Computed tomography is an advanced and highly informative examination method for diseases and non-obvious pathological processes of a wide range. For the discovery of this method and the development of scanning technology, inventors Allan Cormack and Godfrey Hounsfield received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1979, and their development helped to significantly increase the detection rate of dangerous diseases (oncology, strokes, vascular pathologies).
What is special about CT? What does the examination show? Let's look at it in this article.
What is the essence of the EEG procedure?
An electroencephalogram records electrical signals from brain cells and allows us to identify epilepsy, trauma, neoplasms, inflammatory processes, and changes in blood vessels. Pathology is indicated by disturbances in the electrical activity of neurons, which are recorded using special sensors placed on the patient’s head.
Using an electroencephalogram, the doctor can:
- analyze the performance of the brain;
- identify foci of pathologies;
- assess the nature and extent of damage;
- confirm or clarify the diagnosis;
- monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
What causes vascular diseases of the brain?
1. Vascular atherosclerosis;
2. Hypertension;
The intracerebral vascular system, carotid artery and other areas are damaged, after which the first signs and symptoms of the disease appear.
Forms of the disease
- transient disorders affecting the circulatory system in the brain;
- failure to supply power to the brain, which leads to necrosis and resorption of the organ;
- arterial blockage;
- damage to the walls of blood vessels;
- bleeding in the brain (stroke).
Stroke is a disruption in the circulatory system that is accompanied by tissue damage and functional disorders of the body. The main symptoms signaling the risk of a stroke: increasing tinnitus, a feeling of heaviness in the skull, loss of strength, dizziness. The severity of the disease depends on the degree of arterial disorders and the volume of the affected area of the brain. Since a stroke takes the patient by surprise, it is not always possible to call doctors for help in time, who could influence the further consequences of such a serious and dangerous disease, often leading to death.
Another name for transient disorders is discirculatory encephalopathy, accompanied by vascular spasms in the form of a headache of a strong or weak nature. These are changes and disorders characterized by vascular insufficiency of brain cells. The disease occurs against the background of atherosclerosis, hypertension problems or diabetes mellitus of any stage. It is important to diagnose the disease at an early stage to stop or minimize the progression of encephalopathy. Symptoms of the disease: headaches, emotional instability. Over time, serious problems with intellectual abilities, speech, memory loss, fainting and partial blindness, numbness, impaired tactile functions, and a feeling of weakness throughout the body are observed.
3. Atherosclerosis.
At the initial stage, the disease does not always make itself felt, so it is possible to detect the presence of the disease only with the help of special medical means of modern diagnostics. Timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment make it possible to save as many patients as possible and reduce the risk of dangerous prognosis of the disease to a minimum.
In what cases is EEG prescribed?
After a conversation with the patient and studying the medical history, the specialist decides to prescribe encephalography. Typically, indications for an EEG are frequent headaches, sleep problems, fainting, fatigue and chronic fatigue.
Deterioration in well-being may be a sign of disorders in the functioning of the brain. The above ailments often arise due to:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head;
- inflammatory processes in meningitis and encephalitis;
- endocrine disorders;
- malignant or benign neoplasms.
For patients suffering from epilepsy who have undergone neurosurgical interventions and head injuries, EEG monitoring is mandatory.
Causes and consequences of headaches
To get rid of headaches caused by ordinary overwork, it is enough to get a good night's sleep, adjust your lifestyle and diet. But this does not help in all cases, just like taking pills in an attempt to numb the pain. If painful sensations in the head are caused by developing pathological processes, it is necessary to identify and eliminate their causes. It can be:
- hormonal disbalance;
- vascular diseases;
- neurological disorders;
- viral diseases;
- inflammation of ENT organs;
- cranial injuries and post-traumatic pathologies;
- tumor processes.
A specially designed check-up program will help you find out what triggers your headache. Many diseases can develop for years without any symptoms. The examination results in such cases come as a complete surprise to patients.
How to prepare for an electroencephalograph examination?
Monitoring the electrical activity of the brain does not require complex training. During the examination, it is important to simply follow the doctor's instructions and remain calm. Flashes of light and noise are part of the procedure.
Three days before the examination, it is recommended to stop taking tranquilizers, anticonvulsants and sedatives. 24 hours before the examination, do not drink tea, coffee, energy drinks, or eat chocolate. The day before monitoring, wash your hair. Have a snack an hour before the examination. Before starting, loosen your hair and remove metal jewelry.
Educational program on diagnostics: electroencephalography
Human examination techniques based on monitoring and studying the electrical activity of cells exist not only in cardiology. The electrical activity of brain cells in higher animals was discovered in the 19th century - and after that, physiologists immediately began to analyze the recording of these signals. This is how electroencephalography appeared.
D.C
The history of EEG dates back to the middle of the 19th century, when the German physiologist E. G. Dubois-Reymond first discovered an electrical signal from the brain of a laboratory animal. And in 1875, almost simultaneously, the Englishman Richard Cato and our compatriot Danilevsky reported recording currents emanating from the brains of rabbits, dogs and monkeys. V. Ya. Danilevsky, among other things, proved that the animal’s brain constantly emits such a signal, that is, there is a certain background “direct current” that changes under the influence of various kinds of stimuli.
However, a lot of time passed before electroencephalography could enter medical practice. Firstly, brain currents are quite weak, so scientists had to develop amplifying equipment. Secondly, the question of which organ should be considered their source has long been questioned. Many experts considered the received signals to be a recording of skin galvanic processes or the conduction of cardiac currents to the surface of the body.
The issue was resolved in 1934, when at a meeting of the Cambridge Physiological Society, the Englishmen Adrian and Matthews conducted a demonstration experiment. The scientists simultaneously recorded currents from the animal's scalp, from its exposed brain, and a regular ECG (electrical activity of the heart). The first two records coincided with each other, but did not coincide with the third. The dispute was resolved.
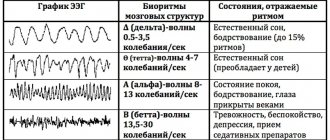
Berger's rhythms and pathological rhythms
The German psychiatrist Hans Berger is considered the father of clinical EEG. In 1928, he proposed the term itself and described the main types of electrical activity of the human brain, which became known as “Berger rhythms.” The alpha rhythm is characteristic of a calm state, readiness to work; its main source is the occipital region. Beta rhythm is faster; at rest, it is noted in the frontal lobes, and during active activity it covers the entire surface of the brain.
Slow ones - delta rhythm and theta rhythm - are recorded during sleep in adults and during wakefulness in very young children. The appearance of slow rhythms during wakefulness in adults is a sign of pathology.
In pathological conditions, unusual figures appear in clear, repeatedly repeating patterns of basic rhythms - for example, “peak-wave” complexes, “bursts of sharp waves”, etc. Depending on which electrode the “abnormal” recording comes from, the localization of the brain area with painful activity. This is how epileptic foci are detected in the unchanged brain matter, tumors, and vascular pathologies.
Conventional EEG and additional studies
Assessment of background brain activity is carried out in a dark, quiet room, shielded from electromagnetic radiation. The patient lies reclining and tries to relax as much as possible. It is important that the subject's eyes are closed.
The fact is that open eyes - even if a person is in complete darkness - immediately transfer the brain from “sleep” mode to active perception mode. The activity that the device will register in this case will already be a reaction to the stimulus. That is why the doctor asks you to open your eyes at very specific moments.
In addition to eye-opening tests, there are other “extensions” of the technique - the study of the brain’s reaction to provoking factors. For example, rhythmic photostimulation is used: a bright light flashes at a certain frequency in front of the patient’s closed eyes. Another provocation test is hyperventilation, where the patient is asked to breathe deeply for 3–5 minutes. All this additionally allows us to clarify the presence of pathological brain activity.
Who should do an EEG?
Indications for an EEG are mainly fainting or convulsive conditions of unknown origin. And don’t be surprised if a cardiologist refers you to an EEG: this test is widely used to distinguish fainting of “heart” origin from “brain” origin.
In addition, mandatory EEG studies are carried out for people in certain professions (professional drivers, professions related to carrying weapons, etc.). Family members of a person diagnosed with epilepsy will also be sent for an EEG.
There are no contraindications for this study. However, since EEG with provocative tests can cause a seizure in a person who is not aware of the presence of epilepsy, this technique should be used only if it is possible to provide immediate assistance to the patient. As a rule, the examination is carried out either in a hospital or in clinics with special equipment, where in the event of an unexpected reaction, doctors are always ready to help.
Lidiya Kulikova
Photo depositphotos.com
How is an EEG performed?
The examination takes place in several stages.
Preparatory stage
- the patient enters the office, protected from light and sound;
- an encephalograph “cap” consisting of special sensors is put on it;
- The sensor wires are connected to a device that records the bioelectric impulses of the brain.
Diagnostic stage
- the encephalograph transmits data to the monitor in the form of a graph;
- the power of electric fields and its distribution in different parts of the brain are recorded;
- Functional tests are carried out: the patient is asked to blink, look at flashes of light, breathe less often or deeper, listen to a sharp sound.
Final stage
- the electrodes are removed from the patient;
- print out the results.
Treatment of headaches at the Federal Research Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency
If
- intense headache occurred acutely and for the first time;
- acute headache is accompanied by a rise in body temperature;
- the onset of pain was preceded by a head injury;
You should immediately seek emergency medical help!
The main goal of chronic headache therapy is to reduce the intensity and frequency of headache episodes. For this, various conservative and interventional techniques are used. The key to achieving lasting results is an accurate and targeted diagnosis of the cause of the headache. The best effect is achieved when using a multidisciplinary approach, which includes components aimed at correcting the main links in the pathological chain that causes headaches in each specific case.
Conservative therapy consists of selecting the optimal regimen of medications: non-steroidal analgesics, triptans, antidepressants, antispasmodics, antihypertensive drugs, etc. Extended intravenous administration of drugs and oxygen therapy are also used.
If the headache has a localized cause, as in the cases of neuralgia, tension headaches, and vertebrogenic pain, various interventional techniques are used. Drugs administered specifically to the desired point block nerve impulse transmission from the affected area, relax spasmodic muscles, improve tissue trophism and relieve pain. At the same time, the absence of a systemic effect eliminates the side effects of drugs on other organs and systems.
How long does the electroencephalogram procedure take?
A regular encephalogram (routine EEG or diagnosis of a paroxysmal state) takes from 20 to 30 minutes.
During the examination, a number of tests are carried out:
- rhythmic photostimulation;
- hyperventilation;
- load in the form of slow blinking.
If it is necessary to evaluate certain brain functions, the specialist adds additional tests, which he informs the patient about in advance. Such tests include:
- clenching your fingers into a fist;
- being in the dark;
- sleep deprivation for a certain period;
- night sleep monitoring.
What the results look like
After performing an MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck and head, the doctor receives layer-by-layer images of the vascular pattern with the ability to construct a three-dimensional model. The patient can pick up the images on electronic media or in printed form. The photographs are accompanied by a report from a radiologist.
Normally, the internal carotid arteries are located symmetrically, have clear contours, are not displaced, and are not compressed. The cerebral arteries arise in a typical place, the diameter is not changed, and there is no pathological tortuosity of the vessels. The cerebral veins and sinuses should be of normal diameter, without areas of blood flow disturbance, filling defects or deformations.
On MRI images of the vessels and arteries of the neck you can see signs inherent in certain diseases:
- an aneurysm is a round formation with a high signal intensity; when a thrombus attaches, a layered structure appears;
- vascular malformations appear as linear or tortuous structures with dilated vessels;
- dissection of the arterial wall is characterized by the appearance of a crescent-shaped hematoma located along the vessel, while the lumen of the artery is narrowed evenly or in the form of a rosary;
- atherosclerosis of the vascular system looks like an area of increased intensity on the vessel wall, the lumen is narrowed;
- hemangioma is a high-intensity formation with clear edges and a lobular structure.
Despite a detailed description of all identified pathological formations, the conclusion of a radiologist is not a diagnosis. The MRI result of the area of the cerebral vascular system should be shown to the doctor who ordered the study. Clinics offer the opportunity to consult with the radiologist who performed the procedure. If necessary, he will recommend contacting specialized specialists - a neurologist, oncologist or surgeon.
Interpretation of survey results
Even a qualified specialist is not always able to accurately name the cause of the patient’s poor health and immediately make a diagnosis. The doctor may be alerted to focal changes on the EEG. In this case, magnetic resonance imaging will be required to exclude a tumor or cyst.
When you contact a medical doctor, you will be able to undergo all examinations as quickly as possible, without delaying your visit to specialists.
If you need to do an EEG of the brain and you want to do it using modern expert-class equipment and in the shortest possible time, call the phone number listed on the website or leave a request in the feedback form.
Medical staff will answer your questions and conduct all necessary examinations within one business day. Let's take care of your health together!
Therapeutic stage of disease treatment
Let's consider the features of treatment of the most dangerous group of brain diseases.
First, the treatment plan is designed to eliminate the symptoms of hypertension and atherosclerosis. Special medical substances prescribed by a doctor normalize fat metabolism and also maintain normal blood pressure. All these stages are extremely important for restoring normal brain activity.
In atherosclerosis, atherosclerotic plaques that interfere with blood vessels and affect the circulatory system are removed. In many cases, the affected vascular part is replaced.
It is impossible not to note the rehabilitation recovery process, which includes not only physiotherapeutic procedures and radiation therapy, but also therapeutic exercises performed under the guidance of a doctor.