Recovery
The skull repair procedure may vary depending on the type of surgery performed and the physical condition of the patient.
As a rule, they try not to keep the patient in for too long and, when the condition stabilizes, they are sent home to more quickly restore the rhythm of life. A long stay does not allow the immune system to strengthen, which leads to an increased risk of getting an infection in the hospital or after discharge. After the operation, the patient is transferred to a ward where his condition is constantly monitored. After getting rid of anesthesia, the breathing tubes are removed, and then the patient is sent to the neurology and intensive care department for further observation, the period of which does not exceed 2 weeks. During this period, you need to lead a sedentary lifestyle as much as possible, try to make as little body movements as possible.
After discharge, you should take all medications prescribed by your doctor, but you should not exceed or, conversely, decrease the dosage without first consulting your doctor. The patient is prohibited from driving, performing any physical or mental activity, or performing exercises until the doctor gives permission. Not following your doctor's instructions may cause difficulty in recovery and unwanted side effects in the future.
Once cleared by your surgeon, you can begin a program of early exercise, such as stretching your neck and back. You should also take frequent walks in the fresh air, although initially their duration should be minimal.
The recovery process can last up to 4 weeks, and by the final date it will be possible to return to your normal work
However, you will still need to take precautions until your rehabilitation is complete, which can last up to 3 months. Ignoring your doctor's instructions may result in the above consequences, as well as paralysis, loss of mental function, and permanent brain damage.
Craniotomy or craniotomy is a complex medical operation known since ancient times. It is carried out in special cases when the doctor needs to gain access to the brain and its membranes, emerging pathologies and blood vessels. Modern medicine makes surgery safer for the patient compared to past times when it was associated with high mortality.
Craniotomy: when necessary, implementation, rehabilitation
Craniotomy is rightfully considered one of the most complex surgical interventions. The operation has been known since ancient times, when they tried to treat injuries, tumors and hemorrhages in this way. Of course, ancient medicine did not allow one to avoid various complications, so such manipulations were accompanied by high mortality. Now trepanation is performed in neurosurgical hospitals by highly qualified surgeons and is intended, first of all, to save the patient’s life.
Craniotomy consists of creating a hole in the bones through which the doctor gains access to the brain and its membranes, vessels, and pathological formations. It also allows you to quickly reduce the growing intracranial pressure, thereby preventing the death of the patient.
The operation has strict indications, and the obstacles to it are often relative, since in order to save the patient’s life, the surgeon can neglect concomitant pathology. Craniotomy is not performed in terminal conditions, severe shock, septic processes, and in other cases it can improve the patient’s condition, even if there are serious disorders of the internal organs.
Third Eye
Tibetan monks also used craniotomy in their practices. They noticed that the gift of clairvoyance was often revealed in people who had suffered a brain injury. Having reasoned that the same effect could be achieved artificially, they began to use an operation to open the “third eye”.
A monk prepared and selected according to special criteria, ready to acquire the gift of clairvoyance, had a hole drilled in his forehead, which was closed with a wooden stopper soaked in healing ointments. After a few days, when the damaged tissues had healed, the plug was removed.
The operation was not only extremely painful, but also dangerous - quite often it ended in the death of the “chosen one”. Sometimes this was due to the carelessness of those who made the hole. And sometimes - an infection introduced into the wound during the healing process. However, those who managed to survive trepanation and successfully open their “third eye” acquired a reputation as holy clairvoyants. They say that their consciousness really changed, and they began to see and hear things inaccessible to ordinary people.
Historical reference
In neurosurgery, trephination is the making of a hole in some part of the skull to gain direct access to brain tissue. However, such surgery should not be considered an invention of modern medicine. Archaeological finds indicate that our ancestors could have drilled holes in the skull for medicinal purposes several thousand years ago. Since the Late Paleolithic era (40-11 thousand years ago), trepanation has been used in almost all corners of the planet. The operation was used by ancient Greek and Roman doctors, healers of several parts of Africa, South America and the South Pacific.
Hippocrates proposed trepanation as a way to treat head wounds, including removing bone fragments from the brain after injury. For this procedure, his followers came up with a special drill. Prehistoric trepanations in the culture of ancient civilizations of Peru were performed with a ceremonial knife called a tumi. Residents of the southern regions of the Pacific Ocean performed surgery using sharply sharpened shells. In Europe, flint and obsidian were used for the same purposes.
The purpose of trephination was not always to open access to the brain for further manipulation. In ancient times, a hole in the skull often served as an outlet for evil spirits, which were considered the cause of disease. Also, the hole in the skull was seen as a kind of channel for obtaining special knowledge and spiritual experience. In Egypt, pharaohs underwent such an operation, presumably to make it easier for the soul to leave the body after death.
The Mystery of the Left Brain
“The Biology of God” is what the French scientist Patrick Jean Baptiste called his book. He collected and summarized many unusual experiments conducted in the USA, which testified to the biological and mental ability of man to penetrate into the highest echelons of the information universe, which lies beyond the boundaries of the ordinary material world.
The experiments were carried out by neurosurgeons on volunteers and concerned the clarification of the brain's reactions to a sharp reduction in the exchange of information between the two hemispheres. When the connections between the left and right hemispheres were broken, the person became able to reach new levels of cognition that were inaccessible to him before the operation.
These connections were so stable that they were recognized as really existing. It was found that the reason for the “exit” of human consciousness beyond the boundaries of the everyday world was the operation of disconnecting the left hemisphere from the area located on the right side. It was the zones of the left hemisphere, responsible for the individual’s awareness of the environment, that served as a kind of barrier to the expansion of consciousness.
Representatives of ancient civilizations achieved this state either through long meditations or by moving away from the world into a desert area. There, in the absence of external influence, the centers of the left hemisphere turned off on their own. In this unusual way, the prophets of Babylon and Judah received their messages - visions declared to be messages of God for their peoples.
Consequences after craniotomy
The severity of the consequences in the postoperative period depends on the reason for the operation, the age of the patient, and the presence of concomitant diseases. If neurological disorders were not immediately detected after trepanation, this does not mean that they will definitely not arise in the future. If the cerebral cortex is damaged, hearing and vision impairment of varying severity, up to complete loss, may occur.
The consequence may be a stroke due to thrombosis or thromboembolism. During trephination for abscesses, pathogenic flora may spread through the membranes of the brain, which will lead to meningitis and encephalitis. After many hours of anesthesia, disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are possible. If the neurovascular bundles are damaged, numbness, complete loss of sensitivity, and movement of certain areas of the skin, muscles, and limbs are possible. Postoperative consequences can manifest themselves in the form of mental and behavioral disorders.
Tests that a patient should undergo before craniotomy
Before surgery using craniotomy, the patient is prescribed the following tests:
- CT angiography (for visualization of cerebral vessels);
- CT scan of the brain;
- angiography (brain catheterization);
- positron scanning;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- detailed blood test.
Patients whose age exceeds 40 years are also prescribed an ECG of the heart, and patients over 60, as well as long-term smokers and patients suffering from obesity, diabetes, heart disease, lungs, and respiratory tract are prescribed a chest x-ray. In addition, consultations with a neurosurgeon and anesthesiologist are also mandatory.
How is craniotomy performed?
There are 6 main steps during a craniotomy. Depending on the underlying problem being treated and the complexity, the procedure may take 3 to 5 hours or more.
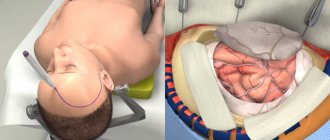
Step 1 - patient preparation. No food or drink is allowed after midnight the night before surgery. Patients with craniotomy are admitted to the hospital in the morning. General anesthesia is administered intravenously while the patient lies on the operating table. The person falls asleep, and his head is in a 3-pin cranial fixation device, which is attached to the table and holds the head in an upright position during the procedure. Inserting a lumbar (spinal) drain into the lower back helps remove cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), allowing the brain to relax during surgery. The patient may be given the drug Manit, which relaxes the brain.
Step 2 - skin incision. After the scalp has been coated with antiseptic, a skin incision is made, usually behind the hairline. The surgeon tries to ensure a good cosmetic result after the operation. Sometimes the hair can be shaved sparingly.
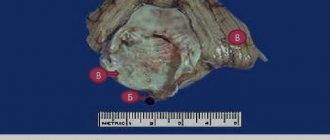
Step 3 - performing a craniotomy, opening the skull. The skin and muscles rise to the bone. Next, the surgeon uses a drill to make one or more small holes in the skull. By inserting a special saw through the holes of the burrs, the surgeon reduces the contour of the bone flap. The cut piece of bone is lifted and exposed to the protective covering of the brain called the dura mater. The bone flap is stored securely until it is replaced at the end of the procedure.
Step 4 - opening the brain. After opening the dura mater with surgical scissors, the surgeon places it back to expose the brain. Retractors placed on the brain need to be repaired or removed. Neurosurgeons use special magnifying glasses (loupe, or operating microscope) to see fine nerves and blood vessels.
Step 5 - fix the problem. Because the brain is tightly enclosed within the bony skull, tissue cannot be easily moved to the side, making it difficult to access and correct any problems. Neurosurgeons use a variety of very small instruments to work deep within the brain. These include long-handled scissors, dissectors, drills, lasers, ultrasonic aspirators (to break up tumors and suck up debris), and computer imaging guidance systems. In some cases, monitoring is used to stimulate specific cranial nerves while the response is monitored in the brain. This is done in order to preserve the function of the nerves and ensure that they are not damaged later during the operation.
Step 6 - closing the craniotomy. With the problem of removing or repairing retractors, the dura mater, closed with sutures, is also removed from the brain. The bone flap is placed back in its original position and secured to the skull with titanium plates and screws. The plates and screws are permanently left to support the skull, which can sometimes be felt under the skin. In some cases, drainage tubes may be placed under the skin for several days to remove blood or surgical fluid. The muscles and skin are stitched back together.
The entire procedure lasts 180-240 minutes.
Craniotomy - types
To eliminate many pathologies, trepanation is used, the types of which are named based on the location of access to the brain and the method of performing the operation. The bones of the skull (on the vault) are represented by several plastics, covered with periosteum on top and adjacent to the braincase below. If the periosteum, as the main nourishing tissue, is damaged, there is a risk of necrosis and bone death. To avoid this, craniotomy is performed using the following methods:
- classical osteoplastic;
- resection;
- for the purpose of decompression;
- conscious operation;
- Stereotaxy is a study of the brain using a computer.
Osteoplastic craniotomy
The most famous type of craniotomy, a classic method of opening the skull, during which a small section of the parietal bone is sawed out without damaging the periosteum. The cut piece is connected with the periosteum to the cranial vault. The pedicled skin flap is folded back and, after the operation, is placed in place or removed. The periosteum is sutured. After surgery, no bone defect is observed. Trepanation (osteoplastic) of the skull is divided into two types:
- With cutting out a skin-periosteal-bone flap at the same time (according to Wagner-Wolf).
- With cutting out a skin-aponeurotic flap, which has a wide base, and then an osteoperiosteal flap on a narrow stalk (Olivecron trepanation).
Decompressive trephination
One of the methods designed to reduce intracranial pressure and improve the condition (and function) of the brain is decompressive craniotomy (DCT) or Cushing trephination, named after the famous neurosurgeon. With it, a hole is created in the bones of the skull, through which the harmful element that caused the resulting hypertension is eliminated. This could be pus, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, or edematous fluid. Negative health consequences after surgery are minimal, rehabilitation is short.
Resection trepanation
Resection surgery has a less favorable prognosis for rehabilitation; craniotomy is performed by applying a burr hole and then expanding it to the required size (for this, wire cutters are used). The sawed area is removed along with the periosteum without possible restoration. The bone defect is covered with soft tissue. As a rule, this technique is used when trepanation of the posterior cranial fossa is necessary, as well as treatment of cranial wounds.
Awake craniotomy
One of the modern methods of surgery is trepanation without anesthesia. The patient is conscious, his brain is not turned off. He is given relaxation drugs and local anesthesia is injected. Such intervention is required when the pathological area is located too close to the reflexogenic zones (and there is a danger of damaging it). During the operation, surgeons constantly monitor the patient’s condition and the activity of organs, monitoring the process.
Preparing for surgery
If penetration into the cranial cavity is necessary, good preparation of the patient for surgery is important. If there is enough time, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination, including not only laboratory tests, CT and MRI, but also consultations with specialists and examinations of internal organs. An examination by a therapist is required to decide whether the intervention is safe for the patient.
However, it happens that the opening of the skull is performed urgently, and then the surgeon has very little time, and the patient undergoes the necessary minimum of studies, including general and biochemical blood tests, a coagulogram, MRI and/or CT scan to determine the state of the brain and the localization of the pathological process. In the case of emergency trephination, the benefit in the form of preserving life is higher than the probable risks in the presence of concomitant diseases, and the surgeon decides to operate.
During a planned operation, after six o'clock in the evening the day before, it is forbidden to eat and drink, the patient once again talks with the surgeon and anesthesiologist, and takes a shower. It is advisable to rest and calm down, and in case of severe anxiety, sedatives may be prescribed.
Before the intervention, the hair on the head is carefully shaved, the surgical field is treated with antiseptic solutions, and the head is fixed in the desired position. The anesthesiologist puts the patient under anesthesia, and the surgeon begins the manipulations.
Opening the cranial cavity can be done in different ways, therefore the following types of trepanation are distinguished:
- Osteoplastic.
- Resection.
Regardless of the type of surgery planned, the patient must be placed under general anesthesia (usually nitrous oxide). In some cases, trepanation is performed under local anesthesia with a solution of novocaine. To enable artificial ventilation of the lungs, muscle relaxants are administered. The surgical area is carefully shaved and treated with antiseptic solutions.
Rehabilitation after craniotomy
The first day after the end of the operation, the patient is in intensive care, connected to devices. The next 3-7 days should be spent in a hospital under the supervision of doctors. This period of time allotted for recovery after craniotomy is very conditional; if a person experiences complications, it can increase. During the rehabilitation period, the patient is prescribed medications:
- painkillers;
- antibiotics - to prevent inflammation;
- antiemetics;
- sedatives;
- anticonvulsants;
- steroid drugs that remove excess water from the body.
The sterile dressing is removed from the wound within 24 hours. The skin around the wound should be constantly treated and kept clean. After 2 days, the patient is allowed to get up and walk a little. After discharge home, rehabilitation continues. The following conditions must be observed:
- do not lift objects weighing more than 3 kg;
- stop smoking;
- eliminate nervous unrest;
- take a course with a speech therapist to restore speech;
- bend over as little as possible;
- go on a diet prescribed by a doctor;
- Take short, supervised walks every day.
You should very carefully monitor the emotional state of a person after surgery. Some people become susceptible to depression and nervous disorders
It is necessary to surround them with care and attention, to protect them from unnecessary worries. If you can’t cope with anxiety on your own, you need to consult a psychologist.
What are the consequences for children and adults?
- Asthenia – constant feeling of fatigue, depression, sensitivity to atmospheric phenomena, insomnia, tearfulness;
- Speech disorders are common in both children and adults. It is difficult to immediately determine whether this phenomenon is temporary. So you just have to wait and watch;
- Psychosis;
- Forgetfulness;
- Paralysis;
- Convulsions (more often in children);
- Loss of coordination (more pronounced in children);
- Hydrocephalus (in children, less often in adults);
- ZPR (in children).
Infectious complication
As after any surgical intervention, trepanation negatively affects the body's protective functions, which increases the risk of infection.
Brain infections are extremely rare, but the wound itself can easily become infected by poorly handling the instruments
The lungs, intestines, and bladder suffer from infection. All these organs tend to catch infections first.
After surgery on the skull, the likelihood of developing a number of infections increases significantly, and infection of the brain tissue itself occurs much less frequently, which is associated with appropriate sterilization of the area undergoing surgery.
The greater risk of infection is the lungs, intestines and bladder, the functions of which are regulated by parts of the brain. This circumstance is largely due to forced restrictions on a person’s mobility and lifestyle changes after surgery. Prevention of such complications is physical therapy, diet, and sleep. Treatment of infections is carried out medically - by prescribing appropriate antibiotics.
Blood clots and blood clots
Pathological processes and changes in brain tissue, poor mobility in the postoperative period can cause blood stagnation, which causes the formation of blood clots. The veins in the legs are most often affected.
If a blood clot breaks loose, it can migrate throughout the body, settling in the lungs or heart. Very often, the detachment of a blood clot leads to death. There are also cases of pulmonary artery thrombosis, which is a very dangerous consequence and requires immediate intervention. This disease leads to very serious consequences, including death.
The best prevention against clots is exercise, plenty of fresh air and anticoagulants (blood thinners).
Neurological disorders
To speed up the healing process, steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
With more serious errors made during surgery, pathologies may last longer. There are many causes for symptoms, and they all depend on more than one factor.
Bleeding
Bleeding is one of the most common phenomena after trepanation. For several days after surgery, the vessels may bleed. This problem is eliminated by drainage. Usually there is little blood and it does not cause problems.
But there are cases when the bleeding is so profuse that repeated trephination has to be done to stop it and prevent more serious consequences.
Blood that accumulates in the cranial cavity can affect motor centers or nerve endings, causing seizures. In order to avoid such manifestations during surgery, the patient should be given intravenous anticonvulsant drugs in advance.