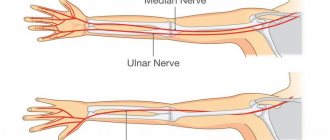
Our clinic diagnoses and treats the nerves of the hands (radial, ulnar, median). To treat neuropathy of the ulnar, radial, and median nerves, you will need to be examined by a neurologist; if any studies have been previously performed, be sure to take their results for consultation, incl. the x-rays themselves . If the studies have not been performed, we will do everything necessary in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
- What are the causes of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves?
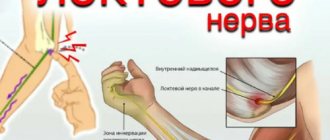
- Ulnar nerve neuropathies: symptoms
- Radial nerve neuropathy: symptoms
- Median nerve neuropathies: symptoms
- Diagnosis of neuropathies of the ulnar, radial and median nerves
- Treatment of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves at the Echinacea clinic
- When is surgery necessary?
How can we help you:
- We will establish a diagnosis, find the point of damage or the cause of nerve inflammation. We perform a wide range of electromyography and ultrasound of nerves and have accumulated considerable experience. According to needle myography data, it is possible to predict the prospects of non-surgical treatment or determine clear indications for surgery (the risk of complete loss of the nerve).
- We will find out and discuss with you the prospects and chances of non-surgical treatment. Medicines can be used here, incl. administration of anti-inflammatory and absorbable drugs directly to the point of compression or damage to the nerve. In terms of rehabilitation treatment, magnetic stimulation of the nerves of the hands has proven itself well: the effect is visible several days after stimulation.
- If the chances of restoring the radial, ulnar or median nerve without surgery are low, we recommend surgical treatment . We perform most of the operations on an outpatient basis. You will be able to go home on the day of surgery. In addition, surgery without hospitalization is significantly cheaper. After surgical treatment, we will offer a course of rehabilitation treatment.
What are the causes of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves?
The radial, ulnar and median nerves pass through narrow canals formed by bones, ligaments, tendons and muscles. Nerve tissue is very delicate and vulnerable. Often we detect nerve suffering even with slight narrowing or deformation of the nerve canal. Narrowing or deformation of the canals of the radial, ulnar and median nerves occurs:
- In case of injury (bone fracture, bruise, hemorrhage, sprain or wound); Often, when injured, the nerve is pulled into scarred tissue or compressed by a bone fragment; nerve injury can also be represented by a nerve bruise, partial or complete interruption.
- When squeezed in an uncomfortable position (tucked or pinned hand while unconscious or intoxicated, under anesthesia);
- With thickening and deformation of the elbow or wrist joints and ligaments , with chronic injury and overload of the joints, often associated with the type of activity (athletes, musicians, drivers, cooks, dentists, working with vibration and metalworking tools). Very often, such changes are facilitated by diseases of the cervical spine. These types of neuropathy are called tunnel syndromes of the ulnar, radial and median nerves (cubital tunnel syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome) .
Stimulation electromyography of the upper extremities, electroneuromyography (ENMG) of the upper extremities / EMG of the arms
The function of the nerves is to conduct electrical impulses from the brain to the muscles and organs, and to the brain from the sensory receptors of the body. Any damage to the nerve leads to disruption of the conduction of excitation along the nerve, which means disconnection of the affected part of the body from the brain.
Therefore, if the radial, ulnar or median nerve suffers, the following are possible:
- Decreased strength and weight loss of arm muscles
- Decreased sensitivity (numbness).
Carpal tunnel syndrome - symptoms and treatment
The initial method of treatment for patients with carpal tunnel syndrome can be a change in daily activity, the elimination of harmful occupational factors, and ergonomic organization of the workplace when working at a computer - the use of special mice, rugs and keyboards [23].
Another method that has been shown to be effective and safe is wrist orthosis, in which the wrist joint is placed in a neutral position. This minimizes the negative impact on the median nerve from the surrounding structures [5].
Many other techniques can be used in complex treatment: manual therapy, physiotherapy, kinesiotaping, but data on their effectiveness are contradictory [5].
Drug treatment is also used as therapy for patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. It is aimed at reducing inflammation and swelling in the carpal tunnel area, which leads to relief of symptoms.
A fairly large number of drugs are used in clinical practice, but for most drugs the effect is short-term and insignificant. An exception is corticosteroid drugs, especially when applied locally in the form of drug paraneural blockades (injection of an anesthetic into the space near the kidneys) [5].
There is also a wide variety of surgical treatment methods, which differ only in the options for surgical access [24]. However, the basis of any intervention is the dissection of the transverse ligament of the carpal tunnel and the release of the median nerve from compression (squeezing) by surrounding tissues.
The choice of surgery and treatment technique depends on many factors:
- degree of compression of the median nerve;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- features of the anatomy of the carpal tunnel;
- surgeon preferences [25].
Surgery is a radical treatment method that normalizes the pressure inside the carpal tunnel. The effect of surgical treatment is superior to all currently existing conservative methods. In addition, people can return to their professional activities within two weeks after the operation. However, despite the widespread prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome, there is still no uniform tactic for determining indications for surgery. Various authors offer their own criteria that allow selecting patients for surgical treatment, and in each case the decision is made individually [2][5].
Despite the variety of methods, there is no single approach to treating patients with carpal tunnel syndrome.
One point of view is that surgical treatment should be used only as a last resort: when conservative treatment is ineffective and in the presence of severe symptoms in the form of weakness and muscle wasting [26].
There is also an opinion that despite the wide variety of conservative treatment methods, their effectiveness is extremely low, so the achieved treatment result is short-lived. In this regard, it is not recommended to delay surgical intervention, since it is the most effective method of treatment [2][5].
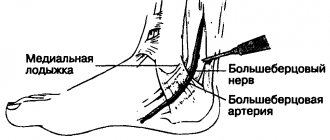
Diagnosis of neuropathies of the ulnar, radial and median nerves
The most successful treatment for neuropathy is treatment directly at the point of nerve damage. For successful treatment, your treating doctor will find out:
- At what exact point is the nerve damaged (compressed); this helps us provide targeted treatment;
- What exactly led to the nerve suffering (trauma, scar, compression);
- The degree of nerve suffering (complete or partial damage, the presence of a recovery process, the presence of complete death of the nerve, etc.).
Often, to establish the cause of nerve pain, a detailed neurological examination is sufficient , during which the strength of the muscles controlled by the nerve, the possibility of certain movements, sensitivity, the presence of pain points and seals along the nerve are assessed. Auxiliary diagnostic methods are electroneuromyography, radiography and computed tomography.
Electroneuromyography allows you to assess the speed and volume of impulses along the nerve, detect the location of damage/compression, and determine the prognosis for recovery. Electromyography helps us evaluate the effect of certain types of treatment and choose the most suitable ones. The Echinacea clinic uses a modern computer electroneuromyograph.
X-ray and computed tomography of the joints will provide complete information about the deformation of the joints and bone canals of the nerves, the causes and points of nerve compression.
Symptoms
The radial nerve consists almost entirely of motor fibers, so the symptoms of this disease are associated specifically with impaired motor activity in the damaged area. Among the signs of the development of this type of neuritis are:
- complete or partial decrease in the strength and tone of the muscles innervated by the radial nerve;
- muscle fiber atrophy;
- deterioration of tendon reflexes in the area of development of the disease.
Also, the symptoms of radial neuritis in each specific situation may vary depending on where the inflammatory process is localized:
- If the source of inflammation is located in the armpit or in the area of the upper third of the shoulder, then the patient cannot straighten the hand and forearm, or move the thumb to the side. It also becomes difficult to bend the arm at the elbow, a tingling sensation appears in the affected area, and the sensitivity of the skin on the fingers decreases. If you stretch your arms forward, then on the affected arm the patient will not be able to straighten the hand and turn it palm up, the thumb pressed tightly against the index finger. The ulnar reflex disappears completely, the carporadial reflex is significantly reduced.
- Inflammation localized in the middle third of the shoulder is characterized by preservation of the extensor reflex in the elbow joint and forearm.
- When neuritis affects the lower third of the shoulder or the upper segment of the forearm, the patient is unable to independently straighten the fingers and the hand as a whole, and sensitivity on the dorsum of the hand decreases.
Treatment of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves at the Echinacea clinic
When it is clear where, how and why nerve compression occurs, local treatment in the form of physiotherapy, therapeutic blockades, massage, and manual therapy becomes much more effective. Therefore, treatment in our clinic begins with finding out the cause and location of nerve damage .
The main goals of treatment for nerve compression:
- Remove nerve compression. To do this, we use powerful resorption therapy: we use enzymes that resolve and soften scar tissue, bone and cartilage growths (Karipazim enzyme, etc.), massage, and injecting medications directly into the site of nerve compression. Sometimes, to release the nerve, manual therapy and massage of the areas of compression of the ulnar, median and radial nerves (cervical spine, elbow, wrist joints, etc.) are sufficient.
- Accelerate healing and restoration of the nerve. To do this, we use modern medications that help restore the nerve freed from compression and scarring.
- Restore muscle function and volume. Special exercises, electrical stimulation of muscles, and physiotherapy are used here. The rehabilitator will tell you in detail and show you how to perform rehabilitation procedures at home.
Diagnostics
The following functional tests allow our specialists to make a diagnosis of “Radial nerve neuritis”:
- with the hands lying palms down on the table, the patient is unable to place the middle finger on the adjacent ones;
- if the hands are placed palms up, the patient is unable to move the thumb to the side;
- if you press your hands tightly with your palms to each other and try to spread your fingers, then on the affected hand the fingers will bend and slide over the skin of the healthy palm;
- if you lower your arms along the body in a standing position, the patient will not be able to turn the hand on the side affected by neuritis and move the thumb to the side.
However, the diagnosis of neuritis is not limited to functional tests alone. Depending on the patient's condition, the specific nature of the symptoms involved, and other factors, various electrophysiological procedures may be prescribed. In each specific case, the list of required examinations is determined individually by our neurologists.
When is surgery necessary?
In case of nerve injury, it is very important to decide in a timely manner whether conservative or surgical treatment is advisable. The answer to this question can be obtained after conducting needle myography, which will answer the question of what is the degree of damage to the nerve and whether it has a tendency to recover. If during this study it turns out that at least partially the nerve is preserved, we carry out active conservative treatment, after which we must repeat the study to make sure that the treatment had an effect . If, during needle myography, it turns out that the nerve is completely damaged and its restoration is impossible, we resort to the help of a neurosurgeon who suturing the nerve or releasing it from significantly narrowed canals. Then we perform the entire range of restoration procedures.
Treatment of neuritis of the radial nerve of the hand
Depending on the causes of the disease, the doctor may prescribe:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antibiotics - if the pathology is caused by an infection.
- Drugs that normalize metabolic processes in nervous tissue.
- Means for improving blood flow in small vessels that supply nerve fibers.
- In case of poisoning - intravenous infusions of solutions through a dropper to remove toxic substances.
- Physiotherapy: magnetic therapy, UHF.
If the damage to the nerve fibers is caused by injury, it is necessary to carry out timely and correct treatment: straighten the dislocation, match the fragments of the broken bone and apply a plaster cast.
For severe injuries, surgical treatment may be considered.
The prognosis is usually favorable; with timely treatment, after some time, complete restoration of impaired functions occurs. Often, after conditions such as “Saturday paralysis,” recovery occurs on its own without therapy. If the disturbances persist, it is better to see a neurologist.
For effective treatment of radial nerve neuritis, which will help restore its functions as quickly and fully as possible, contact a neurologist. Do not engage in self-diagnosis, especially if movements and sensation in the hand are severely impaired, and these disorders persist for a long time. You can make an appointment with a doctor at the Medica24 international clinic at any time of the day and any day of the week by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Symptoms of radial neuritis depend on the level at which it is damaged:
In the armpit area and at the top of the shoulder:
- The thumb and index finger are connected.
- It is difficult to straighten the forearm and hand.
- It is difficult to rotate the forearm outward when the arm is extended.
- Sensitivity on the skin in the area of the thumb, index and middle fingers is reduced, “crawling goosebumps” and numbness occur.
In the middle of the shoulder:
- Extension of the elbow joint is not impaired.
- The sensitivity of the skin of the shoulder is preserved.
- All other symptoms that are described above for neuritis of the radial nerve in the upper part are present.
At the bottom of the shoulder and at the top of the forearm:
- The sensitivity of the skin on the back of the forearm is not impaired.
- The sensitivity of the skin on the back of the hand is reduced.
- It is difficult to straighten the hand.