Damage to the abducens nerve of the eye is one of the ophthalmological pathologies that have much in common with neurological disorders. With this disease, the movements of the eyeball are distorted. It often happens that it does not move, especially when you need to look to the right. Let's tell you more about this disease and its treatment.
In this article
- Pathogenesis of the disease
- Causes of abducens neuropathy
- Symptoms of pathology
- Diagnosis of abducens neuropathy
- Treatment of abducens neuropathy
Pathogenesis of the disease
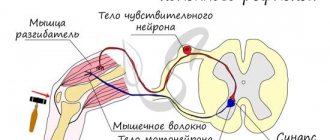
The abducens nerve of the eye is included in the category of fibers of the central nervous system. Its main function is to ensure the mobility of the visual organs. The nerve is responsible for the movements of the eyeballs, eyelids, dilation and constriction of the pupil. With neuropathy of the abducens nerve, a malfunction of the extraocular muscles occurs, and communication with the central nervous system of the body is disrupted. Thanks to the work of the abducens nerve, a person can look around without turning his head. Impaired functioning leads to ophthalmological pathologies, the most common of which is strabismus - strabismus.
Lesions of the abducens nerve cause the eyeball to not move evenly in different directions. Problems arise when the pupil moves in the opposite direction from the bridge of the nose. The mobility of the rectus lateral muscle of the eye is impaired. This leads to the development of a converging form of heterotropia, as the intrinsic muscle “pulls” the eyeball towards itself. People who are faced with this problem suffer from dizziness, diplopia - double image, and lose orientation in space.
Strabismus is not the only problem that a person with abducens neuropathy may face. This pathology is especially dangerous in childhood. It often causes the development of amblyopia. This condition is often called "lazy eye." The disease occurs due to the fact that the organs of vision do not participate in the visual process at the same time. Against the background of neuropathy, paresis often develops - peripheral paralysis. This disease is included in the neurological group. It is characterized by damage to the facial nerve, impaired facial expressions, and disruptions in the production of tear fluid.
Does your clinic perform surgery for paresis of the external rectus muscle of the eye?
To clarify the possibility of performing an operation for paresis of the eye muscle, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnostic examination of the visual system with consultation of an ophthalmologist. This is a comprehensive study of all parameters of the visual system. After determining the indications for surgical intervention, you must undergo a consultation with an anesthesiologist, during which he will prescribe the necessary tests and studies for the operation individually based on your health condition. The cost of a consultation with an anesthesiologist is 1300 rubles.Our clinic has the opportunity to undergo the necessary clinical tests, the so-called Operational Screen (general urine test, general and biochemical blood test, blood test for infections - hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, RW). The cost of the Operational screen is 3150 rubles. On the same day we can take an electrocardiogram from you, its cost is 500 rubles. Test results will be ready in 2-4 days. All you have to do is have fluorography (no older than 6 months) at the clinic at your place of residence or at any other medical center.
As soon as the tests and fluorogram are ready, based on them you will need to obtain a physician’s opinion. A consultation with a therapist can also be done either in our clinic (its cost is 1,300 rubles), or in a clinic at your place of residence (free of charge) or in any other medical center. When the tests are ready (no older than 10 days) and the conclusion from the therapist, you call us and make an appointment for a preoperative consultation with an anesthesiologist and ophthalmologist on the same day. These consultations at our clinic are free. If the tests are in order, then after the examination the anesthesiologist includes the patient in the operation plan on the next surgical day - the doctor and the patient first agree on a convenient date for the operation. At the moment, the wait for surgery, provided we have good tests, does not take more than one week. On the day of preoperative consultations, we conclude a contract with the patient for surgical intervention and pre-pay for the operation. To do this, it is necessary to make a deposit for the operation in the amount of at least 10% of the cost of the operation (or, if for some reason it is more convenient for the patient, the total amount at once). Operations in our clinic are performed personally by the head physician of the clinic, Boris Vitalievich Romanenko, Candidate of Medical Sciences. Sciences, ophthalmic surgeon with more than 25 years of medical experience. The cost of surgical treatment on one muscle is 16,000 rubles, on two muscles 25,000 rubles. After surgery, you will be enrolled in a free post-op follow-up program for four weeks. The first examination must be carried out by an ophthalmic surgeon the next day after the operation. Next, the doctor prescribes the frequency of postoperative consultations based on the individual condition of the patient.
What else is important? For diagnosis, you need to: 1) take with you the medical documents you have on hand about previous examinations (if any), so that the doctor can familiarize yourself with it (it is very important to have dynamic observation data); 2) take glasses/information about contact lenses if you use them; 3) if you wear contact lenses, you must remove them at least 30 minutes before your appointment. Diagnostics of the visual system is carried out on a dilated pupil, so we advise you not to come for diagnostics while driving your own vehicle, and also not to plan to read, write or work on a computer after the examination, because near vision will be blurry. This effect will last for 3-5 hours, perhaps a little more. It is also advisable to have someone meet you after the examination, when your vision is reduced due to pupil dilation. Even in cloudy weather, it is better to take sunglasses with you to reduce photophobia, so that you will be comfortable outside when returning after the examination.
Causes of abducens neuropathy
The disease rarely develops on its own. It is usually a consequence of other diseases. Most often, neuropathy of the abducens nerve occurs against the background of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, after traumatic brain injury and neurosurgical operations. Much less often, the disease is congenital. Cases of a hereditary form of pathology are not excluded, but they are not so common in medical practice. Doctors consider the main causes of the development of abducens nerve neuropathy
- endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism);
- neurological pathologies (osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, multiple sclerosis, stroke);
- complications of infectious diseases (encephalitis, diphtheria, meningitis);
- intoxication of the body (poisoning with ethyl alcohol, chemicals, alcohol);
- chronic arterial pathologies (atherosclerosis, arteritis, phlebitis);
- cardiovascular diseases (varicose veins, arrhythmia, angina).
Doctors cannot always immediately determine what exactly caused the development of neuropathy of the abducens nerve of the eye. Diagnosis of this disease is often carried out by several specialists simultaneously, including: neurologists, cardiologists, endocrinologists, and traumatologists.
The disease is easier to detect in children than in adults. One of the causes of abducens neuropathy is hydrocephalus. This disease allows doctors to immediately carry out procedures that will allow them to diagnose the pathology.
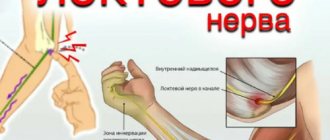
Facial nerve paresis - symptoms and treatment
Paresis of the facial nerve is a polyetiological pathological condition, which is manifested by weakness of the facial muscles innervated by the facial nerve. It occurs at different ages, both in adults and children.
Causes of facial muscle weakness:[4]
1. Causes due to damage to the central motor neuron:
- stroke (ischemic - 85%, hemorrhagic - 15%);
- brain tumors (metastatic or primary, localized in the hemispheres of the brain or its stem);
- brain abscess;
2. Causes due to damage to the peripheral motor neuron:
- Bell's palsy;
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (may be HIV-associated);
- infection caused by the herpes simplex virus;
- vasculitis;
- sarcoidosis, Behçet's disease, periarteritis nodosa, Sjögren's syndrome, syphilis;
- meningitis: bacterial (pneumococcus, meningococcus, Haemophilus influenza, tuberculosis, borreliosis, syphilis, fungal infections);
- temporal bone fracture;
- temporal bone tumors: metastatic, invasive meningioma;
- middle ear infections and tumors;
- tumors or infections of the parotid gland;
- traumatic injuries to the face;
- internal rupture of the carotid artery;
- effect of drugs (chemotherapeutic agents);
- consequences of installing a cochlear implant;
3. Diseases that affect neuromuscular synapses:
- myasthenia gravis;
- botulism;
4. Diseases that affect the facial muscles:
- muscular dystrophy;
- myopathies.
Of the most common causes, idiopathic neuropathy of the facial nerve (Bell's palsy) is detected in 2/3 of cases of paresis of the facial muscles. Infectious lesions of the nerve by the herpes zoster virus can occur in Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Among other infections, neuropathy of the facial nerve can occur with Lyme borreliosis and mumps. In the pontine form of polio, the motor nucleus of the facial nerve may be affected. In addition, damage to the facial nerve can occur with many systemic infections (syphilis, tuberculosis, HIV infection and others). With Guillain-Barré syndrome, paresis of the facial muscles is included in the clinical picture of the disease. Many authors consider bilateral neuropathy of the facial nerve as an erased form of this syndrome.[2][6] Involvement of the facial nerve can also occur in systemic connective tissue diseases (nodous periarteritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome and others), as well as sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, etc.
Inflammatory processes in the middle ear can spread to the facial nerve. Recurrent neuropathy of the facial nerve in young people may be a manifestation of Melkerson-Rossolimo-Rosenthal syndrome, which is hereditary and localized in the 9p14 gene.[6][9]
Other causes include a tumor process, for example, damage to the facial nerve with acoustic neuroma, carcinomatosis of the meninges, arachnoid epithelioma of the base of the skull and others. Traumatic lesions occur with fractures of the base of the skull. Nerve damage can also occur after operations on the middle ear, temporal bone pyramid, and salivary gland.
Metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus can also manifest themselves by involving the facial nerve with a complex mechanism characteristic of diabetic neuropathies. In older patients, damage to the facial nerve can occur with hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis and other angiopathy, when small vessels supplying the nerves are involved in the process.
Paresis of the facial muscles can also develop with supranuclear damage to the corticonuclear pathways during focal processes in the hemispheres and brain stem above the nucleus of the facial nerve. The so-called “central paresis of the facial nerve” occurs. In rare cases, other causes of facial muscle paresis are possible (for example, myasthenia gravis, facial forms of myopathies, etc.).
Symptoms of pathology
The disorders that occur in the human body with this pathology affect various areas. The extent of optic nerve damage may also vary from patient to patient. Much depends on the immune system and the general condition of the body. Sometimes it happens that neuropathy affects the oculomotor nerve completely. In some cases, a partial disruption of its functions occurs. Therefore, it is very important for the doctor to analyze in detail the symptoms, which can be varied. The main signs of the disease include:
- drooping eyelid;
- pain in the eyes;
- immobility of the eyeball;
- decreased visual acuity;
- dilated pupils;
- diplopia.
A common consequence of abducens neuropathy is heterotropia. Typically, the patient develops convergent strabismus. More often this occurs in advanced forms of the pathology. Some people complain of high blood pressure, which is often due to problems with the brain. Headaches are another common symptom of this disease. It often happens that patients do not pay attention to the malaise and associate it with prolonged visual work.
Diagnosis of abducens neuropathy
The level of development of medical technologies does not cause problems with the diagnosis of pathology. Abducens neuropathy does not occur overnight. Its development occurs gradually. Diagnosis of the disease is usually carried out not only by an ophthalmologist, but also by a neurologist. First of all, the doctor interviews the patient, collects a detailed history, and inquires about the presence of other diseases.
The first thing the doctor must do is to determine the cause of the neuropathy. Usually, an ophthalmoscopy is performed by an ophthalmologist for this purpose. This procedure allows you to analyze in detail the condition of the fundus. Ophthalmoscopy is performed to diagnose retinal breaks, identify thinned areas of the eye nerve, and analyze the condition of the fundus vessels. To carry out the procedure, oculists use an ophthalmoscope or fundus lenses.
If neuropathy of the abducens ophthalmic nerve is suspected, doctors often prescribe angiography of the ocular vessels to patients. Using a fluorescent dye and a special camera, the doctor takes a series of pictures called angiograms. They depict the vessels of the retina. Angiography allows you to identify pathologies of the optic nerve, a predisposition to blockage of blood vessels, and inflammatory processes occurring in the tissues of the eyeball.
If the patient's condition is severe, doctors may recommend magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography. This study allows you to obtain accurate data on the condition of the tissues and blood vessels of the eyeball. MRI and SCT diagnostics can be performed on adults and children. The list of contraindications to these procedures is quite small, which is why doctors often prescribe these studies to their patients.
Treatment of abducens neuropathy
Treatment of pathology largely depends on the causes of its occurrence. The basis of treatment for this disease is strengthening the muscles of the eyeball. This allows you to activate blood flow. For this purpose, ophthalmologists prescribe eye drops, including:
- "Taufon";
- "Irifrin";
- "Emoxipin";
- "Vita-Yodurol";
- "Visiomax".
If pain occurs, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- "Tegretol";
- "Finlepsin";
- "Amelotex";
- "Dexalgin";
- "Baklosan";
- "Rekoksa";
- "Timonil."
These drugs have both an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, relieve muscle spasms, and reduce the excitability of nerve fibers. Any medications must be prescribed by a doctor. He will select a maintenance daily dose and frequency of administration.
Physiotherapy procedures, such as electrophoresis, have a good effect. To carry it out, doctors use the drug Neuromidin. It improves and stimulates impulse conduction in the nervous system. Treatment of neuropathy often includes wearing occlusive dressings and training glasses. In pediatric therapy, ophthalmologists often use stereo images, which they offer patients to view on a computer monitor.
It is very important to keep the muscles of the eyeball toned. To do this, doctors recommend that patients perform eye exercises. There are special complexes that are aimed at treating abducens nerve neuropathy. Most of them include exercises such as closing your eyes, alternate winking, and moving your eyes to the right side.
Treatment of optic neuritis
If inflammation covers the optic nerve, then treatment of ocular neuritis is most often carried out with steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If they are ineffective, the neurologist may prescribe plasmapheresis, immunoglobulins, and vitamin B12. Sometimes decreased vision can be a manifestation of multiple sclerosis, a chronic demyelinating disease. This requires special treatment.
If the disease is trigeminal neuritis, in the initial stages anticonvulsants, antispasmodics, and physiotherapy are used. If they do not help and the pain persists, the question of surgical intervention arises. There are different types of operations - they all involve the destruction of nerve fibers, as a result of which the transmission of pain impulses to the brain stops.
A neurologist and an ophthalmologist are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of these diseases. The neurological center of the International Clinic Medica24 employs experienced specialists who adhere to the standards developed by experts. And the coordinating doctor will help you get an appointment with the right doctor and receive the most effective medical care.
In any case, treatment of neuritis should be started as early as possible - in this case the prognosis will be better. And in order for treatment to be effective, it is first necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and understand the causes of the disease.