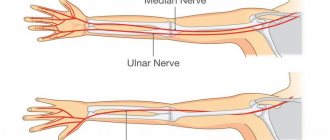
Everyone is familiar with the feeling of sharp pain as a result of an elbow strike. It’s as if an electric current shoots through the arm from the elbow joint to the little finger, sometimes radiating up the shoulder. This occurs due to contusion of the ulnar nerve. Compression of the nerve at the elbow joint is called cubital tunnel syndrome or cubital tunnel syndrome.
The disease is the second most common among carpal tunnel syndromes, second only to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Anatomy of the ulnar nerve and cubital tunnel
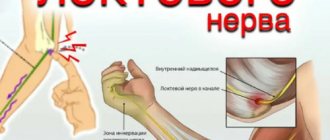
The ulnar nerve originates in the cervical plexus, being one of the three main nerves of the upper limb. It runs along the inner surface of the shoulder, then lies in the canal formed by the olecranon process, the internal epicondyle and the ligament that connects these two bone formations, forming a rather narrow cubital canal.
Next, the nerve passes through the intermuscular space of the forearm, flowing into another channel, this time on the wrist. This canal is called the Guyon Canal. It is at the level of this canal that the ulnar nerve begins to divide into 3, sometimes 4 branches, ending with the sensory branches of the 5th and inner half of the 4th fingers, as well as the motor branches of the 3-4-5 lumbrical muscles of the hand.
Criteria for evaluation
- Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) is a 30-question questionnaire designed to assess patient function and symptoms.
- The Patient Specific Functional Scale (PSFS) is a questionnaire used to assess a patient's activity limitations and functional outcomes.
- The DASH assessment criteria are a questionnaire that assesses a patient's functional ability and symptom severity.
- The Upper Extremity Functional Inventory (UEFI) is a 20-question questionnaire designed to measure the severity of complex tasks performed throughout the day.
Causes of cubital tunnel syndrome
The cause of this particular disease is compression of the nerve in the cubital canal. In this article we do not discuss nerve injury.
There are several causes of cubital tunnel syndrome:
- repeated trauma to the ligaments and bone structures of the elbow joint that form the canal,
- intense sports,
- arthritis, arthrosis of the elbow joint
- synovitis of the elbow joint or hemarthrosis
- repeated monotonous activities,
- consequences of fractures can also be the causes of the syndrome.
For drivers, the disease can be caused by the habit of placing their elbow on the window opening of the car door. When symptoms appear, this habit will have to be eradicated.
At the computer, you should pay attention to the position of your hand when working on the keyboard and mouse. When doing this type of work, the forearm should rest completely on the tabletop. You can put something soft under the sore elbow.
Compression of the ulnar nerve in the canal can be caused by inflammatory processes not only in the nerve tissue, but also in the soft tissue component of the cubital canal wall. For example, with medial epicondylitis, inflammation in the projection of the internal epicondyle can cause swelling and compression of the nerve. Failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner and delays in starting treatment can lead to organic damage to the wall and the process becoming chronic. As a result of the thickening of the nerve sheath, the transmission of nerve impulses may become difficult, leading to loss of sensation and motor function in some muscles of the hand and forearm.
Prevention of elbow pain
The health of the joints plays an important role because it has a direct impact on a person’s quality of life. Restriction in their movements and pain symptoms do not allow them to perform usual actions and reduce it. Preventive measures are as follows:
- A diet containing essential vitamins, microelements and substances beneficial to the body;
- The use of orthoses for intense loads on the joint;
- Performing exercises to strengthen ligaments and muscles;
- Elimination of hypothermia;
- Timely seeking professional medical help in case of loss of sensitivity and limited movement.
CELT specialists know how to restore your joy in life and relieve you of discomfort. Contact us!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Signs and symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome
Symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome include each of the following:
It is not necessary to have all the signs.
- Stiffness, loss of sensation, or significant dull or sharp pain in the ulnar part of the hand, 4th and 5th fingers.
- Pain and weakness when attempting to grasp an object with a brush.
- Discomfort in the elbow area.
Such symptoms indicate ischemia (lack of blood supply) of the nervous tissue. These symptoms are most pronounced in the morning, after the hand has been resting overnight. After some time, when the patient performs a certain amount of movements, the pain and numbness slightly recedes.
Physical therapy
- An impairment assessment approach may be used to identify strength deficits, decreased range of motion, and problems in achieving functional goals.
- The source of pain must be treated in conjunction with the disorder.
- After treatment, re-evaluate the functional tasks that caused pain to determine the effect of treatment.
- Create an exercise program to do at home to treat impairments and perform functional tasks.
A study conducted by Swernlov compared three types of treatment for patients with elbow tunnel syndrome. All three groups showed positive results; the control group showed similar improvement as the intervention groups.
- Splint group protocol —patients wore an elbow splint every night for 3 months to prevent elbow flexion greater than 45 degrees.
- Neural glide protocol – patients did neurodynamic exercises twice a day in six different positions, which were held for 30 seconds (three sets); the break between repetitions was 1 minute. Patients were instructed how to perform these exercises until their next follow-up visit, which was 1–2 weeks later. If no symptoms were found at the next visit to the doctor, the frequency of exercise was increased to three times a day with the position held for 1 minute (every day for 3 months).
- Control Group Protocol – The control group received only educational recommendations.
According to a study report by Coppieters, administration of elbow joint mobilization, thoracic spine and rib thrust manipulation, and ulnar nerve glide/tension techniques for 6 sets was associated with a reduction in elbow pain and a significant improvement in scores on a self-assessment questionnaire. cervical spine for at least ten months of observation. Patients reported a history of symptoms in the two months prior to physical therapy.
Diagnosis of cubital tunnel syndrome
When examining the elbow joint by a doctor, the patient may notice a significant increase in pain. A painful examination is necessary for a specialist to make an accurate diagnosis:
- If the nerve is compressed in the canal, there will be a positive Tinnel's sign, which is manifested by the sensation of a current shooting through the nerve into the little and ring fingers when the doctor taps with a neurological hammer - although this can happen when the nerve is without pathology, with a strong blow.
- The doctor will check to see if the nerve slips out of the canal when the patient bends the arm at the elbow.
- Tests sensitivity and strength in the hand and fingers.
If the doctor has doubts about the causes of cubital tunnel syndrome, the patient may be recommended to undergo additional examinations, such as MRI, ENMG, and radiography.
Radiography. Based on radiographs, it is possible to determine bone exostoses in the projection of the canal, which compress the nerve. But most of the causes of compression of the ulnar nerve cannot be seen on x-ray, since they are of soft tissue etiopathogenesis.
Electroneuromyography (ENMG). This study makes it possible to determine how well the impulses are transmitted along the nerve and to determine at what level and how much the nerve is compressed.
During nerve conduction testing, the nerve is stimulated proximally and the time required to conduct the impulse is measured and compared with normal values.
Features of diagnosing diseases whose symptom is elbow pain
During the consultation, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints and conducts an examination, during which he finds out the area of pain and its nature. He palpates both elbows and often detects changes in the anatomical structure of the joint. To make an accurate diagnosis, he prescribes the following diagnostic tests to the patient:
- Radiography - makes it possible to visualize the consequences of injury or generative processes;
- Neurological tests - identify existing neurological problems (for example, pinched nerve endings);
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging - prescribed for chronic degenerative pathologies or suspected neoplasm of malignant etiology;
- Electrocardiography - for burning pain;
- Ultrasound scan of the elbow joint.
In addition, the patient will have to undergo a general blood test and a rheumatic test, as well as undergo arthroscopy. This comprehensive approach will allow you to accurately identify the cause of the problem and take action to eliminate it.
Treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome
The vast majority of such cases of the disease require non-surgical treatment. Non-surgical treatment options for cubital tunnel syndrome include:
- load reduction,
- temporary refusal of intense training,
- taking anti-inflammatory non-hormonal drugs.
Good remedies for treating cubital tunnel syndrome are anti-inflammatory non-steroidal ointments, taking vitamins and the patient undergoing a course of physiotherapy.
Surgical treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome is prescribed if therapeutic methods have not produced results after 12 weeks. During surgery, segments of the canal wall are removed from the patient and the tendon arches are cut. If it is impossible to expand the canal surgically, the nerve is completely removed from it, placing it between muscle tissue and fatty tissue.
Treatment for elbow pain
Treatment tactics are determined individually, depending on the identified disease that provokes pain symptoms. It may involve taking pharmacological medications, physiotherapy and professional massage.
| Types of treatment | Details and Features |
| Medication | Pharmacological drugs are selected individually, based on the identified disease. They are presented as follows:
|
| Non-drug |
|
| Surgical | It is carried out only when indicated. Depending on the situation, it may be aimed at replacing seriously damaged bones and removing its fragments. |
Key Points of Physical Therapy
- Special tests used in diagnosing ulnar nerve entrapment have very high sensitivity - 0.98 or higher - and are therefore very useful in making the diagnosis.
- Conservative treatment is effective in approximately 50% of cases, while surgery is effective in 60-95% of cases.
- Conservative treatment has been shown to be effective when introducing the use of orthoses and manual therapy, including neurodynamics and joint mobilization; however, a recent study highlighted that more research is needed to know when conservative versus surgical treatment is needed.
- A patient who begins conservative treatment earlier has a 30% higher chance of avoiding surgery.
Differential diagnosis
The cervical spine and shoulder girdle should be examined to rule out diagnoses that may relate to the elbow joint. There are many differential diagnoses for ulnar nerve entrapment.
- Elbow fracture/dislocation.
- Cervical radiculopathy.
- Thoracic outlet syndrome.
- Peripheral vascular disease.
- Damage to the collateral ligament of the elbow joint.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Medial epicondylitis.
- Acute polyradiculoneuritis (Guillain-Barré syndrome).
- Neuropathy associated with alcohol (ethanol) consumption.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
- Tumor of the apex of the lung.
- Primary bone tumors.
- Peripheral polyneuropathy.
Read also
Chest pain
The first thing a patient thinks about when he feels chest pain is a heart attack.
Of course, chest pain is not something that can be ignored. But you need to understand that pain behind the sternum is not... Read more
Periarthrosis or periarthritis?
Let's imagine that you are driving a luxury car along our wonderful roads and suddenly notice that something persistently creaks in the area of the front wheel on the right. Moreover, this creaking intensifies periodically...
More details
Heel spur
Have you been bothered by pain in your heel when walking for some time (or maybe quite a long time)? The feeling of stepping on a sharp nail or pebble, constant discomfort and unpleasant sensations during…
More details
Joint pain
The joint may simply be painful (arthralgia) or may also be inflamed (arthritis). Arthritis usually causes warmth, swelling and rarely redness of the overlying skin. Pain may occur during movement and...
More details
Pain in the gluteal region
Clinical manifestation of pain in the gluteal region Pain in the gluteal region is quite common. Although this pain can be caused by a number of reasons, it is most often associated with thoracolumbar syndrome,...
More details
Features of the anatomical structure of the elbow
The elbow is a complex articular joint formed by the radius, ulna and humerus. Each bone involved in creating an articulation plays an important role and has certain characteristics:
- humerus - a tubular bone, the ends of which have strong differences (the upper one is predominantly rounded, and the lower one is triangular), which provides the opportunity for ideal articulation;
- ulnar - in combination with the radial one, forms the forearm, is thicker and resistant to external influences;
- radial - is a structural element of the forearm, is smaller in thickness, but is surrounded by an impressive muscle frame (a set of flexor/extensor and rotatory muscles).
The joint is nourished by a large number of veins and arteries. Innervation (supply of tissues with nerves) is realized thanks to large nerve fibers, which explains the increased sensitivity of the upper extremities.
Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Mizonov Sergey Vladimirovich
The doctor is a neurologist. Chiropractor. Osteopath. Physiotherapist. Experience: 8 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
Dyachenko Ksenia Vasilievna
Head of the center for the treatment of dizziness and balance disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category.
Angioneurologist. Neurorehabilitation specialist. Physiotherapist. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 19 years.Volkova Svetlana Anatolevna
Head of the Center for Parkinsonism and Extrapyramidal Diseases.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Epileptologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 26 years.
Classification of pain sensations and features of their manifestation
An injury, bruise or fall is manifested by stabbing pain, a person cannot bend the elbow, and is unable to rotate the arm in different directions. Dislocations are a common elbow injury that occurs due to a fall. With such an injury, overstretching of muscles and tendons occurs, blood vessels and nerves are pinched. For various types of fractures, the recovery is usually long, you will need rehabilitation, wearing an orthosis or a plaster cast. After such an injury, the stability of the joint is lost.
When tendons rupture, a characteristic cracking sound is heard, hematomas are visible under the skin, it becomes impossible to bend the joint, and the pain is severe. When the ligaments are torn, a stabbing pain occurs, the hand becomes very swollen, and bruises are visible under the skin. In this case, the joint is unstable, sensitivity is significantly reduced. With a dislocation, the symptoms are similar. Treatment begins only after the traumatologist resets the dislocated joint.
When the ulnar nerve is pinched, painful stabbing sensations also occur, the fingers go numb, it is difficult to move the elbow, sensitivity and grasping function are impaired. When a fracture occurs, the pain is stabbing, it is impossible to straighten the arm, it is difficult to bend, the joint becomes swollen.
The development of epicondylitis is accompanied by stabbing pain, which intensifies with flexion or extension of the joint.
Bursitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling;
- swelling;
- pulsating pain;
- the skin turns red;
- joint mobility is limited.
Arthrosis is accompanied by pain in the morning, limited mobility, swelling, and gradual deformation. With osteochondrosis dissecans, motor function is limited, the pain is dull or shooting. At rest, the pain is dull, the articular cartilage wears out.
When the tendon sheath becomes inflamed, the pain is pronounced, nagging in nature, a crunching sound is also present, and a hygroma grows on the surface of the tendons. Carpal tunnel syndrome is manifested by stabbing pain, numbness of the fingers, and poor grasping function.
With gout, the pain is sharp, shooting in nature, the skin is red and hot, swollen. Arthritis, arthrosis and osteoporosis are manifested by similar symptoms - aching, dull pain, motor function is difficult, the elbow is hot.