Depending on the area of the body being examined, your doctor may order a contrast-enhanced MRI. Before an examination with contrast, a special substance is injected into the patient’s body - contrast, which improves the visualization of the organ or system being examined and contributes to the most accurate diagnosis. High diagnostic accuracy is a guarantee of adequate treatment with a sustainable therapeutic effect.
Magnetic resonance imaging using contrast is based on the ability of the bloodstream to carry intravenously administered drugs throughout the body and accumulate them in places with a developed network of medium and small blood vessels. This method examines blood vessels, identifying neoplasms that are characterized by hypertrophied blood supply, and other pathologies.
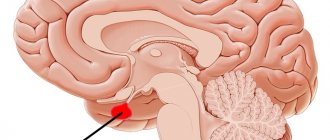
MRI of the brain with contrast - what is it?
MRI of the brain with contrast is a technique that allows you to increase the diagnostic value of the method by introducing special contrast agents (containing gadolinium).
What is contrast used for?
Gross pathologies that disrupt the anatomy of the brain are easily detected on MRI images taken under normal conditions. But this doesn't always happen. Inflammatory processes, some types of tumors, hemorrhages and other diseases are not accompanied by changes in tissue contrast. They are difficult to distinguish on ordinary photographs, since there is no clear boundary between pathology and normality. In such cases, contrast agents are used.
Mechanism of action
Gadolinium, which is part of the contrast, has 7 free electrons in its orbits. Getting into the intercellular space, it forms weak bonds with the hydrogen of water molecules. This leads to a strong decrease in the T1 and T2 relaxation times for the tissues under study. But since gadolinium does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier (the boundary between the bloodstream and brain cells), its direct administration does not affect tissue contrast.
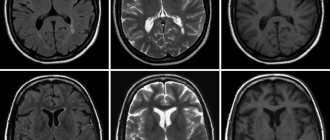
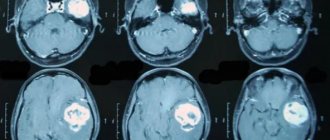
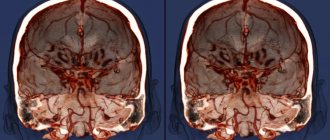
The photo on the left is without contrast. The image on the right with the use of contrast clearly visualizes the area of hemorrhage during a stroke.
Inflammation, infections, hemorrhages, death of brain cells, tumors and metastases lead to disruption of the blood-brain barrier, resulting in gadolinium freely penetrating into pathologically altered tissues. A sharp reduction in relaxation time in T1 and T2 modes for this area, under the influence of gadolinium, is accompanied by an increase in tissue contrast between healthy and altered areas of the brain.
This difference is clearly reflected in the resulting image of the organs being examined, which makes it possible to diagnose certain diseases with greater accuracy. The technique is used for MRI of head vessels with contrast to improve tissue contrast between brain tissue and vascular bed.
Valuable information is provided by the parameters of the rate and degree of accumulation of contrast in the tissues of the tumor. Benign tumors slowly absorb and release moderate amounts of contrast. Malignant neoplasms, due to their developed vascular network, quickly capture large amounts of contrast and also quickly release it. Thanks to this, it is possible to preliminarily determine the nature of the tumor.
It is a misconception that contrast increases the overall quality (brightness, contrast, clarity, or resolution) of an image. The quality of the image depends on the strength of the magnetic field and the sequence of radio frequency signals used. Contrast accumulates only in pathologically changed areas of the brain and cannot affect the clarity of the image.
WHERE DOES THE INVESTIGATION START?
At the beginning of the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the person, after which a layer-by-layer image of a specific organ is taken.
A magnetic resonance imaging scanner is capable of taking images in three planes. After this, the resulting images must be processed by a specific program that is capable of detailing and enlarging the affected areas of the organ, for example, the intestines.
Interestingly, if there are no contraindications, this examination can be carried out several times and at short intervals. The magnetic field of the device is not capable of irradiating the human body. Therefore, even pregnant women undergo such an examination in the 2nd – 3rd trimester.
Today, specialists in Russia and the CIS use gadolinium as such a contrast agent. This drug is very less likely to cause an allergic reaction than iodine-containing drugs. But if it has developed, it can be cured without effort. Most often it manifests itself in the form of hives and itchy eyes. More serious allergic reactions are extremely rare, since before an MRI and the introduction of a special substance, a sensitivity test to this drug is carried out. Such a test consists of a significant dilution of the drug, approximately 1:10, after which 0.1 milliliter is injected on the inside of the forearm. This procedure is carried out for all people who undergo this examination.
The drug in question contains seven unpaired electrons, which can significantly reduce the time of spin-lattice relaxation (transfer of nuclear energy to the environment, as a result of which it turns into thermal energy). As a result, the pathology of the organ under study becomes clear. But individually, gadolinium is a toxic substance and has many contraindications. That is why it is included in chelate compounds (these are compounds that are identical to the natural structure, and it is also perfectly absorbed in the body without causing harm). This compound is found in the following drugs: Omniscan, mangevistin, vasovist, and so on. These are just some of the medications that include this drug and are used during MRI.
For what diseases is MRI of the brain done with contrast?
Contrast enhancement is used to diagnose the following CNS diseases:
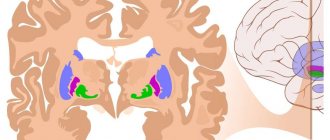
· Tumors of the pituitary gland and tissues surrounding the sella turcica;
· Brain tumors and metastases;
Tumors of the cerebellopontine angle;
· Chronic inflammatory diseases of the nervous system of an autoimmune nature (multiple sclerosis, leukoencephalopathy, leukodystrophy, neuromyelitis optica, concentric sclerosis, etc.);
· Acute cerebrovascular accidents (stroke) of ischemic or hemorrhagic type;
· Vascular diseases of the central nervous system (MRI of cerebral vessels with contrast);
· Detailed study of the structure of already discovered formations;
· Infectious diseases of the central nervous system (encephalitis, meningitis).
In other cases, the use of contrast is not necessary.
The following symptoms are indications for the use of MRI with contrast of the brain:
· Migraines, headaches;
· Convulsions, epileptic seizures;
· Progressive loss of hearing and vision;
· Dizziness;
· Noise in ears;
· Impaired tactile, temperature, pain sensitivity;
· Feeling of goosebumps crawling on the skin.
Gadolinium contrast
All contrast agents used for MRI contain gadolinium compounds. They are hypoallergenic and quickly eliminated from the body, so most often they do not cause side effects. In clinical practice, such paramagnetic contrast agents are used as: “Magnevist”, “Omniscan”, “Dotarem”, “Gadovist”, etc. Any of the above paramagnetic agents are always used in MRI of the mammary glands (if the purpose of the study is not to assess the condition of the implants) . Contrast contrast is often required for MRI of the pituitary gland, abdominal organs, pelvis and soft tissues.
MR angiography usually does not require additional examination, because in this case, the natural contrast is fast-moving blood.
If a tumor process or demyelinating disease is suspected, the attending physician, as a rule, pre-refers the patient for an MRI with contrast. But in some cases, the decision to administer contrast is made by the radiologist directly during the MRI - which is why his presence is necessary during the examination. At the slightest suspicion of a tumor process, the radiologist immediately prescribes an MRI with contrast to the patient.
The contrast agent is safe and is not a contraindication for MR imaging of women during breastfeeding, as well as in studies of children of all ages. However, MRI with contrast is contraindicated during pregnancy.
In addition, MRI with contrast is also contraindicated for patients with polyvalent allergies, acute and chronic renal and liver failure. You can learn more about the limitations of MRI with contrast in a special section of our website.
Contraindications to the use of contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging
Gadolinium, which is part of the contrast agent, is a substance with a high safety profile. Despite this, the use of contrast agents in patients with severe renal failure and impaired renal function is not recommended. If the patient is receiving hemodialysis, an MRI with the introduction of contrast agents is performed before the procedure in order to remove the drug from the body artificially and reduce the load on the excretory organs.
To minimize the possible impact of contrast on the human body, there is no need to overuse the method. Contrast does not affect the overall quality of the resulting images - MRI of the brain with contrast has strict indications (do not ask for a “higher contrast” image). In all other cases, magnetic resonance imaging without contrast is sufficient.
Contrast-enhanced MRI of the head is not recommended during pregnancy. Gadolinium crosses the placental barrier and can accumulate in the fetus. A detailed study of the effect of contrast agents during pregnancy has not been carried out, since such experiments are prohibited for ethical reasons.
Individual intolerance or allergic reactions to contrast agents for MRI and their components are a contraindication for the use of contrast. If necessary, the problem can be solved by prescribing antihistamines and corticosteroids.
Preparing for MRI of the brain with contrast agents
No special preparation is required for contrast-enhanced MRI of the brain.
MRI procedure with contrast
To compare the results obtained and a more complete clinical picture, contrast is used after performing a conventional MRI. The procedure involves two ways of administering the drug:
- instantaneous - a full dose of medication is injected into a vein and pictures are taken immediately after that;
- bolus: the substance enters the circulatory system gradually, synchronously with scanning the area of interest - this method allows you to observe the processes occurring in the body in real time.
Comparison of native and contrast MR tomograms
During the procedure, the patient is located in a tunnel-shaped capsule of the device on a retractable table. Depending on the area in question, a person should spend from 30 minutes to an hour in the tomograph. To avoid distortion of pictures, you cannot move.
The unit makes loud noises. If the examination does not involve listening to the doctor's instructions, the patient is asked to use headphones or ear muffs.
The tomograph is equipped with a “panic button” and a communication device with personnel. If health deteriorates, the examinee can stop the process at any time.
How to do an MRI of the brain with contrast
A contrast study of the brain is carried out as follows:
1. Indications, contraindications and procedures for carrying out the procedure at the Northern Capital Medicine diagnostic center are no different from those for MRI of the brain without contrast.
2. The only difference is the introduction of contrast into the patient’s body (Omniscan).
3. The first series of images is taken without introducing the Omniscan. Then the laboratory assistant administers the drug intravenously using an injector. After the Omniscan is administered, a second series of images is taken.
The volume of the administered drug depends on the patient's weight. For body weight up to 20 kg, 10 ml is administered (the cost of contrast is 2400 rubles); 70-90 kg - 15 ml (3200 rub.); over 90 kg - 20 ml (4400 RUR). The use of contrast increases the duration of the study by 15-20 minutes.
Contraindications
There are relative and absolute contraindications. In the first case, research is possible under certain conditions, in the second it is unacceptable.
Absolute contraindications:
- pacemaker;
- middle ear implants;
- metal body prostheses made of ferromagnetic alloys;
- presence of insulin pumps;
- pregnancy in the early trimester;
- Ilizarov apparatus.
Relative contraindications:
- claustrophobia;
- mental disorders in the patient;
- prosthetic heart valves;
- Bracket system;
- patients under 5 years of age.
The examination is performed as prescribed by a doctor to clarify the diagnosis, as well as to monitor the dynamics of treatment. In most cases, MRI of the brain makes it possible to correctly diagnose and identify diseases at an early stage.
The result of using contrast agents
The use of contrast with gadolinium increases the sensitivity and specificity of the method and makes it possible to identify all brain pathologies. After an MRI with contrast, doctors have no questions left - making an accurate diagnosis will not be difficult. Contrast enhancement in MRI is not intended to overcome the disadvantages of the method (unlike computed tomography, which has low tissue contrast), but provides more effective selection of healthy and pathologically altered tissues using the advantages of magnetic resonance imaging.
“Clinic Medicine of the Northern Capital - a wide range of diagnostic procedures using modern equipment for MRI and CT. Specialists of the highest qualifications and extensive practical experience, regularly improving their level in leading clinics in the Russian Federation and abroad. A unique system that allows you to control the accuracy of decoding and interpretation of examination results. Discounts and promotions that allow everyone to take advantage of expensive medical services. A special offer for all clients of our center - absolutely free consultation with specialist doctors in 15 clinics in St. Petersburg. We work for you 24 hours a day, 7 days a week without weekends and holidays.