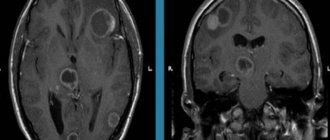
A brain lipoma is a tumor consisting of adipose tissue and is localized in the brain under the frontal cortex. The common name for lipoma is wen. The cavity of the formation is filled with a fatty substance located in the subcutaneous capsule. The size of the wen reaches several millimeters at an early stage of development and five centimeters at a late stage.
This pathology is characterized by painlessness, mobility, slow growth and a latent form of development, due to which the lipoma cannot be detected independently at the initial stage of the disease. Gender, age and body weight are not determining factors in the occurrence of intracranial wen. The ICD-10 code D17 defines a wen as a benign neoplasm. Despite this, the disease can transform into a malignant pathology.
Types of intracranial lipoma
There are a number of types of brain lipoma with characteristic features and different locations in the head.
- Interhemispheric lipoma forms in the callosal tissue of the brain. The most common form of wen is multiple. The tumor interferes with the normal functioning of the cerebellum and provokes disturbances in human behavior and cognitive functions. Wen provokes the occurrence of massive mental disorders, affecting both hemispheres of the brain. Against the background of the disorder, the appearance of hallucinations, memory disorders, and even progressive dementia is observed.
Brain lipoma
- A lipoma of the interhemispheric fissure of the brain is discovered by chance during a full profile examination of the human body, since it is secretive at the initial stage of development. Most people can live with a brain tumor for many years and be unaware of the pathology. Increasing in size, the lipoma interferes with normal blood circulation in the intracranial area, which is fraught with frequent loss of consciousness, dizziness, nausea and headaches. The mutated tissue of the wen adversely affects the central region of the brain, causing visual and auditory hallucinations, behavioral disturbances and motor dysfunction. The fatty tissue puts pressure on the central nervous system, disrupting the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The human brain is considered the most dangerous place to localize a wen, as it causes mental disorders and, spreading to the pituitary gland, can lead to paralysis.
- The pericallosal tumor does not affect the corpus callosum and is localized nearby. The pathology is characterized by large size and rapid growth. This type of pathology is recognized as congenital.
- A spinal cord tumor is a neoplasm that is localized in the spine and has the ability to grow deep into the spinal canal. The wen is soft and elastic to the touch. The disease is easily diagnosed by palpation. Most often the disease occurs in newborns. Spinal cord fatty tissues have three types: intradural, filum terminale and lipomyelomeningocele. The pathology of the filum terminale consists of a fatty consistency and is located in the upper region of the intergluteal fold. The main symptom of this disease is the appearance of a skin growth over the buttocks. Skin pathology does not have hair. Wen of the filum terminale is considered a rare phenomenon and occurs in only 5% of the population, mainly in children. Spinal cord adipose tissue occurs as a result of traumatic brain injury, hereditary predisposition, pathological changes in surrounding tissues and diseases of the internal secretion of glands and diabetes mellitus. The pathology can be congenital or acquired. In a child, the first symptoms appear as they grow up in the form of headaches, pelvic dysfunction, pain and compression in the area where the pathology occurs.
Spinal cord lipoma
- Lipoma of the falx cerebri, or Falx's wen, is a capsule filled with fatty fluid, which is located in the area of the frontal lobe of the skull. This type of wen causes frequent headaches, motor dysfunction and involuntary twitching of the limbs. The size of Falx lipoma can reach five centimeters in diameter. The first symptom of the presence of a falx lipoma is behavioral disturbances in a child, which is caused by the localization of the tumor.
- Lipomas of the corpus callosum of the brain spread to the subcortical formations and adjacent parts of the cerebral cortex, which complicates the timely diagnosis of primary symptoms. Location: frontal, temporal and occipital regions of the skull. Located in the frontal lobe, the tumor provokes the occurrence of apathy, lethargy, dysarthria, early pelvic disorders and bilateral motor disorders. Lipoma of the occipital lobe does not have a negative effect on the human mind, but sensory and psychosensory disorders are noticed. The fatty tissue located in the temporal lobe provokes memory impairment and impairs the quality of speech. Any type of lipoma of the corpus callosum is accompanied by the occurrence of mental disorders.
- Intracranial quadrigeminal lipoma is a congenital pathology of low density, located in the occipital region. This phenomenon occurs in adults and children. The pathology is characterized by slow growth. The first symptoms manifest themselves in impaired functioning of the respiratory organs, decreased mobility of the limbs and the occurrence of regular headaches. The localization of this pathology provokes visual impairment.
- A calcified lipoma has a capsule consisting not only of adipose tissue, but also of calcium. Pathology of this type can form necrosis of the corpus callosum.
- Interhemispheric tumor occurs as a result of underdevelopment of the corpus callosum and occurs mainly in children. Lipoma of this type is considered congenital.
Brain lipoma in section
- Fibrolipoma is a congenital pathology of the spinal cord. The disease is characterized by fatty transformation, thickening, shortening and loss of elasticity of the dorsal filament. Most often occurs in children during progressive growth and development - from 4 to 18 years. The greatest growth of the tumor occurs in the first year of a child’s life - the size can reach 24 centimeters in diameter. During a general examination of the skin, 30% of hidden skin abnormalities are detected. Symptoms of fibrolipoma include pain in the lumbar region and thoracic spine, functional disorders of the pelvic organs, the occurrence of meningitis, hair growth in the area where the pathology appears and pain in the lower extremities during physical activity.
Clinical picture
The tumor does not produce symptoms for many years. However, its gradual growth presses and pushes apart the surrounding brain structures in the unchanged volume of the cranium. As a rule, they easily adapt to this pressure, since a lipoma is a formation of soft consistency.
But if it reaches large sizes, then neighboring structures can no longer function normally. This becomes the cause of the first complaints of patients, as well as objective symptoms.
Symptoms common to brain tumor pathology
General symptoms consist of signs of increased pressure in the cranial cavity and focal symptoms.
The type of focal symptom depends on the location of the wen (gap between the hemispheres, quadrigeminal, falx).
Liqueur hypertension (hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome) manifests:
- general symptoms (complaints of dizziness, increasing cephalalgia in the morning, nausea, vomiting);
- autonomic dysfunction (sudden changes in blood pressure, slight tremors of the limbs, loss or suppression of appetite, intestinal dysfunction);
- movement disorders (obsessive movements, attacks of epileptic seizures);
- mental disorders (decreased memory, attention function, difficulty falling asleep, sleep duration at night, increased irritability, slow reactions, apathy).
Symptoms depending on the location of the tumor
The clinical picture differs depending on the location of the lipoma:
- an interhemispheric lipoma (pericallosal) can penetrate into the 3rd ventricle (located under the callous body), as well as into the paired lateral ones. The spaces of the ventricles of the brain contain cerebrospinal fluid, so when they are damaged, symptoms of high pressure in the cranial cavity, as well as signs of hypothalamic insufficiency, vary. Patients complain of hearing continuous ringing or knocking, seeing a glow (halo) over objects, and making uncontrolled movements of their limbs.
- Due to its localization, lipoma of the interhemispheric fissure Its presence is manifested by a severe decrease in vision, hearing, and frequent and sharp fluctuations in blood pressure. Intense pain, insomnia, weakness, and poor memory constitute the range of complaints of patients.
- Falx lipoma becomes the causative factor of persistent cephalalgia in the forehead. Patients feel tightness, a lump in the throat, tremors of the left arm and leg.
- A fatty tumor of the frontal lobe always causes sudden changes in the psyche and dysfunction of vital centers.
- The lipoma, located near the epiphysis , blocks the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the 3rd ventricle as it grows. The result is the formation of pronounced hydrocephalus.
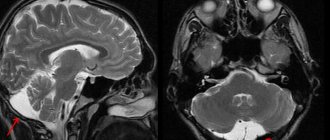
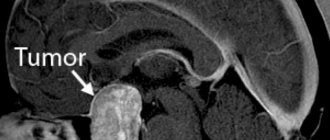
Lipoma on MRI - sagittal plane
Impaired blood supply is fraught with the formation of a stroke. It is especially alarming if the patient’s vomiting becomes persistent, there is a feeling of double vision, the patient is drowsy, and consciousness is depressed.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
This phenomenon often accompanies various brain defects, including lipomas. Agenesis of the corpus callosum develops in the fetus and is predominantly found in children. The disease manifests itself in the form of delayed physical and mental development of the child, convulsive seizures and paralysis. Isolated agenesis is asymptomatic and is discovered accidentally during a profile examination.
Pathology occurs at the 12th week of fetal development. In medical practice, total agenesis occurs, when the posterior part of the corpus callosum is absent, and partial agenesis, in which the anterior part of the corpus callosum is absent.
Brain pathology negatively affects the functioning of the nervous system and significantly slows down mental development in children: cases of mental retardation, idiocy, and dysfunction of the speech apparatus have been recorded.
Survival and prognosis
Due to its benign nature, lipoma has a favorable outcome. Treatment started at an early stage will get rid of the formation with 100% probability. After surgery, a person quickly recovers, returning to his normal life.
At an advanced stage of the disease, damage occurs to nerve cells and their processes. Eliminating the problem will be much more difficult, and many of the consequences may be irreversible.
It is possible to get rid of the tumor in 70-95% of cases. If treatment is refused, the tumor poses a serious threat to the patient's life.
Surgery should be taken seriously. Any manipulation of the brain is dangerous. The professionalism of the neurosurgeon and his experience in this field are of great importance.
If the wen capsule is completely removed, the likelihood of relapse is minimal. Also, to reduce the risk of recurrence of a wen, you should exclude factors that provoke the disease from your life.
General symptoms of the disease
Common symptoms of the disease by which wen can be recognized include:
- aching pain in the frontal region of the head;
- involuntary movement of limbs;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- compression in the temporal region of the head;
- deterioration of vision and concentration;
- decreased mental abilities;
- a sharp increase and decrease in blood pressure;
- insomnia, lethargy, apathy;
- lack of appetite and constipation.
Life forecast
The life prognosis depends on the degree of malignancy of the brain tumor. Anaplastic meningioma in more than half of cases leads to relapse 5 years after surgical treatment. A neurological syndrome may occur.
It is important to pay attention to even minor clinical manifestations. It is recommended to consult a specialist if you experience frequent headaches, nausea, vomiting, or episodes of loss of consciousness. With the help of CT and MRI, even minor pathological lesions that require surgery can be identified.
The Burdenko Research Institute provides professional surgical treatment of extracerebral neoplasms using modern technologies and safe techniques. You can make an appointment with the best neurosurgeons, conduct a comprehensive examination, and begin effective treatment that will fully correspond to the clinical situation.
Causes
The factors influencing the occurrence of wen have not yet been fully elucidated, but probable causes include:
- heredity;
- bad habits, especially abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products, as they have a direct effect on the brain;
- infectious diseases of the central nervous system increase the risk of tumor development;
- foci of inflammatory processes located in the brain;
- polluted environment;
- unhealthy diet, especially abuse of fatty, sweet and spicy foods;
- physical and chemical effects on the brain;
- presence of mental illness, especially schizophrenia;
- stress, lack of sleep, nervous tension.
Lipoma of the interhemispheric fissure of the brain: treatment, symptoms
Not all tumors are dangerous; some are benign, such as brain lipomas. However, despite its benign nature, such a pathology still requires adequate therapy.
Statistical studies show that every year the number of deaths from malignant diseases is gradually increasing. But no less dangerous are benign neoplasms consisting of various tissues if they are located in the brain.
Diagnostics
Wen in the brain at an early stage of development is difficult to detect due to the lack of symptoms. Cases have been recorded where people lived with a tumor for decades and were not aware of the existence of the phenomenon. The pathology is discovered accidentally during a profile examination of the patient. You should not wait for the first symptoms of a tumor, because modern methods for diagnosing such pathologies are known.
CT scan
CT is an informative and safe examination of the intracranial area. The method allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and replaces ultrasound or radiography, or saves time and makes it possible to find out the results immediately. Using computed tomography, the tumor is visualized in detail, down to the vessels and nerve endings.
Neurosonography
Ultrasound examination of the brain, or neurosonography, is actively used in pediatrics and helps to obtain information about the location, size and degree of tumor growth within the cranial space. Already in the first month of life, a newborn should be examined for the presence of congenital tumors. With the help of neurosonography, even a small tumor at an early stage of development can be detected. It is advisable to undergo examination for children born with low body weight, birth injuries, developmental pathologies and intrauterine infection.
MRI
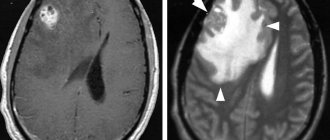
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, provides accurate information about the extent of tumor development. Diagnosis using this method is much more effective than CT or ultrasound, since MRI makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of a lipoma, which is a more detailed image. The wen has a sharply defined shape in the resulting images. The main sign of lipoma detection is the high signal intensity of adipose tissue when pathology is detected.
What does a lipoma look like?
Slow-growing soft growths under the skin - wen - are usually lipomas.
A lipoma looks like a “ball” or “lump” under the skin. The size of the formation varies; it can be from the size of a pea to several centimeters in diameter. When palpated (palpated), the lipoma is soft, resembles rubber in density, and is not fused to the underlying tissues.
Treatment
Most often, patients seek medical help when the lipoma needs to be removed. This is due to the absence of symptoms at an early stage or medical wait-and-see tactics. Doctors do not recommend treating at the initial stage of development, so as not to provoke changes or growth of pathology, and observe the patient for a long time until the first symptoms appear. Increasing in size, the wen brings discomfort and pain, and then the question arises of removing the tumor.
Surgical intervention
The fatty tissue poses a threat to the life and mental health of a person, increasing to a substantial size, so surgeons carry out radical removal along with the capsule to avoid further relapses. During the operation, craniotomy is performed, that is, part of the skull is removed.
Brain surgery
Minimally invasive intervention
This method includes endoscopic tumor neutralization, which is carried out using an endoscope and a video camera. The doctor removes the fat along with the capsule using this method. Minimally invasive intervention also includes the puncture-aspiration method of removal.
During the procedure, a hole is made in the patient's skull through which the operation takes place. A tube is inserted into the hole and the pathological fatty tissue is removed using an electric suction. The only drawback of the operation is that the wen capsule remains in the human brain and this causes the recurrence of lipomatosis.
Drug therapy
Proponents of the medicinal method are confident that the brain wen can be removed without surgery. To do this, the doctor prescribes medications that help reduce the size of the lipoma. Most often, hormonal treatment is used, since hormone imbalance is one of the reasons for the appearance of wen, according to theoretical assumptions. Therapy gives results at the initial stage of development, but at the same time it turns out to be ineffective when the wen grows rapidly. To eliminate the wen, non-traditional methods are actively used: people are sure that herbal decoctions and compresses cause complete resorption of the tumor, but often folk remedies are ineffective. Treatment should be carried out comprehensively and only as prescribed by a doctor.
Lipoma removal with laser
More modern technique. Its essence is the same, only a laser beam of a certain spectrum is used as a cutting tool. At the same time, thermocoagulation of the blood vessels occurs with a laser. The laser is completely safe in terms of bleeding and possible wound infection. With laser removal of lipomas, the skin receives less traumatic impact, but each node must also be removed through an individual incision. After the procedure, internal and external sutures are applied.