How is amniocentesis done?
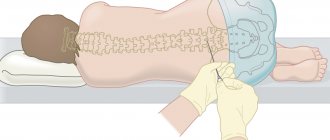
This invasive procedure is performed using a syringe connected to a long, hollow needle. It punctures the abdominal wall, uterus and amniotic membrane, after which a sample of amniotic fluid is “pulled” through it with a syringe or, conversely, a medicinal solution is injected.
The procedure is carried out in two ways:
- Free hand method.
The puncture is carried out under ultrasound control, with the help of which the area of needle insertion is specified. It is selected in such a way that there is no placenta in this place or its wall has a minimum thickness. This avoids possible complications and reduces the risk of damage to the fetus. - Using an adapter.
The difference between this method is the pairing of the needle with an ultrasound sensor, with the help of which the trajectory of its movement is first calculated depending on the insertion in a particular place. At the same time, the doctor performing the procedure has the opportunity to observe the needle itself and its trajectory, thereby choosing the most optimal route for its advancement. However, even in this case, the operation requires highly qualified and experienced surgeons.
The total duration of the procedure including preparation is approximately 5 minutes. Of these, 1 minute is spent on the puncture, and the remaining time is taken to collect amniotic fluid and remove the needle. For 2 hours after the operation, the patient rests and is under the supervision of a doctor to avoid possible complications. To reduce pain during the puncture, local anesthesia can be used. However, doctors recommend doing without it - the pain from an anesthetic injection is in no way inferior to that of the operation itself. In addition, the anesthetic may cause individual intolerance.
To find out more, you can consult with our specialists by filling out the form: Make an appointment
In what cases should the child be shown to the doctor after the procedure?
If you notice any signs or symptoms, take your child to the doctor:
- Seizures and Convulsions : If your child experiences seizures or has had a seizure at least once after surgery, contact your doctor immediately. This may be due to low/high cerebrospinal fluid pressure or mixing of blood and fluid.
- Vomiting : Some children vomit immediately after a lumbar puncture, but if it occurs even hours or days after the procedure, it may be a sign of a complication.
- Frequent crying : If your baby screams and cries a lot, it may be due to pain.
- Refusal to eat or drink : If he does not consume food, including breast milk, or does not eat for more than a few minutes, he requires medical attention.
- Drowsiness : The baby seems tired and semi-conscious. He has a low level of alertness and gets tired quickly.
Rate
—
Preparing for amniocentesis
To increase the effectiveness of the study and reduce the risks of possible complications, the patient should carry out the following preparatory measures:
- Have a consultation with a doctor, where he will tell you in detail about the procedure, its possible complications, contraindications, etc.
- Take tests and undergo an ultrasound to identify hidden infectious or inflammatory diseases, the presence of neoplasms, the volume of amniotic fluid, to confirm or refute a multiple pregnancy. They also help determine the gestational age, condition and viability of the fetus.
- Approximately 4-5 days before amniocentesis, the patient should avoid taking acetylsalicylic acid or similar drugs, and 12-24 hours before, stop taking drugs that reduce blood clotting to reduce the risk of bleeding.
These measures must be performed in order to increase the safety of amniocentesis, reduce the risk of complications for the woman and her child, and increase the efficiency of diagnosis.
Preparatory stage
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes an examination, which consists of a general blood test, a general urinalysis, a vaginal smear and an ultrasound. During an ultrasound examination, the gestational age, location of the placenta and other indicators are clarified.
If on the eve of the procedure the pregnant woman’s health worsened, her temperature rose, or other pathological symptoms appeared, she should consult a gynecologist. The study may be contraindicated and will have to be postponed.
Before amniocentesis, the woman must give her written consent to the procedure. Before signing the document, the doctor is obliged to inform the patient about the features of the operation and possible risks.
What to do after amniocentesis?
Since this procedure is invasive, there are a number of rules that a woman must follow to avoid possible complications:
- It is necessary to exclude or, as far as possible, reduce any physical activity, especially heavy lifting.
- Immediately after the procedure, ensure that you rest for several hours.
- Patients with a negative Rh factor who are carrying a child with a positive Rh factor must undergo a course of injections of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin for 72 hours. This is necessary in order to exclude Rh conflict due to the entry of amniotic fluid containing the genetic material of the fetus outside the amniotic sac.
Sometimes, to eliminate discomfort after amniocentesis, patients are prescribed painkillers. Also, in order to exclude inflammatory processes, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed.
What care is needed after a lumbar puncture?
You need to take care of the child so that he recovers as soon as possible.
Here are some points to remember after a lumbar puncture in an infant:
- Rest is essential: Your baby should sleep well for the next 24 hours. Make sure that there is no bright lighting in his room and that silence is maintained.
- Give him fluids to drink : If your baby is older than six months, give him small sips of water once every couple of hours. You can continue breastfeeding as usual to ensure you are getting enough fluids. If the child is less than six months old, then the only source of fluid is breast milk. You might want to keep your baby breastfeeding for the first 24 hours after a spinal tap to replenish the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Avoid vigorous play : Children can be quite active and playful, but you should avoid this for one week after a lumbar puncture. The hole at the puncture site has not yet healed, and cerebrospinal fluid may drip during active movement and play, thereby complicating the healing process.
- Dress the injection area with new bandages : You must apply fresh bandages to the puncture site as prescribed by your doctor. Changing the dressing at regular intervals will maintain asepsis and speed up the healing process.
A spinal tap in infants does not have any long-term consequences, and your child can lead a normal life immediately after the procedure. Caring is all that is needed for a speedy recovery.
However, the process does not eliminate side effects, and your child may experience them immediately after the procedure.
When is amniocentesis performed?
This procedure can be performed at various stages of pregnancy, but not earlier than 10 weeks after conception. It is then that the formation of the main systems and organs of the fetus occurs, so amniocentesis will be effective as a diagnostic procedure. The optimal period for performing this operation is from 15 to 20 weeks. This is due to the fact that during this period the risk of damage to the fetus is significantly reduced, the volume of amniotic fluid increases, which makes it easier to take a sample for analysis.
The optimal period for amniocentesis is determined based on its goals:
- to identify genetic disorders of the fetus, the puncture is performed at 15 weeks;
- to check the formation of the respiratory system of the embryo, the optimal period is the 3rd trimester;
- to determine the condition of the fetus in case of Rh conflict, amniocentesis is performed in the last months of pregnancy.
If for some medical reason (often these are fetal pathologies incompatible with life) a woman is prescribed an abortion, then through amniocentesis, injectable abortifacient drugs are injected into the bladder to terminate the pregnancy.
What is lumbar puncture - benefits of the study
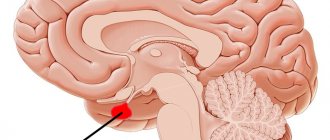
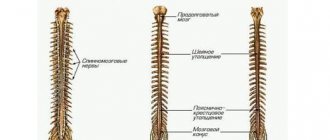
A lumbar puncture, also called a spinal tap, is the process of inserting a special needle into the lower part of the spine to remove a sample of cerebrospinal fluid. It is a clear fluid that circulates around the organs of the central nervous system, from the brain to the lower part of the spine. The sample is removed from the subarachnoid space , which is a cavity containing cerebrospinal fluid that bathes the entire nervous system.
Video: Trainer for practicing lumbar puncture in infants
Cerebrospinal fluid is a vital substance because it softens spinal shock, protects the brain and spinal cord from physical impact, and carries vital nutrients for nerve cells. Therefore, it can provide valuable information about the health of the nervous system and indicates the presence of pathogens in the event of neuroinfection.
Lumbar puncture: advantages of manipulation
While many parents are unsure about the need for an invasive test such as a lumbar puncture to detect the presence of an infection, research has shown that a lumbar puncture is the best way to confirm the presence of some diseases.
It is so safe and accurate that it is also performed on premature babies.
The benefits of a lumbar puncture certainly outweigh the risks, making it an effective way to diagnose life-threatening illnesses in a child.
Application of amniocentesis
Amniocentesis during pregnancy is used primarily as a diagnostic procedure to detect certain genetic disorders in the fetus - for example:
- Down syndrome
, characterized by abnormalities in mental development, defects of internal organs and abnormal appearance; - Patau syndrome
, which is characterized by external abnormalities, developmental disorders of the central nervous system and brain, incompatible with life (the newborn dies a few days later); - Edwards syndrome
, accompanied by disturbances in the structure of internal organs (most often the heart), mental retardation, early mortality (the average life expectancy of such children is several months); - Turner syndrome
, which manifests itself exclusively in girls in the form of malformations of internal organs, infertility, short stature (although people with such pathology do not have deviations in intellectual development and can lead a full life); - Klinefelter syndrome
, characteristic only of men and accompanied by elongation of the limbs, high waist, gynecomatia, delayed puberty, testicular atrophy, infertility.
In addition to identifying genetic abnormalities in the fetus, amniocentesis during pregnancy is used to monitor the overall development of the child’s organs and systems in women at risk.
Indications for amniocentesis are:
- The presence of genetic abnormalities in a pregnant woman or her relatives;
- A woman’s age exceeds the 35-year mark (after which the risk of the formation of an extra 21 chromosome pair in the ovaries increases);
- Results of an ultrasound examination - for example, identification of an enlarged gap between the neck bone and the skin of the fetus, characteristic of Down syndrome;
- The results of biochemical screening are an excess of the normal level of hCG or an abnormally low concentration of PAPP-A (a specific protein contained in the blood plasma).
Another area of use of this technique is artificial termination of pregnancy. In this case, using a puncture needle, solutions of drugs that kill the fetus and promote its rejection and expulsion from the uterus are introduced into the amniotic fluid.
Introduction
Today, an ultrasound device has become indispensable in intensive care units and intensive care units at the bedside of the most critically ill patients.
Anesthesiologists and resuscitators use ultrasound to visually guide central venous access procedures, peripheral nerve blocks, pericardiocentesis, and pleural puncture [1]. Ultrasound control increases the safety of the manipulations due to direct visualization of the anatomical features of the area of interest, as well as direct control of the needle in real time. And although most colleagues easily and with a high success rate perform lumbar punctures on patients of any age, there is a category of patients in whom this standard procedure is complicated and may require several attempts. These are patients with a violation of the anatomy of the spine - with scoliosis or spastic tetraparesis. In patients in this group, the probability of a successful lumbar puncture on the first attempt does not exceed 80%, even if the manipulation is performed by an experienced doctor [2]. Another unfavorable prognostic sign for lumbar puncture is increased body weight (BMI>35) [3, 4]. We believe that ultrasound can solve this problem, since the ultrasound machine allows us to obtain important anatomical information (depth of the ligamentum flavum, width of the intervertebral space and the optimal angle for needle insertion) in each patient at risk [5]. The purpose of this work
was an assessment of the effectiveness of lumbar puncture under ultrasound control in children with impaired spinal anatomy.
Contraindications to amniocentesis
This diagnostic procedure is excluded if the patient has:
- Elevated temperature;
- Acute stage of chronic diseases;
- Infectious diseases;
- Factors that threaten the life of the fetus (placental abruption, uterine contractions);
- Bloody discharge;
- Congenital or acquired disorders of the structure of the uterus;
- Infectious lesions of the abdominal cavity and its organs;
- Low blood clotting; v
- Benign neoplasms of the uterus (fibroids).
When is the method contraindicated?
There are no absolute contraindications to the study. Relative contraindications are:
- threat of placental abruption;
- · bloody discharge from the cervix;
- acute inflammatory processes or exacerbation of chronic pathologies;
- pronounced hypertonicity of the uterus.
Online consultation with a gynecologist
consultation cost: from 500 rubles
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Complications during amniocentesis
Due to the invasive nature of this procedure, there are certain risks for the health of the child and the mother herself:
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy (miscarriage) or premature birth;
- Violation of the integrity of the placenta or the tissues of the embryo itself with a puncture needle;
- Damage to the bladder, uterus or other pelvic organs;
- Inflammation of the amniotic sac, infection of the amniotic fluid with infectious agents;
- Placental abruption, bleeding, damage to the umbilical cord, etc.
Even if amniocentesis is performed correctly, the patient may experience discomfort and pain in the abdominal area, bleeding, release of a small amount of amniotic fluid, etc.
Although in a medical setting the occurrence of these complications is minimized, the likelihood of them still remains. Therefore, doctors use this procedure relatively rarely, and when using it, they first warn the patient about the possible consequences. Often, alternative methods to amniocentesis are used to identify congenital defects in the fetus - for example, genetic analysis of embryonic DNA isolated from the woman’s blood plasma. Although this method shows less accurate results, it does not pose any threat to the life and health of the child.
The decision to perform amniocentesis is made by the pregnant woman herself after consultation with a specialist.
At her request, this procedure can be canceled or replaced with a safer or more effective one. However, amniocentesis remains one of the most effective ways to detect congenital abnormalities in the fetus, and therefore continues to be actively used in gynecological practice. To find out more, you can consult with our specialists by filling out the form: Make an appointment
Why do you need to get a puncture?
With sinusitis, a large amount of pathogenic mucus accumulates in the nasal sinuses (special cavities located near the nose and filled with air; another name for them is “sinuses”), which after some time turns into pus. The inflammatory process leads to the nose becoming very swollen. As a result, mucous masses from the sinuses cannot be evacuated naturally through the nasal passages. The mucus stagnates - and this is the most favorable environment for the life of bacteria. Mucous masses turn into pus. Symptoms of the disease are gaining momentum, and the patient’s condition is greatly deteriorating.
If the swelling cannot be removed with antibacterial drugs and washing the maxillary sinuses, then a puncture is used against the disease. Because this is the only way to free the nose from pus and relieve unpleasant symptoms.