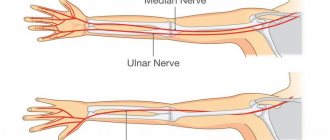
Feeling weak in your hand? Do you feel a sharp numbness in your fingers? Can't perform basic hand movements? Having trouble moving your hand? Perhaps we are talking about the problem of ulnar nerve neuropathy, which requires complex treatment under the supervision of professionals.
At Medical, they will help you determine the exact causes of ulnar nerve neuropathy, prescribe treatment and prevention of the disease, help you quickly relieve pain and recover as quickly as possible.
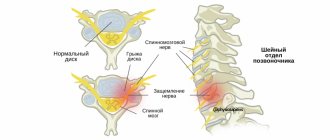
Ulnar nerve neuropathy is a common condition in which the nerve becomes compressed or pinched. It is this nerve that is responsible for the sensitivity of the fingers (little and ring fingers), and also plays an important role in the movement of the hand. It is considered the longest nerve of the brachial plexus.
Causes of ulnar nerve neuropathy
Ulnar nerve neuropathy is a lesion of the peripheral nervous system, accompanied by injuries in the elbow joint.
Causes of ulnar nerve neuropathy
Common causes of ulnar nerve neuropathy include:
- Traumatic nerve damage.
- Injuries to the ulnar nerve: bruise of the arm, dislocation of the forearm, fracture of the shoulder joint, shoulder, forearm, fracture of the ulna, dislocation of the hand.
- Inflammatory or anatomical changes in structures that cause compression of the nerve in the elbow.
Ulnar nerve neuropathy is observed in the following pathologies: osteoma, sprain, deforming osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, bursitis of the elbow joint, post-traumatic arthrosis of the wrist joint.
Causes of the disease
Most often, arthritis of the elbow joint develops due to injury. The elbow is often injured. With sports and household injuries, an aseptic inflammatory process develops, usually ending in recovery. But if an infection gets into the joint, the inflammation becomes purulent.
With microtraumas (professional - tennis players, massage therapists, carpenters), arthritis develops with prolonged minor trauma to the joint tissues. This is how chronic elbow arthritis is formed.
In the development of elbow arthritis, great importance is attached to heredity. In many patients, close relatives with a similar pathology can be found.
Elbow arthritis is sometimes caused by infection. The elbow is often involved in the pathological process of gonorrhea. The elbow can become inflamed due to gout, various hormonal disorders, diseases of the blood, stomach and other internal organs.
With a hereditary predisposition, the onset of the disease is associated with some provoking factor: a cold, a previous infection, stress, acute intoxication (for example, alcohol abuse, drugs, excessive smoking), etc.
Symptoms of ulnar nerve neuropathy
Symptomatic manifestations of the ulnar nerve are accompanied by weakness in the hand, which occurs when trying to pick up something in the hand (for example, lifting a pot, kettle, frying pan), when typing on a keyboard and various similar actions. Sensory dysfunction manifests itself in the form of a feeling of numbness in the little finger, ring finger and ulnar edge of the palm. Significant discomfort is felt in the elbow joint. Pain sensations are often transmitted to the forearm along the left edge. The described symptoms intensify in the morning when placing the hand under the head or under the pillow.
Upon examination, hypotrophy of the palm muscles is observed, the appearance of the fingers resembles a clawed paw. Ulnar neuropathy in Guyon's canal is caused by similar manifestations. The main difference is pain discomfort at the base of the hand, the presence of sensory disturbances on the surface of the little finger and ring finger, while the sensitivity of the base of the hand is fully preserved.
Approach to treating the disease in our clinic
The Paramita clinic in Moscow has developed its own method for treating elbow arthritis. After a mandatory examination with an MRI, complex therapy is prescribed, which is based on two different approaches to treatment:
- modern Western, including all the achievements of modern medicine in the treatment of elbow arthritis;
- traditional oriental, which considers the body as a single whole and regulates the interaction of all its systems, which leads to the elimination of the pathological focus and restoration of the patient’s health.
The approach used makes it possible to immediately relieve the patient of pain, and then effectively influence the cause of the disease, eliminating it. Regular courses of maintenance therapy allow our patients to lead a full life without inflammation and pain.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Diagnosis of ulnar nerve neuropathy
When conducting a diagnostic study, a neurologist reveals hypoesthesia, incomplete flexion of the fingers when trying to clench the fingers into a fist, and the presence of trigger points in the area of the radial joint and radial nerve. To correctly assess the movements of the hand, the patient is asked to place the hand on the table with the palm up and, holding it pressed to the table, try to move the little finger along the edge of this table. Difficulty performing these movements indicates the presence of ulnar nerve neuropathy.
To establish damage to the radial nerve, the specialist prescribes the patient to undergo electromyography and electroneurography. Ultrasound examination allows us to determine the etiological changes in the pathology and the degree of compression of the nerve in the elbow joint. The specialist analyzes the condition of the joints and bone structures based on the results of x-rays of the elbow joint, forearm and wrist joint. Depending on the results of the study, a CT scan of the joints may be additionally prescribed.
Clinical forms of elbow arthritis
There are several clinical forms of elbow arthritis, which have their own characteristic symptoms and course features.
Post-traumatic
Acute post-traumatic arthritis begins several hours after a fall, a blow to the arm with a hard object, or a twisted joint and occurs with severe pain, swelling, and limited mobility of the arm. The inflammation is aseptic in nature, so in most cases it ends with complete recovery. When an infection enters a joint, the disease can be long-term, chronic, with subsequent disability.
Chronic post-traumatic elbow arthritis is an occupational disease of tennis players, carpenters, painters, and massage therapists. When performing work, they constantly injure the elbow, causing a small but constantly maintained inflammatory process.
Read more about post-traumatic arthritis here.
Acute purulent
Acute purulent elbow arthritis develops only if the infection enters the blood and then into the joint
This form of the disease is caused by a nonspecific purulent infection that enters the joint through open wounds or with blood from other lesions. Arthritis may initially be purulent in nature. The main symptoms of the purulent process are: significant fever, chills, increasing swelling of the periarticular tissues, redness of the skin. The patient requires surgical assistance.
Infectious
The cause of this arthritis is a specific infection. The elbow is most often affected by gonorrhea and brucellosis. Gonorrheal elbow arthritis occurs with high fever, severe joint pain, and severe swelling of the periarticular tissues. The process can become protracted with the subsequent formation of ankylosis.
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Joint pain at rest
Rheumatoid
Elbow arthritis of autoimmune origin develops against the background of a hereditary predisposition. The starting factor (trigger) is usually previous infections. Women get sick more often. The elbows may be primarily affected.
Symptoms: elbows swell slightly, pain and stiffness appear in the morning. The disease progresses slowly, chronically, the symptoms either increase or decrease. Elbows become deformed, over time they can develop subluxations and dislocations, and function suffers. But with proper adequate treatment, it is possible to suppress the progression of the inflammatory process.
Read more about rheumatoid arthritis in this article.
Psoriatic
Joint damage in psoriasis most often occurs 5 to 6 years after the onset of skin symptoms. But sometimes arthritis develops first, and then psoriatic rashes appear. Characteristically, the small distal (end) joints of the fingers and nails are affected.
Large joints are affected asymmetrically, no more than 2–3 are involved in the process, including one of the elbows. Elbow arthritis begins acutely with swelling and redness of the periarticular tissues, accompanied by severe pain. The disease occurs in waves, with exacerbations and remissions, and in the absence of proper treatment leads to permanent dysfunction of the hand.
Gouty
The development of elbow arthritis is associated with a violation of purine metabolism, which leads to the deposition of uric acid crystals in the articular and periarticular tissues. The skin over the pathological focus swells, turns red, and body temperature may rise. The pain is very strong. The attack lasts from several hours to several days, after which all symptoms disappear on their own. With frequent relapses in the same joint, degenerative-dystrophic disorders develop and function is lost.
Deforming arthrosis-arthritis
It develops mainly in people over 60 years of age due to metabolic disorders and the gradual destruction of articular cartilage. Constant irritation of articular and periarticular tissues causes the development of a chronic inflammatory process, which is combined with degenerative-dystrophic and leads to a gradual loss of joint function. The process is slow with mild symptoms, but over time it leads to disability.
If left untreated, deforming arthrosis-arthritis of the elbow joint can lead to loss of joint function.
Treatment of elbow neuropathy
Treatment of ulnar nerve neuropathy depends on the etiology of damage to the peripheral nerves in the elbow area. Surgical intervention is required when removing tumors, neoplasms, hematomas that compress the nerve trunk or are caused by compression of the musculoskeletal canal in which it is located. Surgical treatment is also used in the absence of positive dynamics from the therapeutic measures taken.
Therapeutic treatment includes taking anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ketorolac), painkillers (metamizole sodium, anesthetic injections), nicotinic acid, B vitamins. Drug treatment is combined with physiotherapeutic procedures: UHF, magnetotherapy. To eliminate muscle atrophy, a course of massage and electrical myostimulation is prescribed.
In acute cases of ulnar nerve neuropathy, it is not recommended to perform dynamic exercise, which aggravates the pathological state of the disease. During night sleep, patients should bandage a rolled towel to the bend of the elbow joint. With a decrease in pain and a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a specialized complex of exercise therapy is prescribed.
What are the dangers of elbow arthritis?
The elbow joint is the main articular joint that determines the movement of the arm. With functional insufficiency of this joint, a person becomes disabled. This is the main danger of elbow arthritis. No less dangerous are various purulent complications.
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
Stages
During elbow arthritis there are 4 stages:
- Initial
– occurs with inflammation and pain, but without structural changes. - Explicit
– the process proceeds subacutely, in waves. On an x-ray you can see a widening of the joint space, on an ultrasound - an increased content of exudate. At this stage, pannus begins to form - the proliferation of granulations. - Soft ankylosis
- delicate pannus cells are transformed into connective tissue cords that close the joint space. This impairs the function of the hand, and soft ankylosis forms. - Bone ankylosis
- instead of connective tissue, bone grows between the joint-forming surfaces. The elbow completely loses mobility.
Possible complications
If the disease is not treated, it is difficult to avoid the most serious consequences:
- suppuration involving surrounding periarticular tissues; untreated purulent arthritis, abscesses and phlegmon can cause the death of the patient;
- restrictions on movement in the hand;
- ankylosis of the elbow joint and disability.
It is better to avoid such complications and contact a specialized clinic in a timely manner. But if you have missed time and have complications, do not despair: you can help in any condition.
What to do if you relapse
If elbow arthritis worsens, there is no need to self-medicate; it is better to immediately see a specialist or call a doctor at home. But sometimes joint pain can be very severe. How can I help myself before the doctor comes? Algorithm of actions:
- calm down - stress increases pain; you can take any sedative - valerian, motherwort, Novo-Passit, etc.;
- take any painkiller - Naise, Dexalgin, Analgin tablet; You can quickly reduce pain with Diclofenac rectal suppositories;
- Apply anesthetic ointment, gel or solution to the elbow area - Voltaren emulgel, Pentalgin gel, Menovazin rubbing solution;
- call a doctor at home or go to a clinic.
General clinical recommendations
To get rid of the symptoms of arthritis of the elbow joint, one course of treatment is not enough; after it, the patient must follow the following recommendations:
- lead an active lifestyle, engage in exercise therapy;
- eat properly and fully;
- do not load your arms with heavy lifting and monotonous professional work, leading to microtrauma to the elbow; if the cause of arthritis is professional activity, it is worth changing jobs;
- promptly treat all acute and chronic diseases, eliminate foci of infection;
- carry out courses of anti-relapse treatment prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention of arthritis is necessary primarily for people with a family history. To prevent the development of elbow arthritis, it is necessary to eliminate as much as possible cases of exposure to provoking (trigger) factors: hypothermia, stress, various acute and chronic diseases, heavy physical and professional stress. It is also recommended to get rid of bad habits: smoking and alcohol abuse.
There is no special diet for arthritis; regular nutritious meals are necessary, excluding foods that can provoke the development of the inflammatory process; fatty, fried, spicy foods, a lot of sweets and baked goods. The diet should contain enough lean meat, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables, fruits and cereals.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
Which doctor treats elbow arthritis?
Rheumatoid, psoriatic – rheumatologist, acute purulent – surgeon; post-traumatic and deforming arthrosis-arthritis – traumatologist.
Can you join the army with elbow arthritis?
If there is a violation of joint function, then no.
My elbow has been hurting for several months now after an injury. What to do?
See a doctor and get examined. Once the cause of the disease is determined, you will be prescribed treatment.
If you suspect arthritis of the elbow joint, you should not self-medicate. It is necessary to immediately consult a doctor before joint dysfunction occurs. The Paramita clinic will definitely help you!
Literature:
- Asin B.A., Pavlov V.P., Zagorodniy N.V. Surgical treatment of elbow joint arthritis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scientific and Practical Rheumatology, 1982; 2, 7.
- Brion PH, Kalunian KC; Oxford textbook of medicine. 4th edn. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Section 18.8. Osteoarthritis (2003) Warrell DA, Cox TM, Firth JD, Benz EJ Jr(Eds.)
- Reichenbach S, Sterchi R, Scherer M, et al; Meta-analysis: chondroitin for osteoarthritis of the knee or hip. Ann Intern Med. 2007 Apr 17;146(8):580-90.
- Herrero-Beaumont G, Ivorra JA, Del Carmen Trabado M, et al; Glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study using acetaminophen as a side comparator. Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Feb;56(2):555-67.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 12/09/2020 Date of update: 03/12/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (1)