Choroid plexus cyst in fetus and adult: causes, symptoms
Choroid plexus cyst (CPC) in the fetus and newborn is an ultrasound term formed due to excess accumulations of cerebrospinal fluid along the vessels. In most cases, as the baby grows, the formations go away on their own. If the structures are preserved, they do not pose a danger to the child's health. If the structures are preserved, they do not pose a danger to the child's health. Only in rare cases is surgery required to remove an overgrown cystic cavity.
The optimal period for diagnosing formations is the fetus at 18-22 weeks, when the structure of the brain is formed. Repeated ultrasound at 24-28 weeks notes a decrease in the number of cystic cavities.
Choroid plexus cyst in the fetus - what is it?
CSS is dangerous in children with chromosomal abnormalities such as Edwards disease (trisomy 18). The nosology is characterized by multiple malformations, so intracerebral cavities with cerebrospinal fluid are a minimal problem in treatment.
Down's disease is not characterized by the formation of the cerebral coronary artery system.
Interesting facts about choroid plexus cysts in children:
- Spontaneous disappearance in 90% of fetuses by 28 weeks of development;
- The prevalence rate of nosology among pregnant women is 2%;
- The shape, size, number of cavities varies;
- Found in adults and healthy people;
- The frequency of villous and choroid plexus cysts is about 3%.
It is impossible to determine the initial type of formations in the fetus due to physiological degradation. The absence of pronounced symptoms does not allow doctors to accumulate enough information about the pathology.
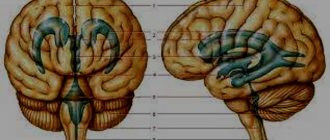
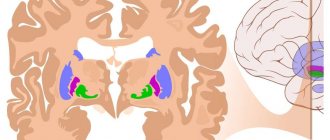
Morphological structure of choroid cystic cavities in a child
The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid inside the choroidal formations does not pose a threat to the health of the baby. Morphologically, the cavity is represented by a thin wall, capable of changing size and shape.
Vascular plexuses are early structures in the formation of the central nervous system of the fetus. Bilateral localization is due to the presence of two hemispheres that require the content of cerebrospinal fluid. Scientists were unable to explain the need for the formation of limited cavities around the plexuses. Presumably, the structures are part of the formation of the central nervous system, and therefore disappear by 28 weeks. If development slows down, CSS can be observed in newborns, infants 3 months and somewhat older.
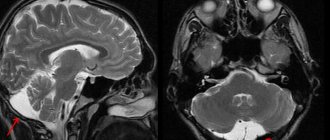
Cystic cavities of the brain are sometimes observed in adults. The pathology does not produce clinical symptoms, so they are detected by chance on an MRI performed due to the verification of another etiology.
Practice shows that there is no health hazard in the persistence of choroid plexus cysts after 30 weeks, with the exception of Edwards disease.
Characteristics
The formation is an isolated cavity filled with clear liquid.
Structure Features:
- They are small in size and tend to dissolve on their own.
- More often they are localized closer to the caudal part of the choroidal glomus.
- It has clear, even contours.
- Does not show any upward trend.
- The presence of signs of malignancy is not typical. Due to the location, it should be differentiated from choroid carcinoma and choroid papilloma.
- There are no clinically significant symptoms. The exception is the development of occlusive hydrocephalus (disruption of the normal outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and its accumulation in the head). It is extremely rare.
- It is regarded as a stigma of dysembryogenesis (developmental defect). These newborns are at high risk of having chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy 18 - Edwards syndrome).
- The main diagnostic method is ultrasound. Discovered as an incidental finding during screening.
- The pathology does not have serious consequences and does not affect the life and health of the child, therefore it does not require treatment.
- The prognosis is favorable.
Causes of CSS
The etiology has not been established. It is considered likely that cystic cavities will persist for a long time against the background of viral infections, herpes, or complicated pregnancy. The absence of clinical manifestations until the end of a person’s life indicates the absence of harm from the pathology. The formations require dynamic monitoring. Blind fontanelles in a child allow an ultrasound of the skull to be performed, and periodic MRI is recommended for adults.
Viral cysts can change: they grow, they degenerate. Dynamic observation determines the prognosis of consequences for a person with CSS.
Two different diagnoses should be distinguished: “fetal choroid plexus cyst” and “cerebral vascular cyst”. The first nosology is harmless, goes away on its own or persists without dynamics for many years. The second type is dangerous, as it sometimes provokes symptoms.
There is a definition of “pseudocyst”. On the screen of an ultrasound monitor, doctors can detect a cavity formed by physiological structures.
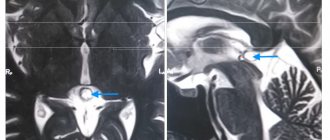
The exclusion of pathological conditions after the diagnosis of “choroid plexus cyst” in a newborn and fetus is ensured by an additional comprehensive examination. Genetic counseling rules out Edwards disease. Magnetic resonance imaging shows the structure of the soft tissues of the brain with high resolution, three-dimensional modeling of the area under study.
Detection of a choroid plexus cyst in a child requires verification of provoking factors: viral and bacterial infections, changes in the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid, increased intracranial pressure. If there are no additional changes, it can be argued that there are no conditions for the negative development of a vascular cyst.
Choroid plexus cysts of a newborn baby
Detection of CSS after birth is not a dangerous condition, but requires examination of the newborn baby. Herpetic infection is activated when the immune system is weakened and can cause changes in the choroid plexus. As the baby grows, the immune system strengthens, so after 3 months, active development of immunity is observed. A decrease in viral activity stabilizes the condition. Cystic cavities can be observed in infants in the absence of clinical pathology. According to the standard scheme, children are examined three times:
- 3 months;
- 6 months;
- 12 months.
The absence of progression indicates the absence of changes that will contribute to the development of dangerous conditions.
Left choroid plexus cyst in a child
The choroid plexus is formed in the fetal body quite early. Education takes part in the formation of cerebrospinal fluid, which provides nutrition to the brain.
The diagnosis of left plexus cyst is common in newborns, although bilateral localization is more common. Pathology develops before the age of 1 year, when intrauterine infections are present. Cystic cavities are equally likely to form in any part of the brain.
Choroid plexus cyst of the right lateral ventricle
The nosology is considered the most benign, since most variants disappear on their own. Found after 22 weeks. An ultrasound scan after 28 weeks shows no pathology. The cystic cavity of the right ventricle can resolve. If there is no associated pathology (with damage to other ventricular spaces), this location of the cyst will not cause complications throughout life, even if the nosology persists in the child after 1 year. In adults, the nosology is rare.
Bilateral choroid plexus cysts
The pathology can persist into adulthood. Some cavities disappear, some remain. Despite the bilateral location, no clinical symptoms occur. Dynamic observation can reveal an increase in size and a change in shape. Only then is conservative treatment carried out. Chromosome mutations are preliminarily excluded. Geneticists can identify a genetic predisposition to Edwards disease. True, pathology can be determined without consulting on the external symptoms of the nosology, characterized by multiple malformations.
Ultrasound examination every 3 months allows you to monitor the condition of the brain parenchyma in infants. The procedure is sufficient to obtain information about the degradation or progression of cystic cavities.
Small cystic cavities in a child's brain
The nature of the CSS has not been reliably established. The pathology is an incidental finding. Small lesions do not affect the human psyche or metabolic reactions. There is no metabolic disorder, so there is no danger.
Small plexus and vascular cysts should be differentiated. The latter option provokes some symptoms. There is no threat to life or health. In adults, minor hemorrhages may occur, soaking into surrounding tissues.
Intrauterine infection provokes inflammatory damage to the walls of the cavity. Detection of infection requires the prescription of antibacterial drugs.
Detection of a plexus cyst at 19 or 20 weeks is not a reason for parents to worry. A repeat examination at week 29 will show no cavities.
Most scientists consider a cystic plexus of intracerebral vessels to be normal. The absence of a clinic suggests that the nosology is a variant of the norm. Improvements in diagnostic methods have made it possible to detect the disease in fetuses and infants more often.
You should pay attention to late cyst formation, which is the result of infection with herpes and a number of other viruses.
Prevention measures
Since the reasons for the formation of CSS are not known for certain, and such a cyst itself is not considered a pathology, there are no specific preventive measures. A woman is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and nutritiously, walk in the fresh air, do gymnastics for pregnant women and do breathing exercises, and take complex vitamin preparations as prescribed by a doctor.
Particular attention should be paid to protection against all kinds of infections. You should not visit crowded places, especially during the seasonal rise in the incidence of ARVI and influenza. In intimate life, it makes sense to use a condom.
Symptoms of choroid plexus cysts
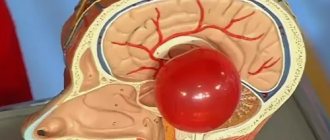
A brain cyst in adults can be a consequence of a hematoma. Limited accumulation of blood (subdural, epidural) with penetration into the ventricles of the brain contributes to ventricular cyst formation.
Pathology contributes to the appearance of clinical symptoms:
- Dizziness, headache;
- Movement coordination disorder;
- Muscle cramps, epilepsy;
- Hypertonicity in newborns.
Localization of manifestations near important nerve centers contributes to the emergence of specific symptoms.
The presence of cytomegalovirus or herpetic infection complicates the course of the disease. Detection of a pathogen and CSS in an adult with a high degree of probability indicates a viral etiology of cystic cavities.
Microcyst of the choroid plexus of the right lateral ventricle rarely causes neurological disorders.
In children, vascular microcysts and larger formations are not accompanied by pathological symptoms. The International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10) does not classify nosology as a number of pathological conditions.
Treatment and prognosis
The main treatment method for choroid papilloma is surgery. The complexity of neurosurgical operations to remove tumors of this kind lies in the rich blood supply of the tumors and their localization near vital brain structures. In this regard, to improve the effectiveness of surgical interventions, embolization of neoplasm vessels is performed as preoperative preparation. When performing surgical intervention, various approaches can be used: transcortical, transcallosal, etc. The use of modern microsurgical and endoscopic techniques makes it possible to remove areas of tumors that are not visible to the naked eye. In addition, modern techniques make it possible to perform operations through small incisions, which minimizes trauma for the patient and makes it possible to operate even on elderly patients. Radiosurgery methods are widely used to remove small tumors that are located in hard-to-reach places. These technologies make it possible to effectively influence the tumor site with large doses of radiation with almost complete absence of damage to neighboring healthy tissues. The highest precision of the technology is ensured by strict planning of the treatment program using such high-precision diagnostic methods as MRI and CT. The prognosis for choroid papilloma is relatively favorable. With timely and competent treatment, the annual survival rate of patients with this disease reaches 90%, the 5-year survival rate is 81%, and the 10-year survival rate is 77%.
Consequences of choroid plexus cysts
Complicated cystic formations cause specific manifestations:
- Hypertonicity of newborns;
- Neurological symptoms due to compression of brain structures;
- Epilepsy (muscle cramps);
- Slight loss of vision and hearing.
Magnetic resonance imaging will need to distinguish a true vascular cyst from a pseudocyst. The latter type is a variant of the physiological development of the brain, but the anatomical structure when examined by ultrasound resembles a cavity. Magnetic resonance imaging is an accurate study (informativeness is about 96%). The three-dimensional modeling mode will allow you to correctly verify the nosology.
Edwards syndrome can be detected by ultrasound by identifying abnormalities of the limbs and changes in internal organs. Additional diagnostic tests:
- Determination of the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin;
- Blood chemistry;
- Analysis of amniotic fluid.
A special risk group is women aged 32 years and older with hormonal disorders.