- What is brain cancer
- First manifestations and symptoms
- Possible treatment
- Stages of brain cancer
- Prognosis for brain cancer
Malignant brain tumors (BM) are not the most common type of cancer. But such diseases are more life-threatening for patients, as they directly affect a vital organ. Brain cancer is confidently associated in people’s minds with an incurable disease, however, methods for diagnosing and treating malignant neoplasms of this localization have rapidly developed over the last decade, which makes it possible to successfully cope with such a disease.
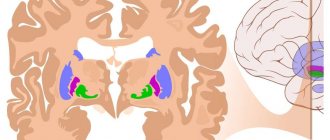
Brain tumor – what is it?
A tumor is a voluminous formation, which is a group of atypical cells that are rapidly increasing their population. A tumor in the brain can be either benign or malignant.
All neoplasms of the central nervous system are divided into primary and secondary:
- Primary - those that developed directly in the brain
- Secondary - are metastases of malignant neoplasms of a different location (lungs, kidneys, etc.)
There are a large number of different classifications of tumors of the nervous system. But the histological structure of the neoplasm and its location are of greatest clinical importance.
Based on location, primary tumors are divided into two large groups:
- Brain tumors – account for up to 90% of all central nervous system tumors
- Spinal cord tumors – 10% of central nervous system neoplasms
There are also oncopathologies localized simultaneously in the brain and spinal cord. But their share of the total number of tumors is insignificant - it is a fraction of a percent.
Neoplasms can also be of origin:
- Intracerebral - originate from brain cells
- Extracerebral - comes from blood vessels, nerve sheaths, fragments of embryonic tissue, pituitary gland
Malignant primary brain tumors of intracranial localization have a number of features that distinguish them from cancer of any other location:
- They practically do not metastasize. That is, they do not form daughter tumors in the lymph nodes and other organs.
- The central nervous system is separated from the rest of the body by the blood-brain barrier. Therefore, such tumors usually do not extend beyond the brain.
- Due to the high risk of damage to functionally important areas of the brain, most of these tumors are inoperable.
Due to the above reasons, the classification of tumors according to TNM (tumor size, regional and distant metastases) is practically not used in neuro-oncology. Stages are determined based on the histological type of tumor, and not the extent of the oncological process.
According to WHO, there are 10 histological types of tumors of the central nervous system:
- From neuroepithelial tissue
- From the meninges
- From the nerves
- From hematopoietic tissue
- Germinogenic - from germ cells
- Cysts and tumor formations
- Neoplasms growing into the cranial cavity
- Tumors of the sella turcica (this is a fragment of one of the bones of the skull in which the pituitary gland is located)
- Metastatic tumors
- Unclassified neoplasms
Symptoms
Clinical signs of tumors are the same as for brain damage of any other etiology (infectious, vascular, traumatic, etc.). They are divided into general cerebral and focal. General cerebral symptoms of brain cancer:
- headache;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- decreased visual acuity;
- dizziness;
- epilepsy;
- disturbances of consciousness;
- mental disorders.
Focal symptoms depend on which parts of the brain are damaged by the tumor. Paresis and paralysis, disorders of speech, writing, memory, etc. may occur.
In the early stages, brain cancer usually has no symptoms. Their appearance most often indicates that the tumor has reached a large size.
Enduring pain is life-threatening!
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Gliomas
Gliomas are tumors of neuroepithelial tissue. They make up more than half of all tumors of the central nervous system. This type of brain tumor is most often the result of genetic mutations. These include glioblastomas, astrocytomas, and ependymomas. Some develop for a very long time - years. Others progress rapidly and lead to the death of the patient within a few months.
Gliomas have 4 degrees of malignancy. Typically, grade 1-2 tumors are called benign, grade 3-4 tumors are called malignant. The latter include glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma, the most common neuroepithelial tumors of the central nervous system. They account for up to 80% of all neoplasms of this type.
Tumors from the meninges
Neoplasms from the meninges account for about 20% of primary CNS tumors. 95% of cases of cancer of this type are meningiomas. The remaining 5% are fibrous histiocytomas, hemangiopericytomas, melanomas, diffuse sarcomatosis and others.
Some risk factors for tumors from the meninges have been established. Here's what can cause a brain tumor:
- Head injuries
- Ionizing radiation (including radiation therapy)
- Eating Nitrites
Genetic defects in chromosome 22 have been identified, due to which a brain tumor can develop. The cause is a mutation at the 22q12.3-qter locus.
According to malignancy, meningiomas are divided into 3 groups:
- Grade 1 - includes 9 histological types, the most common of which are meningoepithelial (60% of cases), transitional or mixed (25%) and fibrous (12%)
- Grade 2 – these are atypical meningiomas, which are marked by rapid cell division and rapid growth
- Grade 3 – anaplastic meningiomas (old name – meningosarcoma)
Rarely, multiple brain tumors occur. The reasons for their occurrence are not known. They make up about 2% of all diagnosed meningiomas. Such neoplasms are characterized by a favorable clinical course. In 90% of cases, a person lives a full life with them, without any symptoms. Only 10% of cases require surgical removal of tumors.
Send a request for treatment
Pituitary tumors
Up to 10% of all intracranial neoplasms are pituitary tumors. They are almost always benign. They usually develop from cells of the adenohypophysis (the anterior lobe of this gland). Such neoplasms are called adenomas, and if they have a diameter of less than 1 cm - microadenomas. What causes a brain tumor of the corresponding localization has not yet been established.
Although some risk factors are known:
- Brain infections
- Traumatic brain injuries
- Toxin poisoning
- Use of oral contraceptives
- Obesity
The causes of a tumor in the brain that grows from pituitary gland cells may be due to gene mutation. Hereditary predisposition is of no small importance. At what age can a brain tumor of adenohypophyseal origin develop? This is one of the “youngest” tumors. It occurs in everyone, including children. The peak incidence occurs in working age - from 30 to 50 years.
Most pituitary adenomas are not accompanied by severe symptoms, so their detection rate is low. Treatment is usually carried out conservatively (normalizing the level of hormones in the blood). When it stops working, surgery is used.
Germ cell tumors
Germ cell tumors in the brain develop from embryonic tissue. These neoplasms include germinoma, choriocarcinoma, yolk sac tumor, and embryonal carcinoma. They are located in the area of the epiphysis. The most common is germinoma. It accounts for up to 0.5% of all brain tumors in representatives of the European race, and up to 3% in Asians. The reasons why this brain tumor occurs more often in the Asian population are not known. It is diagnosed more often in boys. The tumor is malignant - it metastasizes through the cerebrospinal fluid (the fluid that washes the brain).
Metastatic brain tumors
About 20% of the structure of CNS neoplasms are metastatic brain tumors. The causes of these diseases are obvious: the spread of metastases from other parts of the body. It is believed that their actual prevalence is even higher. After all, cancer patients with stage 4 cancer are often not examined too carefully due to the inappropriateness of in-depth diagnostics. Even if there is a suspicion that they have a brain tumor due to cancer of another location, such patients are no longer referred to neurosurgeons.
What can cause such a brain tumor? Here are the most common reasons:
- Lung cancer – 40% of cases of metastatic damage to the central nervous system
- Breast cancer – 10%
- Kidney – 7%
- Stomach or intestines – 6%
- Melanomas - on average 5%
Symptoms
Symptoms are almost absent in the early stages of the disease and appear when the tumor enlarges and puts pressure on the brain. Then memory deteriorates and dizziness and numbness in the fingertips occur.
Further, intracranial pressure increases and intoxication progresses. The pain becomes stronger when the person is in a horizontal position. He may feel nauseous regardless of food intake, and vomiting may occur. The patient experiences weakness and drowsiness, and becomes very tired. Some lethargy and depression arise, and the person begins to think worse. Convulsions may occur, speech, hearing, sense of smell, and vision may deteriorate, sensitivity may disappear, hallucinations may occur, limbs may be paralyzed, coordination of movement may be impaired, and breathing problems may arise.
Tumors of childhood
Even children can get a brain tumor. Among childhood cancers, brain tumors account for about 20%. This is second only to leukemia. More often they are observed in children of the first year of life. Teratomas are found mainly in children. In older children, benign astrocytomas (more than 30%), primitive neuroectodermal tumors (medulloblastoma, pineoblastoma - 20%) and ependymomas (15% of cases among children over 1 year of age) predominate.
At present, it is not known for certain how brain tumors form in children. It has been established that they develop more often in boys than in girls. The reasons why brain tumors are more common in male children have not been established.
Causes
The most likely occurrence of the disease:
- due to radioactive exposure;
- due to congenital mutations;
- in old age;
- in males;
- among residents of Latin America, Asia, Europe;
- in the presence of Turcotte syndrome;
- with neurofibromatosis;
- with tuberous sclerosis;
- in the presence of a benign astrocytoma;
- due to human herpes virus type six;
- due to polymavirus;
- due to cytomegalovirus.
Chondrosarcoma
How can you get a brain tumor?
Patients often ask their doctor how they can get a brain tumor. They suggest that knowing the causes will help prevent the disease. Unfortunately, it is not. For many types of cancer, the underlying etiological factors have indeed been established. For example, it is well known that lung cancer occurs mainly due to smoking, cervical cancer is caused by human papillomavirus infection, and liver cancer is caused by viral hepatitis C. But what causes a brain tumor is still not known. Despite numerous clinical studies, scientists have not been able to establish the causes of brain tumors.
However, some risk factors have been identified:
Radiation . There are many ways you can get a brain tumor due to radiation. Most often this is radiation therapy for cancer or occupational hazards (radiologists, nuclear industry workers). In children, in the old days, the cause of brain tumors was radiotherapy used for fungal infections of the scalp.
The connection is not always clearly visible. After all, the first symptoms appear only 10-15 years after irradiation. But a retrospective analysis of medical records shows what can cause a brain tumor. Anamnesis data demonstrate that neoplasms of the central nervous system are more often observed among individuals exposed to radiation exposure.
Does this mean that a brain tumor occurs from radiography, fluorography or computed tomography? After all, these methods are based on the effects of ionizing radiation. No, no such connection has been established. Even decades ago, when the devices were much less advanced and gave tens of times more radiation load, there was no reason to believe that a brain tumor could occur as a result of the diagnostic procedures performed. Today, the devices used are so precise and perfect that the radiation is minimal, without damaging cells or causing mutations.
Heredity . Some genetic abnormalities have been identified that may cause a brain tumor. These include neurofibromatosis type 1, type 2, tuberous sclerosis, Hypeel-Lindau disease, Li-Fraumeni syndrome. There are other genetic causes of brain tumors, but they are much rarer.
Immunity . One of the types of neoplasms of intracranial localization is lymphoma. This brain tumor can occur due to decreased immunity. This is caused by AIDS, treatment after organ transplantation (immunosuppressive therapy), long-term use of immunosuppressants and glucocorticoids for dermatological diseases or systemic connective tissue lesions.
There are also several mythical reasons worth noting. Many people are afraid of them, but these fears are false.
So, here's what a brain tumor can't cause:
- Using a mobile phone – contrary to popular belief, it does not emit ionizing radiation
- Playing soccer (soccer players often head the ball)
- Exposure to electromagnetic fields
- Hair dye
- Stress and bad habits
We also note several controversial reasons why a brain tumor can occur. These risk factors are suspected but not yet definitively proven.
Among them:
- Aspartame (sweetener for diabetics)
- Exposure to vinyl chloride (occupational hazards in plastics production)
- Viral infections
- Exposure to petroleum products
Thus, scientists do not yet know exactly what causes a brain tumor. Therefore, the only thing you can do to prevent this disease is not to expose yourself to massive ionizing radiation and, if possible, maintain a good immune system.
Prevention
Having heard from doctors such a terrible diagnosis as brain cancer, many fall into numbness and mentally begin to say goodbye to this world. This is a completely wrong attitude. Doctors have long been telling stories about miraculous healings of people in serious condition who believed in the best.
In order not to encounter this terrible disease, doctors recommend trying to follow simple rules:
- you need to exclude processed meat products (sausages, smoked meats, ham) and chips from your diet;
- you should spend less time talking on your mobile phone, use headphones or a speakerphone for these purposes;
- You should avoid interaction with radioactive radiation, vinyl chlorides and other toxic substances;
- It is not advisable to use the sugar substitute aspartame;
- You should regularly undergo preventive diagnostics in the form of MRI;
- you cannot smoke tobacco, cigarettes and cigars;
- you need to spend more time in the fresh air, on walks and outside the city. Oxygen saturates and restores brain cells;
- Avoid drinking energy drinks and large amounts of caffeine;
- you should try to worry less and avoid nervous situations;
- you need to stop eating fried foods;
- You should not take vitamin supplements (BAS);
- You should eat healthy foods containing vitamins (vegetables, fruits). Oranges, tangerines, lemons, bell peppers, red cabbage, carrots, legumes, green leafy vegetables (spinach and lettuce), broccoli, beets, and green tea have anti-carcinogenic properties. And onions, garlic, whole grains and brown rice will strengthen your immune system. Pasta should be chosen from wholemeal flour, whole grain bread;
- If you experience any unfavorable symptoms, you should consult a doctor;
- It’s worth leading a healthy lifestyle, playing sports (not necessarily professionally, just doing exercises or walking 30 minutes a day). Regular physical activity will strengthen the cardiovascular system and thereby improve blood supply to the brain;
- You should adhere to a sleep schedule, which means getting enough sleep at night, since the hormone melatonin, which strengthens the immune system, is produced only at this time of day. Reduced immunity is a “green signal” for cancer;
- Under no circumstances should you drink alcohol, much less abuse it. Getting rid of this bad habit will reduce the risk of disease by 30%;
- You should also be careful with a tan.
By adhering to these rules, a person does not give cancer any reason to arise. The disease will almost certainly not occur in people who lead a healthy lifestyle and take care of themselves.
A brain tumor is a serious disease that is difficult to treat, and if in the case of the first stage of brain cancer there is a chance to forget about this disease forever, then starting from the second stage the patient is forced to fight the disease for the rest of his life, adhere to the treatment and recommendations of doctors, or fight off the disease precious time (third and fourth stages). But it is always worth remembering that there are exceptions to everything and miraculous recovery is not at all uncommon among cancer patients.
Meningeal brain tumor - prognosis
The survival rate for meningiomas is high. The clinical course of the disease is favorable. Usually these are neoplasms of 1st degree of malignancy. If there are no symptoms of pathology, an observation strategy is used. Surgery may not be necessary because most of these brain tumors have a good prognosis.
The first thing patients are interested in is how long do they live with a brain tumor of meningeal origin? This depends on a number of factors. First of all, it depends on the degree of malignancy, as well as the treatment performed.
If the brain tumor was completely removed during surgery, how long people live depends solely on their age and health status, because meningioma does not recur with a 95% probability. Only 5% of patients experience recurrences within 15 years after surgery.
But sometimes the neoplasm is localized in functionally active structures of the central nervous system. In such cases, complete removal is not possible. However, even if it was partially removed, the risk of recurrence within 15 years is only 50%. In the remaining 50% of cases, the tumor remains the same size - it does not grow. If growth of meningioma is observed, it responds well to treatment with radiation therapy. Even for malignant meningioma, radiation helps control tumor growth for at least 5 years.
The age of the patient is also important. Below you can see data on how long people live with a meningeal brain tumor, depending on age.
The percentage of five-year survival is indicated - that is, the number of people who will live for 5 or more years after diagnosis:
- Up to 45 years – 87%
- Up to 55 years – 77%
- From 55 to 65 years – 71%
In most cases, after 5 years the tumor no longer recurs if it was completely removed during surgery.
Stages: features of diagnosis and treatment
How long a person with signs of cancer can live depends directly on the degree of neglect of the disease. The difficulty of timely diagnosis lies in the asymptomatic transition between stages of the pathology. The first signs are nonspecific and are often mistaken for symptoms of general somatic diseases.
The first stage is characterized by a benign course. In this case, cancer cells grow slowly and are localized in the superficial layer of brain tissue. Surgery at this stage is the most effective method, since a small number of neuroglial cells are affected. The initial stage is almost impossible to diagnose, since the symptoms are very similar to the clinical picture of colds.
The main features include:
- general malaise;
- headache;
- dizziness.
During the transition to the second stage, degeneration of glioblastoma cells from benign to malignant is observed. The cells begin to multiply uncontrollably, destroying healthy brain structures. Characterized by moderate growth. With timely surgery, proper postoperative care and rehabilitation, the life expectancy of patients averages three years.
This stage is characterized by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- epileptic seizures;
- intense headache;
- vomiting of central origin - numerous, not bringing relief;
- convulsions.
Surgery is completely contraindicated in the third stage. The tumor begins to grow rapidly, affecting the deep layers of the brain matter. This appears:
- dysarthria, decreased vision and hearing;
- increasing absent-mindedness;
- fluctuation of pupils;
- weakening of memory with the gradual development of amnesia;
- disturbance of gait and balance.
The life prognosis is unfavorable. Patients, constantly receiving a course of painkillers, rarely live beyond two years.
At the fourth stage of the disease, operations are no longer performed. For therapeutic purposes, specific medications, painkillers and radiation therapy are used.
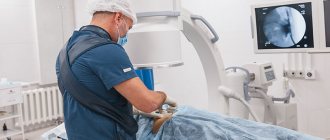
To visualize the tumor, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- MRI and CT of the spinal cord and brain;
- MRS;
- PET brain;
- open and stereotactic biopsy.
Among the laboratory tests, the most indicative are histological typing, molecular test, immunohistochemistry and gene activity analysis.
Neuroepithelial brain tumor – how long to live?
If you have been diagnosed with a neuroepithelial brain tumor, how long to live cannot be definitely said without establishing its histological type. It is the structure of the neoplasm that determines how long a brain tumor takes to develop.
Based on this parameter, there are 4 degrees of malignancy of neuroepithelial neoplasms of the central nervous system:
- Grade 1 – pilocytic astrocytoma
- Grade 2 – protoplasmic, pleomorphic, hemistotic, fibrillary astrocytoma, xanthoastrocytoma and ependymoma
- Grade 3 – anaplastic astrocytoma
- Grade 4 – glioblastoma
Grade 1 and 2 neuroepithelial brain tumors are considered low grade. They have a more favorable prognosis. Grades 3 and 4 are neoplasms of high malignancy or simply malignant. The worst prognosis is characterized by a grade 4 brain tumor.
How long do people live with glioblastoma ? Unfortunately, this tumor has a worse prognosis. It develops very quickly and is manifested by necrosis (death) of parts of the brain. From the moment the tumor appears to the first symptoms, sometimes not even months, but weeks pass. The average life expectancy for patients under 40 years of age is no more than one and a half years, and for patients over 40 years of age – less than 1 year.
Five-year survival rate in developed countries, depending on age:
- Up to 45 years old – 19%
- From 45 to 55 years – 8%
- From 55 to 65 years – 5%
Patients do not even always undergo surgery, since they die from a grade 4 brain tumor quite quickly. Often only radiation and chemotherapy are used. But these methods do not significantly prolong the patient’s life. Unfortunately, glioblastoma is the most common glioma (neuroectodermal tumor). It makes up about 50% of the structure of these neoplasms.
Anaplastic astrocytoma is another malignant brain tumor. How long do people live with this disease?
Average life expectancy, depending on the patient’s age at the time of diagnosis:
- Up to 40 years – about 3 years
- From 40 to 60 years – on average 2 years
- After 60 years – less than 1 year
Five-year survival rate, depending on age:
- Up to 45 years old – 54%
- From 45 to 55 years – 32%
- From 55 to 65 years old – 14%
The pathology is characterized by infiltrative growth. That is, the tumor penetrates the brain tissue, rather than displacing it. Anaplastic astrocytoma is the second most common neuroectodermal tumor after glioblastoma. In the structure of these neoplasms it makes up about 30%.
The next most common tumor of the central nervous system from neuroectodermal tissue is oligodendroglioma . It accounts for about 5% of all gliomas. The average life expectancy of patients in developing countries, including the CIS, is 6 years. In developed countries (Germany, USA) the indicators are much better.
The five-year survival rate, depending on the age of the patient at the time of diagnosis, is:
- Up to 45 years – 88%
- From 45 to 55 years – 81%
- From 55 to 65 years – 68%
Unfortunately, sometimes oligodendroglioma becomes malignant. In this case, it acquires grade 3 malignancy, and the prognosis worsens. It is not known for certain what causes the brain tumor anaplastic oligodendroglioma. However, the life expectancy of patients is reduced.
Five-year survival rates for this type of neoplasm in developed countries:
- Up to 45 years – 71%
- From 45 to 55 years – 61%
- From 55 to 65 years – 46%
Ependymomas make up about 3% of gliomas. They are more common in children than in adults. Most often these are benign tumors. Anaplastic ependymomas (grade 3 malignancy) are rare. There is no data on what causes this brain tumor in children. Survival rates vary significantly between countries. In the CIS, the five-year survival rate for children over 3 years of age is about 50%, for adults – 70%. In developed countries, the statistics are much better due to better treatment.
Five-year survival rate for patients with ependymoma in countries with well-developed medicine:
- Children's age – 75%
- Patients from 20 to 45 years old – 92%
- From 45 to 55 years – 89%
- From 55 to 65 years – 86%.
How long do they live with a brain tumor from fetal tissue?
Germ cell tumors are malignant. They occur in children. They are characterized by metastases. The most common tumor is germinoma. It is also the most favorable. In the vast majority of patients, even without the use of surgical methods, this malignant brain tumor is cured. How long do they live after treatment? Life expectancy is potentially the same as that of a person who has never suffered from this pathology. To cure the disease, radiation therapy and sometimes chemotherapy (in children under 4 years of age) are sufficient. The younger the age, the better the prognosis. Unfortunately, the prognosis for other types of germ cell tumors is much worse. They are very rare. But patient survival is extremely low. These are inoperable brain tumors. How long do patients live? Only 5% of patients will live more than 2 years after diagnosis. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are used for treatment, since surgical treatment does not improve the prognosis. Only palliative operations are performed. For example, shunting surgical interventions for blockage of the cerebral aqueduct.
Treatment
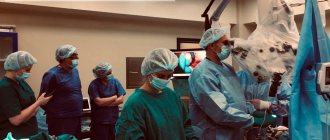
Today, treatment of patients with brain cancer is carried out in the following ways:
- Neurosurgery. Not always possible due to the dangerous and inaccessible location of the tumor. In surgery, cryosurgery is actively used (exposure to affected tissues with liquid nitrogen), which is considered very effective. Gamma Knife and CyberKnife are very indispensable in the initial stages of the disease. They remove the DNA of harmful cells, thereby blocking the development of the source of the disease.
- Chemotherapy. Pharmaceuticals are prescribed by injection or orally. As a rule, it does not bring the desired results and is prescribed only after completing a course of radiation therapy. This treatment method affects the entire body as a whole, and not just the affected tissues. Chemotherapy is carried out in a course of several cycles, with breaks between which are necessary. The consequences of this type of treatment may include hair loss, brittle nails, impaired skin integrity and the appearance of cracks in it.
- Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is prescribed after surgery to get rid of damaged tissue that doctors have not removed or in cases of contraindications for surgery, the duration is from 7 to 21 days. Brachytherapy is a therapy during which a radioactive substance is injected into the affected tissue. External beam radiation therapy is a course during which the patient is exposed to radiation.
- Drug treatment. It is effective only in combination with other therapy and is carried out before surgery. The drugs can be anticonvulsants (relieve symptoms of stage 2 and later) and steroidal anti-inflammatory (relieve pressure on healthy areas). Often the patient is prescribed medications to relieve unpleasant symptoms, such as painkillers or antidepressants.
- Endoscopic treatment. This is a less traumatic method than neurosurgery. This method of surgery minimizes damage to nerves and blood vessels, but increases the recovery time for the patient due to craniotomy.
The rehabilitation period after surgery lasts more than one month, because the patient will need a lot of strength to get back into action.
Metastatic brain tumor – how long to live?
In many cases, cancer is detected after metastases have appeared in the central nervous system. How long people live with a metastatic brain tumor depends on the treatment provided. In the natural course of the disease, the average life expectancy of patients is about 3 months. With surgical treatment or radiation therapy, it can reach 2 years or more. Life expectancy also depends on the histological type of cancer, location and number of metastases. In approximately 50% of cases they are multiple, which worsens the prognosis.
Send a request for treatment
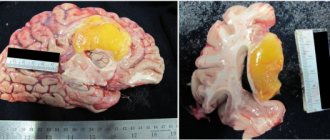
Glioblastoma surgery
First of all, the specialist needs to excise the tumor tissue around the perimeter of healthy tissue (in order to minimize the likelihood of relapse). This approach to the operation makes it quite traumatic. In addition, if the cancer focus is large or if it is located near important brain regions, surgery is completely impossible.
Based on the size, location of the cancer, its type, and the patient’s condition, the neurosurgeon makes a decision regarding the volume of such intervention and how it will be carried out.
The use of modern equipment (lasers, ultrasound) when carrying out such interventions has made it possible to increase their effectiveness. The route of surgery and the method of execution are selected individually.
Where to go if you have brain cancer?
The diagnosis and treatment of brain cancer and astrocytoma are the most successful in Germany and other developed countries, which is confirmed by patient survival statistics. If you want to use the services of German doctors, please contact ]Booking Health[/anchor]. We organize treatment abroad.
Our advantages:
- A team of doctors who understand modern methods of treating various diseases will select the best clinic for the treatment of brain cancer for you.
- Thanks to direct contracts with the best medical institutions in Germany, you can save up to 70% of the cost of the treatment program. In addition, the waiting time for a doctor’s appointment will be reduced.
- The initially agreed cost of treatment is guaranteed not to change. Even if complications arise and additional therapeutic measures are required, all unforeseen expenses will be covered by insurance.
- A full package of services: we will completely organize the entire treatment process in Germany, provide an interpreter, and provide transfer from the airport to the clinic.
- Absolute transparency of financial relationships: you can always find out what services you paid for and in what volume. Unused funds after treatment will be returned.
To take advantage of all the benefits of German medicine, leave a request on our website. After processing it, we will contact you and you will be able to receive comprehensive advice on the treatment of brain cancer abroad.