Why do my legs and arms go numb? What diseases can lead to these symptoms? Which doctor should I contact? How to diagnose the cause?
Numbness in the arms and legs is a neurological symptom that most often indicates damage, inflammation, or compression of sensory nerves. Often, numbness is accompanied by pain and unpleasant sensations such as tingling and “crawling goosebumps.” Many nerves are mixed, that is, they contain both sensory and motor fibers. In such cases, numbness is combined with a decrease in muscle tone and impaired movement.
There are many reasons for numbness in the limbs. Most often they are associated with pathological processes in peripheral nerves. The larger the nerve, the larger part of the limb loses sensation. In rare cases, the symptom is caused by disorders of the brain and spinal cord.
Numbness from compression of nerves and nerve roots
One of the most common conditions that leads to compression of the nerve roots is intervertebral hernia. Most often it forms in the lumbar spine, as it experiences the heaviest loads. Fortunately, in most cases, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, intervertebral hernias can be treated without surgery.
Carpal tunnel syndrome leads to numbness, tingling in the hand and other symptoms. In the wrist area there is a tunnel formed by bones and ligaments. It contains a nerve that, under certain conditions, can be compressed.
In the area of the shoulder girdle and collarbone is the brachial nerve plexus - all the main nerves innervating the arm depart from it. During injuries (most often road accidents), these nerves are stretched and compressed, resulting in numbness and, in severe cases, paralysis of the arm.
With spondylolisthesis, the upper vertebra “slips” a little from the lower one, this leads to compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots, and sensitivity disorders.
Causes
Numbness can be a sign of a wide range of diseases or conditions that involve restricted blood flow or nerve damage.
Temporary numbness can be caused by any activity that puts prolonged pressure on the nerve(s), such as sitting cross-legged or cycling long distances. Numbness can also occur due to moderate to severe orthopedic or vascular pathology, as well as conditions and diseases that lead to damage to the nervous system. In some cases, numbness is a symptom of a life-threatening condition that requires emergency medical attention.
Cardiovascular causes of numbness
Numbness can be caused by a lack of blood flow to a certain area due to conditions such as:
- Arteriovenous malformations
- Buerger's disease
- Deep vein thrombosis (a blood clot in the legs can break off, which can lead to pulmonary embolism in the lungs, heart attack, stroke)
- Frostbite
- Diseases of peripheral arteries (vascular atherosclerosis, in which narrowing of the arterial bed occurs).
- Raynaud's syndrome, in which persistent spasm of peripheral vessels occurs and blood circulation in the distal extremities is impaired. Vasospasm is usually triggered by cold or sometimes stress.
Orthopedic causes of numbness
Numbness may also occur due to minor or serious orthopedic conditions that cause nerve damage:
- Whiplash neck injury
- Bone fractures
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Degenerative diseases of the intervertebral disc
- Herniated disc
- Compression pinched nerve
- Osteoporosis
Neurological causes of numbness
Numbness due to nerve compression or nerve damage may be due to conditions such as:
- Alcoholism
- Brain tumors
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Encephalitis
- Heavy metal poisoning such as lead poisoning
- Hypothyroidism
- Multiple sclerosis
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Spinal cord injury or tumor
- Stroke
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Myelitis
- Myelopathy
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
Numbness during pregnancy
Pregnant women face many changes in the body, and numbness is one of them. Some pregnant women develop carpal tunnel syndrome and it is believed to be due to water retention in the body during pregnancy.
As the fetus develops, fluid accumulates in the body, tissues swell, including in the wrist area, compression of the median nerve occurs and carpal tunnel syndrome develops. Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome are more pronounced in the morning hours, as fluid accumulates in the body at night. As a rule, carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnant women heals on its own after delivery.
Numbness in children
There are many reasons why children may experience numbness in different parts of the body. Eating disorders, lack of vitamins and minerals can cause numbness in the lower extremities, this is especially typical for a deficiency of B vitamins. Sports injuries can also cause numbness. Therefore, in childhood, parents need to pay attention to children’s complaints of numbness, which lasts more than a few minutes and may be a sign of damage to ligaments, tendons or bone fractures. Often, anxiety in childhood can be a source of numbness in the lips and face.
Vascular disorders
One of the complications of diabetes is diabetic neuropathy, damage to sensory, motor and autonomic nerves as a result of impaired blood flow in small vessels. One possible symptom is numbness in the limbs.
There is a large group of diseases - vasculitis. Autoimmune inflammation develops in the vessel wall, it thickens, becomes weakened, and scarring occurs. In the lumen of the vessel, areas of narrowing appear in which blood flow is disrupted. Various organs, including nerves, can suffer from this.
With one of the systemic connective tissue diseases - Raynaud's disease - a spasm of the small vessels that supply blood to the fingers and toes occurs. In response to cooling or stress, a feeling of coldness and numbness occurs in the fingers.
Diseases of the brain and spinal cord
One of the most common causes of numbness in different parts of the body associated with brain damage is a stroke, as well as a transient ischemic attack, which is popularly called a “mini-stroke”. Severe injuries to the brain and spinal cord can lead to sensory impairment.
Less common are such lesions of the central nervous system as an aneurysm (a pathologically enlarged, weakened area) of a cerebral vessel, arteriovenous malformation (incorrect communication between an artery and a vein, when blood is discharged directly, bypassing the network of capillaries), tumors of the brain and spinal cord, paraneoplastic syndrome ( damage to the nervous system caused by a tumor that is located outside the brain).
The article lists only the main common causes of numbness in the arms and legs. There are others. In order to get an accurate diagnosis and begin proper effective treatment, you need to visit a doctor.
A very common manifestation of diseases of the nervous system and musculoskeletal system is numbness . Treatment of this problem can sometimes be very difficult due to the many factors that cause it and the difficulty in treating the underlying pathology.
WHAT IS NUMBITY AND HOW DOES IT OCCUR?
The human brain must constantly receive information from the environment. This is accomplished through receptors, of which there are a large number. These receptors permeate all our tissues, including the skin of the upper and lower extremities. A person’s ability to sense various irritations through receptors is sensitivity, and numbness
- This is a sensory disorder. Receptors with the property of irritability convert this irritation into nerve impulses, which are sent along centripetal fibers to the brain for analysis, bypassing many structures along the way. And a violation in any of these structures leads to sensitivity disorder (numbness).
In medical classifications , numbness
refers to a type of sensitivity disorder such as paresthesia, which includes, in addition to numbness, some other unpleasant sensations. Such unpleasant sensations include: tingling, burning, crawling sensation.
The distal parts of the body, that is, the limbs, are most often affected by numbness. “I have numbness in my hand and fingers,” is such a common complaint, yet people so rarely seek medical help. More often, these symptoms occur at night, when a person wakes up from the fact that his entire hand, or only his fingertips, are numb. This can happen at any time and under any conditions, however, depending on a particular disease, the symptoms will still change. Let's look at some characteristic symptoms that relate to one or another disease.
SYMPTOMS OF NUMBENCY IN VARIOUS DISEASES
Numbness in spinal osteochondrosis and discogenic disorders
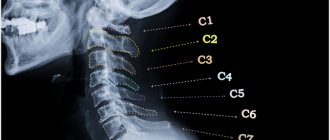
With osteochondrosis of the spine, damage to bone structures and intervertebral discs occurs due to degenerative-dystrophic processes. Protrusions and herniations of intervertebral discs will play a key role in impaired sensitivity (numbness). How does this process happen? A hernia or protrusion compresses the spinal roots, or the nerve itself, which exits the intervertebral foramen. As is known, the nerves contain sensory fibers from the corresponding dermatomes. From the dermatomes of the upper extremities - this is the cervical spine, from the lower extremities - the lumbar spine. Nerves compressed by spinal hernias lose their ability to conduct impulses and this is how numbness
. This type of sensitivity disorder is characterized by concomitant vertebrogenic pain syndromes, muscle weakness, stiffness and difficulty moving.
Numbness due to Raynaud's disease
Raynaud's disease is a numbness of the fingertips of both hands, which is often provoked by cold, and they first acquire a pale tint, and then turn blue and become red-purple. All these symptoms relate to Raynaud's disease, which is associated with impaired blood circulation and filling of the smallest vessels (arteries and arterioles) of the distal (end) parts of the fingers. This disease is 5 times more common in women. If the above symptoms of numbness occur, you should contact a neurologist and rheumatologist, who will rule out diseases of the cervical spine or a concomitant autoimmune process and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Numbness due to carpal tunnel syndrome
The following disease is characterized by numbness of the first three fingers of the hand - these are the first, index and middle fingers of the hand. There may also be tingling and soreness that can spread to the entire hand. The condition for the occurrence of numbness in this pathology can be monotonous work of the hands, for example, in a programmer, seamstress, and so on. The pathogenetic cause of this condition is compression of the median nerve in the canal, which is formed by the ligamentous and muscular apparatus. As a result of increased pressure in the wrist, compression of the venules and arterioles supplying the epineurium of the median nerve occurs. Subsequently, intraneural edema forms, myelin fibers are affected and the above symptoms occur (in particular, numbness
). This disease is 2 times more common in women and in obese people. To make a diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome, it is necessary to perform specific test symptoms and exclude radiculopathy of the cervical spine and brachial plexus diseases.
Numbness due to polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathies are characterized by numbness and impaired sensitivity of the distal (end) parts of both the upper and lower extremities. Symptoms such as tingling, itching, swelling, a feeling of “cotton wool” in the legs while walking, and lack of temperature sensations may also occur. Impaired temperature sensations in patients are manifested in the identification of burns on the hands, unsteadiness of gait in the dark, the presence of painless ulcers and peeling of the skin, especially on the dorsum of the lower limb. Major diseases that can lead to polyneuropathy and sensitivity disorders ( numbness
), these are: diabetes mellitus (thirst will also be observed), consequences of operations (laminectomies), drug intoxication, drug addiction, toxic effects of various substances in case of poisoning. Alcohol abuse can be identified as a special group. This is the so-called alcoholic polyneuropathy.
In all these conditions, the nerve sheath is affected, resulting in loss of sensation (numbness).
Numbness due to scalene syndrome
The name of the syndrome indicates the scalene muscle, which is where the pathology is formed. This muscle is attached to the first rib and lower cervical vertebrae, forming an opening through which the subclavian artery and the brachial plexus pass, innervating the upper limb. With cervical osteochondrosis, the scalene muscles are spasmed and cause compression of the subclavian artery and branches of the brachial plexus. As a result, blood flow and innervation of the upper limb decrease, and the hand suffers the most, because it is there that we feel this unpleasant symptom - numbness
. Treatment also occurs after a full examination.
Numbness in ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack
With ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack, there is a disruption of blood circulation in the brain with damage to its structures. Numbness during an ischemic stroke is not difficult to suspect, since it will be characterized by damage to half of the body, for example, the right arm, right leg, or, on the contrary, symptoms such as paresis and paralysis in these or opposite limbs (movements in them are impaired). It all depends on the localization of the pathological process; there may also be visual impairment, speech impairment, memory loss, and so on. In these cases, you should immediately seek medical help for timely provision. The situation is different with a transient ischemic attack, in which symptoms tend to occur unnoticed with low intensity and pass over time. Numbness during a transient ischemic attack persists and the patient, without giving it much importance, usually seeks medical help less often, which can aggravate the condition and then, most likely, a transient ischemic attack will develop into an ischemic stroke, which already directly threatens the patient’s life.
Numbness in demyelinating diseases
Demyelinating diseases are, as a rule, hereditary diseases that affect the nervous tissue of the brain and spinal cord, or the nerve trunks themselves. With these types of diseases, symptoms can be very diverse: from local lesions with numbness of one finger or the whole hand, to mosaic lesions with numbness in various areas of the body. This lesion is characterized by persistent symptoms with possible increasing dynamics. As with other pathological conditions, consultation with specialists and a thorough examination are necessary.
CAUSES OF NUMENCE
Considering the symptoms described above, it is worth summarizing the conditions that can provoke its appearance:
- osteocondritis of the spine;
- pinching (compression) of the roots of the spinal nerves, trunk or branches of the corresponding nerves along the course of innervation;
- discogenic disorders;
- Raynaud's disease;
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- demyelinating diseases;
- ischemic stroke;
- transient ischemic attacks (TIA);
- scalene muscle syndrome;
- polyneuropathy (diabetic, alcoholic);
- hypothermia;
- injuries;
- tumor lesions of both the brain and spinal cord, as well as structures adjacent to the trunk or branches of the nerves along the innervation to the site of numbness.
TYPES OF NUMENCE
Numbness of the limbs
The upper and lower extremities become numb quite often. This may indicate temporary compression of the nerve, or the presence of vascular or endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus). It is important to seek help in time and find the cause of the disease.
Numbness of the hand
The hand also becomes numb quite often. The most common cause of this condition is compression of the nerves or blood vessels in the hand area, as well as the median nerve. The consequences of such a pathology can be quite serious.
Numb hand
The most common cause of this pathological condition is pinching of the neurovascular bundle by the muscles and connective tissue. The condition is very unpleasant, as the activity of the entire limb is partially impaired.
Numbness of fingers
Carpal tunnel syndrome is often involved in the occurrence of numbness in the fingers. Damage to the cervical spine may also be the cause. If the fingers of both hands are affected at the same time, we can talk about Raynaud's disease and other causes. Interestingly, at the end of the last century, numbness of the fingers was extremely rare, but now it is one of the fairly common symptoms.
Numbness of the leg
Quite often it occurs in young, working people and this type of numbness is often associated with professional activities. In addition to numbness, there is often a crawling sensation in the legs. Damage to the lumbar and sacral spine is one of the main causes of this symptom.
Numb toes
There are many reasons why the toes go numb: these include spinal diseases, diabetic polyneuropathy, alcohol abuse (alcoholic polyneuropathy), and vascular problems. The pathology is very unpleasant, especially for the female population.
PREVENTION
Prevention will consist of eliminating factors that lead to diseases accompanied by numbness. Loss of sensation ( numbness)
) is already a consequence of a pathological process that has arisen in the body. To avoid these diseases, it is necessary, first of all, to undergo courses of preventive examinations from specialists who will be able to identify diseases hidden about the symptoms of numbness in the early stages. In addition, eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, control your sugar levels and numbness can be avoided.
DIAGNOSTICS
For any type of sensitivity disorder, consultation with a specialist and a thorough examination are necessary. It is quite difficult to determine the cause of numbness on your own without auxiliary methods, especially when this process is caused by a huge number of diseases.
To diagnose numbness, almost all known examination methods are used: survey, visual and manual examination, radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, angiography, myography, as well as laboratory tests (blood tests for inflammation, glucose levels). It is very important to conduct a full diagnosis of numbness; treatment should be appropriate.
Who should I contact?
A neurologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders, such as sensory loss and numbness in the extremities. In order to correctly assume what was the possible cause and choose the right direction of the diagnostic search, the neurologist must examine the patient, find out in which parts of the body numbness occurs (only in the fingers, in the hands or feet, in the entire arm or leg, in one limb , or right and left symmetrically), are there any other neurological symptoms or concomitant diseases.
Depending on the results of the examination, the neurologist may refer you to other specialists:
- For vasculitis, Raynaud's disease - see a rheumatologist.
- For cardiovascular pathologies, see a cardiologist.
- For diabetes mellitus, see an endocrinologist.
- In case of tumors or injuries, see a neurosurgeon.
- For infectious diseases - see an infectious disease specialist.
- In case of poisoning with harmful substances at work, contact an occupational pathologist.
Examination for numbness of extremities
- Depending on the suspected cause of numbness in the limbs, the doctor may prescribe different types of diagnostics. X-rays help diagnose diseases associated with disorders of the skull and spine, such as intervertebral hernia. If there is a suspicion of vascular pathology, angiography is performed - an X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast solution into the vessels.
- If necessary, you may be prescribed other imaging methods: ultrasound, CT, MRI.
- In order to check in which nerves the conduction of impulses is impaired, electroneuromyography is used - a study using special electrodes.
- Sometimes they resort to the method of evoked potentials. Special sensors are placed on the patient's head to record brain activity. The affected nerve is stimulated through the skin using electrical impulses and the brain is observed to respond to the stimulation.
Since dozens of different reasons can lead to numbness in the arms and legs, the diagnostic program must be individual for each patient. In some pathologies, if left untreated for a long time, even more serious, irreversible neurological disorders may occur. Visit a neurologist, make an appointment by phone: +7 (495) 120-08-07
Why do my arms and legs go numb?
To answer this question, it is necessary to undergo a competent and comprehensive diagnosis at the Alan Clinic Center for Neurology and Orthopedics, where an integrated approach is used to identify problems when making a diagnosis.
Research methods applied to our center:
- consultation with a neurologist;
- special neurological tests;
- dynamic active and passive tests;
- special reflex tests;
- assessment of the condition of the musculoskeletal system, posture, gait, uniform distribution of load on joints, range of motion, stability and strength of the joint;
- making and explaining the diagnosis;
- selection of individual complex motivated treatment.
Prescribing examinations if necessary.
If necessary, the doctor may also prescribe:
- MRI;
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray;
- lab tests;
- ENMG;
- VEP;
- puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis.