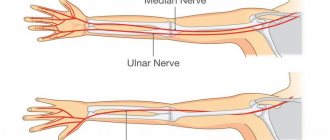
Ulnar nerve neuritis is often accompanied by numbness and paralysis of the affected limb. This is due to a violation of the innervation of skeletal muscles in the forearm, hand and some fingers.
In the absence of timely treatment, muscle tissue atrophy and irreversible changes in the structure of the ulnar nerve are possible. The latter leads to complete loss of sensitivity and various motor activity disorders without the possibility of recovery.
What is the ICD-10 code?
Ulnar nerve neuritis is an inflammation of various etiologies affecting the myelin sheath and axial cylinders of the nerve fiber.
The pathology is accompanied by acute pain, loss of sensitivity and decreased motor activity of the affected arm.
Disruption of innervation gradually leads to atrophy of the surrounding muscles of the forearm and hand. The nerve is most often damaged in the area of the ulnar groove : at the entrance and exit from the cubital canal.
In the ICD-10 classification, inflammation of the ulnar nerve is not classified as a separate niche. Therefore, such neuritis has code G56.2.
Causes
The most common cause of a neurological disorder is elbow injury . Neuritis of this etiology occurs in 28-34% of patients.
Prolonged bed rest with squeezing the arm between the body and the bed, puncture and cutting wounds, fractures and dislocations can lead to damage to the cubital canal.
In this case, there is a malnutrition and gradual destruction of the nerve fiber, accompanied by acute inflammation. In such a situation, the pathological process becomes chronic.
In some cases, neuritis manifests itself decades after the injury . This is due to the gradual progression of ligament fibrosis. Another name for the pathology is Miche's ulnar neuropathy.
Other causes of neuritis include:
- prolonged hypothermia;
- infectious lesions: diphtheria, typhoid fever, herpes virus, measles and brucellosis;
- vascular pathologies, ischemia in the elbow joint, in which the nerve stops receiving the required amount of oxygen and nutrients;
- alcohol poisoning, intoxication with heavy metal salts;
- epicondylitis, periarthrosis of the head of the humerus;
- diseases of the endocrine system: diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders;
- compression of nerve tissue during sleep, with a sudden change in hand position;
- cervical osteochondrosis, herniated intervertebral discs: lead to compression of the vessels supplying the ulnar nerve.
In children, ulnar nerve neuritis often appears in the absence of timely vaccination against measles and typhus . The cause of the disease can be hypovitaminosis, congenital pathologies of the cubital canal.
In the latter case, there is compression of the nerve in the ulnar groove by a fibrous arch stretched between the heads of the flexor carpi.
Development of the disease due to work characteristics
Neuritis, which occurs due to pinching of the ulnar nerve, develops in office workers, operators or people in industrial production. The costs of the profession force people to often rest their elbows on the table, armrests or machines.
The disease can occur with prolonged overexertion of the arms in patients whose activities involve heavy physical labor. Over time, mechanical stress leads to injury, which causes neuritis.
Arthrosis of the shoulder joint
Due to the encryption features, it is quite difficult to find a code for arthrosis of the shoulder joint using ICD 10, primarily because you need to compile it yourself.
In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, only three localizations are specified:
- hip joint (coxarthrosis);
- knee joint (gonarthrosis);
- first carpometacarpal joint.
The remaining types of lesions are included in the category of other arthrosis, which is encrypted as follows: M 19. After this, you should select the unspecified version of arthrosis under the code M19.9. Additional numbers that are written after the second nine can be found in the description of the disease class. It says that for the collarbone, scapula, shoulder and sternoclavicular joints the number 1 is added. The girdle of the upper extremities should not be confused with the arm itself, since the number 2 implies the presence of a lesion in the shoulder and elbow area and, having indicated it in the coding of shoulder arthrosis, the doctor will make a mistake.
It turns out that arthrosis according to ICD 10 has code M19.91, which hides a protocol for diagnosis and medical care for patients with this pathology.
By mixing up the code, the doctor can worsen the patient’s condition by prescribing the wrong treatment.
General information about the disease
Arthrosis is the abbreviated name for a disease such as osteoarthritis or deforming arthritis of the articular surfaces. The pathology is characterized by a chronic course and leads to the gradual destruction of articular cartilage with transition to bone tissue. As the disease progresses, it irreversibly deforms the joint, which is why timely diagnosis and treatment comes to the fore.
Arthrosis of the ankle, elbow, shoulder and other localizations is characterized by the same clinical picture. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
soreness (at first only during physical exertion, hypothermia or prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, and then becomes constant); stiffness (decreased range of motion in the joint apparatus, bothers you in the morning); crunching (almost the first sign of a pathological process is periodic clicks or crunches in the affected area, which people rarely pay attention to); pathological mobility (the more the pathology progresses, the less limited the articular surface is by physiological norms); deformation (the latest sign of pathology, avoiding which is the priority task of the attending physician).
Since the arthrosis code in ICD 10 is represented by a larger number of symbols than other pathologies, you should carefully approach the issue of therapeutic measures, choosing the right protocol.
During therapy, systemic medications are used to stop tissue destruction, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures. In advanced cases, radical surgery is performed, the indications for which are determined individually.
Save the link, or share useful information on social media. networks
Clinical picture: symptoms and manifestations
The intensity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the ulnar nerve and the individual characteristics of the patient. Peripheral nerve fibers consist of sensory, autonomic and motor neurons.
When each of them is damaged, the following clinical picture is observed:
- With neuritis, changes in tactile perception are observed in the area of the hand and fingers. Sensory neurons of the ulnar nerve do not innervate the skin of the forearm.
Numbness may develop, which is accompanied by a decrease or complete loss of sensitivity in the affected area.In some cases, paresthesia appears. When they occur, the patient feels tingling and frequent goosebumps.
- Impaired motor activity is accompanied by the appearance of paralysis or paresis.
The pathological process can cover the area from the elbow joint to the fingertips. There is muscle weakness in the skeletal muscles innervated by the ulnar nerve. If left untreated, atrophy and loss of tendon reflexes may develop. Due to lack of physical activity, the muscles decrease in size, so the affected forearm appears thinner when compared to the healthy arm. - Autonomic disorders are accompanied by trophic changes. The limb swells, blueness of the skin and depigmentation are observed. Hair falls out on the arm and sweating increases. Nails often break and trophic ulcers appear.
- When the ulnar nerve is pinched in the musculoskeletal canal, tunnel syndrome occurs.
The pathology is accompanied by pain . As the disease progresses, it leads to numbness of half the ring finger and little finger on the palmar side.
On the back of the hand, there is a loss of sensitivity in half of the middle finger and a complete loss of tactile perception in the ring and little fingers.
Numbness of the fingers is accompanied by muscle weakness, muscle wasting and atrophy. The brush resembles a bird's paw .
Possible patient complaints
Patients come with complaints of periodic numbness of the arm in areas innervated by the ulnar nerve. Loss of sensitivity is observed in the IV, V, half of the third finger on the back of the hand, the skin on the palms .
Numbness can be complete or partial depending on the severity of the pathological process. People report that after sensation is restored, there is tingling, burning, or cramping in the affected area.
Pain appears on the outside of the elbow joint . The pain syndrome often radiates to the thumb, ring finger, and little finger. The pain may spread to the shoulder area, the first third of the forearm.
Due to muscle weakness, patients cannot clench their hand into a fist. They often lose the ability to coordinate the movements of the affected arm. In severe cases of the pathological process, paralysis is observed .
How other types of neuritis of the extremities manifest themselves:
- brachial and median nerves;
- sciatic nerve;
- femoral, tibial and fibular.
List of degenerative diseases of this joint
Arthritis is a pathological condition manifested by inflammation and deformation of bone structures. If a patient is diagnosed with this pathology in the elbow joint, then according to the international classification of diseases, a code indicating unspecified arthritis is placed on the patient’s medical record. By looking at the code, the doctor will immediately understand what is wrong with the person who contacts him.
There is no misunderstanding between the patient and the medical staff, since the code on the card provides understanding regarding the person’s visit to a medical facility. A note in the patient's document - arthritis ICD 10 - will give doctors an idea of what they are faced with. Elbow pathology belongs to inflammatory polyarthropathies. According to the ICD, 10 arthritis codes range from M00 to M99. There are many types of degenerative pathologies. At first glance, by comparing the clinical pictures of patients, they can be classified into the same class, but radiological signs may indicate completely different nosologies. Codes by which doctors determine the type of disease localized in the elbow joint:
- other seropositive rheumatoid arthritis - M05.82;
- seronegative rheumatoid arthritis - M06.02;
- juvenile rheumatoid arthritis - M08.02;
- juvenile with systemic onset - M08.22, M08.23;
- youth unspecified - M08.93;
- unspecified - M13.92.
This is not the entire list of codes for degenerative pathology localized in the elbow joint. This classification is used all over the world. It is convenient for maintaining electronic documentation.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis and determination of further treatment regimen is carried out by a neurologist. The specialist collects anamnesis and records the patient’s main complaints in the medical history. After this, the neurologist conducts a visual examination.
With ulnar nerve neuritis, the hand takes on the appearance of a bird's paw: the third and fourth fingers are bent, the little finger is moved to the side. The doctor notes cyanosis, hair loss, brittle nails, and weight loss in the affected limb.
After the examination, the neurologist conducts a series of neurological tests to determine muscle strength, degree of numbness and loss of reflexes and makes a preliminary diagnosis.
To confirm the initial conclusion, the specialist prescribes laboratory and instrumental examinations , which allow us to find out the cause of neuritis:
- General and biochemical blood test . Necessary for identifying pathogenic agents of infectious diseases, the presence of produced antibodies and leukocytes.
- X-ray using contrast .
Allows you to assess the condition of the vessels supplying the ulnar nerve. X-rays also make it possible to take into account the anatomical features of the elbow joint and cubital canal, and to identify the degree of damage to the musculoskeletal tunnel in the event of injury. - Ultrasound and MRI . Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging help assess the condition of blood vessels, soft tissues and bone structure in case of fractures, pinched nerves and other injuries.
- Electroneuromyography . The procedure helps determine the extent of damage to the skeletal muscles.
Special diagnostic criteria for determining the disease
Neurological tests to make a preliminary diagnosis of ulnar neuritis often include the following:
- Pitre's test. To carry it out, the patient must place his palm on the table and try to spread and close his fingers. With neuritis, the patient cannot bring the ring finger and little finger to the midline.
- Afterwards, the doctor asks the patient to try to scratch the surface of the table with his little finger. Due to inflammation of the nervous tissue, he is unable to do this.
- With neuritis, the patient cannot clench his hand into a fist, or hold a sheet of paper with two fingers. When you clench your hand into a fist, the middle, ring and little fingers do not bend.
- If the patient presses the hand firmly to the table, the little finger moves to the side. In this position, the patient cannot make horizontal movements of the third, fourth, fifth finger.
What diseases should be distinguished from?
After recording the patient's complaints in the medical history, differential diagnosis with radial nerve neuritis is carried out . In contrast to damage to the ulnar nerve, in this situation the hand hangs down and a strong muscle spasm is observed.
If the radial nerve is damaged, the patient cannot straighten the hand independently; the thumb is reduced to the index finger. The sensitivity of the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd fingers of the affected limb is impaired.
It is difficult to distinguish ulnar nerve neuritis from damage to the C8 nerve root in the neck due to radiculopathy . With radicular syndrome, numbness is observed on the ulnar surface of the forearm, which is not typical for neuritis. With inflammation of the ulnar nerve, only numbness of the hand is observed.
When conducting a differential diagnosis, the neurologist pays attention to the presence of a specific symptom of ulnar nerve neuritis - numbness of the radial surface of the ring finger.
When the nerve roots of the spine, spinal cord, or plexus are affected, there is a loss of sensation in the entire finger.
When is surgery necessary?
In case of nerve injury, it is very important to decide in a timely manner whether conservative or surgical treatment is advisable. The answer to this question can be obtained after conducting needle myography, which will answer the question of what is the degree of damage to the nerve and whether it has a tendency to recover. If during this study it turns out that at least partially the nerve is preserved, we carry out active conservative treatment, after which we must repeat the study to make sure that the treatment had an effect . If, during needle myography, it turns out that the nerve is completely damaged and its restoration is impossible, we resort to the help of a neurosurgeon who suturing the nerve or releasing it from significantly narrowed canals. Then we perform the entire range of restoration procedures.
Features of treatment
Treatment begins with fixation of the hand and forearm in a plaster splint , thanks to which the elbow joint remains at rest.
The hand is in a half-bent state. The patient should suspend the limb using a scarf or bandage.
When developing a treatment regimen, the neurologist focuses on eliminating the cause of the neurological disorder. For this purpose , drug therapy is carried out, physical therapy and massage are prescribed .
In case of infection, after identifying a pathogenic pathogen, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs or antibiotics. If blood circulation is impaired, the patient is prescribed a vasodilator to restore trophism of the nervous tissue. It allows you to eliminate the consequences of ischemia.
To eliminate swelling of the ulnar nerve, the patient should take potassium-sparing diuretics and NSAIDs.
For pain relief in high intensity pain syndrome, the use of analgesics is indicated. B vitamins help speed up the recovery of nervous tissue.
After 2 weeks from the start of drug therapy, complex treatment is supplemented with physiotherapy:
- ultraphonophoresis;
- electrophoresis with the introduction of analgesics and biogenic stimulants;
- UHF therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrical stimulation for muscle tissue damage;
- acupuncture.
Massage technique
Massage helps relieve pain, accelerate nerve fiber regeneration , and restore original sensitivity and motor activity. The patient must undergo a course of 15-20 procedures.
Massaging begins with the cervical and thoracic spine. This is necessary to ensure blood flow to the affected limb.
Afterwards, a preliminary massage of the sore arm is carried out using the following techniques:
- tong-like rubbing;
- kneading stiff muscles;
- stroking.
After this, the specialist massages the skeletal muscles innervated by the ulnar nerve . To do this, he uses muscle kneading, vibration, rubbing with his fingers, and pressing with the pad of his thumb. The total duration of the procedure is about 10-15 minutes.
Massaging the ulnar nerve is carried out in the area between the process of the ulna and the medial epicondyle of the head of the humerus. To gain access to the lesion, the arm is slightly bent at the elbow.
Exercise therapy
Physical activity is introduced into the treatment program 48 hours after the splint is applied . Physical therapy consists of the following exercises:
- It is necessary to bend your arm at the elbow and lean on the table so that your forearm is perpendicular to its surface. After this, you need to bend your index finger down, then raise your thumb up. Movements should be alternated.
- The arm bent at the elbow joint should be placed on the table top. Then you need to bend the second finger down, lift the third up. With the other hand, you should alternately bend and straighten the remaining fingers in the middle and main phalanx.
Exercises are repeated at least 10-15 times . To increase the effectiveness of therapeutic exercises, it is recommended to lower the sore hand into a basin of warm water.
Therapy for post-traumatic joint inflammation
Treatment of neuritis resulting from injury is carried out depending on the nature of the injury. Penetrating wounds are sutured and treated with medications and physical procedures .
If neuritis appears due to compression in the cubital canal with the subsequent occurrence of tunnel syndrome, the patient is prescribed local administration of drugs.
Painkillers and hormonal medications necessary to relieve pain, soft tissue swelling and reduce the activity of the inflammatory process are injected into the musculoskeletal canal .
In case of severe compression of the nerve, which usually occurs with fractures and dislocations, surgery is prescribed. Surgery is performed for the purpose of decompression .
Patients with destructive changes in the ulnar nerve resulting from prolonged inflammation may be referred for surgery. In such a situation, the damaged nerve fiber is sutured and repaired.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment, a favorable prognosis for recovery is observed.
With mild to moderate severity of the pathology, sensitivity and motor activity are restored within 8-10 weeks. Rehabilitation against the background of severe pathology takes a longer time.
To prevent the development of neuritis, it is recommended to resort to the following preventive measures:
- promptly treat infectious and viral diseases;
- keep the body warm, prevent hypothermia;
- balance the diet;
- avoid increased physical stress on your hands;
- to refuse from bad habits.
People who are indicated for long periods of bed rest are advised to take a comfortable position . Paralyzed or comatose patients need to change body position every 2 hours and massage the elbow joint area.
Ulnar nerve neuritis is accompanied by inflammation of the nerve tissue, which impairs sensitivity and motor activity of the hand.
The disease is easy to diagnose by the external manifestations of the pathological process : the hand bends like a bird's paw, the patient feels tingling, numbness and muscle weakness.
To treat the disease, complex therapy is carried out with drugs, exercise therapy, massage and physiotherapy. Rehabilitation with timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment is possible within 2 months.
Basic principles of therapy
In case of acute polyneuropathy, patients are hospitalized in a neurology clinic, where the necessary conditions for their treatment have been created. For subacute and chronic forms, long-term outpatient treatment is carried out. Prescribe drugs to treat the underlying disease, eliminate the causative factor in case of intoxication and drug-induced polyneuropathies. In case of demyelination and axonopathy, preference is given to vitamin therapy, antioxidants and vasoactive drugs.
Rehabilitation specialists provide hardware and non-hardware physiotherapy using modern techniques. Patients are advised to avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, heavy physical activity, and contact with chemical and industrial poisons. If you have signs of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, you can consult a neurologist by making an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.