Myopathies represent a very large group of diseases with different causes, different courses and prognosis. A common feature is muscle weakness—affecting the muscles in the thighs and arms, although facial muscles may also be weakened. Sensory disorders do not occur in myopathies. Muscle weakness is usually bilateral and symmetrical from the outset, that is, similar on both sides of the body - left and right. Myopathies can be genetic or acquired. Genetically determined myopathies include, for example, muscular dystrophies, which are characterized by abnormal muscle cell structure (eg, due to a congenital deficiency of any of its components). On the other hand, acquired myopathies have inflammation (inflammatory myopathies), may accompany endocrine diseases (eg, hypothyroidism), and may also result from muscle damage by certain drugs or toxic compounds (eg, alcohol).
How common is myopathy?
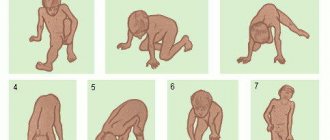
The term "myopathy" is very broad and covers many different diseases. Therefore, the overall incidence of myopathy is difficult to determine. As a rule, myopathies are rare diseases. How does myopathy manifest? The main symptom of myopathy is muscle weakness. This most often affects the muscles of the thighs and arms - patients, for example, have difficulty climbing stairs, rising from a sitting position, sitting, or performing activities with raised arms (for example, hanging curtains or doing hair). Muscle weakness may be accompanied by pain. Some myopathies involve the muscles of the face or throat. There may be drooping eyelids, decreased mobility of the eyeballs, slurred speech, and difficulty swallowing. Sometimes the neck muscles are weak - then the head cannot be held up. In some myopathies, weakness of the respiratory muscles may occur, leading to shortness of breath. Sometimes with myopathies there are problems with muscle relaxation, for example, the patient cannot quickly unclench his fingers after clenching a fist. With progressive and long-term myopathies, muscle atrophy occurs. These symptoms may be accompanied by signs of damage to other tissues and organs outside the muscular system.
Forecast
Different types of muscle myopathies have different degrees of severity: from severe, leading to disability, to minimal manifestations. The prognosis depends on the type of pathology. An important criterion for prognosis is the rate of increase in muscle weakness: the slower it progresses, the better the prognosis.
References
- Desnuelle C. Late form of Pompe disease: diagnostic and therapeutic approaches // Neuromuscular diseases, 2012. No. 3.
- Vlodavets D.V. et al. Congenital structural myopathies // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2007. T. 52. No. 5.
- Sukhorukov V.S. et al. Clinical and pathogenetic significance of mitochondrial changes in muscles with congenital myopathy of the central core // Issues of Practical Pediatrics, 2011. T. 6. No. 6. P. 36-39.
- Sukhorukov V.S. et al. Congenital “multi-core” myopathy // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2012. T. 57. No. 4-1.
- Congenital myopathies. MSD Handbook. URL: https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru (accessed 10/30/2019).
- Romero N. B. Nemaline myopathies: clinical diversity and genetic heterogeneity // Neuromuscular diseases, 2013. No. 1.
GZEA.PD.18.09.0435v
How does a doctor diagnose myopathy?
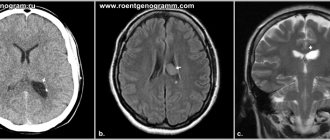
The doctor takes the patient's medical history and performs a test, which usually shows paresis of the muscles (hips, arms, sometimes the face), sometimes also weakening of the reflexes caused by tapping with a neurological hammer. He then orders additional tests. Typically these are laboratory blood tests, including electrolyte, TSH, inflammation and creatine kinase levels. It is a sensitive indicator of muscle breakdown and is elevated in most patients with myopathy. It can also be increased in diseases where muscle damage is caused by nerve damage, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or polyneuropathy, and sometimes in healthy people, for example after exercise or muscle injury. Electromyography (EMG) is another additional test important for diagnosis. EMG can confirm myopathy or indicate another disease that causes similar symptoms. A definitive diagnosis of myopathy, that is, determination of its type and cause, is most often possible after a muscle tissue test (for this purpose, a small piece of tissue is taken under local anesthesia for microscopic examination) or genetic analysis from a blood sample taken from the patient. Genetic testing is only available for some genetic myopathies.
Etiology and pathogenesis of myopathies
The development of myopathy is most often due to hereditary causes. The genetic types of this disease have different forms, which are characterized by certain types of inheritance. An important role in the etiology of myopathies is played by acute and chronic infections, injuries and injuries, nutritional dystrophies and other unfavorable environmental factors. Experts also point to overexertion, which can cause the development of myopathy in people predisposed to it due to heredity.
Thus, almost any unfavorable factor in human life can become an impetus for the manifestation and development of myopathies. The nature of the predisposition of some patients to the development of myopathies was made possible by biochemical and genetic studies. It is known for sure that patients have metabolic defects caused by heredity. They provoke dysfunction of certain enzymes, which causes a lack of aldolase, transaminase, creatine phosphokinase and other vital substances in the blood serum.
In the pathogenesis of myopathies, in addition to genetic metabolic abnormalities of varying degrees, a violation of the sympathetic innervation of muscles has been identified. The lesion affects mainly the proximal arms and legs, where it is richer than in other areas. The central autonomic apparatus of the diencephalic level also suffers from myopathies. This is manifested by a violation of some centrally conditioned autonomic reflexes.
How to treat myopathy?
As in the case of polyneuropathy, causal and symptomatic treatment can be distinguished. Causal treatment is possible, for example in inflammatory myopathies. In these cases, glucocorticoids (steroid hormones), immunosuppressants or intravenous immunoglobulins are used. Causal treatment of myopathy arising from endocrine diseases (eg, thyroid disease, hyperparathyroidism, or hyperadrenocorticism) involves treatment of hormonal disorders. For drug-induced or toxic myopathy, you should try to stop taking the medication or stop exposure to the toxic compound that caused the muscle damage. In rare cases of genetic myopathy, the essence of which is the absence of one of the enzymes necessary for the proper functioning of muscles, causative treatment is possible in the form of administration of the missing enzyme.
Symptomatic treatment is primarily rehabilitation. In the event that rapid muscle relaxation is a burdensome experience for a patient, pharmacological treatment is used to alleviate the symptom. Some muscle diseases affect other organs, such as the heart muscle. Then it is important for patients to undergo regular examinations with a cardiologist. In addition, genetic counseling should be given to patients with genetic myopathy.
Treatment
There is only symptomatic treatment for the disease. First of all, it is aimed at maintaining breathing, since these disorders are considered one of the most severe complications. To correct respiratory disorders, physical therapy, massage, and other therapeutic procedures are prescribed.2
To correct contractures and postural disorders, exercise therapy, physiotherapeutic treatment, and acupuncture are recommended. But there are no drugs that can effectively alleviate the course of these pathologies.2 Unlike Pompe disease, for the treatment of which pathogenetic therapy is available.1
Folk remedies
Photo: medaboutme.ru
Since in most cases the cause of myopathy is a hereditary pathology, it is impossible to alleviate your condition without medications, but by independently following certain measures you can improve your general condition.
For example, nutrition plays a big role, so it is important to follow some recommendations. Firstly, you should add more fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products, eggs, honey, nuts, and cereals (especially oatmeal and buckwheat) to your diet. Secondly, it is important to give up coffee, alcohol, potatoes, cabbage, and spicy foods.
In order to prevent accelerated muscle atrophy, it is necessary to constantly perform therapeutic exercises. But you should also remember that the condition of the muscles in myopathy is far from the condition of the muscles of a healthy person. Accordingly, the load should be minimal so as not to cause overvoltage. Swimming pool exercises are perfect for this purpose.
Also, do not forget about the importance of breathing exercises. A common occurrence in myopathy is damage to the respiratory muscles, resulting in impaired ventilation of the lungs, which subsequently leads to an inflammatory process (the development of pneumonia). Breathing exercises are aimed at improving gas exchange in the lungs.
It is not recommended to develop a list of exercises on your own; it is better to contact a specialist for an individual selection of the necessary exercises. After training at a medical institution, you can continue gymnastics at home.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Neuropsychological development of children with neuromuscular pathology
The muscles contain a huge number of receptors that transmit information about muscle function to the brain. The flow of impulses from these receptors enters the brain and participates in the formation of higher cortical functions, such as writing, reading, counting, and logic. With myopathy and amyotrophy, these receptors do not provide proper impulses, which reduces the rate of development of the child’s intelligence.
Therefore, our clinic pays great attention to exercises for the development of intelligence. Regular classes over a long period of time are required, so a child psychologist teaches the parents of our little patients how to independently conduct developmental activities.
Causes of the disease
The disease, depending on the type, has different causes.
Inflammatory forms develop against the background of autoimmune reactions - a disruption of the immune system, due to which the body “attacks” its own tissues and organs. Some inflammatory forms are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and polyarteritis nodosa4.
Infectious causes can be viruses, bacteria and other pathogens, for example:
- Trichinella;
- Toxoplasma;
- HIV infection;
- Coxsackie viruses;
- Influenza viruses;
- Bacteria of the genus Borrelia are the causative agents of Lyme disease;
- Staphylococcus aureus.
Drug-induced myopathies can develop while taking a number of drugs:
- Glucocorticosteroids;
- Lovastatin, other statins - drugs that lower cholesterol levels;
- Colchicine is an anti-gout drug;
- Amiodarone is a drug used for cardiac arrhythmias.
1.General information
If a medical nosological term ends with “-pathy”, in different cases this may mean a diagnosis that needs clarification, a collective and too general, etiologically unclear diagnosis. Myopathy (Greek lit. “muscle disease”) is a group of diseases, congenital or acquired, the general characteristics of which are disorders of neuromuscular metabolism, degenerative-dystrophic processes and, accordingly, progressive functional failure of muscles, especially skeletal ones.
Epidemiological data regarding myopathies are contradictory and, apparently, incomplete. In any case, this group is one of the rare diseases, and even the most common of them, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, occurs no more often than 14 people per 100,000 population. Mostly men suffer.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Medicines
Photo: smartmoney.today
The goal of treatment is to reduce muscle tissue atrophy. Anabolic hormones (retabolil, nerobol) provide significant assistance in this regard. Their action is expressed in stimulating the growth of muscle cells, which is necessary to maintain muscle mass. Due to this, there is an increase in strength, performance and endurance. However, there is a downside to taking these drugs. With long-term use, accompanying effects may occur in the form of baldness, increased hair growth on the face and body. In addition, there is such a concept as masculinization, which refers to the appearance of secondary male sexual characteristics in women. In this case, the physique changes to a male type, the voice becomes rougher, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, the elasticity of the skin changes, and acne appears.
Anticholinesterase drugs include drugs such as prozerin and neuromidin. Preference is given to neuromidin, since its spectrum of action is much wider than proserin. Also, with long-term use of proserin, various unpleasant side effects are observed, so in most cases the drug is prescribed in short courses.
In turn, neuromidin has a good stimulating effect on neuromuscular transmission and also increases muscle contractile activity. In addition, neuromidin has sedative and analgesic (relieves pain) effects.
Vitamin preparations include vitamins E, B and C, as well as nicotinic acid.