Many patients report that they have goosebumps on their heads, but they don’t understand what they are. Therefore, they are often asked to explain the reason for the appearance of such a symptom and talk about how treatment can be carried out effectively and safely. In this article you can find out what goosebumps mean and what diseases manifest themselves in this way. Advice is also given on choosing a specialist and conducting treatment.
Let's start with the fact that goose bumps on the scalp are a sign of neurological or vascular problems. To make this clear, let’s talk about how the innervation and blood supply system works.
So, in the cervical spine there is a segment of the spinal cord of the same name. The radicular nerves extend from it. They branch and form plexuses, nerves. Some of them are responsible for the innervation of the scalp. Also, paired cranial nerves depart from the brain through the foramen ovale of the occipital bone. They also branch and are partially responsible for the innervation of the tissues of the head. In particular, the facial and trigeminal nerves are formed exclusively by the branches of the cranial pairs. Also, their branches are part of the nerve plexuses that innervate the hair follicles and small blood vessels. They provide tone to the posterior vertebral arteries.
Blood supply to the tissues of the head and brain is carried out by four arteries. Two posterior vertebrates and two carotid. They branch, giving rise to many arterioles, which pass into a network of capillaries. Each nerve ending in the thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer has its own capillary vessel.
When a capillary spasms, the blood supply process is disrupted and the nerve ending enters a state of ischemia. This may feel like numbness or crawling. Also, similar sensations occur in clusters (in a certain area of the scalp).
The lower the area of negative impact is located, the larger area of the head is subject to paresthesia, in which the patient feels that goosebumps are crawling on or under the skin. Therefore, an accurate description of the area of distribution of the clinical sign will allow the doctor to quickly make a diagnosis and develop an effective treatment regimen for the underlying disease.
Please note that the feeling of crawling sensations in some cases can be a physiological phenomenon. This may occur due to short-term compression of blood vessels or nerves by external factors. For example, if a person was in an uncomfortable static position for some time. Or if he was wearing a tight headdress. Similar sensations can occur after exposure to low temperatures. When hypothermia occurs, blood vessels in the epidermis and subcutaneous fat layer spasm. After the cessation of cold exposure, the vessels begin to restore their tone. Fresh capillary blood enters the tissues. And this may be accompanied by the effect of crawling goosebumps. If this is a physiological condition, then all unpleasant sensations disappear within 30 - 40 minutes.
If they continue for hours or do not stop at all, you need to see a doctor for help as soon as possible. It is necessary to visit a neurologist or vertebrologist. These doctors have the necessary medical qualifications to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
In Moscow, you can make a free appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. Experienced specialists work here. They will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective course of treatment. You will receive comprehensive individual recommendations regarding eliminating potential negative impact factors. This will help stop the destructive pathological process and allow the necessary treatment to be carried out more quickly.
Description of the phenomenon
Goosebumps appear when nerve endings in the spinal cord or brain are irritated. The reason is the stimulation of individual nerves, which has such an effect on their endings. The irritation causes muscle contraction, causing a sensation as if the hair on the head has risen, and tiny bugs have begun to run across the skin itself. This phenomenon can affect not only the head, but also any other part of the body where there is at least a little hair.
Goosebumps can be one-time (temporary). In this case, they appear for completely natural reasons in a healthy person. Sometimes they can be combined with seizures, loss of sensation, dizziness, but no medical intervention or medication is required. Goosebumps appear for the following reasons:
- Emotional arousal (joy, surprise, fear);
- Touching sensitive skin;
- Low air temperature, hypothermia;
- High body temperature;
- Poor health (weakness, fatigue, headache).
When such sensations appear under the conditions listed above, there is no need to worry. After some time, the goosebumps will disappear on their own, and not a trace will remain of the unpleasant feelings.
Sometimes goosebumps may appear during sexual arousal. Humans experience this much less frequently than most living beings.
Characteristics of the symptom
Goosebumps is a comparative description of a sensation that is similar to a slight tingling, tightening, or moving of the skin. In medical terminology, this phenomenon is called paresthesia. It arises as a response to irritating factors of an endogenous and exogenous nature.
The symptom is a type of sensory disorder and has several characteristic features.
The following properties of pathology are distinguished:
- wave contraction of the middle layer of skin (dermis), with changes in sensitivity;
- spontaneous occurrence of sensations, without a specific chronological periodicity;
- the duration of the episodes increases, depending on the worsening of the provoking factors.
As the symptoms increase, the goosebumps may spread to the cervical spine, upper and lower extremities, or enter a more severe phase, which is accompanied by numbness and soreness of the skin.
Features of the symptom
In some cases, paresthesia is of a reflex nature and is called the pilomotor reflex or piloerection. The condition occurs in response to a pronounced emotional outburst, which can be caused by the following emotions:
- joy;
- fear;
- sexual arousal and other feelings.
In addition to the causes of the emotional spectrum, pilomotor paresthesia can be triggered by a feeling of cold, a reaction to anti-stress toys, or unexpected sounds (grinding metal, creaking foam). The effect can also be caused by dosed physical activity and massage, even if a simple hand massager is used.
The origin of this reflex is the stimulation of peripheral nerve endings and is manifested in the contraction of smooth muscle of conical connective tissue fibers. As a result of the contraction of the hair follicles, the hairs rise and the “goose bumps” effect is observed. The mechanical movement of the skin is accompanied by the sensation of goosebumps running over the head.
Causes associated with pathologies
Goose bumps on the head can be chronic. They are caused by the development of various diseases and are almost always combined with other more serious symptoms. The frequency and regularity of manifestations depend on what particular pathology caused them. In the most dangerous diseases, convulsions, tingling and numbness of the skin appear in damaged areas, sensitivity is lost, temperature is disturbed, and hair falls out.
What diseases can cause goosebumps:
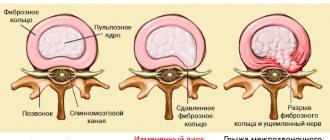
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Curvature, combined with constant compression of nerve endings, is one of the most common causes of goosebumps. The patient may also feel slight numbness, dizziness, pain in the neck, head and torso, and tingling. If left untreated, symptoms will accompany the person throughout his life.
- Cardiovascular diseases. Most diseases associated with the heart or blood vessels cause many unpleasant symptoms. Patients may have a numb head, they often feel crawling, pain inside the skull, weakness, nausea, their skin becomes paler, their mood and general well-being worsen. Sometimes symptoms can affect the head only on one side, and also “give” to certain parts of the face and arms.
- Micro stroke. If a micro-stroke occurs, the patient’s brain cell nutrition will be disrupted. In this case, the serious symptoms inherent in a regular stroke will be absent. Everything is limited to goosebumps that appear for a short time, painful sensations inside the head, weakness, and dizziness. A microstroke is also called a transient ischemic attack.
- Hypoparathyroidism. The disease is combined with functional disorders of the parathyroid glands, which cause goose bumps on the scalp, very strong nervous excitability, and numbness in the limbs. If left untreated, complications may develop that cause increased symptoms.
- Atherosclerosis. Vascular damage that occurs with this disease can cause chronic goosebumps, pale skin, memory loss, and the formation of small ulcers. There are frequent cases of complications of the disease in the form of acute vascular insufficiency of the brain, which can lead to death.
- Cervical plexus neuropathy. A pinched nerve often occurs against the background of severe curvature of the spine, but this is not a prerequisite for such a phenomenon. If this happens, the person will feel like there are goosebumps running all over the head, and there will also be severe pain radiating to the back of the head, neck, shoulders and the bone behind the ear.
- Neuropathy of the greater occipital nerve. With this disease, damage occurs to the nerve in the back of the head. The patient's skin will become numb and the sensitivity at the back of the head will decrease. Sometimes he may feel tingling in certain areas of the skull.
- Bell's palsy. This name refers to inflammation of the facial nerve, in which goose bumps begin to run on one side of the face, affecting the upper part of the head. Along with this sensation, weakening of the muscles in certain parts of the face may occur. In some cases, the muscles stop working completely, which requires serious medical supervision.
- Avitaminosis. A lack of vitamins leads to a deterioration in the health of the skin, due to which it begins to peel, crack, and a person experiences a burning sensation, itching, is faced with decreased immunity, pain in the back and head, weakness throughout the body, and bad mood.
- Hypoxic conditions. Lack of oxygen occurs when you spend a long time in a stuffy room, as well as when there are disorders in the brain. In both cases, the person will have a crawling sensation in the head, as well as severe pain affecting one temple, the back of the head, the forehead, or one side of the brain. Often the cause of mild hypoxia is vegetative-vascular disorders, as well as a sympatho-adrenaline crisis against the background of VSD, which causes vasoconstriction, causing a full range of unpleasant symptoms.
- Nervous and mental disorders. With various deviations in a person’s mental state, sensations may appear as if bugs began to crawl on the head, dizziness, weakness, headaches, and discomfort in the stomach. Also, as a rule, there are also psychological symptoms, expressed by increased nervousness, moral instability, bad mood, lack of interest in life, and excessive aggression towards others. All this can appear even with regular overwork or stress.
- Cold. ARVI, acute respiratory infections or influenza are always combined with weakness, runny nose, nasal congestion, sore throat, cough, and high body temperature. Some people experience crawling sensations all over their head. Sometimes complications develop, for example, sinusitis. It causes the same goosebumps, as well as severe pain in the forehead, bridge of the nose and temples, which intensifies when turning the head. A person in this condition should definitely call an ambulance.
- Climax. During menopause, women face vascular disorders accompanied by unstable blood pressure. For this reason, they may experience crawling sensations, a headache, numbness in their limbs, and a convulsive syndrome. In some cases, menopause is accompanied by digestive problems, which cause constipation, bloating, colic, vomiting, heartburn, belching, and increased gas formation.
The regular occurrence of goose bumps, combined with other serious symptoms, requires a medical examination. This is the only way to be sure of the presence or absence of any diseases. If the symptoms seem particularly dangerous, you should immediately call an ambulance to eliminate all possible risks.
Risk factors
Guillain-Barré syndrome can occur in any age group, but young and old adults are most susceptible.
Guillain-Barré syndrome can be caused by:
- The most common infection is the bacterium Campylobacter, which is often found in undercooked food, especially poultry.
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Infection due to surgery
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Influenza virus
- Hodgkin's disease
- Mononucleosis
- HIV
- In rare cases, rabies or influenza vaccination
Visit doctor
With occasional goosebumps, there is no reason to worry. However, if you suspect the development of other diseases, you should still think about visiting a doctor. Therefore, you need to know what exactly may indicate serious illness. But no less important is the diagnosis itself, which includes several procedures.
When to visit a doctor
Many people choose to turn a blind eye to minor sensations, which is why they face serious complications. It is very important to promptly notice changes in your body and go to the hospital. You should go to the doctor under the following conditions:
- Symptoms are episodic and last for more than an hour.
- Pain in the head, dizziness, and increased blood pressure appear.
- During an attack, problems with vision, speech or hearing occur.
- It becomes difficult to turn your head.
- The skin changes with each attack.
Even one point is enough to make an appointment now. It is better to get examined and make sure there are no diseases than to risk your health.
Adults should be very attentive to their children. If your child complains of a crawling sensation in his head, you should take him to the doctor. This is especially true in cases where the child’s behavior has changed dramatically.
Diagnostics
The first doctor a patient visits should be a neurologist. It is he who will prescribe all the necessary examinations, and also refer you to other specialists, if necessary.
What procedures will you need to undergo:
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- CT, MRI of the brain;
- ENMG;
- ECG, ECHO ECG;
- EEG;
- RVG;
- Ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound.
After all the studies have been completed, the doctor will make a final diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment. In some cases, constant monitoring of the patient may be required, for which he will be admitted to the hospital.
Complications
Guillain-Barré syndrome affects the nerves and can cause a domino effect on other systems in the body, such as breathing and cardiovascular function. Complications of Guillain-Barre Syndrome include:
- Breathing problems. A potentially fatal complication of Guillain-Barré syndrome is that weakness or paralysis can spread to the muscles that are involved in breathing. In such cases, artificial mechanical ventilation may be required in a hospital setting.
- Residual numbness or other sensations. Most people with Guillain-Barré syndrome recover completely or experience only mild residual weakness or unusual sensations such as numbness or tingling. However, full recovery can be slow, often a year or more, with 20 to 30 percent of patients experiencing incomplete recovery.
- Cardiovascular disorders. Fluctuations in blood pressure and abnormal heart rhythms are common side effects of Guillain-Barré syndrome, requiring monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate.
- Pain. Almost half of patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome have neuropathic pain, which is quite easily relieved with analgesics.
- Impaired bowel and bladder function. Sluggish bowel function and urinary retention may be a consequence of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Thrombosis. Patients who are immobile due to Guillain-Barré syndrome are at increased risk of developing blood clots. Therefore, as long as the patient is able to walk independently, it is necessary to take blood thinners and wear compression stockings.
- Bedsores. Immobility also increases the risk of developing pressure ulcers and therefore frequent repositioning is recommended to minimize the occurrence of pressure ulcers.
- Relapse. Almost 10 percent of patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome experience a relapse.
Severe, early symptoms in Guillain-Barré syndrome significantly increase the risk of serious long-term complications. In rare cases, death may occur from complications such as respiratory distress syndrome and acute cardiovascular failure.
Treatment
Treatment options depend on what is causing the problem. If the doctor has made a diagnosis, then you should take a course of the medications that he prescribes. Only getting rid of the root cause will allow you to forget about unpleasant symptoms forever. The treatment itself includes two methods of influencing the body: medicinal and folk. They can be used simultaneously if there are no contraindications.
Drug treatment
Only the attending physician can prescribe medications. It is highly not recommended to purchase and take medications on your own, because... This can cause irreparable harm to your health.
Your doctor may prescribe the following types of medications:
- Sedatives (Glycine, Motherwort, Valerian). Calms the nervous system.
- Antihypoxants (Mexidol, Preductal). Reduce the risk of developing hypoxia.
- Vasodilators (Cavinton, Nicergoline). Improves blood circulation.
- Angioprotectors (Ginkgo-Biloba, Ascorutin). Tones the veins and blood vessels in the head.
- Preparations with vitamin B (Thiamin, Pyridoxine). Improves the quality of nerve tissue.
You can only take mild sedatives (Valerian, Glycine) and painkillers (Nurofen, Paracetamol) on your own. However, it is important to consider the dosage and also try to see a doctor as soon as possible.
You can also be treated with non-drug means. Some patients are prescribed massage, magnetotherapy, peloid therapy, therapeutic exercises, and electric shock. Also, to increase effectiveness, you may need to adhere to a daily routine, quality sleep and a light diet.
Sometimes the reason why you get goosebumps is the medications themselves. For example, they can be caused by Naphthyzin, which is used to relieve nasal congestion.
Traditional methods
You can cope with goosebumps at home using traditional methods. They will improve the general condition of the body, after which all unpleasant symptoms will disappear. To do this you will need to use the following recipes:
- Parsley root, flax seeds, pumpkin leg, lilac and chicory flowers, horseradish, dandelion, watermelon rinds - take 2 tbsp. l. and pour 300 ml of boiling water. Let it brew. Take 50 ml every morning and evening.
- Nettle leaves, lingonberries, clover, dill, mint, echinacea - mix all ingredients 2 tbsp. l. and pour 500 ml of boiling water for half an hour. Take 50 ml at night.
It is important to drink the first tincture first, and only then the second. Additionally, you can drink tea with mint or lavender, because... they have a relaxing effect.
Diagnostics
Guillain-Barré syndrome is often difficult to diagnose in its early stages. Its symptoms are similar to other neurological disorders and can vary from person to person.
The first step in diagnosing Guillain-Barré syndrome is a thorough analysis of the patient's medical history and symptoms. A spinal tap and nerve function tests are often necessary to confirm the diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Spinal tap - This procedure involves the removal of a small amount of fluid from the spinal canal in the lumbar spine through a puncture. A sample of the cerebrospinal fluid is then analyzed to look for changes in the fluid that are characteristic of the syndrome. Electromyography detects electrical activity in muscles, which can help determine whether weakness is due to muscle damage or nerve damage. Electroneurography allows you to determine the speed of impulses propagating through nerves and muscles.
When goosebumps are harmless
The well-known phrase “It will go away on its own!”, which is sometimes used by people who do not feel well enough, can turn out to be quite prophetic. The appearance of an “anthill” at the roots of the hair or even on the surface of the skin as a whole is a normal reaction of the body to the emotions experienced:
- fear;
- Delight;
- delight;
- excitation;
- pleasure;
- satisfaction.
- Numbness of the tongue: causes. Why do my lips and the tip of my tongue go numb?
- Burning tongue: main causes and methods of treatment
If you find yourself with paresthesia during an unexpected - unwanted or, conversely, joyful - meeting, watching an exciting program, listening to your favorite music, reporting amazing news and other events that make you experience a whole range of feelings, do not worry. Additionally, paresthesia may result from:
- exposure to cold air;
- annoying sound, such as squeaking or noise;
- excessive skin sensitivity.
If the reason for the appearance of goosebumps walking on the scalp (and, possibly, on other parts of the body) is one of the ones listed above, rest assured: they will disappear immediately after the provoking factor is eliminated.
Comments
Hello, recently I began to notice a feeling of goosebumps all over my body during the day, it happens from excitement, when I get nervous, almost instantly goose bumps appear, my hair stands on end and I get a feeling of goosebumps. Sometimes this happens at rest. Is it dangerous? And what disease could cause this? Tell.
12/09/2018 at 17:51:27
Apparently I have something similar, something unimaginable has been going on for the last 3 days! I feel like goosebumps are crawling all over my body, and it would be okay if it were due to excitement or cold, but the problem arises absolutely spontaneously, without any systematicity. A wave of goosebumps will roll over your head, then through your torso, then through your arms or legs. I can’t understand what it is... Nothing hurts, it doesn’t itch, the skin has not visually changed. I'm already tired of this, it's wildly annoying! I can't concentrate on work. What should I do?
12/09/2018 at 20:03:50