The life of a modern person is associated with many unfavorable factors - stress, conflicts, poor environment, low-quality products, and little physical activity. The result of their influence is the development in the body of various functional and organic disorders, sometimes very severe. Such, for example, as neuritis .
This inflammatory disease of the peripheral nerves is characterized by paroxysmal pain, decreased or complete loss of sensitivity, as well as movement disorders including paresis and paralysis.
With mononeuritis, only one peripheral nerve is affected (ophthalmic, facial, radial, etc.), with inflammation of the nerves from one plexus, we talk about plexitis .
Neuritis is dangerous due to its complications. Particularly severe consequences of the disease include paresis, paralysis, and muscle atrophy.
1 Neuritis. Diagnosis and treatment
2 Neuritis. Diagnosis and treatment
3 Neuritis. Diagnosis and treatment
Symptoms
With neuritis, the nerve fiber is damaged, and therefore the functions suffer, the main ones being sensitive, motor and trophic, therefore the following symptoms are clinically noted:
- In the phase of irritation of the nerve fiber: pain, burning, feeling of “crawling goosebumps”, feeling “as if many needles are being pricked”.
- In the phase of loss of functions: decreased muscle strength, muscle atrophy, decreased reflexes, decreased sensitivity, tissue atrophy including skin, subcutaneous fat, muscles, bone tissue.
Causes
The main causes of neuritis:
- infectious (viruses, bacteria, their toxins);
- exposure to toxic factors
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, deficiency of vitamins B1 and B6);
- allergic reactions;
- injuries;
- oncological diseases;
- hereditary diseases;
- diseases of the spine leading to mechanical compression of the nerve trunk (intervertebral hernia, tunnel syndromes, etc.).
The mechanism of nerve damage when exposed to various unfavorable factors is associated with the launch of a cascade of inflammatory reactions. Swelling of the nerve trunk occurs, damage to the myelin sheath and subsequently to the axial cylinder, which in turn leads to the death of the nerve cell.
Make an appointment
Clinical picture of some individual nerves
- Trigeminal nerve – pain is sharp, piercing, in series, along one or several branches of the nerve.
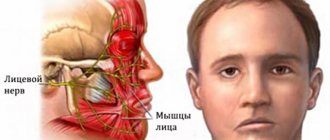
- Facial nerve – muscle weakness on one side of the face. It is difficult to close the eye, the corner of the mouth on the affected side is drooping. When liquid food or drink is taken, everything comes out of the mouth.
- Diaphragmatic – feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath, hiccups.
- Median – impaired flexion of the hand, fingers I, II and III and decreased sensitivity on the palmar surface.
- Ulnar – weakness of the flexors of the IV, V and partly III fingers, decreased sensitivity on the palmar surface of the above fingers.
- Radial – impaired extension of the hand and fingers, decreased sensitivity in half of the back of the hand (I and II fingers). It is difficult to move the thumb away.
- External cutaneous nerve of the thigh (Roth-Bernhardt disease) – pain, numbness and burning along the outer surface of the thigh.
- Femoral – impairment of leg extension at the knee joint and hip flexion. Pain and sensory disturbances on the lower 2/3 of the anterior surface of the thigh, the anterior inner surface of the lower leg.
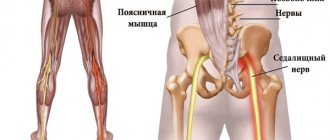
- Sciatic – pain along the back of the thigh and lower leg, weakness of the flexors and extensors of the foot.
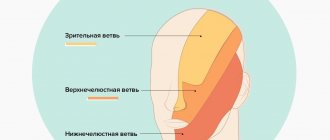
- Olfactory – anosmia on one side (lack of sense of smell). When a nerve is irritated, foreign odors may appear.
- Visual – decreased acuity and loss of visual fields. The phenomena of nerve irritation manifest themselves in the form of photopsia (sensation of light, flames, sparks, etc.).
- Oculomotor – drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis), limited mobility of the eyeball, dilated pupil, diplopia (double vision).
- Block - restriction of the mobility of the eyeball downwards and outwards.
- Auditory – hearing loss, often accompanied by a feeling of noise or ringing in the ear.
- Glossopharyngeal - twitching pain in the tonsils, root of the tongue, pharynx and taste disturbances in the back third of the tongue, impaired salivation and swallowing.
- Wandering – manifested by disturbances in swallowing and speech. On the affected side, the soft palate is lowered, the uvula is deviated to the healthy side. There are also disturbances in the functioning of internal organs - bradycardia, shortness of breath, motility disorders of the esophagus, stomach and intestines (spasms), etc.
- Additional – difficulty turning the head in the healthy direction, the head is tilted towards the affected nerve, the shoulder is lowered.
- Tibial – the foot is extended, but the patient cannot bend it. Cannot stand on toes. Sensitivity is reduced along the back of the lower leg and on the sole.
- Peroneal – the impossibility of standing on the heels and straightening the foot, it hangs down. Sensitivity is reduced on the outer surface of the lower leg and the back of the foot.
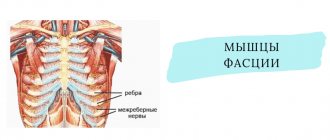
- Intercostal nerves – pain in the intercostal space, often radiating into the chest, simulating pain in the heart, chest, lungs, and stomach. Often, pain in the paravertebral muscles is detected at the level of the thoracic spine.
How to get rid of nervous tics
In order to free yourself from unpleasant sensations, you must first eliminate their problem. Sometimes all it takes is a good night's sleep. In another case, you need to change the situation for a while, get out of the destructive environment.
Among the auxiliary methods used are herbal soothing teas, baths with the addition of aromatic oils, swimming, walks in the fresh air or sports: running, yoga.
Add ingredients with a high content of calcium and magnesium to your menu. These include fermented milk products, buckwheat, bran bread, red fish, eggs, and meat. Vegetables and fruits include beets, currants, dried fruits, nuts and parsley.
If these foods do not fit into your diet, consider taking appropriate vitamin supplements. Do not overuse strong tea and coffee.
And most importantly: remain optimistic and calm in any situation!
In cases where the condition worsens, psychotherapy is sought. Cognitive behavioral therapy is especially effective in helping to stop tic disorders at the stage of their precursors.
Habit reversal therapy teaches patients movements that help prevent the development of neurological facial symptoms.
Medications include anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants, Botox injections, and antidepressants.
If the above methods are ineffective in combating nervous tics, they turn to deep brain stimulation. A device is installed in the GM that controls electrical impulses.
Diagnosis of neuritis
The symptoms of neuritis are in many ways similar to the clinical manifestations of various diseases, including non-neurological ones. Therefore, the doctor should conduct a thorough differential diagnosis to make an accurate diagnosis.
Primary diagnosis consists of a thorough collection of patient complaints, identification of possible preceding factors, and direct examination of the patient. Most symptoms of neuritis are specific, so depending on their severity, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis.
Stimulation and needle electroneuromyography are used to diagnose peripheral nerve damage. This study makes it possible to answer the questions - which nerve is damaged, in what place it is damaged, what percentage of nerve damage, as well as give a prognosis for its recovery and monitor its recovery.
Diagnostic methods
Electroneurography is used to measure the speed of passage of nerve impulses through the fibers of peripheral nerves from their exit point to the nerve endings in ligaments and muscles. The technique allows you to determine the damaged nerve, determine the location and extent of damage, and identify the severity of the process.
Electromyography – used to study the bioelectrical activity of muscles. This method allows us to answer the question: what is the problem - damage to the nerve or damage to the muscle itself? EMG allows for differential diagnosis of neuropathy with muscle pathology (myasthenia, myotonia, myoplegia, polymyositis).
Ultrasound is a method for diagnosing damage to peripheral nerves. Evaluates changes in nerve diameter, continuity, and deterioration of sound conduction. Ultrasound clearly shows swelling of the nerve trunk and surrounding tissues
MRI – visualizes nerves and soft tissue structure, detects malignancies and provides information about muscle atrophy and nerve damage. With the help of MRI diagnostics, it has become possible to detect nerve damage in areas that are difficult to examine using electrodiagnostics or ultrasound.
Make an appointment
What are the symptoms of nerve irritation?
How to recognize inflammation of nerve endings and the symptoms of this disease? The main symptom is pain, while neither the focus nor visible changes indicating the disease can be identified. The pain may worsen in the cold, during movement or at night, even with slight touch. Another characteristic symptom is the so-called paresthesia: tingling and burning sensations in the affected area. Often in this area one can find, upon examination, spasmodic, tense muscles that are painful on palpation.
Treatment of neuritis
Treatment must be comprehensive. It is necessary to fight both the damaging factor and restore the damaged nerve trunk.
In treatment I use the following groups of drugs:
- Vascular;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- B vitamins;
- Improving the conduction of impulses along the nerve, etc.
Non-drug treatment methods are also used:
- Acupuncture - exposure to biologically active points of the skin leads to signal transmission along the nerve trunk to the spinal cord and brain, resulting in a complex cascade of reactions, which includes improved blood circulation, release of biologically active substances, and hormonal response, which in turn accelerates restoration of nerve fiber.
- Physiotherapy is designed to locally influence reflex zones. The main effects achieved after physiotherapy are: analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, fibrinolytic.
- Massage (improves microcirculation, reduces swelling).
- Therapeutic exercise (by working out muscle groups using a feedback system, the recovery period is accelerated).
To relieve pain and accelerate the recovery of nerve fibers, local injection techniques are used - therapeutic and diagnostic blockades, pharmacopuncture - with various mixtures of drug solutions, if necessary, together with ultrasound navigation. Due to the local administration of drugs (vitamins, anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthetics), it is possible to quickly relieve pain, reduce swelling and the inflammatory reaction, and restore the nerve trunk.
What is back myositis and how to cure it
Some people believe that the back muscles rarely get sick, but they are wrong. Myositis can develop for many reasons, for example, due to a weakened immune system or injury. However, the etiology of the disease is one thing, and its treatment is completely different. Meanwhile, if you have myositis, you should be well versed in both.
Causes leading to the development of back myositis
As is known, the described disease is accompanied by inflammation of the spinal muscles. This may happen due to:
- Parasitic infection;
- Injuries;
- Autoimmune disease;
- General or local infection;
- Hypothermia;
- Tensions of a particular muscle group.
In this regard, it is not surprising that the risk group includes people who, due to their occupation, must either work in conditions of negative temperatures or keep their backs in one position for a long time. In particular, we are talking about drivers, production line operators, and pianists.
Drug treatment
Spinal diseases are most often treated with medications. This method is the most common and effective, because thanks to it you can get rid of pain, relieve swelling and normalize body temperature, if necessary.
The choice of medications for back myositis is made by the attending physician. As a rule, patients take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ketanov, Ibuprofen, Baralgetas, Meloxicam and others. These drugs have an analgesic effect. In addition, they slow down inflammatory processes and help fight swelling.
Warming ointments are considered no less effective than tablets. They are good because they improve blood circulation, relieve pain and swelling. In addition, gels are often prescribed to patients who suffer from infectious myositis. In particular, the following drugs have gained popularity: Ceftriaxone, Amoxicillin, Cefepime, Augmentin.
If back myositis has developed as a result of immunological disorders, then it can be cured by taking glucocorticoid hormones. In this case, treatment is structured in the form of a course developed by a specialist.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
If we consider physiotherapy as a method of treating myositis, then its high effectiveness should be highlighted. In particular, the following procedures help overcome the disease:
- back massage. Its main benefits are warming up the muscles, improving blood flow, relieving swelling;
- Ozokerite, which involves heating the affected areas using bags of salt;
- Ultrasound, which relieves pain and stops the spread of pain;
- Acupuncture.
To everything written above, it is necessary to add that sanatorium-resort treatment is recommended for patients suffering from a chronic form of myositis. It includes taking mud baths, physical therapy exercises and other procedures under the supervision of specialists.
Surgical intervention
Surgery for back myositis is necessary if the foci of inflammation have festered. In this situation, they are opened, the purulent membrane is removed and drainage is installed. After surgery, the patient must undergo a course of antibiotics.
Treatment of myositis at home
If you want to get rid of your illness on your own, then stay in bed. It is required so that the load on inflamed muscles is reduced and metabolic processes return to normal. In such cases, experts recommend keeping movement to a minimum. Warming up the affected areas will also be beneficial. Taking this into account, apply a heating pad and heated bags of salt to the sore area.
Among other things, do not forget that nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of myositis.
In particular, you need to reduce your fluid and salt intake and give up alcohol. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr