Quite a significant number of people from time to time face such a problem as a feeling of pressure in the ears. According to some sources, at least 20-30% of the world's population has experienced this sensation at least once for no apparent reason. Anyone can experience this pain syndrome - the likelihood of its occurrence practically does not depend on age or gender, nor on social status or financial condition.
If we do not take into account the natural cases of the occurrence of this pressure - when flying on an airplane, diving to great depths, sudden rises to altitude, and so on, then the occurrence of this symptom is a sign of a person’s existing health problems. It is worth noting that the occurrence of pressure in the ear does not mean at all that the problem is associated with this organ - simply all the systems of our body are interconnected and the symptom of the disease can manifest itself in this way.
Isolated cases of feeling pressure in the ears may not be a sign of pathology, but they should not be completely ignored either. If you experience these sensations regularly, and are also accompanied by other alarming symptoms (head pain, nosebleeds, dizziness, nausea, weakness, etc.), then delaying a visit to the doctor is simply unacceptable. A combination of several symptoms or multiple repetitions of one - these cases undoubtedly require examination and an accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms
When visiting a doctor about pressure in the ears, some patients mention other symptoms accompanying this sensation:
- dizziness;
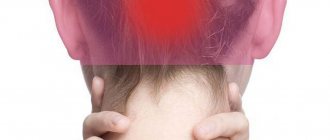
- ear congestion;
- associated pressure in the head;
- various noises of varying degrees of volume (ringing, clicking, hum, etc.);
- acoasmas (auditory non-speech hallucinations);
- nausea and headaches;
- increased sensitivity to sounds or light.
The presence of these additional symptoms gives the doctor reason to suspect a serious illness and suggest that the patient undergo a comprehensive examination. An otolaryngologist can also offer consultations with other specialists, since the alleged ailments may not be within his competence.
Non-pathological causes of distension
Both illnesses and features of a person’s life can cause feelings of fullness in the head. Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to control them all.
- Constant stress. Residents of megacities are more susceptible to them, even during simple work that does not involve emotional and mental stress. Stress can be triggered by intense experiences, shocks and tragedies.
- Junk food and drinks. Fatty dishes, spicy, salty combined with alcohol, and even flavored with smoking. All this has an extremely negative effect on blood vessels. Improper nutrition provokes atherosclerosis, which can lead to strokes and heart attacks.
- Abrupt climate change. Weather dependence can cause severe discomfort. Such sensations can only be controlled by taking special medications.
- Use of medications. Various dietary supplements can cause discomfort. Some medications, such as antidepressants, sleeping pills, anticonvulsants and painkillers, also have similar side effects.
- Lack of sleep and rest. If a person constantly sleeps for 4-6 hours, sooner or later he will encounter unpleasant neurological disorders. They can also be provoked by incorrectly selected accessories - mattress, pillow.
- Fasting and dangerous diets. Many women follow aggressive nutrition programs, causing enormous harm to the body. It is not recommended to do this without medical supervision.
- Overexertion and heavy physical labor. Intense sports and exercise for the purpose of losing weight can affect the condition of blood vessels and the nervous system. It is not recommended to lose more than 1 kg per week.
If the symptoms accompanying the feeling of fullness in the head occur regardless of adjustments in diet and rest regimen, the person will need a comprehensive diagnosis. After all, the reason may be hidden in pathological disorders.
Causes
Pressure in the ears occurs due to a number of factors and ailments. These may include serious illnesses and completely harmless ones, for example, prolonged listening to music at high volumes in headphones. The most common causes of pressure in the ears are:
- otosclerosis (bone growth) and inflammation in the middle ear;
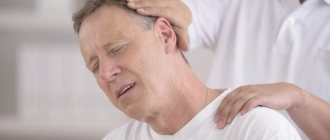
- pathologies of a neurological nature (cervical osteochondrosis, pinched vertebrae)
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels in the brain;
- high/low blood pressure of various etiologies (obesity, alcohol and tobacco abuse, depression, stress, heart problems, physical exercise, vascular disorders, etc.);
- injuries of the skull, head;
- tumor (acoustic neuroma) of the auditory nerve;
- otitis, sinusitis, rhinitis, earwax, aerootitis;
- everyday (natural) reasons - long telephone conversations, sleep disturbances, prolonged listening to music, overwork, sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, water getting into the ears, flying on an airplane, diving, etc.
Patient examination methods
If you have a constant headache, you need to do an MRI.
To identify the reasons why your head seems to be bursting from the inside, you need to turn to instrumental techniques:
- do a CT scan to detect cysts, tumors and changes in the brain;
- perform an ultrasound to analyze blood vessels;
- undergo an MRI if circulatory pathologies and tumors are suspected;
- take an x-ray if there are changes in cartilage and bones;
- sign up for electromyography to study the state of neurons and the muscular system.
Patients are also prescribed blood and urine tests. They are necessary to assess inflammatory reactions and hormone levels.
After diagnosis, the doctor evaluates the results. Based on them, an accurate diagnosis can be made for further therapy.
Treatment
Obviously, treatment for ear pressure can only begin after a diagnosis has been made. Until the cause is identified, the otolaryngologist is unlikely to be able to prescribe medications or take any other action. In addition, if the cause of the disease is beyond his competence, then it will not be possible to do without the help of an appropriate specialist (therapist, surgeon, neurologist, etc.).
The reception is conducted by specialists
Kirillov Evgeniy Sergeevich
Audiologist
Cost of services
Initial consultation with an audiologist
1200₽
Repeated consultation with an audiologist
1000₽
Treatment methods
Herbal compresses will alleviate the condition.
To treat a bursting feeling in the head, it is important to establish the cause of the disorder. Next, treatment tactics are prescribed. General recommendations to reduce pain are required:
- You should not take medications without a doctor’s examination;
- You can relieve tension by taking a comfortable position and relaxing;
- a towel soaked in cool water will help with feeling unwell;
- you should open a window or window so that it is not stuffy;
- if there is no nausea, you can drink warm tea.
When it becomes easier, you should not immediately start heavy work or exercise.
Folk recipes
During treatment, you can use decoctions of chamomile, mint, and St. John's wort, but only after discussion with your doctor. You also take 40 drops of propolis tincture and add honey to your drinks. Cosmetic clay compresses applied to the forehead before bed will also help combat discomfort.
Medicines
Prescription of medications depends on the cause of the condition. Sometimes taking an NSAID is enough to relieve pain. But in most cases an integrated approach is required. They use medications to improve blood circulation, take analgesics and vitamins in courses.
When using medications, it is important to follow the instructions and not ignore contraindications.
Diagnostic methods
If the patient often suffers from headaches and stuffy ears, it is necessary to contact us for a full examination. A simple examination will only indicate visible deviations from the norm, therefore, to understand a more accurate picture, additional techniques are prescribed:
- tonometry – blood pressure measurement;
- MRI of the head and cervical spine is one of the most informative diagnostic methods, which will indicate hidden disorders and neoplasms;
- blood tests - prescribed to determine the causative agent of bacterial diseases, as well as to assess hormonal balance;
- additional methods for diagnosing diseases of the hearing organ, including audoscopy, smear tests, and ultrasound examination.
The Clinical Brain Institute has modern equipment for diagnosing diseases that are accompanied by headaches and ear congestion. Here you can quickly and accurately determine the underlying disease that causes deterioration in well-being.
Some statistics
Headache is the most common nonspecific symptom worldwide. Almost every person on earth has at least once experienced a feeling associated with a headache, and on an ongoing basis this symptom occurs in more than 60% of the world's population, which makes the introduction of the latest laboratory diagnostic and therapeutic measures an urgent problem in modern healthcare in the largest countries of the world.
Most people simply complain of headaches and do not realize that in 75-80% of cases they suffer from tension-type headaches - the main type of cephalgia in neurological practice.
Treatment of headaches and ear congestion
Treatment tactics are selected individually, depending on the cause of the headache and ear congestion, as well as the patient’s age, concomitant diseases and other factors. To eliminate both the root cause and symptoms of diseases, the following methods can be proposed:
- antibiotic therapy is the main stage in the treatment of bacterial inflammatory processes, as well as the prevention of purulent complications;
- symptomatic treatment , which includes anti-inflammatory, painkillers, ear drops;
- surgical methods - necessary to remove sulfur plugs, neoplasms, as well as to extract the contents of the paranasal sinuses for sinusitis;
- physiotherapy – prescribed for chronic ENT diseases.
Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain prescribe a minimum of therapeutic techniques that will bring maximum results. Here are specialists of a wide and narrow profile with many years of experience in treating various diseases that manifest themselves as headaches and hearing impairment.
Clinical picture
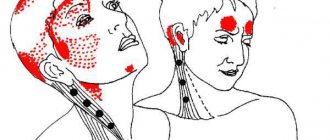
Tension headaches have the following characteristic symptoms:
- Painful sensations of a diffuse nature.
- Pain can come from the parietal part of the head, forehead, temples, but the entire head is necessarily included in the pain process.
- Patients describe the nature of the sensation as squeezing, pressing or twisting.
- The intensity of pain can vary from mild to moderate intensity. With tension headaches, the pain is never too intense or severe.
- The duration of pain can vary significantly, from a few minutes to several days.
It is important to note that a small proportion of people with tension headaches may experience additional symptoms, such as photophobia.
The symptom of head compression in neurological practice is sometimes called the “neurotic helmet”, since many patients complain of a feeling of head compression in all areas. In most patients, tension-type headaches are symmetrical, but asymmetrical headaches may also occur.
Two thirds of patients experience episodic headaches, i.e. they occur only with any functional impairment, but approximately 30% of patients are diagnosed with chronic tension-type headache. The main criterion is the frequency of occurrence of attacks; to establish a chronic form, headaches must occur at least 15 episodes of headaches within a month and over a period of three months.
The Clinical Institute of the Brain is actively studying the processes of formation and manifestation of tension headaches, which makes it possible to introduce new original, and most importantly, effective treatment regimens into medical practice.
Development mechanism
The above causal factors trigger overexcitation in the median subcortical structures of the brain. The tone of the muscles of the neck and head increases. The pain sensitivity threshold decreases.
How to help
Tension headaches occur sporadically and do not require special treatment for a short time. In this case, it is enough to take a break from work, switch your attention, and give minimal physical activity (10 squats or push-ups).
Such pain should be treated as a signal of increased stress on the nervous system and psyche.
If the pain lasts more than 10-15 minutes, causes discomfort, distracts and interferes with current activities, you should do what is listed in the previous paragraph, take a shower or go out into the fresh air and walk (or jog) until you feel tired.
Drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help: acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, diclofenac. This is first aid. Next, you should consult a neurologist or psychotherapist.
Treatment for noise in the head
The doctor decides how to treat noise in the head after the examination results are ready. The therapeutic regimen to reduce painful symptoms is developed based on the cause.
Noise can be treated using the following treatment methods:
- Drug therapy. Medicines are prescribed by a doctor. These can be antibiotics, medications for hypertension, drugs that dilate blood vessels in the brain, medications that thin the blood, lower cholesterol, nootropics and others.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. Eliminates the consequences of otitis, labyrinthitis, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Laser therapy, electrophonophoresis, magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation, UHF, acupuncture, and massage are effective.
- Physiotherapy. A set of physical exercises is made up for diseases of the blood vessels and the spinal column.
- Operation. If the tinnitus is caused by a tumor, then its removal is required.
Neurologists at the SmartMed clinic are proficient in all modern methods of treating noise in the head and prescribe the newest and most effective medications.
Secondary
Secondary headaches can be a sign of other diseases. Most often it is caused by the following diseases:
| Cause of headache | Manifestations of the disease |
| Cervical osteochondrosis | Headache appears with a sharp turn of the head, prolonged neck tension, or an uncomfortable position of the head during sleep. The pain intensifies in the morning, often spreading to one side of the head. May be accompanied by hearing loss in one ear, tinnitus, and spots before the eyes. |
| Flu or cold | The headache is not very severe, localized in the forehead, eyes, temples on one or both sides. In addition to the headache, the patient’s temperature rises above 37 degrees, a runny nose, cough, sore throat and other cold symptoms appear. |
| Increased intracranial pressure | Prolonged frequent headaches are combined with nausea and vomiting. A person often feels sick in the morning. If these symptoms and mild headaches occur, you should consult a doctor. |
| Brain concussion | The headache may last for several years after the injury. Accompanied by anxiety, irritability, decreased concentration, and dizziness. The person may suffer from depression. |
| Vegetovascular dystonia | Causes dizziness, nausea, neurotic disorders, and surges in blood pressure. Exacerbations occur with weather changes and emotional overload. |
| Hypertonic disease | A bursting headache is felt in the back of the head. Combined with heat in the head, dizziness, noise in the head, spots before the eyes, staggering. A person may feel nausea and heart pain. |
| Sinusitis, sinusitis, sinusitis | Chronic long-term pressing headaches in the forehead, eyes, cheeks. Accompanied by nasal congestion, runny nose, and slight fever. |
| Horton's headache | Characterized by attacks of severe boring pain. It spreads around the eye, temple and forehead. The attacks usually occur at the same time. This type of headache is more common in men. |
| Hypertonic disease | A bursting headache is felt in the back of the head. Combined with heat in the head, dizziness, noise in the head, spots before the eyes, staggering. A person may feel nausea and heart pain. |
Causes of vascular headache development
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is an outdated name for autonomic dysfunction of the cardiovascular system. VSD is characterized by more than 150 symptoms, the most common of which is vascular headache.
The causes of headaches are:
- decreased tone of the blood vessels supplying the brain, which causes hypoxia (usually occurs with a systematic increase in pressure, which stretches the walls of blood vessels),
- pressure on nerve bundles specifically at the moment of a pressure surge (expansion of the walls of blood vessels),
- venous congestion and cerebral edema,
- arterial spasm.
Preventive actions
Physical activity and a healthy diet are the main protectors of the body.
To prevent unwanted symptoms and diseases associated with them, it is necessary:
- sleep and work in a ventilated area;
- regularly walk in parks, visit the forest if possible;
- engage in physical exercise without excessive stress, but do not give up sports completely;
- attend professional head and neck massage courses, as well as master self-massage techniques;
- sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- take natural sedatives if you are prone to anxiety and stress;
- stop smoking and frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages, normalize your diet.
Preventive measures must be taken constantly, not only when unwanted symptoms appear. It is recommended to take vitamin courses every year and monitor your blood pressure levels.