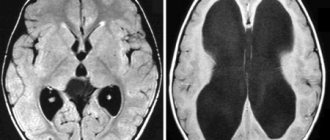
- On MRI scans of the spinal cord, foci of inflammation and demyelination are clearly visible.
- Blood tests for antibodies to various infections and rheumatic indicators make it possible to differentiate between neuroinfection and autoimmune inflammation.
- Blood biochemistry data will help identify possible metabolic disorders, which will allow you to select medications correctly.
- A detailed immunogram will allow you to clearly assess the cause of what is happening and select the appropriate treatment for this situation.
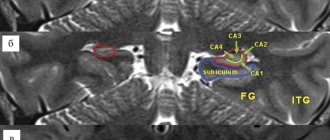
- ENMG (electromyography, electroneuromyography, myography) is a set of studies to assess muscle function and the quality of transmission of nerve impulses along peripheral nerves and pathways of the brain and spinal cord. ENMG helps us pinpoint the location of the injury (brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerve or muscle)
Information for patients and their relatives
Rules for hospitalization
Services and prices of the department
Treatment of neurological diseases in a hospital
If you are experiencing headaches, neurology can help solve the problem. And it is not at all necessary to go to the hospital; you can often recover at home. But for those who have a more serious diagnosis, have suffered a stroke, hospitalization is indicated, neurology in this case can provide significant assistance. Our specialists will strictly monitor the patient’s condition and ensure that all patients receive maximum care and assistance. If you receive a referral to neurology, the hospital becomes an opportunity to restore your health in a comfortable environment.
How are NS pathologies diagnosed?
To identify and diagnose a vascular problem in the nervous system, a neurological examination is needed. The neurologist evaluates the following indicators: the patient’s intelligence and awareness, his ability to navigate reality and space, reflexes, etc.
Often, tests and hardware studies are necessary to establish and clarify the diagnosis. For this, patients are prescribed:
- CT;
- various types of ultrasound diagnostics;
- electroencephalography;
- X-ray examination;
- angiography;
- lumbar puncture;
- clinical blood tests;
- other diagnostic methods.
Types of vegetative vascular dystonia
With a more accurate diagnosis, three types of vegetative-vascular dystonia are distinguished:
- if, with general signs of fatigue, you sometimes have a feeling of lack of air, you complain of irregular heartbeats, then this is vegetative-vascular dystonia of the cardiac type;
- The hypotensive form of vegetative vascular dystonia is characterized by low blood pressure, general weakness, headaches, coldness of the fingers and toes, and a tendency to faint;
- periodic surges in blood pressure indicate hypertensive vegetative-vascular dystonia.
If you have the above symptoms, then, first of all, you should reconsider your work and rest schedule, and of course it is advisable to consult a neurologist. Since vegetative-vascular dystonia is directly related to the condition of the blood vessels, you may be offered to undergo Dopplerography of the cerebral vessels.
How vascular lesions affect the brain
For proper functioning of the brain, it is important to maintain cerebral blood flow at a constant level. That is why this organ has a fairly intense blood supply. Blood flows to the brain through four main vessels in the neck: two carotid and two vertebral arteries. They connect at the base of the brain, forming the so-called Circle of Willis. From it, many smaller vessels diverge to different parts of the brain. This is a defense mechanism in case a catastrophe occurs in one of the four main vessels. The problem is that vascular diseases also affect smaller vessels that supply blood to distant parts of the brain and do not have collaterals (side or bypass blood flow paths) and compensatory mechanisms.
Dementia
With significant severity of the above symptoms, vascular dementia develops with its characteristic slowdown and stiffness of all mental processes (torpidity and rigidity), mood variability (emotional lability), and a significant narrowing of the sphere of interests.
Patients with vascular lesions of the brain often become helpless in their mental state and cannot care for themselves. Moreover, during periods of confusion, they tend to leave home and may not find their way back. Thus, there is a danger to the patient’s life due to his mental illness. There are delusional variants of the course of dementia, which, combined with a pronounced decrease in criticism of one’s own behavior, can create a danger to the lives of others.
The treatment of mental disorders in vascular diseases of the brain is carried out by a psychiatrist. In connection with the development of new drugs, significant correction of the psychopathological picture is now possible.
All materials on the site are presented for informational purposes only, approved by certified physician Mikhail Vasiliev, diploma series 064834, in accordance with license No. LO-77-005297 dated September 17, 2012, by a certified specialist in the field of psychiatry, certificate number 0177241425770.