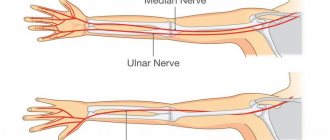
The radial nerve is a structure of mixed fibers. It starts from the cervical plexus and goes towards the hand.
Responsible for the innervation of the arm, flexion movements of the hand and skin sensitivity.
If it is damaged and left untreated, a person is deprived of the ability to act with this limb, to make subtle movements with the hand and fingers. This leads to disability.
The article discusses what radial neuritis is, how it manifests itself, and how it is treated.
What is it and the ICD-10 code
Radial neuritis is an inflammatory pathology that affects the nerve fiber itself and its sheath. Its ICD-10 code is (G56.3) .
Nerve damage is often caused by pinching. This is accompanied by pain, loss of motor function of the arm in the forearm, shoulder and hand with decreased skin sensitivity.
The arm stops bending at the wrist and elbow joints . Its frequent development is facilitated by the anatomical features of the location of this nervous structure.
These include:
- spiral course of the nerve trunk;
- close to the surface of the skin.
Thanks to this, it is easily and quickly affected by any adverse effects.
Manifestations of neuralgia, inflammation of the radial nerve
Functionality of nerve n. radialis - innervation of the muscles of the arm from the shoulder to the fingers. Neuropathy in any area of the limb has its own causes:
- metabolic (exchange);
- post-traumatic (fractures, dislocations, blows);
- compression (from squeezing);
- ischemic (circulatory disorders).
Its symptom is the “drop hand” effect, when the mobility of the joints of the hand and thumb is limited. The patient cannot hold it horizontally, there is no mobility of the fingers, there is numbness in the forearm, shoulder (its back surface), fingers (from the palm). The examination also reveals the absence of neurological reflexes.
Causes of inflammation
There are several causes of damage to the radial nerve for the right and left arms.
These include:
- complications after an infectious disease, bacterial or viral;
- traumatic effect on the nerve fiber - this can be prolonged compression and disruption of blood supply due to an uncomfortable sleeping position, using a crutch or a tourniquet to stop bleeding;
- direct injury to the nerve due to injury or bruise, injection into the outer surface of the shoulder;
- compression of the nerve by a keloid scar formed after injury in the space between the muscles;
- toxic effects on nerve fibers from household and industrial toxic substances, carbon oxides, salts of heavy metals (lead, mercury).
These reasons lead to disruption of the conduction of impulses along the nerve fiber of the radial nerve.
Causes of peroneal nerve neuropathy
The etiology of peroneal neuropathy is impressive. Doctors name the most common causes of the disease:
- Various injuries of the lower extremities. For example, a fracture resulted in a pinched nerve.
- Compression of fibers due to impaired blood supply. Varicose veins, blood clots, ischemia.
- Metabolic disease.
- Various infections.
- Severe general diseases.
- Malignant tumors in any organ of the body.
- Endocrine pathologies.
- Toxic poisoning.
- Blood diseases.
Neuropathy can occur with injuries of various locations. This is especially true for a fracture or bruise of the lower leg. The functioning of the peroneal nerve is significantly impaired. A fall or blow to any part of the leg or hip can also damage the nerve.
Stroke, various ischemia, osteoarthritis, joint inflammation lead to compression of the nerve with the subsequent development of neuropathy and neuralgia.
People who spend time in a bent position for a long time, for example, at work, risk getting nerve compression. This is the “sin” of farmers, harvesters and other people who are “fed by their feet.”
Patients suffering from diabetes mellitus or some kind of endocrine disorders receive a side effect of their illness. Blood sugar decreases, and “diabetic neuropathy” develops.
Alcoholism itself is a factor in the development of the disease. The chain is simple: alcohol - damage to the gastrointestinal tract and other body systems - metabolic disorders - neuropathy.
In oncology, symptoms arise as a result of cancer cell division and the appearance of metastases.
Symptoms and manifestations of damage
When the radial nerve is damaged, the patient loses fine motor skills of the hands, and movements in the hand are impaired. He cannot perform both complex and elementary actions with it. There is a loss of sensitivity or a decrease in it in characteristic areas.
Pain along the nerve trunk is extremely rare in patients. This only happens with infectious and traumatic lesions. The right upper limb is more affected.
Manifestations of neuritis of the radial nerve of the right and left hand depend on the location of the inflammation.
Depending on this, the following symptoms occur at different levels:
- With high nerve damage in the armpit area, paralysis of the extensor muscles of the fingers, hand and forearm is observed.
- For lesions in the middle third of the nerve trunk (at the level of the middle third of the shoulder), extension of the forearm and hand is typically affected. Movement in the shoulder is preserved.
- Damage to the nerve in the lower third of the shoulder is manifested by impaired flexion of the fingers and hand. All other movements in the arm (flexion of the weep and forearm) are preserved.
- If the nerve is damaged at the level of the lower part of the forearm, the ability to extend the fingers disappears or decreases. All other functions are retained. Patients develop a “dangling hand” typical of this nerve lesion. The thumb is pressed against the index finger. The patient is unable to shake hands and the fingers are fully extended.
Find out about the symptoms of other types of neuritis of the extremities:
- upper - brachial, ulnar, median nerves;
- sciatic nerve;
- lower - femoral, tibial and peroneal nerves.
Possible patient complaints
Patients present a variety of complaints of weakness in the arm, fingers and hand, and decreased range of motion. Their pain radiates or even shoots into the third, second and first fingers of the hand.
They complain of numbness in the affected hand, goose bumps in the fingers of the hand, except for the fourth and fifth, the outer side of the shoulder and the inner side of the forearm.
There is a violation of deep and superficial sensitivity in the area of the fingers (I-III) and forearm on the inside. The brush swells and acquires a bluish-purple color.
The patient notes a violation of the flexion of the wrist joint, the fingers do not straighten . Occasionally, numbness along the nerve trunk is possible.
Peroneal nerve neuropathy - causes, symptoms, treatment
At a doctor’s appointment, you may hear three incomprehensible words addressed to you – peroneal nerve neuropathy. In medicine it is called peroneal neuropathy.
You can suspect a problem in yourself simply by standing on your heels.
If you can hold on easily, then the nerve is fine. If not, then you need to find out more about the disease. Perhaps it has already begun to imperceptibly undermine the body.
Diagnostic methods
A neurologist treats radial nerve neuritis . First, he asks the patient about complaints and medical history.
Finds out under what circumstances and when the signs appeared. Then the doctor proceeds directly to examining the patient. Based on this, he makes a preliminary diagnosis.
A neurological examination reveals:
- During examination of the patient's hand, a characteristic drooping hand is revealed when the arm is extended forward.
- Difficulties in bending joints are revealed. The patient does not straighten his hand, forearm, and his arm does not straighten at the elbow joint.
- When examined with a neurological hammer, the doctor detects a decrease in the carporadial and extensor reflexes.
- There is a violation of skin sensitivity in the area of the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd fingers.
- A series of tests are performed to determine the level of radial nerve damage. He cannot move his thumb to the side. The patient is unable to simultaneously touch the back of the hands with all fingers. He cannot place his palms on the table and cross his middle and second fingers. A patient with damage to the nerve trunk is unable to spread his fingers to the sides.
Tests and neurological examination data may suggest damage to the radial nerve. It can be confirmed by performing a series of instrumental studies.
Electroneuromyography plays a leading role in making a diagnosis. It allows you to determine a violation of the conduction of a nerve impulse along a nerve fiber and a defect in the innervation of certain muscle groups. There is a decrease in the amplitude of the muscle response to electric current stimulation.
They also conduct electroneurography , which reveals a slowdown in conduction along the nerve trunk.
In addition to these studies, additional testing is carried out. They are carried out to identify the cause of damage to the radial nerve.
These include:
- consultations with a traumatologist, orthopedist and endocrinologist;
- blood biochemistry;
- determine blood sugar levels;
- general blood analysis;
- radiography of the bones of the shoulder, forearm, hand;
- CT scan of the elbow and wrist joints.
What diseases should be distinguished from?
Differential diagnosis for neuritis of the radial nerve is carried out with neuropathy . It is characterized by all the same symptoms, but there is no pain syndrome.
Neuritis should also be distinguished from post-traumatic compression of the radial nerve . To do this, a hydrocortisone-novocaine blockade is carried out in the area of its membranes.
When the nerve fiber is compressed, relief of symptoms is observed, which is absent with neuritis.
Symptoms of peroneal nerve neuropathy
The clinical picture shows that when the nerve fiber is damaged, the sensitivity of the limb necessarily suffers, to one degree or another.
When a leg is sharply injured, pain occurs, and all accompanying manifestations are clearly expressed.
Whereas with the chronic development of the disease there is a tendency for a gradual and slow increase in symptoms.
As a result of damage to the peroneal nerve, the following occurs:
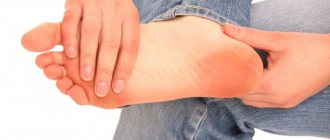
- Impaired foot function. Inability to bend or straighten fingers normally.
- The leg is slightly concave inward.
- Inability to stand on your heels, much less walk on them.
- Edema.
- Loss of sensation in any part of the lower limb: feet, calves, or even thighs. It is especially noticeable between the first two fingers.
- Pain that gets worse when trying to sit up.
- A burning sensation in the toes or other part of the foot, as well as in the calf muscles.
- Weakness in one or both limbs.
- Feelings of heat are replaced by a feeling of cold in the lower part of the body.
- Feeling of "pins and needles".
With a long-term illness, atrophy of the muscles of the affected leg may occur.
Features of treatment
Treatment of the radial nerve is carried out only by a neurologist or a rehabilitation specialist. Self-medication is unacceptable. The limb must be immobilized during treatment.
Therapy has two goals. The first is treatment of the underlying disease or injury that led to the nerve damage. The second is the removal of symptoms: pain, swelling, sensory disturbances and decreased muscle strength. Its tactics are determined by the cause of the disease and the level of damage.
The following drugs are used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Nimesulide) reduce hand swelling and nerve inflammation.
Angioprotectors are used to improve regional blood circulation and blood supply to the nerve trunk. Used: Actovegin, Pentoxifylline, Trental.- Anticholinesterase drugs (Prozerin) enhance the conduction of impulses along the nerve.
- B vitamins improve metabolism in nerve fiber.
For treatment, drugs high in vitamins B1, B6 and B12 are used. Vitamin complexes are used: Neuromultivit, Neurodiclovit and others. - To treat severe pain and swelling, I use glucocorticoids; they have anti-edema and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Antioxidants (Vitamin E, Vitamin C) reduce the severity of damage in the nerve fiber.
In the recovery period for neuritis , physiotherapy, electrical myostimulation, acupuncture, massage, and exercise therapy are prescribed .
Physical therapy plays an important role in the treatment of neuritis of this localization. A set of exercises is developed by a rehabilitation specialist for each patient.
The following exercises are used:
- The patient is seated at the table. He bends at the elbow joint and rests against the surface of the table. In this position, he raises his index finger up and lowers his thumb down. The exercise is performed ten times.
- In the same position, raise your thumb up and your index finger down. The exercise is performed ten times.
- Extend the fingers of the healthy hand ten times. Then grab the fingers of the affected hand into a fist with your healthy hand and squeeze ten times.
In rare cases, if there is no effect from conservative treatment, surgery is performed . With them, the nerve is released from compression.
Peroneal nerve neuropathy - treatment
To literally put a person back on his feet, a complex treatment is usually selected: medication, physiotherapy, and surgery. Or just one method. The general condition of the patient and the “stage” of damage to the peroneal nerve are assessed.
Medication
Treatment tactics are aimed at reducing the activity of the disease, with which the patient has been living for many years. It was this that became the culprit of neuropathy in most cases. These are drugs against diabetes, kidney diseases and others.
Then the following is prescribed to help the patient:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets or injections. "Ketorol", "Diclofenac" and so on. They relieve pain, burning and other unpleasant symptoms.
- In tandem with analgesics, B vitamins. For example, Milgamma.
- Restoring and improving blood flow drugs. These are calcium channel blockers, such as Cordaflex; "Cavinton".
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Conservative treatment includes proven methods.
- a set of exercises from exercise therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- exposure to heat;
- massage;
- reflexology.
Massage and physical therapy should initially be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. The principle of “do no harm” applies here. The specialist will tell you what exercises are allowed and what you should forget about.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is a last resort. The decision to operate is used in cases of frequent relapses of the disease, ineffectiveness of medications and physiotherapy, as well as in cases of complete damage to the nerve fibers.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed bed rest, and after a while, exercise therapy.
There is no need to rush to get back on your feet. It is necessary to carefully monitor the operated limb. Ulcers and wounds should not form on it.
Among the unpleasant neurological pathologies is inflammation of the sciatic nerve. Read about how to treat the disease at home on our website.
Types of ganglionitis and methods of its treatment will be discussed in detail in the next article.
Prognosis and prevention
Radial neuritis responds well to treatment in young people . In the elderly, neuritis, in the presence of concomitant diseases, is difficult to treat. Complications develop quickly.
To prevent diseases, it is necessary to promptly treat the pathologies that cause them. Radiation neuritis is caused by a complex of causes.
With minimal manifestations of illness, numbness, or weakness in a limb, you should consult a doctor and follow all his prescriptions and recommendations .
Otherwise, paralysis and paresis occur, and disability develops. This significantly reduces the patient’s ability to work and quality of life.