Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- Cost of services
- Sign up
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
Loss of motor coordination (ataxia) is a symptom that accompanies many diseases. This condition is accompanied by a violation of the coordination of movements and motor skills. The person looks awkward, movements are uncoordinated, and balance is often disturbed.
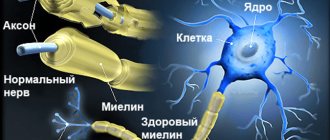
The central nervous system is responsible for the coordination of movements; when this department is damaged, a disturbance in movements and coordination occurs.
Sensitive ataxia
In most cases, this pathology occurs due to damage to the posterior columns, posterior nerves, peripheral nodes, thalamus opticus, and parietal cortex. Signs of sensitive ataxia can be observed in all limbs at once, or in only one of them. Doctors often diagnose signs of ataxia, which occurs due to a disorder of the joint-muscular sensation in the legs.
Characteristic signs of ataxia will be the patient's instability, excessive bending of his legs at the knee and hip joints. Many patients often feel as if they are walking on cotton wool or a carpet. Patients try to compensate for walking impairments with the help of vision, as they begin to constantly look at their feet. Due to severe damage to the posterior columns, patients almost completely stop walking.
Diagnostic measures
The disease can be easily identified through various types of examination techniques. Neurologists observe muscle hypotonia, which appears in extensor and flexion reflexes, inhibition of deep types of sensitivity. When testing the patient according to Romberg standards, the patient is diagnosed with staggering, which increases its activity when the eyes are closed. When it is necessary to stretch your arms forward, uncontrolled movements appear. Individuals diagnosed with sensory ataxia have complaints about coordination abilities: the inability to place a finger on the tip of the nose or place the heel of the left foot to the knee of the right. An abnormal gait of the “table” type is noted. The neurological picture is presented along with deficits and cerebral manifestations. The main task of doctors when examining a patient’s condition is to correctly distinguish sensitive ataxia from other types. The main factor is an increase in symptoms when the eyelids close. Instrumental tests help identify the source of the disease. For diagnosis, doctors prescribe:
- Donation of blood cells for biochemical analysis.
- Electroencephalogram.
- MRI scan of the brain.
- Computed tomography of the spine.
- Electroneurography.
- Assessment of evoked potentials.
- Electromyography.
In cases where the anomaly may be hereditary, the attending physician will prescribe a consultation with a geneticist and DNA testing and genealogical research.
Cerebellar ataxia
It occurs due to serious damage to the cerebellar vermis, as well as its legs and hemispheres. However, it is worth noting that cerebellar ataxia can be a symptom of diseases such as multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, or a malignant neoplasm in the cerebellum or brain stem. Patients with this pathology usually fall toward the damaged cerebellar hemisphere when walking. During such episodes, even falls are possible.
The patient usually staggers greatly when walking, and also places his legs too wide, his movements are slow, sweeping and awkward. Impaired coordination remains virtually unchanged even with vision control. Patients may experience serious speech disturbances, which gradually slow down, become scanned and drawn out. There are also problems with handwriting, which becomes uneven and splayed.
Main sources of occurrence
The anomaly is associated with a malfunction in the pathways of deep sensory ability. The deviation originates in different areas of the proprioceptive system (on the back of the spinal cord, ganglia, roots, in the medulla oblongata, thalamus and cortex). The disorder is caused by vascular diseases (stroke), tumor formation, cerebral neoplasm, multiple sclerosis, and damage to the spinal cord. In some cases, sensitive ataxia appears as a result of a complication reaction after surgery. Doctors observe the development of the disease in Guillain-Barre syndrome and other types of polyneuropathy (diabetic, alcoholic, infectious-toxic type, etc.). Impaired vibration sensation can provoke symptoms of hereditary abnormalities.
Vestibular ataxia
This pathology occurs due to damage to the vestibular nerve, labyrinth, cortical center and nuclei in the brain stem. This type of ataxia is observed in various ear diseases, brainstem encephalitis, Meniere's syndrome, and tumors of the fourth ventricle of the brain. The main sign of the pathology is considered to be regular severe dizziness, as a result of which the patient begins to feel as if all objects are moving in the same direction. Turning his head, the patient feels increased dizziness.
Severe dizziness leads to unsteady gait and falls. It is also noticeable that the patient tries to make very careful head movements. Vestibular ataxia is also characterized by symptoms such as vomiting, nausea and horizontal nystagmus.
Stabilometry
As the most accurate method for diagnosing such a pathological condition as vestibular ataxia, stabilometry is used in modern medicine. This is a method of functional diagnostics that allows us to objectify the fluctuations of the center of gravity of the human body over the support area. In other words, stabilometry is an electronic analyzer that helps determine how much a patient is able to maintain balance.
The stabilometry method is based on the use of computer technology and a special stabilometric platform. The use of innovative equipment makes this research as accurate as possible and allows it to be used not only in neurology, but also in other areas of medicine. During stabilometry, the tested patient stands on a platform and performs a series of necessary movements for one minute according to the instructions of a specialist.
Cortical ataxia
Cortical ataxia in most cases occurs due to damage to the frontal lobe of the brain. Its most common causes include tumors, circulatory disorders in the brain, and abscesses. In the case of this type of ataxia, symptoms such as unsteadiness when walking, falling over, or bending to the side appear.
Due to severe damage to the frontal lobe, patients may lose the ability to walk and stand. Cortical ataxia is also characterized by other symptoms: mental changes, grasping reflex, impaired sense of smell. In many ways, the clinical picture of cortical ataxia is similar to the symptoms of cerebellar pathology.
1.General information
Neurodegeneration is a pathological process, with the development of which nervous tissue loses its complex organization, degenerates, gradually atrophies (decreases in volume and dies), becoming, in general, functionally untenable. Considering that the nervous system controls and regulates literally everything in the body, neurodegenerative diseases, even the slowest and most indolent ones, always constitute a serious problem, which is aggravated by the fact that at the moment all efforts to develop reparative (restorative) and etiopathogenetic ( eliminating the root cause of the disease) types of therapy have not brought tangible results.
For the most part, neurodegenerative diseases are caused by, or at least reliably associated with, hereditary, chromosomal factors. These diseases are traditionally considered rare, and in terms of tens and hundreds of thousands of people, many of them really seem to be sporadic, almost random anomalies. However, if we sum up the incidence of the fairly well-known diseases Alzheimer's, Pick's, Parkinson's, demyelinating multiple or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and DLB (dementia with Lewy bodies), the picture will look more alarming. Thus, with reference to data from post-mortem pathomorphological studies, it has been repeatedly emphasized in the literature that the same DLB (one of the frontotemporal variants of neurodegeneration) is diagnosed much less frequently than it actually occurs.
A large number of individual nosological units (i.e., officially established diagnoses of this group) are the subject of critical discussions, since degeneration of neural tissue is the main and common mechanism for the development of such diseases; for example, the extreme wing of supporters of generalization proposed “for convenience” to consider all diseases of this kind as only particular variants of Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s diseases. This approach can hardly be considered justified: the clinical picture, rate of progression, prognosis, strategy of symptomatic treatment - all this is determined by a number of significant factors (primarily the predominant localization of the process) and differs sufficiently to speak of independent diseases.
The above fully applies to spinocerebellar ataxia. This is a hereditary neurodegenerative disease with its own distinct specificity, which can manifest at any age (usually in the range of 5-40 years) and is distinguished by a variety of forms: to date, over twenty relatively independent types have been identified and described (SCA, SCA 2, Friedreich's disease and many others). etc.).
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Cerebellar Pierre-Marie ataxia
The main manifestation of the disease is cerebellar ataxia. The disease occurs due to hypoplasia of the cerebellum, atrophy of the pons and inferior olives. Typically, the first signs of pathology appear in a patient at the age of 35 years.
The most characteristic symptoms of the disease are considered to be disturbances in gait, speech and facial expressions. In addition, patients usually experience dysmetria, static ataxia, adiadochokinesis, increased tendon reflexes, and decreased strength in the muscles of the limbs. Patients are often diagnosed with oculomotor disorders:
- lack of convergence;
- ptosis;
- paresis of the abducens nerve;
- Argyll-Robertson sign;
- decreased visual acuity;
- narrowing of visual fields;
- atrophy of the optic nerves.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 1 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
Familial Friedreich's ataxia
This disease is hereditary and occurs due to damage to the spinal systems. As a result of research, it was found that many patients with this type of ataxia often have consanguineous marriages in their pedigree. The main symptom of ataxia is an unsteady and clumsy gait.
The gradual development of the disease leads to impaired hand movements, problems with facial expressions, slowed speech, and hearing loss. Further development of ataxia leads to changes in the skeleton, heart rhythm disturbances, endocrine disorders, frequent dislocations, and kyphoscoliosis.
Quick Facts
Impaired sensory perception is associated with problems of proprioceptive types of sensitivity, which doctors include:
- A muscle-joint reflex that perceives information about the position of the body in the environment.
- Vibration sensitivity.
- Understanding mass and pressure.
Motor and coordination failures are formed as a result of the absence or lack of kinesthetic information in the central areas of the proprioceptive apparatus, which provides data on muscle contractions. Ataxia of the sensitive type is not capable of developing independently; it manifests itself as a symptom complex in neurological disorders. In different situations, the disease progresses depending on the topical nuances of damage to the proprioceptive nerve channels.
Diagnosis of ataxia
- Diagnosis of the disease begins with the collection of complaints and anamnesis. Namely, the doctor must ask the patient how long ago he began to have complaints about unsteadiness of gait and poor coordination of movements, and how often and regularly these symptoms appear. It is definitely worth checking with the patient whether his relatives have had this disease. It is also necessary to find out whether the patient has taken any medications such as benzodiazepines and barbiturates.
- Patients suspected of having ataxia require a neurological examination. This examination involves assessing coordination of movements and gait, assessing strength in the limbs and muscle tone, the presence of nystagmus, and strength in the limbs.
- A correct assessment of hearing will also require an examination by an otolaryngologist.
Term designation
Sensitive ataxia is a disease that is manifested by a violation of the sensory sensation of pressure, vibration responses and body position in space, causing motor disturbances and incoordination. The characteristic symptoms of the anomaly are: a disorder of standard gait and coordination, low blood pressure in the skeletal muscle regions, uncontrolled movements of the distal areas of the arms. Deviations from the norm in medical institutions are identified in the presence of specific neurological data. The main diagnostic methods include the collection of blood cells for biochemical testing, neurophysiological testing, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain or spinal cord, and genetic testing. Neurometabolic techniques are prescribed as therapeutic therapy, since the etiotropic method is not effective. Patients are prescribed anticholinesterase medications, vitamin complexes, ATP, massage sessions, etc.
Additional tests
For a more detailed study of the disease, a consultation with a neurosurgeon will be required, as well as a number of instrumental studies.
- In particular, a lot of information about the disease can be obtained using electroencephalography. This technique evaluates the electrical activity of various parts of the brain, which tends to change in various diseases.
- No less effective techniques are also CT and MRI of the brain. They allow you to study the structure of the brain layer by layer, detect violations of the structure of its tissues, identify ulcers, tumors, and hemorrhages.
- Magnetic resonance angiography will help detect tumors in the brain and assess the integrity of the arteries in the skull.
Complications of ataxia
Treatment of ataxia must be timely, as otherwise serious complications are possible. One of the most dangerous complications of ataxia is heart failure. This is an acute or chronic condition, which is accompanied by shortness of breath, swelling, and frequent fatigue. The danger of the pathology is that it can cause pulmonary edema. Today, heart failure is one of the common causes of death. No less dangerous complications of ataxia are repeated infectious diseases and respiratory failure.
Recommendations
A consultation with a neurologist and DNA diagnostics are recommended.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Russian State Medical University, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Gusev E.I. | |
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in the world: |
| G. AVANZINI, Italy. |
Treatment of ataxia
Treatment of ataxia is aimed at eliminating the etiological factor that triggered the development. Depending on the specific disease, the following operations may be prescribed:
- tumor removal;
- elimination of hemorrhage;
- removal of the abscess and subsequent antibiotic therapy.
In rare cases, a procedure to relieve pressure in the posterior fossa may be necessary. Namely, this procedure is carried out if a patient has an Arnold-Chiari malformation, which is characterized by a slight descent of part of the cerebellum into the opening of the skull, which ultimately leads to severe compression of the brain stem. Ataxia can also be caused by hydrocephalus, which is characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system of the brain. In this case, doctors create an outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which normalizes metabolism in the brain.
If the cause of this serious disease is high blood pressure, it is imperative to normalize it with the help of drug therapy. In case of circulatory problems in the brain, drugs that improve metabolism and blood flow are also indicated. These primarily include nootropics and angioprotectors.
Ear diseases can also lead to the development of ataxia. In case of infectious brain damage caused by ear pathology, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed. If there is a lack of vitamin B12, it must be compensated. To eliminate poisoning, vitamins A, B, and C are prescribed. For demyelinating diseases, hormonal medications are indicated, as well as plasmapheresis. This procedure involves removing blood plasma, but preserving blood cells.
Ataxia is a dangerous disease because, due to lack of coordination, the patient can experience serious injuries. This can be prevented by following a few rules:
- It is better for all patients, regardless of the stage of their disease, to avoid driving a car and working with power tools. In these situations, poor coordination can cause serious injury.
- Patients with ataxia should always keep the room well-lit to increase depth of perception and avoid injury. Twilight is especially dangerous for patients.
- Many patients experience serious difficulty climbing stairs. To avoid injury, be sure to hold on to the railing or use outside help when climbing stairs.
- If it is very difficult for a patient to move independently due to lack of coordination, he should use a walker or cane while moving.
- If you experience a feeling of nausea or severe dizziness, you should immediately sit down or lie down.
- Doctors also advise listening to your body. Therefore, if the disease worsens, you should make an appointment with a neurologist.