How does a child develop?
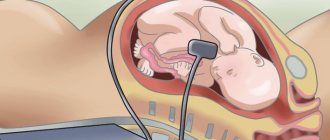
This week, the baby actively continues to grow and gain weight, his height is already about 44 cm, and the weight of his tiny body is approximately 1,800-1,900 g. During this period, the baby is no longer so easy to turn around, he takes up more space, which is why his movements. This week the baby sleeps a lot and therefore moves less, and the amplitude of his movements decreases. The muscles become stronger, so the shocks, although rare, are quite strong and more concentrated. For the mother, the baby's movements can be very sensitive and painful, causing internal organs to suffer. The baby’s blood vessels are already expanding and contracting, their walls are becoming thicker and their tone is higher. Brain cells undergo a process of adhesion. The baby’s skin turns pink, and thanks to the increase in subcutaneous fat, all wrinkles on the body are smoothed out. The hairs on the baby's head become darker and thicker, and the hairs covering the body become less and less. This fluffy hair is called lanugo. At week 33, the baby’s skin is covered with a special lubricant that protects it and ensures an easier birth. The lubricant mostly covers the face, back, folds under the arms, groin and neck.
Increase in basal temperature.
The indicator measured rectally varies depending on the woman’s hormonal background. Basal temperature can indirectly determine both ovulation and pregnancy. In the early stages, the rectal temperature rises, and pregnancy is indicated by the fact that there is no decrease in the value after a few days, as with normal cyclic changes. If this is not your first attempt to find the happiness of motherhood, then you most likely know the rules for measuring basal temperature: the correct value is the one obtained immediately after a night's sleep, without getting out of bed. Stress can affect your test results, so it's a good idea to calm down or take a medication approved by your healthcare provider before going to bed.
How does mom feel?
The uterus of the expectant mother rises higher and higher, to a distance of up to 34 cm from the pubis, and the tummy grows significantly. This is due to the large weight of the baby, amniotic fluid and placenta. At the same time, it is harder for mom to squat and make other movements. Strong and sudden kicks from the baby, as well as an enlarged uterus, can cause pain. But the expectant mother can already determine what exactly the baby pushed her with: his knee or his fist. If the kicks are light, this may indicate that the baby is hiccupping. At this time, the woman is recommended to do light physical activity, which allows for frequent breaks. Hiking or fitness is best. Due to the fact that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on many organs, the mother may experience temporary discomfort, which is not related to any diseases. A high load is placed on the spine, causing pain in the sacrum, lower back and pelvis. A pregnant woman has a liter more circulating blood volume, which has a strong effect on the functioning of the kidneys, oppressing the bladder and causing frequent urination. Sometimes mom can get up up to six times a night. The cause of heaviness in the stomach, heartburn and nausea is the pressure of the uterus on the stomach. In this case, frequent meals in small portions will help alleviate the condition.
Sudden mood swings.
You woke up in a good mood, but a minute later absolutely everything irritates you? This is not a mental disorder. Until hormonal levels stabilize, constantly changing emotions, a sudden transition from negative to positive, can accompany a woman throughout pregnancy. Explain to your loved ones that now you are more sensitive to everything that happens around you. When your hormonal levels return to normal, you will feel better. This usually happens in the second trimester of pregnancy. If emotional problems bother you too much, be sure to ask your doctor to prescribe you a mild sedative that is not contraindicated for pregnant women.
How does mom feel?
This week of pregnancy requires conscientious monitoring of the condition of the expectant mother. This is exactly the period when a woman can feel false contractions. Painful sensations appear in the upper part of the uterus and gradually subside. As pregnancy progresses, contractions become more pronounced. They resemble short muscle contractions lasting from a few seconds to five minutes. In this way, the body prepares for the upcoming birth. This process accompanies every woman’s pregnancy with varying intensity. Experts call this Braxton-Hicks contractions. How can an expectant mother distinguish labor pains from warning signs, especially if she is expecting a baby for the first time?
Let's look at the main differences:
- Preparatory contractions are characterized by a high interval between them, which varies in duration. And prenatal contractions are regular, with a gradually decreasing interval.
- Preparatory contractions may stop immediately after resting or changing the body position of the expectant mother, and labor contractions gradually intensify regardless of the change in position.
- The pain sensations are also different. Labor pains are accompanied by severe pain, which becomes more and more noticeable. Preparatory contractions are characterized by either sharp pain or can be completely painless.
- False contractions can stop with the use of antispasmodics approved by doctors. While such drugs will not have any effect on labor contractions or will be minimized.
- A woman can feel false contractions in various places. This could be the lower abdomen, the side walls of the uterus, or the entire abdomen. Pain during labor may resemble premenstrual pain. Also, pain may begin in the lower back, gradually covering the front of the abdomen.
It is very important for a woman with such symptoms to provide a sense of security; in case of any contractions, the pregnant gynecologist must be informed.
Dizziness, fainting.
Brief loss of consciousness is usually associated with pressure changes. Even if a woman has never lost consciousness before, she should be especially careful. If you feel dizzy, you should provide access to fresh air: ask those nearby to open the window and ventilate the room. To avoid fainting, try to choose loose clothing made from natural materials that is appropriate for the weather. If your job involves physical labor, then you should consider reducing your workload during the day.
How does mom feel?
During this period, the mother has difficulty breathing. This is caused by the growing uterus, which pushes aside the lungs first. The lungs cannot fully expand, making breathing difficult. Also, the enlarged uterus pushes aside the bladder and intestines. This week, almost every pregnant woman feels short of air, has shallow and rapid breathing and a constant desire to take a deep breath. The cause of shortness of breath during this period may be a long walk or climbing stairs, as well as prolonged lying down. A competent alternation of rest and physical activity will help alleviate the condition. The fundus of the uterus rises 35 cm from the pubis and 15 cm from the navel, this is the highest point during the entire period of bearing a baby. This feels like one of the most difficult weeks of pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is actively preparing for the upcoming birth, all ligaments become more extensible and elastic. It can also lead to an increased risk of injury and falls. During this period, doctors do not recommend flying or long trips. If you need to go somewhere, it is important to have a loved one present and to change your position approximately every 15 minutes. This week, mom needs to rest more often. Special physical exercises will be useful to help reduce back pain.
Taste preferences change.
A woman may have an aversion to food that she used to love. Another option is also possible: a sudden craving for foods that you don’t like in taste or smell. Loss of appetite, especially against a background of constant nausea and malaise, as well as constant hunger, are common signs of pregnancy in the early stages. The desire to try something inedible or in an unusual combination is more typical for 4-12 weeks of pregnancy, but there are cases when a woman notices this symptom already at 2-4 weeks. It is quite possible that the desire to taste chalk or eat a sausage sandwich thickly spread with orange jam is the body’s attempts to report a lack of microelements in the body. There is no need to worry ahead of time: carrying a child requires a large amount of resources, so the body tries to prepare in time and collect reserves “for two.”
How does mom feel?
During this period, a pregnant woman feels very tired. The tummy becomes heavier, making it difficult to choose a body position. The baby begins to sink lower, preparing for birth, and the mother begins to breathe easier. But this increases pressure on the bladder, causing more frequent urination. The uterus is located at a distance of 36 cm from the pubis. This is the highest point during the entire pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is being rebuilt, making intensive preparations for childbirth. Hormonal changes cause an increase in hormone levels. The pelvic bones soften under the influence of hormones, trying to make it as easy as possible for the baby to pass through the birth canal. At the same time, contractions intensify and more abundant vaginal discharge appears. A pregnant woman this week needs to listen more to her body and carefully monitor it. If you have nagging pain in the lower abdomen, as well as pain in the lower back, you should pay attention to its duration and frequency. If all indicators are present, you should immediately contact a gynecologist: premature birth is not uncommon this week, so it is important to respond to the body’s signals in a timely manner. Mom should be very careful: do not make sudden movements, control her posture, moderate walks and sitting time. During this period, sleep is disturbed, thus the body also prepares for the baby’s night feedings. This week, mom can fully feel what swelling is. It is necessary to control swelling, which can cause organ dysfunction.
Breast sensitivity increases.
Even a slight touch to the mammary glands can cause pain; some women experience colostrum discharge from the nipples. Later, the breasts swell, enlarge, and the nipples darken. These are some of the signs that pregnancy manifests itself in the early stages. You may notice chest tenderness when moving or playing sports. Try wearing loose underwear that doesn't restrict movement. It is worth stopping active physical activity for a while, replacing it with yoga and stretching. Give preference to clothes made from soft materials that do not cause you discomfort.
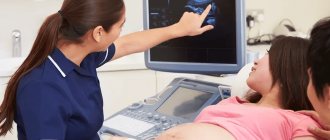
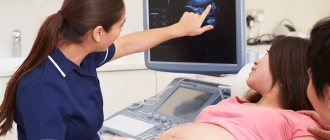
Tests and ultrasound
A planned visit to a gynecologist at the 29th week of pregnancy includes collecting complaints, measuring blood pressure, abdominal circumference and uterine fundal height, as well as body weight. These procedures seem at first glance unnecessary and tedious, but they should not be neglected. Regular doctor's appointments allow timely diagnosis of many complications of pregnancy: inflammatory diseases and gestosis, which is dangerous for mother and child.
In the 3rd trimester, during each visit to the antenatal clinic, cardiotocography is performed - a study that allows you to evaluate the fetal heartbeat. The doctor assesses the child’s condition based on the frequency of contraction of the heart muscle.
An ultrasound at the 29th week of pregnancy is performed when additional diagnostics of the fetal condition is required.
Interesting Facts
| Options | Indications |
| Time from conception | 27 weeks |
| Period by month | 29 weeks |
| What month | 7 |
| Dimensions and weight of the fetus | 385 mm, 1150 g |
| Uterus dimensions | At the middle of the distance between the navel and the xiphoid process, VDM is 27-29 cm |
| Pregnant weight | Gain from the beginning of pregnancy is 8-12 kg; over the last week no more than 400-500 g |
Your baby is the size of
Head of cabbage
385mm Size
1150 g Weight
Perhaps now you are in the sweet anticipation of maternity leave. Hang in there, only one week left! The load on your mother’s body is growing every day; you need a lot of strength and proper rest. What changes should you be prepared for at 29 weeks of pregnancy? Let's look into it in detail.
The appearance of acne.
This symptom is also associated with hormonal changes in the body. Acne can appear even in women who have never suffered from it before. Acne during pregnancy usually disappears when hormonal levels stabilize and no longer bothers the woman. You can often miss this phenomenon, mistaking it for a component of premenstrual syndrome, especially if you have previously been treated for acne. Topical, and especially systemic, retinoids can adversely affect fetal development, so you should stop using these medications if there is a delay.
Toxicosis.
Toxicosis of pregnant women usually appears at 4 or 5 weeks after conception, but nausea and vomiting can begin to bother the expectant mother as early as the first month. Nausea is usually accompanied by weakness, lack of appetite, and headache. These symptoms during pregnancy cause a lot of trouble for the expectant mother, especially if vomiting is repeated and interferes with daily activities. Antiemetics that are not contraindicated for pregnant women are available today at any pharmacy, but you should consult a doctor before using them.
33,34,35,36 weeks of pregnancy: what happens, development of pregnancy and fetus
- home
- Services and prices
- Services and prices
- About Us
- Doctors
- Schedule and appointments
- Reviews
- Doctor training
- Clinic addresses
- Blog
- CIropedia
Week by week 33 - 36 weeks of pregnancy Elena Gevorkova Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow
Week 33
BABY
At the 33rd week, the weight of the fetus is 1800-1900 g, and the body length is 43-44 cm. The amount of subcutaneous fat increases, due to which the folds and wrinkles on the baby’s body are smoothed out, and the skin turns pink. The vellus hairs covering the body of the fetus, called lanugo, become smaller, and the hair on the head darkens and thickens. The baby's skin is covered with a thin layer of cheese-like lubricant, the largest amount of which accumulates in the folds - axillary, cervical, inguinal - as well as on the back of the body and face. Lubricant is a viscous white mass; it is a secretion of the sebaceous glands mixed with skin flakes. Its function is to protect the baby’s skin from damage and facilitate its passage through the birth canal.
By this time, the fetal movements gradually change their usual character - they become more limited and less pronounced in amplitude due to insufficient space.
However, the strength of the movements increases, since by this time the muscular system of the fetus is already sufficiently strengthened. Sharp and strong fetal shocks can be sensitive to the internal organs of a pregnant woman. Depending on the position of the baby, the liver, stomach, bladder, ribs, etc. may “suffer.” By 33 weeks, fetal movements are already sufficiently coordinated. EXPECTANT MOTHER
The height of the uterine fundus from the level of the pubis at this stage is 34 cm. The volume of the abdomen is increased due to the weight of the child, placenta, and amniotic fluid. An increase in uterine pressure and strong fetal thrusts can cause some discomfort in the pregnant woman. Many movements previously available to the expectant mother, such as squats, become limited. Moderate physical activity - walking, fitness, etc. - requires frequent breaks.
A change in the center of gravity increases the load on the spine, which can manifest itself as pain in the lower back, sacrum, and pelvic region. The pressure of the uterus on the stomach can cause or worsen nausea, heartburn, and a feeling of heaviness. An increase of almost 1 liter in the volume of circulating blood in a pregnant woman’s body increases the load on the kidneys, and the growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder. All this can manifest itself as increased urination.
These ailments are usually associated with mechanical pressure of the uterus on surrounding organs; they are not symptoms of the disease and are temporary. And to relieve nausea, heartburn and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, frequent small meals are recommended.
Week 34
BABY
By this time, the weight of the fetus is approximately 2100 g, and the height is 45 cm. The appearance of the baby at this stage is practically indistinguishable from the appearance of a newborn - the body is proportional, the face is without wrinkles and folds. From this period, the cheeks are very pronounced, since, developing the sucking reflex, the fetus often sucks the thumb. This leads to the fact that the baby’s facial muscles, in particular the cheek muscles, are strengthened. The overall muscle mass of the fetus increases, and the bones become denser.
The baby’s internal organs are functioning intensively. During the day, he swallows multiple portions of amniotic fluid. Passing through the gastrointestinal tract, amniotic fluid stimulates the work of the muscle wall. The dense part of the amniotic fluid, which is a suspension of skin flakes, lubricant, vellus hair, is processed by liver and pancreatic enzymes, and the liquid part is intensively excreted by the fetal kidneys.
About 500 ml of amniotic fluid is processed in this way per day.
The production of bile continues, which accumulates in the gallbladder and, as the stomach fills with a suspension of amniotic fluid, enters the lumen of the small intestine. The functional development of the liver and pancreas during the prenatal period does not play a significant role, since the fetus lacks digestion; processes of production of bile and enzymes: lipase, which breaks down fats; trypsin, which breaks down proteins; amylase, which breaks down carbohydrates, etc. - are of a preparatory nature. FUTURE MOTHER
Most pregnant women begin to feel quite intensely false contractions at this stage. Strictly speaking, false or training contractions, also called Braxton-Hicks contractions, can appear after the 20th week of pregnancy: the longer the period, the more frequent and pronounced the contractions. They are episodic contractions of the muscles of the uterus, lasting from a few seconds to 3-5 minutes. Braxton Hicks contractions are not pathological - they are a completely normal process in which the muscles of the uterus prepare for the difficult process of childbirth. This phenomenon is observed with varying degrees of intensity in almost all pregnant women.
Many first-time mothers are concerned about the difference between preparatory contractions and labor contractions.
Here are some differences:
- Contraction frequency. Training contractions do not become more frequent; the intervals between them may vary. Labor contractions are regular, the interval between them is reduced.
- Duration of contractions. Training contractions have different durations, from several seconds to minutes, their duration does not increase over time. Labor contractions tend to lengthen.
- Soreness. Preparatory contractions may not be accompanied by pain at all or may be quite noticeable, even to the point of feeling sharp pain. However, their intensity weakens over time and the pain goes away. Labor contractions are painful and constantly intensifying.
- Localization. Braxton-Hicks contractions can be felt in various places - in the lower part of the uterus, in the area of its fundus, along the side walls, and cover the entire abdomen. Labor contractions begin with a contraction of the lower abdomen, spreading to the front. Often during childbirth, pain in the lower back is felt, and the nature of the pain resembles menstrual pain.
- Connection with body position. Preparatory contractions may disappear after walking or, conversely, resting. Changing your body position can ease the tension in some muscles, which can also reduce the appearance of training contractions. Labor contractions may ease somewhat in a certain position - when bending forward, in a knee-elbow position, etc. - but their frequency and duration will still increase.
- Reaction to taking drugs. The use of antispasmodic drugs - NO-SHPA, BUSCOPANA, PAPAVERINE, etc., approved by the attending physician, can weaken or completely stop false contractions. The effect of antispasmodics on labor pains is minimal.
Any pain or discomfort should be reported to the gynecologist: this will help the expectant mother resolve doubts and cope with anxiety. A sense of security is the best companion of pregnancy.
Week 35
BABY
The body length of the fetus is 46-47 cm, weight - 2200-2300 g. These indicators can vary greatly in the last weeks of pregnancy.
The height and weight of the fetus largely depend on heredity and individual parameters. Starting from 35 weeks, the baby will gain 200-250 g weekly. The fetus occupies almost the entire uterine cavity, its back is rounded, its arms and legs are bent and brought towards the body. The layer of subcutaneous fat increases significantly, which significantly “rounds” the fetal body. Closing the eyelids and contracting the facial muscles changes the baby’s facial expression quite often. The skin of the body becomes pink, smooth, and the amount of cheese-like lubricant begins to decrease. Vellus hair covers certain small areas of the body - shoulders, back. Nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers. FUTURE MOTHER
The fundus of the uterus is 35 cm higher from the pubis, 15 cm from the navel. The uterus reaches such a size that it pushes aside the organs located below - the bladder, intestines, but also those located above the diaphragm, in particular the lungs. The growing uterus does not allow the lungs to expand, respiratory movements are limited, which is manifested by difficulty breathing. Almost all pregnant women, to one degree or another, experience a feeling of shortness of breath - a feeling of lack of air, frequent and shallow breathing, a desire to take a deep breath. As a rule, these sensations occur at 28 weeks and reach their peak at 35-36 weeks. After 37 weeks of pregnancy, the abdomen droops, which makes breathing much easier.
Shortness of breath during pregnancy is associated not only with the mechanical pressure of the uterus on the diaphragm, but also with the relaxing effect of hormones on the muscles of the bronchi and lungs. Most often it is provoked by physical activity - climbing stairs, long walks, etc. However, it is not uncommon for shortness of breath to occur at rest, especially when lying down. Both prolonged exposure to a horizontal position and excessive physical activity can contribute to increased shortness of breath. To alleviate her condition, the expectant mother needs to be rational about her daily routine - it is reasonable to alternate between rest and physical activity. It is important to monitor your posture, since slouching aggravates shortness of breath, reducing the already insufficient lung capacity. If shortness of breath is accompanied by blue lips or nails, sensations of pain behind the sternum, darkening before the eyes, nausea or vomiting, fainting, then you should urgently consult a doctor.
Week 36
BABY
The growth of the fetus by this time is approximately 47-48 cm, and the weight is about 2300-2500 g. The fetus enters a period of intensive preparation for childbirth. Each of the organs is already functionally mature enough to ensure the viability of the fetus. 36 weeks is the beginning of the preparatory journey, and the upcoming weeks of pregnancy are designed to finally shape the baby’s readiness for extrauterine life.
By 36 weeks, the fetus occupies its final position in the uterus. As a rule, this is a longitudinal position, occipital presentation - in this case, the fetus is positioned head down, facing the mother's back. This is the most comfortable position that ensures the greatest safety for the baby during childbirth. More rare is breech presentation, a condition in which the buttocks and legs of the fetus are located at the bottom of the uterus. This is a relative indication for operative delivery. The final decision on caesarean section or spontaneous childbirth is made by doctors in each case individually.
A change in the position of the fetus in the uterus is possible, but this does not happen often, since at this stage the fetus occupies almost all the free space in the uterus, which significantly limits its motor activity.
As a rule, if a change in the position of the fetus occurs, it is only from the pelvic to the head. The opposite cases - the transition of the baby from the head to the pelvic position - are practically impossible, since the fetal head is heavier than the buttocks and occupies a definitive longitudinal position, by analogy with a float in water, the heavy part of which always outweighs. FUTURE MOTHER
The height of the uterus is 36 cm, the volume of the abdomen is maximized, the bottom reaches the costal arches. At this stage, the pregnant woman’s body also begins its journey of preparation for the upcoming birth. Changes begin with hormonal changes: a woman’s level of special hormones – oxytocin and prostaglandins – increases slightly. These active substances play a vital role in the process of preparation for childbirth and directly during it. A slight increase in their level from 36-37 weeks of pregnancy leads to increased Braxton-Hicks contractions, increased frequency of urination and defecation, and the appearance of more abundant mucous discharge from the vagina.