Home > Fingers go numb
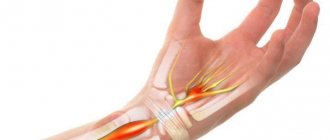
Numbness in the fingers can be caused not only by compression of the median nerve, as in carpal tunnel syndrome, but also by compression of the ulnar nerve. In the latter case, the fingers involved in the process change. The ulnar nerve provides sensory innervation to the fourth and fifth fingers, that is, the little and ring fingers. It is they who become numb when conduction along the ulnar nerve is disrupted.
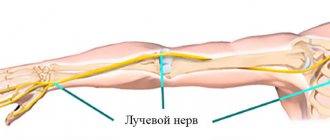
The weak point for the ulnar nerve is, oddly enough, the elbow. At this level, the nerve passes in a special groove between the internal epicondyle and the olecranon process. Because the ulnar nerve runs posterior to the elbow (unlike the other two, the radial and median), its stretch is significantly greater when the elbow is flexed.
If the nerve can slide normally in its groove, then its function does not suffer. And if, for some reason, it is pinched by the surrounding tissues and sliding does not occur, then it is stretched and damaged.
Functions and properties
The cubital vein is located under the skin, forming venous veins. It is replenished with blood from the capillaries, which then moves directly towards the heart.
Blood can move through a vein due to the special suction function of the heart and the presence of negative pressure in the chest area when a person takes a breath.
Superficial veins, namely the cubital vein, are much more developed than deep ones. It is from them that all venous pathways throughout the human body begin. The cubital vein, unlike its other counterparts, does not have valves and is localized in the anterior ulnar region. It runs obliquely from the latent vein to the medial vein, connecting with the deep arteries.
Cubital tunnel syndrome – treatment at the Surgery Center
Ulnar nerve tunnel syndrome can be successfully treated with timely referral to specialists. The Surgery Center offers a full range of services necessary for the diagnosis and successful treatment of the disease.
Why patients choose us:
- Surgeons with more than 8 years of experience.
- We specialize in hand surgery.
- Painless surgery without discomfort.
- There are no hidden fees - the price already includes examination, diagnosis, surgery and subsequent hospital care.
- Convenient work schedule.
- Modern equipment.
- Full support after surgery, including communication with the surgeon or a specialized specialist.
- Possibility of cash and non-cash payments.
Patients of our clinic receive qualified medical care and a comfortable stay within the walls of the center. We will help you regain your health! You can sign up for a consultation by ordering a call back on the website.
Anatomy and structure
The cubital vein is located close to the surface of the skin, it is where drugs are most often administered intravenously, blood transfusions are performed, and blood is taken from it for laboratory tests.
The walls of the vein are made up of three separate layers. Inside each vein there are valves that are part of the circulatory system and it is through them that blood can easily circulate up and down. Blood flows through the veins in defiance of the existing force of gravity. To overcome it, the muscular-venous pump is activated, and the filled valves do not allow the blood to return back, but only direct it upward.
It is thanks to the valves that blood tends to move only towards the heart. The valve is a fold formed from an inner layer consisting of collagen. In their structure, they externally resemble pockets, which, under the influence of the gravity of the blood, close and hold it in a certain area.
Cubital vein
Each valve can have up to 3 leaflets. If the valves malfunction, this can cause stagnation of blood or its erratic movement. It is for this reason that diseases such as varicose veins, thrombosis and other pathologies of the veins and circulatory system develop in the body.
The functions of the veins in everyday life are almost invisible, but they provide a full life to the human body. The blood, dispersed throughout the body, is quickly saturated with carbon dioxide and the products of all internal systems.
The cubital vein, as well as all the others that are in the human body, are actively involved in the work to remove everything harmful and feed only useful substances.
Hormones and nutrition from the digestive system are also carried throughout the body through the veins. The joint work of veins and arteries helps supply blood and nutrients to every, even the smallest part of the body.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
There are a number of fairly typical and recognizable manifestations of tunnel neuropathy
observed in both cubital and carpal syndromes:
- numbness (in the hands, in some or all fingers, in the forearm, in the elbow joint);
- intuitive need to rub, “stretch”, shake the affected limb, incl. with forced night awakenings;
- soreness, muscle weakness (untreated neuropathy can develop from pain to neuromuscular atrophy and partial or complete loss of limb function);
- awkwardness, feeling of incoordination of movements.
Diagnostics
First of all, a thorough analysis of the patient’s complaints and basic anamnestic information is necessary. Then a reflexological examination is performed. In some cases, cubital or carpal syndrome must be differentiated from other conditions. For this purpose, radiography, MRI, ultrasound, electromyoneurography
(a highly specialized technique with electrical stimulation that reveals the parameters of the conduction of nerve impulses).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
1. Pinched or other mechanical damage to nerves
A number of related fields of medicine are involved in the study and treatment of pathological conditions caused by pinched or other mechanical damage to nerves
.
Almost every adult knows firsthand the symptoms of, for example, radiculopathy (radicular syndrome), i.e. pinching and/or inflammation of spinal nerve endings. Somewhat less known are the so-called. tunnel neuropathies caused by compression (pressure, constriction) of nerves located in narrow canals of bones, muscles or tendons. If for some reason the anatomical tunnel is compressed, the nerve finds itself in a rigid “trap” - hence the figurative but precise synonyms: trap neuropathy, trap syndrome, etc. In the total volume of clinical cases of peripheral nervous pathology, tunnel syndromes occupy approximately a third. About 30 variants of carpal tunnel syndrome have been described; The most common are cubital (elbow) and carpal (wrist) syndromes.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Causes of the syndrome
The disease can develop for unknown reasons. It occurs differently in each patient. But usually the development of cubital tunnel syndrome is preceded by an injury in this department, or frequent and sudden movements of the hand, for example, during physical exercise. When the elbow joint is tense, compression of the nerve can occur, which occurs due to muscle tension. If you actively move this muscle, an inflammatory process will develop, the tendons will thicken, and the nerve will begin to hurt greatly.
Sometimes the disease develops due to prolonged pressure on the elbow, for example, when lying in one position, or when lifting a barbell. Another reason may be the habit of placing your hand on the car window in the door area.
The syndrome develops due to changes in anatomy in the cubital canal, which occurs due to the formation of bone spurs. This can happen in the following situations:
- with a fracture of the elbow;
- with a fracture of the shoulder joint;
- due to the formation of a cyst;
- when bone spurs appear;
- bruise in the elbow.
Characteristic
All veins in the human body are needed to pump blood. They consist of 3 separate layers. All of them and their features are described in the table below.
| Layer name | Peculiarities |
| Adventation | This is the outer layer of the vein, which consists of connective tissue, fibers and collagen. It is thanks to this layer that the veins stretch well, preventing the vein from expanding if the pressure suddenly increases. |
| Media | This is an intermediate layer consisting of elastic and durable fibers, as well as smooth muscles. |
| Intimacy | This is the inner layer consisting of smooth epithelium covered with elastic tissues. It is in it that valves are located that do not allow blood to flow to the lower part of the body if it is in an upright position. |
The cubital vein is located in the elbow area. All arm veins are divided into 2 separate categories: superficial and deep. Cubital belongs to the first group. It is the veins from this group, anastomosing among themselves, that form a rather wide-loop network, from which the largest trunks appear in some places. One of these trunks is the cubital vein, which is an obliquely located anastomosis that connects two other superficial veins in the elbow area. A vein flows into it, through which blood moves from the palmar side of the hand and forearm.
4. Treatment of the disease
Typically, therapy begins with conservative, non-surgical measures. The main ones are:
- complete or partial immobilization (immobilization) of the affected limb with the help of various bandages, fixing bandages;
- restriction or exclusion of physical activity, especially stereotypically habitual;
- drugs to relieve swelling and inflammation;
- physiotherapy.
Some researchers believe that smoking and coffee abuse play a provoking role in the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, and therefore it is recommended to give up or sharply reduce these habits.
If conservative treatment is ineffective or the pathology progresses, surgical intervention
. Various techniques have been developed, but their essence boils down to decompression (releasing the nerve from compression) and transposition (moving the nerve in cubital syndrome).
Types of operations
In case of prolonged numbness, as well as in case of fractures, doctors perform an operation, which can be of two types:
- Simple decompression. Part of the thickened walls that compress the nerves is cleaned, and a dissection is made in the area of the tendon arch. The operation is not classified as complex, but its disadvantage is that the effect is unstable.
- Nerve transposition. During surgery, doctors try to move the pinched nerve out of the cubital canal slightly forward. It is moved into the space between the muscles and subcutaneous fat. This operation is called anterior subcutaneous transposition. Sometimes the nerve is moved deeper into the axillary part. In this case, the operation is called “anterior axillary transposition”.
Complications and consequences
If treatment for cubital tunnel syndrome is not started on time, complications will develop in the future. The most common of them is partial paralysis of the arm and subsequent loss of its ability to work.
As the disease progresses, atrophy of the muscle tissue of the hand appears with the spaces between the bones receding.
After the first symptoms of the disease appear, treatment must begin immediately. If therapy is started after 3-4 months, then all measures taken by doctors will not bring the desired effect. Often such people have to change their professional activities, or even register for 3rd degree disability.