Causes of brain germinoma
There is no clear opinion about the cause of the formation of brain germinoma. Scientists and oncologists are more inclined to the version of the disorder in the process of embryogenesis. There is a so-called dysontogenetic theory of the occurrence of this type of tumor. According to this theory, brain germinoma occurs as a result of disorders of tissue differentiation and tissue migration at the very first stages of embryogenesis in the first trimester of pregnancy. The basis of this hypothesis is largely based on the fact that neoplasms are more often detected in people at a young age.
Germinoma is usually classified as a type of embryonic tumor, and these neoplasms arise and develop even before the full formation of the fetus from the rudiments of embryonic tissues. The reason is a violation of embryogenesis, which occurs as a result of changes in the structure of chromosomes and mutation of genes that control the normal development of embryogenesis.
Factors that induce changes and disturbances in embryogenesis may have an indirect or direct effect on the body of the expectant mother. Such provocateurs include contact with toxic substances during pregnancy, the influence of radioactive substances, various types of infections (measles, herpes, severe stages of influenza). The risk factor will also be the influence of carcinogens.
General information
Germinoma is a rare disease that belongs to a type of brain tumor. The neoplasm is formed at the stage of embryonic development. Germinoma can arise from one type of tissue or consist of several types.
Experts have conducted a number of studies, based on which it was found that boys are mainly susceptible to developing the disease.
The tumor is located in the deep parts of the brain, which causes the development of certain consequences and complications. Often, surgical removal of the formation is impossible, due to the location of the germinoma.
Education develops gradually, along with the brain. In certain cases, it is completely inert and appears only when the child reaches 10-11 years of age.
But the tumor may not show signs for up to 20 years. Such a course is considered benign. But in more than half of the cases (about 75%) it is malignant, which is due to the speed of its growth.
Symptoms of brain germinoma
The clinical picture of brain germinoma largely depends on its location. Localization of brain germinoma - deep structures of the brain - area of the pineal gland, third ventricle.
One of the first signs of this neoplasm will be impaired blood flow and hydrocephalus as a consequence. Patients often complain of a bursting headache that is not relieved by analgesics or other painkillers. There is also a feeling of pressure in the eyes, constant nausea, independent of meals, and at times even vomiting. Visual impairment is often observed. This is explained by the fact that germinoma is localized near the chiasm of the optic nerves and, growing, infringes on them. Patients focus on double vision, visual field defects, farsightedness or myopia.
The clinical picture of brain germinoma is also characterized by deterioration or partial loss of memory, mental disorders, and emotional instability. In some cases, various kinds of neuroendocrine syndromes such as diabetes insipidus, as well as menstrual irregularities, anovulation, amenorrhea in women and disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary system may be observed. Developmental disorders of puberty are also diagnosed. All these symptoms are explained by the location of the tumor near the hypothalamus.
Advantages of treatment in Israel
- Specialists with enormous experience, capable of achieving incredible results and treating cases of disease that doctors in many large European and American centers do not undertake.
- Very fast and accurate diagnostics using modern tomography equipment.
- The widest range of treatment areas - operations, radiotherapy, radiosurgery, effective chemotherapy regimens, timely relief of symptoms with the latest medications.
- Accommodation in cozy and comfortable rooms, equipped with everything necessary. Each patient receives individual treatment conditions in accordance with their needs.
- Each patient can use the services of a personal case manager, who helps in matters of communication with the clinic’s medical staff and in solving everyday issues.
- Positive reviews from patients who have already undergone treatment at the Ichilov Clinic.
If your child shows signs of the disease and you want to consult an Israeli neurosurgeon, there is no reason to delay contacting the clinic. Do this today, and our medical analyst will select the right specialist for you and schedule a consultation at a time convenient for you.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
Diagnosis of brain germinoma
The first diagnostic conclusions are made during the first examination by a neurologist. A neurological examination and questioning of the patient, his complaints and accents in the characteristics of general well-being makes it possible to establish or suspect the presence of hydrocephalus.
Methods for diagnosing brain germinoma:
- Echo-encephalogram. Firstly, it allows you to diagnose intracranial pressure, and secondly, in the case of a large tumor, this diagnostic method can reveal displacement of the deep structures of the brain.
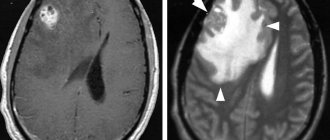
- Tomographic methods - CT and MRI of the brain. They make it possible to identify the nature of the tumor, location and size. Almost half of patients diagnosed with brain germinoma have a clinical picture of tumor infiltration of the visual tuberosities and petrification in the middle (the so-called butterfly symptom). This diagnosis can be confirmed by the presence of tumor bodies in the lateral ventricles and metastases in the infundibular region of the third ventricle.
- Biochemical blood test - establishing markers of hCG, ACE, PAL.
- Steretactic brain biopsy. This method will be the most accurate in making a diagnosis, since a laboratory examination of the tumor body is performed. In some cases, such a study may not give accurate results if the tumor is heterogeneous.
- Morphological examination of tumor areas after its removal. The difficulty of this method is in localizing the tumor in the deep structures of the brain, so doctors often prefer stereotactic biopsy.
Brain germinoma has a similar clinical picture to a number of neoplasms in the central nervous system, and therefore requires careful diagnosis and differentiation from diseases with similar symptoms. Among these diseases:
- astrocytoma;
- glioma;
- ganglioneuroma;
- hematoblastoma;
- medulloblastoma;
- brain abscess;
- intracerebral hematoma;
- cystosis in the third ventricle.
Prevalence
The incidence of such neoplasms is influenced by the patient’s age:
- up to 15 years – 2-4%;
- in adolescence (15-19 years) – about 14%.
For childhood, there are two periods when the incidence is at its peak:
- The first is up to 2 years of age, girls get sick more often than boys (74%). During this period, in most cases, neoplasms are localized in the sacrococcygeal zone.
- The second one is a little different for girls and boys. This peak occurs during adolescence: 11-14 years for boys and 8-12 for girls. Tumors are mainly found in the gonads.
In recent years, most researchers have reported an increase in the number of cases of detection of germ cell formations. This trend can be seen especially clearly in the male part of the population, with tumors localized in the testicles. In men, the incidence has increased in recent years from 2 to 4.4 per 100,000 people.
A common cause of malignant germ cell tumors is various genetic abnormalities, for example, Klinefelter syndrome or ataxia-telangiectasia, pure and mixed gonadal dysgenesis, cryptorchidism, hermaphroditism, etc.
Treatment of brain germinoma
The most common treatment strategy for brain germinoma is radiation therapy. If the patient’s age is too young, their general condition does not allow radiation therapy, or there are contraindications, then polychemotherapy is prescribed. Sometimes surgery will be a mandatory and forced method of treatment and may be accompanied by radiation or chemotherapy. But such a complex method of treating this disease is extremely undesirable for young or child patients, as it entails severe intoxication of the entire body.
Types of germinoma
Oncologists distinguish several types of germinoma.
- Seminoma is a malignant testicular tumor of germ cells. It is quite common, characterized by aggressive growth and actively metastasizes. In most cases, it is accompanied by a clear enlargement of the testicle and severe pain in the scrotum. It is treated like most types of cancer - chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery.
- Dysgerminoma is a malignant neoplasm in women that develops from primary indifferent cells of the gonads. The cause is hypoplasia of the genital organs. Symptoms: pain, difficulty urinating and constant weakness.
- Teratoma is in most cases a benign neoplasm. Localized in the ovaries, testicles or in the pineal area. May consist of muscle or bone tissue, hair. Effective treatment methods are radiation and chemotherapy, as well as surgery.
- Teratocarcinoma is a malignant tumor of the ovary, which is formed from immature and mature tissues, affecting the internal genital organs of men and women.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of brain germinoma can be carried out in various ways and is performed when an accurate diagnosis is made and the location, nature and size of the tumor is established. Often, surgical treatment is the only possible method, since other methods will be ineffective. In some cases, surgical intervention requires additional procedures - ventriculocisternostomy or ventriculoperitoneostomy.
Contraindications for surgical treatment of brain germinoma may include inoperable location of the tumor or disseminated tumor growth, as well as multiple foci. If the size of the tumor is small, then it is advisable to use radiosurgery methods. The essence is a single exposure to the location of the tumor with a high dose of radiation.
Treatment of the disease is within the competence of specialized departments of neurosurgery, which are equipped with equipment and a computer imaging neuronavigation system.
Testicle
Primary formations in the testicles (they are called testicular) are rarely diagnosed in childhood. Most often they are found in children under 2 years of age, with 25% already at birth.
A)
b)
Figure 2. – testicular seminoma: a – gross specimen, b – MRI.
According to the histological (i.e. tissue) structure, these are most often neoplasms of the yolk sac or benign teratomas.
The second peak in the occurrence of testicular tumors is puberty. During this period, the incidence of malignant teratomas increases. Seminomas are extremely rare in children.
Testicular swelling, which quickly increases and does not cause pain to the child, is most often discovered by parents. 10% of such neoplasms are combined with “dropsy of the testicle” (medical “hydrocele”) and other congenital pathologies, especially of the urinary system.
Upon examination, a dense neoplasm is visible, lumpy, without signs of inflammation. Preoperative tumor diagnosis is confirmed by elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels.
The neoplasm contains elements of the yolk sac.
Symptoms of metastases in the para-aortic lymph nodes are lower back pain.
Prognosis and prevention of brain germinoma
The main methods of preventing brain germinoma can be considered the exclusion of any negative impact on the body of the expectant mother. A pregnant woman should lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid contact with radioactive and toxic substances.
This disease, if detected in the early stages, responds well to chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In the future, to monitor your condition and the course of the disease after treatment, you must consult a neurologist at least once a year. Even with surgery, the prognosis can be quite encouraging - the survival rate after such operations is approximately 85 percent.
International classification of germinoma stages
The tumor is small, localized, and must be removed within the boundaries of healthy tissue. During a diagnostic test for tumor markers, their content turns out to be normal or slightly increased (the half-life of the tumor markers is taken into account). Metastases are not detected in nearby lymph nodes. Treatment of germinoma abroad at this stage is the most gentle and effective.
Stage 1.- Stage 2. Microscopic examination reveals cancer cells along the resection line. There is no damage to the lymph nodes. Tumor markers are either normal or elevated.
- Stage 3: Surgical resection does not completely remove the tumor, or only a biopsy can be performed at this stage. Possible damage to nearby lymph nodes. Tumor markers are normal or elevated.
- Stage 4. The process of distant metastasis.
general information
Among all brain tumors, germinoma accounts for only 2%. But among tumors affecting the deep structures of the brain, it is the most common. In approximately 56% of cases, germinoma is located in the region of the pineal gland, or pineal gland, and the pituitary gland area accounts for 25%. In the overwhelming majority, the neoplasm is a single conglomerate.
The period of occurrence of germinoma falls on the age range from 10-15 to 20-25 years. Some medical sources indicate that the tumor is more often found in men. This neoplasm often becomes malignant and grows into the surrounding tissue. A benign course of germinomas is observed in approximately 25% of cases.
conclusions
Germinomas of the subcortical ganglia are a very rare pathology. Based on our experience and publications, subcortical ganglion germinomas are often diagnosed at a late stage, due to atypical clinical symptoms and a variety of neuroimaging manifestations. The manifestation of the disease in boys in the second decade of life can help in diagnosis: bilateral damage to the subcortical nodes according to MRI; neuroendocrine symptoms that occur in some of these patients, despite the absence of MRI signs of damage to the suprasellar region; psychopathological symptoms that are present in these patients and are not pathognomonic for glial tumors of the subcortical ganglia.
There is no conflict of interest.
Clinical picture
For a long time, the tumor may not show any signs. With age, it increases, and when it reaches a certain size, it causes characteristic symptoms. The tumor can be first detected at the age of 10-15 years, however, if malignancy is present, it is detected earlier. With a slow course, the pathology appears closer to 20-25 years.
Hydrocephalus comes to the fore in germinoma. This is due to the topography of the tumor: it is localized in the region of the third ventricle. Having diffuse growth, the tumor impedes the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which leads to fluid retention. Patients complain of intense pain in the head and eyes. Other disorders may include vomiting and nausea.
Often, germinoma, located near the optic chiasm, causes dysfunction of the optic nerves. A person notices a gradual decrease in visual acuity, sometimes double vision appears, and in some cases certain fields of vision are lost. The brain is such a complex and not fully understood structure of the human body that any pathologies occurring in it can cause neuropsychiatric disorders.
The pituitary gland regulates the function of other endocrine glands that are located on the periphery. If the neoplasm is located near it, then this affects the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, which leads to the occurrence of endocrine pathologies.
The malignant course of germinoma is often accompanied by symptoms such as:
- sudden weight loss;
- decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cell count;
- loss of appetite.
Etiology
To date, the exact cause of germinoma has not been established, but most doctors associate it with a disorder of embryonic development. The young age of the patients confirms this. In the first trimester of pregnancy, under the influence of unfavorable factors, deviations in the formation and correct formation of organs can occur. Toxicoses, taking certain medications, and viral and bacterial diseases of the mother can cause improper differentiation of fetal cells.
The most severe factors contributing to the development of pathology include:
ionizing radiation;- contact with toxic substances;
- influence of carcinogens;
- viral infections (herpes simplex, influenza, measles, chicken pox).