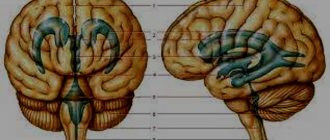
Tumors of the posterior cranial fossa are pathological neoplasms localized in the region of such parts of the brain as the cerebellum, medulla oblongata, lateral cistern, vermis, and fourth ventricle. In these parts of the central nervous system, various neoplasms can develop, originating from cells of the nervous tissue. Thus, among tumors of the posterior cranial fossa one can find meningiomas, acoustic neuromas, hemangioblastomas, medulloblastomas, astrocytomas, and gliomas. In most cases, neoplasms of this localization are detected in early childhood. Most of them are benign in nature and are characterized by slow growth. Cases of malignancy of neoplasms of this type are rare. In elderly patients, neoplasms of the posterior cranial fossa, as a rule, are foci of secondary metastatic growth.
Symptoms of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa
The clinical picture of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa is determined by the degree of damage to the part of the brain that is involved in the pathological process. Most often, patients with this diagnosis develop the following pathological symptoms:
- causeless nausea and vomiting;
- painful headaches that cannot be relieved by taking painkillers;
- hearing loss;
- visual impairment;
- numbness or pain in the face and neck;
- paresis of the area of innervation of the cranial nerves;
- weakness of facial muscles;
- dizziness;
- gait disturbance;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- facial asymmetry;
- swallowing disorder.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
Diagnostics
The similarity of symptoms of neurological diseases requires an accurate diagnosis. Clinical and instrumental research methods are used to differentiate pathology from abscess, stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and encephalitis.
Laboratory methods
To determine the cause of the disease, the following are studied:
- tests for clotting, cholesterol levels;
- tests for neuroinfection (meningitis, arachnoiditis, encephalitis);
- tests for autoimmune disease (multiple sclerosis, Guyon-Baré syndrome).
Blood clotting above normal indicates possible thrombosis of blood vessels. Cholesterol plaques impede blood circulation, which causes disruption of brain activity.
Meningitis of various origins is characterized by high fever, vomiting, and headache due to increased intracranial pressure. The pathogen affects the arachnoid and soft membrane. A barrier to the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is formed.
Autoimmune diseases of the nervous system cause paresis of the limbs, impaired sensitivity, and coordination of movements. To determine the course of treatment, it is necessary to differentiate these pathologies from cysts.
Instruments for examination for the presence of cysts
To clarify the diagnosis, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are performed to determine the location of the arachnoid cyst.
Complications after removal of a dental cyst
Compliance with the rules and recommendations during the rehabilitation period after removal of a dental cyst helps prevent the development of a number of complications.
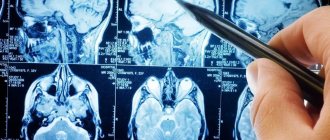
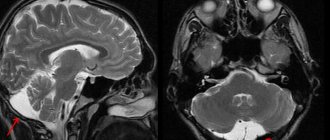
MRI with a contrast agent gives a picture of the size, location, and nature of the tumor (benign or malignant).
Additionally, the following is carried out:
- electroencephalogram;
- rheoencephalography;
- electrocardiogram;
- Doppler scanning of the vessels of the neck and head.
Problems with blood circulation negatively affect brain activity, since in the place of dying cells of the gray matter, cavities are formed that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Diagnosis of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa in Israel
A qualitative examination of patients with signs of brain tumors is necessary to make a correct diagnosis, determine the location and characteristics of tumor growth, as well as determine the tactics of its treatment. To obtain the most complete information about such neoplasms as PCF tumors, advanced diagnostic technologies are used.
- X-ray – a simple X-ray examination makes it possible to determine the presence of signs of damage to the bone tissue of the skull.
- CT is a modern X-ray examination that allows highly accurate visualization of neoplasms of the central nervous system.
- MRI – performing this diagnostic procedure makes it possible to obtain the maximum amount of information about the nature of pathological changes in soft tissues.
- Spinal tap - this procedure is aimed at obtaining samples of cerebrospinal fluid. Laboratory study of cerebrospinal fluid makes it possible to assess the state of the central nervous system and determine the extent of the pathological process.
- EEG - electroencephalographic study is performed to assess the functional state of the central nervous system.
- Audiometry – used to examine patients with signs of acoustic neuroma.
- Genetic testing is performed if the patient has signs of a hereditary disease such as neurofibromatosis.
- Biopsy - in some cases, histological examination of tumor tissue samples is required to make a diagnosis and determine the extent of the pathological process. For this purpose, a surgical procedure is performed to obtain samples of tumor tissue.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
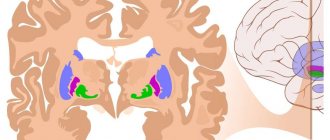
What is an arachnoid cyst
The human brain has 3 membranes: hard (skull), arachnoid (arachnoid) and soft. A cyst is a pathological cavity filled with liquid contents.
An arachnoid cyst is a benign spherical neoplasm in the arachnoid membrane, filled with a liquid substance. Its location is between the vascular (soft) membrane and the bones of the skull or deep in the gray matter.
The arachnoid membrane at the site of cyst formation forms a gap that is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Liquor is a liquid substance, thanks to which the brain and spinal cord are provided with nutrients and protected from external influences.
Cerebrospinal fluid must constantly circulate. If the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted due to a neoplasm (cyst), its physicochemical properties change, which can affect the state of health.
Treatment of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa in Israel
Treatment of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa is best left to experienced neurosurgeons. The use of modern surgical techniques and the experience of a specialist makes it possible to completely remove the tumor without damaging the brain tissue.
- Surgical treatment - the only radical method of combating neoplasms of the posterior cranial fossa is surgery. Today, Israeli neurosurgeons use modern technologies for neuronavigation and removal of tumors of the central nervous system, which make surgical treatment as safe as possible. Thanks to microsurgical instruments and special optical systems, the surgeon performs all actions with maximum precision. This allows you to avoid damage to healthy brain tissue and the development of dangerous complications.
- Radiation therapy - ionizing radiation energy can be used to combat neoplasms of the posterior cranial fossa before and after surgery. In the preoperative period, radiation therapy helps prepare the tumor for surgical removal and reduce its size. In the postoperative period, radiation therapy sessions are used to reduce the likelihood of disease relapses.
- A modern type of radiation therapy is a technique called radiosurgery. This method of fighting tumors is based on the use of targeted energy of ionizing radiation, acting precisely on the tumor tissue. Thanks to the precise determination of the coordinates of the location of the tumor, a large number of radioactive rays are directed precisely at the tumor, without damaging healthy brain tissue. Radiosurgery is used to combat small tumors, while eliminating the need for surgical treatment.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
Causes and symptoms
Arachnoid cysts of the posterior cranial fossa can be primary or secondary:
Primary - formed during pregnancy. When exposed to negative factors, developmental disorders occur and a cyst of the posterior cranial fossa may begin to form in the fetus.
Negative impacts include:
- the presence of bad habits in the mother;
- taking medications;
- inconsistent with the doctor or interruption of dosage;
- irradiation;
- injury during childbirth.
Symptoms may appear immediately after birth. And a cyst in a newborn leads to serious disorders: developmental delay, deterioration of visual and auditory function.
However, in most babies, the formation resolves on its own.
Symptoms of cyst formation in a child:
- General weakness in the limbs.
- Swelling of the fontanel.
- Anxiety, poor sleep, crying for no reason.
- Lack of focus.
- Spitting up like a fountain after feeding.
- Cramps.
- Discoordination.
Secondary - the acquired form is a consequence of serious inflammatory diseases of the brain and spinal cord, Marfan's disease. It is mostly diagnosed in adults.
It develops due to:
- TBI;
- meningoencephalitis;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- ischemic stroke.
The symptoms in the first and second cases are approximately the same:
- Increase in intracranial pressure.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Cramps.
Depending on the size, symptoms may increase:
- Impaired coordination and balance.
- The appearance of hallucinations.
- Feeling of heaviness in the head.
- Feeling of pressure on the eyeballs.
- Speech disorders.
- Loss of consciousness.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the listed reasons for the formation of a cyst in the posterior cranial fossa can stimulate the growth of an existing tumor.
Identification of pathology.
The main diagnostic method, which allows you to obtain all the necessary information about the tumor, is MRI. If the size is small and there are no complaints from the patient, no measures can be taken.
It is mandatory to constantly monitor the dynamics of the condition; in case of cystic enlargement, surgical intervention may be required.
Applicable:
- Laboratory blood tests to determine cholesterol levels and blood clotting, determine infections and inflammation.
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels.
- CT scan.
- Angiographic examination using a contrast agent. ( The method allows you to accurately distinguish benign from malignant formations. )
Additionally, the functioning of the heart is examined, since one of the causes of circulatory disorders in the brain may be pathologies of the cardiovascular system. It is also important to constantly monitor blood pressure.
Methods of therapy.
Treatment is not necessary in all cases of detection of a cerebral cyst, but when there is rapid growth and pressure on the surrounding brain tissue, which leads to the development of various disorders, drug or surgical treatment methods can be used.
If there is a retrocerebellar cyst in the posterior cranial fossa, drug treatment includes:
- Antiviral agents.
- Immunomodulators.
- Preparations for resorption of adhesions.
- Medicines aimed at improving blood supply.
Caripatin is used to eliminate adhesions. Actovegin is used to normalize metabolic processes.
If symptoms increase and the cyst in the posterior cranial fossa increases in size, surgery is prescribed.
The least risky treatment method is endoscopy - This is a minimally invasive technique that involves creating a small hole in the skull through which the cyst is removed. The method is good, but if the tumor is located in a hard-to-reach location, it cannot be used.
During bypass surgery, a special tube is inserted into the cyst, through which fluid flows into the abdominal cavity. When using this method, there is a possibility of infection and clogging of the shunt.
Trepanation is the most effective method, as it allows you to completely remove the formation, regardless of the area in which it is localized.
Advantages of the Israeli Oncology Center
Treatment of neoplasms of the posterior cranial fossa in Israeli clinics is highly effective for the following reasons:
- consultation with experienced specialists in the field of oncological diseases of the central nervous system;
- conducting a high-quality survey using advanced technologies;
- individual approach when leaving the therapy program;
- modern radiation therapy;
- safe and effective surgical treatment.
Tumors of the posterior cranial fossa require timely and high-quality treatment. The best solution when making such a diagnosis would be to contact highly qualified Israeli specialists.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
Treatment
Therapy depends on the size of the cyst, its growth rate and symptoms.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Conservative treatment includes taking medications that affect the immune system, blood circulation, and suppress infections. It is used for frozen cysts, aimed at eliminating the root causes of their formation.
Surgical intervention is necessary if there is a rapid increase in the size of the cerebrospinal fluid cavity, increasing disturbances in brain activity, increased intracranial pressure, or the threat of cyst rupture. At the same time, a therapeutic set of measures is carried out to relieve factors affecting the cystic process.
Surgical methods for removing a tumor are trephination, drainage, shunting, and endoscopy.
Trepanation
The contents of the cavity are removed through an opening in the dura. The disadvantage of this method is the high risk of complications due to trauma to adjacent tissues and infection.
Drainage
Using a needle puncture, a drainage tube is installed, through which the contents of the cyst are removed. Due to the problem of ensuring the sterility of the procedure, infection is possible.
Bypass surgery
A special shunt removes the contents into the abdominal cavity, where it decomposes.
Endoscopy
Used to remove small cavities through micro-punctures in the hard shell. Does not injure adjacent brain tissue, excludes infection, and does not cause complications.
Causes of pathology
The prerequisites for the emergence of education may be different. More often the problem occurs under the influence of radiation and unfavorable external factors. The formation may be affected by:
- inflammatory processes of the lining of the brain,
- changes in nerve fibers
- mechanical injuries,
- absence of part of the corpus callosum.
The reasons have not been fully identified. It is assumed that teratogenic factors that affect a woman during pregnancy play a role.
Prevention
To prevent a congenital cyst, a pregnant woman must get rid of bad habits. During gestation, avoid crowded places to avoid contracting meningitis. A newborn with symptoms of neurological abnormalities should undergo an ultrasound scan of the brain.
If there is a frozen tumor, it is necessary to be under the supervision of a neurologist. Her condition is confirmed by an MRI examination once a year.
Prevention of secondary cysts - monitoring cholesterol levels, blood pressure, maintaining rest and diet during TBI, treatment of infectious and autoimmune diseases.
An arachnoid liquor cyst requires observation if it is small in size and does not increase in size. If it progresses, complex therapy or surgical removal is necessary.