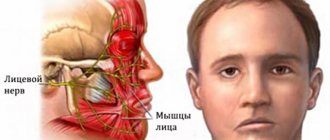
The facial nerve performs an important function - it provides movement in the facial muscles. It is thanks to him that we can express emotions without words and make grimaces - scary or funny. The facial nerve also controls the stapedius muscle, which protects the ear from loud sounds, ensures the perception of taste by the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and increases the secretion of saliva. With neuritis, these functions are disrupted.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Some facts about facial neuritis:
- Another name for the pathology is Bell's palsy. It is associated with the name of the Scottish anatomist Charles Bell, who first described the disease in 1821.
- The disease has different prevalence in different regions and occurs more often in the cold season.
- In the United States, approximately 40,000 people are diagnosed with the disease each year. In the UK this figure is 25-35 people per 100,000 population. In general, Bell's palsy is considered a rare condition.
- You can get sick at any age, but most often neuritis of the facial nerve occurs in people 15-60 years old.
- Men and women get sick approximately equally often.
Suddenly experienced paralysis of one half of the face? Contact your doctor as soon as possible. This could be facial neuritis or a more serious condition such as a stroke.
Treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve
It is currently believed that the most effective treatment for facial neuritis is the use of glucocorticoids (drugs of adrenal hormones). They effectively suppress inflammation, which significantly speeds up the recovery of the affected nerve. The drug prednisolone is used in the form of tablets; the course of treatment usually lasts 10 days. In no case should you self-medicate: glucocorticoids are hormonal drugs, they have serious side effects.
Rehabilitation is of great importance - a set of measures that help restore impaired functions. Rehabilitation measures include:
- Thermal procedures are usually used after the 5-7th day from the onset of neuritis. A neurologist can prescribe mud, ozokerite, and paraffin applications.
- Ultrasound with hydrocortisone, which is also a drug of adrenal hormones.
- B vitamins – help improve nervous system function.
- Acupuncture.
- Massage and therapeutic exercises of facial muscles are prescribed after the symptoms of the disease subside.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
How long does it take to treat facial neuritis? What are the forecasts?
In most cases, the prognosis for facial neuritis is favorable - approximately 75% of patients make a full recovery. If treatment is carried out and the symptoms of the disease do not go away for more than 3 months, then the chances of full recovery are greatly reduced.
If, nine months after the onset of the disease, severe symptoms persist, the neurologist may recommend the following treatment methods:
- Mem therapy is a special set of exercises that helps strengthen facial muscles and improve movements in them.
- Plastic surgery. Improves the appearance of the face, but does not solve the nerve problem.
- Botox injections - in some cases, can help, in combination with therapeutic exercises.
Treatment should begin as soon as the first symptoms appear. Early initiation of therapy increases the chances of full recovery. Make an appointment with a neurologist at the Medical Center International Clinic Medica24 by phone.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The main function of the facial nerve is to innervate the facial muscles. It provides facial expressions, movements of the lips, eyelids. It is also responsible for the following functions:
- Taste sensitivity of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
- Innervation of some salivary glands – increased secretion of saliva.
- In part, the facial nerve takes part in providing sensitivity to the oropharynx and skin.
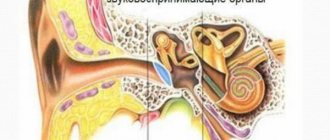
- Innervation of the stapedius muscle in the middle ear (tympanic cavity). It limits the mobility of the auditory ossicles and thereby protects the ear from injury from loud sounds.
Accordingly, the symptoms of facial neuritis represent disorders of these functions. The most striking manifestation is a violation of movements in the facial muscles.
The facial nerve is a pair, that is, a person has two of them - on the right and on the left. Most often, neuritis occurs on one side. Much less often it is bilateral.
If treatment does not bring results. Synkinesia and facial contracture
Facial symmetry returns in an average of 3 months. If your treatment has not brought results, facial asymmetry persists, pain or other symptoms appear, you should immediately clarify the cause of the dysfunction of the facial nerve. The location and cause of the nerve injury may not have been recognized and treatment was prescribed blindly. Perhaps little attention was paid to restorative procedures.
Facial synkinesis is a condition when, for example, closing the eye is accompanied by movement of the mouth and cheek, and smiling is accompanied by closing the eye, etc. Synkinesis occurs more often in cases of long-term, chronic disease of the facial nerve. Most often in these cases we find a chronic inflammatory process in the area of the nerve bed.
The most problematic complication of facial paralysis is contracture, i.e. cicatricial degeneration of facial muscles. The result of contracture is loss of elasticity and immobilization of the facial muscles, even after the function of the facial nerve itself has been restored. Contracture appears as a result of prolonged untreated paralysis of the facial muscles and/or as a result of inadequate recovery procedures (insufficient intensity of exercise or, conversely, excessive stimulation of the facial muscles). Facial contracture is partially reversible. We usually use local injections of the anti-scar drug Longidaza: we inject it with a very thin needle directly into the area of scarring of the facial muscles.
What symptoms occur with facial neuritis?
The main manifestation of the disease is sudden paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face. This becomes especially noticeable when a person tries to frown, smile, or bare his teeth. The face becomes asymmetrical. In approximately two out of a hundred patients, paralysis of the facial muscles occurs on both sides at once.
This picture is reminiscent of another serious condition – stroke. You shouldn't self-diagnose. It is better to immediately call an ambulance. After all, with a stroke, literally minutes count – treatment must begin immediately.
Other possible symptoms of facial neuritis:
- It is difficult to close the eye on the affected side. This condition is called lagophthalmos (in medical jargon - “hare's eye”).
- Excessive salivation occurs.
- Due to the fact that the eye is constantly open, lacrimation and dryness occur.
- Impaired taste perception.
- Pain and discomfort in the ear area on the affected side.
- Increased sensitivity to sounds, loud ones are perceived painfully. In medical language this is called hyperacusis.
Each of these symptoms can be more pronounced or weaker; they are combined differently, depending on which part of the facial nerve the neuritis occurs on.
Proven fact: the success of treatment for facial neuritis directly depends on how early it is started. Therefore, you need to consult a doctor as soon as the first symptoms appear. In neurology at the international clinic Medica24, medical care is available without holidays or weekends.
Trigeminal neuralgia is the most common lesion. Neuralgia is understood as a sensitivity disorder, which is expressed in paroxysmal pain in the zone of innervation of the corresponding nerve. The essence of trigeminal neuralgia is a dysfunction of afferent animal and autonomic fibers.The sensation of pain is formed in the cerebral cortex. In response to painful stimulation, changes occur in the central nervous system. At first, the painful sensation, until it becomes long-lasting, causes subtle changes in the body. Continuing and becoming long-term (chronic), the pain syndrome in trigeminal neuralgia creates a persistent focus of excitation in the cerebral cortex, the revival of which occurs with any additional irritation.
Etiology and pathogenesis. There is no single point of view on the nature of trigeminal neuralgia. There are several reasons for the development of trigeminal neuralgia:
- narrowing of bone openings and canals when nerve compression occurs;
- chronic local infections in the area of the terminal branches of the trigeminal nerve, when the nerve plexuses of the teeth, paranasal sinuses, etc. are affected;
- prolonged hypothermia of the face;
- anatomical, inflammatory changes in the meninges, gasserian node;
- constitutional features that create a high position of the pyramid of the temporal bone, which creates irritation of the trigeminal root on the crest;
— violation of occlusion and changes in the TMJ and the adjacent branch of the trigeminal nerve;
-vascular disorders due to atherosclerosis, which leads to malnutrition of the semilunar node and its compression
-dysfunction of sympathetic innervation;
-destructive changes in central thalamocortical structures
Clinical picture. Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic disease accompanied by sharp paroxysmal pain lasting from several seconds to 1 minute. During an attack, the patient “freezes” with a grimace of fear, pain, and sometimes twitching of facial muscles is noted. Pain is usually limited to the innervation zone of one of the affected nerve branches. Their intensity is different. Over time, they become drilling, cutting, burning, beating like an electric current. Without treatment, attacks of pain become frequent and severe. At the onset of the disease or under the influence of treatment, remissions between painful attacks are long. An attack of pain occurs both spontaneously and as a result of any irritation: movement, changes in ambient temperature, touching allogeneic or trigger (trigger) zones. These zones are small areas of the mucous membrane or skin, usually in the zone of innervation corresponding to the affected branch of the nerve: if the first branch is affected - in the sub-brow region of the inner corner of the eye, the back of the nose, the second branch - in the area of the nasolabial fold, wing of the nose, upper lips, mucous membrane of the upper vault of the vestibule of the mouth, sometimes small molars, the third branch - in the area of the chin, lower lip, mucous membrane of the lower vault of the vestibule of the mouth. Provoking factors for an attack of neuralgia can be talking, chewing, swallowing, washing, or blowing wind. With a long course of the disease, hyperesthesia is observed. At the height of the attack, contraction may occur in the form of “twitching” of the facial and masticatory muscles.
With strong pressure on the affected branch of the nerve, the attack of pain stops, sometimes abruptly. Usually the exact localization of pain is determined, but sometimes it may not correspond to the topography of the nerve and becomes diffuse. Pain often radiates to intact teeth, which is why sometimes wrong decisions are made and healthy teeth are unreasonably removed. In some cases, attacks of pain are accompanied by vegetative symptoms: sweat appears on the affected side of the face, redness (rarely paleness) of the skin, dilation of the pupil, swelling, lacrimation are observed, and increased secretion of saliva and nasal secretions. Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia occurs more often in women. Pain, starting on one side, moves to the other side and rarely occurs on both sides. The second or third branch of the trigeminal nerve is most often affected. The main pathogenetic factors of bilateral neuralgia are age-related, allergic and vascular changes, as well as infections, hypothermia, and mental trauma. The symptoms of bilateral neuralgia are similar to unilateral ones.
Treatment. Treatment methods are divided into conservative and surgical. Conservative methods include: 1) physical - darsonvalization, Bernard currents (diadynamic therapy), fluctuarization, electrophoresis, etc.; 2) medicinal - vitamin therapy (B1, B12, nicotinic acid), the use of sedatives (seduxen, meprobamate, trioxazine, medinal bromide mixture). A solution of sodium bromide is administered intravenously according to the Nesvizhsky method (10 ml daily; up to 25 injections per course of treatment). The concentration of the solution is gradually increased from 0.5 to 10%.
For treatment, nonspecific agents (different blood group, insulin, snake and bee venoms) are widely used, and tissue therapy is carried out. Antiepileptic drugs are effective: carbamazepine (finlepsin), diphenin, tegretol, stazepin, baclofen, etc. The most effective drug for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia is carbamazepine, which is able to block the passage of pain signals. Carbamazepine is prescribed daily at 100 mg (½ tablet) 3 times a day for 2 days, in the next 2 days - 200 mg 3 times. If there is no effect, the dose is increased to 1200 mg. The drug can be used in combination with pipolfen (1 ml of 2.5% solution). It is advisable to periodically change medications, as well as combine them with antidepressants. When treated with antiepileptic drugs, a gradual weakening of their effect is observed, and when they are prescribed in subtherapeutic doses, toxicity develops. In patients with vascular diseases, vasoactive drugs (Trental, Cavinton) should be included in the treatment complex. The homeopathic drug Traumeel in the form of tablets or injections, as well as an ointment applied to the area where the affected branches of the nerve branch, has a good effect. In the absence of a therapeutic effect, surgical treatment is indicated.
Local trimecaine and lidocaine blockades and intravenous infusion of anesthetic solutions provide a good therapeutic effect. Treatment consists of applying a 0.5% or 1% anesthetic solution to the nerve exit sites in a dose of up to 5 ml 2-3 times a week (15-20 injections per course of treatment). Blockades of autologous blood administered perineurally are effective. Local anesthetic ointments applied to trigger areas are also used.
For trigeminal neuralgia, the following operations are performed: 1) operations on the three branches of the trigeminal nerve (transection of the nerve trunk, alcoholization); 2) operations on the trigeminal ganglion and the sensitive root of the trigeminal nerve (transection, decompression, electrical destruction); 3) cutting the pathways of the trigeminal nerve and its sensory nuclei in the medulla oblongata and midbrain, at the level of the thalamus and pain pathways from the thalamus to the cerebral cortex.
Surgical methods such as alcoholization or nerve cutting were previously widely used. Currently, when conservative treatment is ineffective, they are used selectively, sometimes only in very elderly patients when treatment is ineffective. A 2-4% solution of novocaine, trimecaine or lidocaine in 80% ethyl alcohol (no more than 0.5 ml) is injected endoneurally into the affected branch of the trigeminal nerve. The ensuing degeneration of the nerve impairs its conductivity. Perineural injection of alcohol usually does not cause nerve degeneration, and the painful condition is aggravated by the addition of neuropathy. The effect of alcoholization decreases with each subsequent procedure and the period of remission becomes shorter. In addition, with frequent alcoholization, nearby vegetative nodes are excited and gangliolitis may develop. For the same indications, for trigeminal neuralgia, surgical intervention is performed - cutting the peripheral branches on the face and at the base of the brain.
One of the effective methods is percutaneous stereotactic destruction of the trigeminal nerve. It is based on coagulation to turn off the sensory root of the trigeminal nerve, but while maintaining tactile sensitivity. Usually 2 to 8 coagulations are performed. The sensitive root of the trigeminal nerve is destroyed by hydrometric destruction using bidistilled water at a temperature of 95 °C. High-frequency thermoneurolysis and thermogangliolysis are effective in the treatment of neuralgia. Rhizolysis with glycerol is also used. Percutaneous retrogasseral injections of glycerin are made, after which sensitivity in the area of innervation of the nerve may decrease for some time, but the pain syndrome is quickly relieved.
An effective surgical method is microvascular decompression of the trigeminal nerve root, which consists of trephination of the posterior cranial fossa and revision of the trigeminal nerve root, superior cerebellar artery and superior petrosal vein. If compression is detected, the vessels and nerves are isolated and isolated with biomaterial. Decompression operations are also performed to free the peripheral branches of the trigeminal nerve from the bone canals as they exit to the surface of the face. Resection of the peripheral branches of the trigeminal nerve with all its branches is not always effective; in 30-40% of cases, relapses are observed after surgery.
Trigeminal neuropathy
In dental practice, lesions of the trigeminal nerve - neuropathy - are often encountered. They have different etiologies and pathogenesis and can be infectious, infectious-allergic, traumatic, ischemic, immunological, etc.
In dental practice, the disease can be caused by various reasons associated with odontogenic inflammatory processes, trauma and surgical interventions in the maxillofacial area. The alveolar nerves are most often affected after tooth extraction, during injection for anesthesia and endodontic treatment.
Neuropathy of the small branches of the trigeminal nerve can be caused by wearing dentures, as well as the toxic and allergic effects of materials - plastics and metals used in dental prosthetics.
For the development of neuropathy, injuries are of great importance: damage to teeth, bones of the facial skeleton, adjacent perimaxillary soft tissues, as well as damage to the branch of the trigeminal nerve during surgery. Therapeutic measures in the form of alcohol-vocaine blockades and neuroexteresis can also be the cause of the development of trigeminal neuropathies.
Clinical picture. Most often small ones are affected (plexalgia), less often - the main branches of the trigeminal nerve. Odontogenic plexalgia of the trigeminal nerve is manifested by constant pain in the area of innervation of the affected branch, a feeling of numbness of the teeth, gums, skin of the upper and lower lips and chin, sometimes paresthesia in the form of crawling, tingling and other unpleasant sensations.
Damage to small branches of the upper or lower dental plexus is referred to as dental plexalgia. The dental plexuses of the trigeminal nerve system are affected and are more often localized in the branches of the upper dental plexus, less often in the lower dental plexus. Women are predominantly affected.
Dental plexalgia is characterized by acute, burning pain in the teeth and gums radiating to the opposite side. The pain often intensifies with hypothermia or stress.
If the dental plexuses in the upper jaw are affected, pain is observed and radiates along the second branch of the trigeminal nerve and vice versa - the branches of the lower dental plexus irritate the third branch. When examining the exit point of the nerves - at the infraorbital, greater palatine, incisive foramen, at the tubercle of the upper jaw - on the upper jaw and along the inner surface of the branch of the lower jaw, at the mental foramen, no pain is detected. The presence of dental plexalgia requires elimination - treatment of periapical destructive foci and monitoring of osteogenesis for 6 months, treatment of periodontal diseases. Removing intact teeth for dental plexalgia is usually a mistake.
Provoking moments of damage to the branches of the upper dental plexus can be traumatic factors - complex removal, including cutting out impacted and semi-impacted teeth, treatment of teeth with filling material getting behind the root apex, after conduction anesthesia, when the lower alveolar nerve is injured, removal of several teeth. The development of dental plexalgia may be associated with changes in the TMJ in the cervical spine. The occurrence of pain in the area of branches of the maxillary plexus can be influenced by inflammatory processes in the paranasal sinuses.
Bilateral dental plexalgia is often observed, mainly in women aged 40-45 years. The disease is characterized by the development of pain on both sides of the upper jaw or pain in the area of the upper and lower jaws. Pain often radiates to the temporal, frontal, zygomatic and infraorbital areas. When studying the sensitivity of the mucous membrane in the area of branching of the branches of the nerve plexus, hyperesthesia is noted during an attack of pain and the absence of this symptom during remission.
When examining a patient, symptoms of a disorder of all types of sensitivity are detected in the form of a persistent increase (hyperesthesia), persistent decrease (hypesthesia), loss (anesthesia) or distortion (paresthesia) of the sensitivity of the facial skin, oral mucosa, and teeth. The leading symptom of neuropathy of the small branches of the trigeminal nerve is pain, which can occur spontaneously, be constant, aching, intensify with pressure on the affected nerve, periodically become more or less pronounced, but persist for a long time. Characterized by the absence of paroxysms and allogeneic (trigger) zones.
Large branches - the buccal and lingual nerves - may also be affected. Depending on which nerves are affected, numbness of almost half of the tongue is noted with neuropathy of the lingual nerve, pain and numbness of the mucous membrane of the cheek when the process is localized in the buccal nerve, burning and pain in half of the palate with damage to the anterior palatine nerve. The severity of clinical manifestations may also depend on the degree and form of the lesion. In its mild form and chronic course, trigeminal neuropathy does not cause significant disturbances. In severe cases, the patient may develop shock from unbearable pain. If the process continues for a long time, then trophic changes are observed - swelling, redness of the mucous membrane, desquamation of the epithelium. In case of damage to the third branch of the trigeminal nerve due to the involvement of motor nerves in the process, spasm or even paresis of the masticatory muscles often occurs.
In case of neuropathies due to trauma, among the clinical signs, in addition to pain, there is a violation of the sensitivity of the soft tissues of the face and, as an important diagnostic criterion, a violation of the sensitivity of the teeth. Degeneration of the nerve elements of the dental pulp was noted already on the 5-10th day after injury. These phenomena intensify at a later date, but are reactive in nature. Neuropathy of the peripheral branches of the trigeminal nerve is observed after various operations on the jaws: after radical maxillary sinusotomy, removal of jaw tumors, and osteoplastic operations.
Treatment. The basis of treatment for trigeminal neuropathy is elimination of the cause and complex therapy, including local analgesics, tranquilizers, antihistamines, antidepressants, antiserotonin drugs, B-blockers, biostimulants, biocorrectors, as well as drugs that have a resolving effect. In addition to individual and targeted treatment, acupuncture and physical influences are carried out. Carbamazepine remains the main drug for treatment.
For all types of neuropathy, carbamazepine drugs (finlepsin, tegretol, stazepin, baclofen) are used. In case of insufficient effectiveness of these drugs, it is recommended to prescribe sodium hydroxybutyrate or phenibut. Effective tranquilizers are gidazepam, phenazepam in solution, as well as intravenous administration of 10 ml of a 1% solution of trimecaine, mepivacaine, bupivacaine and their combination with nicotinic acid.
For neuropathies associated with inflammatory diseases, conventional anti-inflammatory treatment is supplemented with the prescription of desensitizing drugs (suprastin, tavegil, diphenhydramine, diazolin, pipolfen). At the same time, vitamin therapy is carried out (B1, B12, nicotinic acid).
In case of immunity disorders, especially in the case of deficiency of immunoglobulins of classes M and G, complex treatment is supplemented with the use of immunomodulatory drugs, including milopeptite - B-activin.
In the complex treatment of patients with traumatic neuropathy, biostimulants and immunocorrectors should be prescribed. In case of traumatic pinching of a nerve, it should be freed from traumatic factors - foreign bodies, bone fragments, and if it is ruptured, an epineural suture should be applied.
Neuropathies of ischemic nature are treated with the use of cardiac glycosides and neurotropic drugs. In the case of a combination of trigeminal neuropathy with vascular pathology of the brain, it is advisable to use vasoactive and neurotropic drugs - aminophylline, nicotinic acid, Cavinton, cinnarizine, nootropil, enduracin, which are especially effective if patients have hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, or a combination thereof. It is recommended that such patients be prescribed antispasmodic and antihypertensive drugs.
Physical methods of treatment are also recommended: fluoridation, hydrocortisone phonophoresis, ultrasound, diadynamic currents, longitudinal galvanization of the nerve using lidase, vitamin B, anesthetics, thiamine. Acupuncture gives positive results.
Rational prosthetics are required, especially with a reduced bite.
"Surgical Dentistry" edited by Robustova T.G.
Fourth edition. Moscow "Medicine" 2010
What complications can occur with neuritis of the facial nerve?
In most cases, complete recovery occurs, all nerve functions are fully restored. With severe damage, some complications may occur:
- Involuntary contractions of some muscles due to improper restoration of nerve fibers. For example, when a person tries to smile, his eye closes.
- Loss of sense of taste.
- Ulceration of the cornea. It occurs when the eye is constantly open for a long time and the cornea dries out. In order to prevent this, the doctor prescribes special eye drops - “artificial tears”. Ulceration of the cornea can lead to infection and visual impairment.
- "Crocodile Tears" . There is increased lacrimation, the eye on the affected side constantly “cries”. Usually this symptom goes away after recovery, but sometimes it persists for a very long time.
An experienced neurologist will correctly assess the symptoms of facial neuritis and prescribe effective treatment and rehabilitation. Visit a neurologist. At the Medica24 international clinic, administrators accept calls any day 24 hours a day, please contact us.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The cause of the development of neuritis of the facial nerve is its inflammation. The inflammatory process leads to damage to nerve fibers and disruption of their functions. Why is this happening? Scientists cannot fully answer this question. But there are some considerations.
Diagnosis of NLN
CT scan of the brain
- Cost: 6,000 rub.
More details
If you suspect facial neuropathy, you should consult a neurologist as soon as possible. Other neurological diseases have similar symptoms to NLN. To avoid mistakes, the neurologist prescribes standard examinations.
- Laboratory tests
Blood, urine, blood glucose, serological tests (antigen-antibody) if infection is suspected - Chest X-ray
Detects tuberculosis, tumor process, scars and lumps - MRI and brain
MRI identifies possible pathological processes at the base of the brain, CT scan – to study the temporal bone - Electroneuromyography
Determines the speed of nerve impulse conduction in muscles, reveals connective tissue degeneration of nerve fiber - Consultation with a therapist, ENT specialist, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist
If there are concomitant diseases
When the diagnosis is completed, there is no doubt left.
Electroneuromyography (ENMG) must be performed as early as possible to determine the severity of the disease and prognosis.
This method determines which part of the nerve is more damaged - the myelin sheath or the central axon. Damage to the myelin sheath has a more favorable prognosis because it is restored in most cases. Axonal damage is much more serious.
The main cause of facial neuritis is infection
Experts believe that the main cause of the disease is a viral infection. Neuritis can be caused by the following infectious agents:
- Herpes viruses are pathogens that cause simple and genital herpes.
- The varicella zoster virus also belongs to the herpesvirus family.
- Another representative of this family is the Epstein-Barr virus , which causes infectious mononucleosis.
- Cytomegalovirus is a member of the herpes viruses that causes cytomegalovirus infection.
Facial neuritis is also associated with borreliosis (Lyme disease), a bacterial infection. Similar symptoms occur with the pontine form of polio.
Nerve damage after tooth extraction
As a rule, this problem arises during complex tooth extraction, namely, dystopic or impacted, that is, located inside the bone tissue and has not completely erupted. Removing such teeth requires sawing the bone and using special forceps. If the load is too heavy and the nerve is located close, the doctor may touch it.
The prognosis in such a situation is usually positive - the condition of the nerve is restored after therapy.
Other conditions that may lead to illness
There are some known factors that are thought to contribute to the onset of the disease:
- Hypothermia. Manifestations of the disease can occur after being “blown out” while driving in a car with an open window, or sleeping near an open window.
- Head injuries.
- Atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension - these diseases lead to impaired blood circulation and nerve nutrition.
- Impaired blood flow in the vertebral artery - the cause may be osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia in the cervical spine.
- Unsuccessful anesthesia in dentistry when the tip of the needle hits a nerve.
Sometimes you can hear that vaccination can be the cause of facial neuritis. However, studies have proven that there is no connection between vaccinations and this disease.
International Clinic Medica24 is a modern clinic where medical care is available around the clock.
How does treatment depend on the cause?
Until 2007, experts debated which types of treatment for facial neuritis were most effective. Some insisted on the use of antiviral drugs, since the disease is most often caused by a viral infection, others preferred glucocorticosteroids (hormonal drugs that have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect), while others argued that their combination works better.
After clinical studies, it was decided that glucocorticoids are most effective.
Only a neurologist can correctly determine the cause of the disease and prescribe effective treatment. Visit a doctor as soon as the first symptoms begin to bother you. Make an appointment with a neurologist at the Medica24 international clinic by phone.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The main manifestation of facial neuritis is paralysis of the facial muscles. It usually occurs on one side, but in 2 out of 100 patients it occurs on both sides. This symptom is not unique to facial neuritis. It can also occur with other diseases: stroke, certain infections, Lyme disease, cancer.
An experienced neurologist will be able to understand the causes of facial paralysis and prescribe timely treatment that will help.
Diagnosis of facial neuritis in the clinic: what happens in the neurologist’s office?
During the conversation, the doctor may ask you the following questions:
- When did you notice that you had facial paralysis? How did this happen - abruptly, unexpectedly, or gradually?
- Have you recently had any infectious diseases?
- Have you had similar problems before? Has anyone in your immediate family suffered from Bell's palsy?
- What other complaints do you have?
- Are you bothered by pain in the face or ear?
- Do you taste food well?
Next, the doctor will conduct a general neurological examination, since manifestations of facial neuritis may be caused by another, more serious disease. You will be asked to raise and frown your eyebrows, smile, bare your teeth, stick out your tongue - these tests will help determine the dysfunction of the facial muscles. If after the examination the doctor finds it difficult to establish an accurate diagnosis, you will be prescribed additional diagnostic methods.
The international clinic Medica24 employs experienced neurologists and uses uniform standards developed by experts. You will be carefully examined, all necessary procedures will be prescribed in your case, and an accurate diagnosis will be established.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve on the face
Usually the disease is caused by infection or bacteria. List of reasons why inflammation of the facial nerve may occur:
- Temporomandibular joint injuries
- Tumors (benign and malignant) of the brain and facial area
- Anomalies of skull development
- Skull injuries - birth, fracture, base, damage to the face or jaw
- Polio
- Pulmonary tuberculosis
- Otitis
- Sinusitis
- Chronic caries
- Inflammation after tooth extraction or treatment
- Hypertension
- HIV and AIDS
- Poisoning
- Inflammation of the middle ear
- Severe hypothermia of the head
- Changes in hormonal levels in women
- Gum inflammation
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome
- Stroke
- Bell's palsy
Causes range from minor to life-threatening illnesses. Each of the reasons determines the further treatment of the patient. In some cases, special tests are performed for diagnosis - auditory, lacrimal, infectious, salivary or gustatory. In this way, the functioning of the receptors and sensory organs is checked.
Additional methods for diagnosing facial neuritis at the international clinic Medica24
Electromyography is a study during which, using special electrodes, the nature and quality of signal transmission along the nerve and muscle response are determined. This helps identify facial nerve damage and the level at which it occurred.
Imaging tests – Your doctor may order a CT scan or magnetic resonance imaging scan. These studies help in diagnosing some conditions that lead to symptoms of facial neuritis, for example, skull fractures, cancer.
If the neurologist believes that your complaints could be caused by diabetes or an infectious disease, you will be prescribed appropriate laboratory diagnostic methods.
Private medicine often suffers from the fact that doctors try to prescribe as many diagnostic procedures as possible to patients, “just in case.” At the Medica24 international clinic, you will be prescribed only those tests that are necessary in your situation. We even have specialists - coordinating doctors who make sure that each patient receives full medical care, but does not overpay for anything unnecessary. Our main value is your health.
The Medica24 international clinic is a place where experienced professionals work and use the most modern diagnostic methods, allowing you to quickly establish a reliable diagnosis. We work around the clock, call at any time.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.
Dental restoration in the presence of neuralgia
Neuralgia of the facial or cranial nerve is a curable disease in 70% of cases. However, it can recur. In addition, the patient needs very long-term treatment to recover: he needs to do gymnastics, talk as much as possible, inflate balloons, etc. In addition, impaired facial expression can also affect chewing, which may be difficult. That is why, in the case of missing teeth, very high demands are placed on the prosthesis: it must be comfortable, it must not fall out of the mouth, so that the patient cannot choke on it.
In the acute stage of neuralgia, it is worth postponing dental restoration. After at least 2-3 weeks, if the treatment has given positive results, you can contact your dentist with a question about prosthetics.
Removable prosthetics are not recommended, since the structures are quite massive, causing discomfort and long-term addiction. In addition, they do not have good fixation. Therefore, the best option would be to use implantation. However, not classical, but one-stage - it involves the use of modern technologies for 3D visualization of the treatment process, as well as simpler and less traumatic installation of implants.
We remind you that the most important thing when dental implantation is a professional doctor who conducts a thorough diagnosis of the condition of the patient’s jaw system, knows its anatomical structure and uses progressive methods for planning and installing implants that minimize the risks of complications.
1 According to research conducted at the Department of Surgical Dentistry of Odessa State Medical University. N.I. Pirogov.