Causes
Why does my head hurt? Common causes of headaches are:
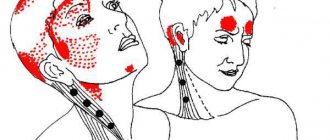
- neck muscle spasm;
- compression of the vessels of the head and neck;
- compression of the membranes of the brain;
- brain nutritional disorders: insufficient blood supply, narrowing of blood vessels supplying the brain;
- smoking, poisoning with alcohol, drugs, medications;
- stress, sleep disturbance;
- due to neck and head injuries;
- birth injuries;
- anomalies in the development of blood vessels in the neck and head.
What pills are best to take if you rarely get headaches?
Any painkillers
will one way or another have pathological consequences. The active ingredient diclofenac affects the stomach, meloxicam - the liver, ibuprofen - the cardiovascular system. Everything has a side effect, but if you take anti-inflammatory pills rarely, nothing bad will happen.
combination drugs :
they include not only the anti-inflammatory substance itself, but also caffeine, phenylephrine, antispasmodics... Such drugs work more complexly and it is better not to use them without the supervision of a doctor. Otherwise, situations arise when a patient without migraine takes pills for migraine, receiving a side effect from them.
Uncontrolled reception
drugs can lead to abusive headaches.
They occur when you take excessive amounts of anti-inflammatory pills. Let’s say you take pills every day according to the scheme “I have a headache - I took a pill - the pain went away - the next day it hurts again - I took a pill”... As a result, your head starts to hurt simply because you need to take an anti-inflammatory drug again. This situation requires treatment
with a specialist.
Primary headaches
| Name | Symptoms |
| Migraine | Throbbing pain in the head, most often occurring after sleep. The severity of the headache ranges from moderate to unbearable. The pain is felt on one side of the head: in the right or left temple, forehead, crown. Migraine lasts up to three days, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. A person does not tolerate bright light and loud sounds. Migraines can be caused by stress, insomnia, or changes in weather. The tendency to migraine is inherited. |
| Tension headache (TTH) | A pressing headache covers the entire head or separately the back of the head, crown, forehead. Cephalgia can be severe. A tension headache attack can last up to 7 days. At the same time, my head hurts every day. TTH occurs due to emotional or physical stress. |
| Cluster headache | Unbearably strong shooting pain in the head. It is felt on one side, in the forehead and eye area. Cluster pain causes redness and swelling of the face and lacrimation on the pain side. Due to a severe headache, a person behaves restlessly. |
| Headache and facial pain due to trigeminal neuralgia | Very strong short-term stabbing pain in the head. The pain is felt in the crown, forehead, and can affect the face and teeth. The headache attack lasts several hours. In this case, spasm of the facial muscles may occur. |
Why does my head hurt every day?
Headaches that appear from time to time are not as bad as daily, exhausting and monotonous ones. Yes, this also happens quite often. Painkillers only temporarily suppress the headache, which returns after a while. What diseases cause daily headaches?
Chronic tension headache
Chronic tension headache is a form of the disease in which the headache occurs 15 or more days per month and for more than 3 months in a row. Initially, tension headaches manifest themselves as episodic, moderately expressed pressing, tightening pain in the forehead and temples on both sides or throughout the head. They arise as a result of stress and overwork and decrease with rest and after physical activity.
If tension headaches occur more than 1-2 times a week, then a course of treatment is required, which is selected by the doctor individually. Patients rarely go to the doctor for headaches and prefer to take painkillers on their own, which only relieve symptoms without affecting the cause of the disease. This leads to the transition of episodic headaches to chronic ones, and also creates a risk of drug-induced headaches.
Chronic migraine
The most common cause of severe headaches that impair performance and well-being is chronic migraine.
With CM, headaches become almost daily (more than 15 days a month), which leads to even more severe maladaptation of patients. They manifest as throbbing pain in the frontotemporal region, accompanied by nausea, intolerance to bright light and loud sounds. If treated incorrectly, migraine pain loses its characteristic features, becomes constant, dull, and less intense. Against the background of a constant dull headache, classic migraine attacks periodically occur with throbbing pain, nausea, and vomiting.
International recommendations have been developed for the treatment of chronic migraine, but this is a very complex and slow process. All over the world, chronic migraine is treated by headache specialists; an ordinary neurologist is often unable to do this task.
The presence of chronic migraine requires long-term preventive treatment for at least 6-12 months. For this, various pharmacological agents are used: antidepressants, anticonvulsants, beta blockers - drugs whose effectiveness has been verified. These drugs restore normal pain perception in the central nervous system. And please note: among the listed medications there are no vascular or nootropic drugs.
A trending method in the treatment of chronic migraine is the use of botulinum toxin type A.
Drug-induced headache
When systematically taking painkillers for headaches, including anti-migraine drugs, for example, sumamigren, amigrenin, imigran, drug-induced headaches may occur. The pain can be of a different nature, but more often it is pressing, squeezing, of low or moderate intensity. In addition to them, patients complain of feeling weak, light-headed, and decreased ability to concentrate.
The main criterion for making a diagnosis for drug-induced headache is the fact of abuse of analgesics for three or more months, 10-15 or more times a month. Treatment of this disease is difficult. It requires, first of all, a drug and the prescription of preventive treatment.
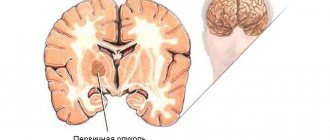
Headache associated with increased intracranial pressure
An increase in intracranial pressure can be observed with the appearance of any tumors of the brain, its membranes or blood vessels, after an injury as a result of a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), as well as due to unclear reasons, then this condition is called idiopathic (benign) intracranial hypertension.
An increase in intracranial pressure leads to the appearance of daily or almost daily headaches, dull, pressing or bursting, which are felt more strongly in the morning and at night, aggravated by coughing and tilting the head. They are relieved in an upright position and become stronger in a lying position. Headaches are accompanied by blurred vision and double vision. In such cases, it is imperative to find out the cause in order to develop the correct treatment tactics.
Headache associated with decreased cerebrospinal fluid pressure
In addition to increased intracranial pressure, the opposite situation may also occur, associated with a decrease in cerebrospinal fluid pressure in the brain. Headaches in this condition are daily, dull, and the person’s whole head hurts. They are strengthened in an upright position and weakened in a lying position. Accompanied by a feeling of lightheadedness, nausea, noise in the head, intolerance to bright light.
This condition may be associated with a defect in the meninges, delayed formation of cerebrospinal fluid, and some congenital characteristics. If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor and conduct a full examination, since further treatment depends on its results.
In case of daily headaches, self-medication is not acceptable. An examination by a neurologist specializing in the treatment of headaches or a cephalgologist is required. In Saratov, such a consultation can be obtained at the Pain Treatment Clinic, located at st. Bakhmetyevskaya 26/28. To make an appointment with a doctor, call: +7.
Secondary
Secondary headaches can be a sign of other diseases. Most often it is caused by the following diseases:
| Cause of headache | Manifestations of the disease |
| Cervical osteochondrosis | Headache appears with a sharp turn of the head, prolonged neck tension, or an uncomfortable position of the head during sleep. The pain intensifies in the morning, often spreading to one side of the head. May be accompanied by hearing loss in one ear, tinnitus, and spots before the eyes. |
| Flu or cold | The headache is not very severe, localized in the forehead, eyes, temples on one or both sides. In addition to the headache, the patient’s temperature rises above 37 degrees, a runny nose, cough, sore throat and other cold symptoms appear. |
| Increased intracranial pressure | Prolonged frequent headaches are combined with nausea and vomiting. A person often feels sick in the morning. If these symptoms and mild headaches occur, you should consult a doctor. |
| Brain concussion | The headache may last for several years after the injury. Accompanied by anxiety, irritability, decreased concentration, and dizziness. The person may suffer from depression. |
| Vegetovascular dystonia | Causes dizziness, nausea, neurotic disorders, and surges in blood pressure. Exacerbations occur with weather changes and emotional overload. |
| Hypertonic disease | A bursting headache is felt in the back of the head. Combined with heat in the head, dizziness, noise in the head, spots before the eyes, staggering. A person may feel nausea and heart pain. |
| Sinusitis, sinusitis, sinusitis | Chronic long-term pressing headaches in the forehead, eyes, cheeks. Accompanied by nasal congestion, runny nose, and slight fever. |
| Horton's headache | Characterized by attacks of severe boring pain. It spreads around the eye, temple and forehead. The attacks usually occur at the same time. This type of headache is more common in men. |
| Hypertonic disease | A bursting headache is felt in the back of the head. Combined with heat in the head, dizziness, noise in the head, spots before the eyes, staggering. A person may feel nausea and heart pain. |
Prevention methods
Most cases of spontaneous headaches can be prevented at home. Doctors have a list of recommendations that will help strengthen and heal blood vessels, improve blood circulation, and stimulate metabolic processes. To do this you need:
- follow a diet that includes sufficient amounts of nutrients, vitamins and microelements;
- carry out moderate physical activity, including in the fresh air;
- normalize work, sleep and wakefulness;
- give up bad habits, smoking and drinking alcohol;
- regularly measure blood pressure, especially if you are overweight and elderly;
- undergo an examination if you experience frequent snoring and determine its causes.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can consult with general and specialist doctors with many years of experience. They will help not only get rid of night headaches, but also find their cause and prevent further development of the disease. However, timely prevention is important at any age to maintain health and prevent most chronic diseases.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 3 votes
Share article on social networks
When you can't put off visiting a doctor
- For an acute headache that suddenly arose and resembles “a blow to the head.” This may be a symptom of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Call an ambulance immediately.
- The pain intensifies when lying down and goes away half an hour after getting out of bed. This is a sign of impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, increased intracranial pressure, and a tumor.
- If the headache appears regularly, is intense, is associated with changes in body position and changes with movement.
Factors associated with internal pathologies
Pain is not a separate disease, but the first sign of the development of any disorders occurring in the body. If the abnormal condition manifests itself sporadically, and a lot of time passes between attacks, it is not advisable to worry about the presence of a complex disease. If discomfort occurs systematically and is complemented by other pathological signs, it is necessary to find out why the head hurts after sleep and what is the primary source of this condition.
Frequent factors causing discomfort and heaviness in the cranium are:
- spasms of the muscles located in the upper shoulder girdle or neck;
- atherosclerotic disorders, increased internal pressure, stroke;
- head injury as a result of mechanical impact or surgery;
- thrombosis of vascular pathways, resulting in a decrease in the intensity of blood supply and nutrition to brain tissue;
- general intoxication with chemical or biological toxic elements;
- tumor formations in the cranium or cervical region.
Pathologically growing objects in brain tissue are capable of compressing parts of the organ, pinching vascular channels and nerves, which leads to pain.
Diagnostics
If you experience frequent headaches, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Diagnostics includes the following activities:
- Examination and interview of the patient. The doctor determines the intensity, nature of cephalalgia, and provoking factors. The patient is asked to keep a self-monitoring diary, where he writes down all his sensations. Based on these records, the dependence of attacks on blood pressure, sugar levels, and time of day is monitored. Intensification of headaches in the evenings, after physical activity or stress allows us to make a preliminary diagnosis.
- Laboratory research. There are no pathognomonic changes in the analyses. The examination is carried out to identify inflammatory changes.
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and brain. Allows you to determine the degree of narrowing of the arteries and the nature of the cerebral blood supply.
- X-ray, MRI of the cervical spine. This is done to detect intervertebral hernias or vertebral deformities.
- REG, EEG. This is a recording of the electrical activity of neurons and blood flow in the vascular system of the brain.
- CT or MRI of the brain. Such a study is necessary to identify organic pathology.
If necessary, perform a lumbar puncture (for meningitis), glucometry (for diabetes mellitus), and blood pressure measurement (for hypertension).
Treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the cause of cephalalgia. The course of treatment for osteochondrosis includes muscle relaxants, NSAIDs, B vitamins, and physiotherapy. To achieve maximum effect, it is necessary to take the prescribed medications in the morning and evening, after meals.
To treat hypotension, restoratives and multivitamins are used. With low blood pressure, the patient should drink tonics or biologically active substances.
For hypertension, hypotonic, vascular, metabolic drugs, and antiplatelet drugs are prescribed. Depending on the blood pressure numbers, it is recommended to take medications in the evening or in the morning, after sleep.
Meningitis is treated in a hospital setting. The patient receives antibiotics, detoxification, anti-inflammatory drugs.
Diabetes mellitus requires regular monitoring by an endocrinologist. Normalizing blood glucose leads to a reduction in headaches.
Cluster cephalgia is treated symptomatically. Prescribe non-narcotic analgesics during the day, and sedative tinctures in the evening.
To treat migraines, a new generation of drugs is used - triptans.