Ear noise and pain - these symptoms often appear simultaneously. This combination of symptoms does not go unnoticed by a person. After all, a disease that is accompanied by ear pain, headache, congestion and tinnitus is quite difficult to tolerate. This condition knocks a person out of the usual rhythm of life, and it is not surprising that the main thought at this time is how to get rid of the painful condition as quickly as possible.
The causes of ear noise, pain and congestion may be completely harmless, but they can also signal serious illnesses, ranging from ear infections to brain diseases and neurological conditions.
As a rule, the average person, if his ear is noisy or there is congestion and pain in it, he tries to independently understand the symptoms and find methods of treatment. But this is initially incorrect. Only a doctor can identify the cause of the disease and suggest the right methods of treatment. Sometimes, to determine the cause of pain, noise in the ear or congestion, consultation with doctors of several specialties is required.
What causes noise, pain and congestion in the hearing organ? And how to cure this condition? You will find the answer in our new article.
What is tinnitus like?
In medicine, such a condition as noise in the ear has its own (medical) name - tinnitus. The noise can occur in the right or left ear, or in both at once.
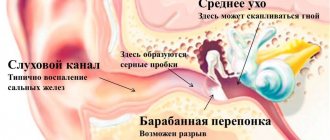
The human ear is an organ with a complex structure. In the inner part of the ear there are special hair cells that convert external sound vibrations into nerve impulses so that our brain can perceive them correctly. If some pathological factors adversely affect hair cells, they begin to move in a chaotic manner - and the brain perceives this chaotic movement as noise.
What else is important to know about tinnitus? That it is a symptom and not a separate disease. Accordingly, treating noise exclusively will not give a positive effect - the person will only waste precious time.
It is necessary to determine the underlying disease that caused the pain and noise and treat it.
It is customary to distinguish two types of noise: subjective and objective. With subjective noise, only the person hears the sounds. At the same time, there are no external sounds. Objective noise is actually present sounds that the doctor also hears during examination.
Noise can manifest itself in different ways. Patients describe their sensations as if they were in the ear:
- rings;
- squeaks;
- buzzes;
- whistles;
- gurgles;
- clicks.
The sooner the immediate cause of tinnitus, which is accompanied by pain and ear congestion, is determined, the sooner the correct treatment will be selected.
How to treat subjective tinnitus
Treatment consists of a set of measures. First of all, the doctor prescribes medications: vasoactive, nootropic, muscle relaxants, vitamins, etc. If the nature of the noise is neurological, the audiologist will send you to a psychiatrist to prescribe antipsychotics or tranquilizers.
An audiologist may also prescribe surgery if he finds pathology in the ear. Surgical intervention is extremely rarely indicated for diseases of the autonomic nervous system. In this case, doctors mechanically act on the nerves of the cervical spine or tympanic plane.
Another treatment method is hearing aids. It is used if there is a tendency to hearing loss. The hearing aid amplifies external sounds, thereby masking the subjective sensation of noise.
Notch therapy has become a new word in the treatment of tinnitus; it alleviates the condition without masking by suppressing neural hyperactivity through lateral inhibition. This function is implemented in Signia primax hearing aids.
Surgeries are increasingly being abandoned in favor of hearing aids
Causes of noise: ear diseases
Tinnitus can be caused by diseases of the hearing organ, which are also accompanied by pain in the ear and a feeling of stuffiness. Similar diagnoses include:
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
- Otitis is an inflammatory process of the hearing organ. Usually otitis media leads to this condition. It is accompanied by severe ear pain and a feeling of stuffiness. With delayed treatment, the disease turns into a purulent form. With purulent inflammation, purulent masses accumulate in the tympanic cavity, causing a feeling of fullness. As soon as there is not enough space for the pus, it breaks through the eardrum and pours out. After this, congestion and pain go away.
- Labyrinthitis is an inflammation that affects the internal part of the hearing organ. With labyrinthitis, the patient also complains of dizziness, hearing loss, impaired coordination and balance.
- Eustachitis is inflammation of the Eustachian (auditory) tube. The infection most often enters it from the nasopharynx due to improper treatment of rhinitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, etc. With this diagnosis, in addition to tinnitus, there is a sensation of fluid transfusion in the ear cavity, a feeling of stuffiness and hearing impairment.
- Mastoiditis is an inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone, which usually acts as a complication of otitis media. Mastoiditis is characterized by severe ear pain radiating to the back of the head, fever, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, attacks of nausea and vomiting.
- Diseases of the auditory nerve - such pathologies include sensorineural, occupational and senile hearing loss. When hearing loss occurs, the auditory receptors are affected, which causes progressive hearing loss.
- Earwax is a common cause of tinnitus and a feeling of stuffiness. Impactions are accumulations of wax that block the outer ear canal and cause hearing problems.
- Ear tumors can also cause noise, pain, dizziness and other unpleasant symptoms.
- Mechanical damage to the hearing organ - problems with the ears can be caused by bruises, head injuries, barotrauma, etc.
- A foreign object getting into the ear canal—parents of young children often turn to an otolaryngologist with a similar problem. While playing, children often stick small toy parts, beads, etc. into their ears.
- Meniere's disease is a non-inflammatory disease of the internal organ of hearing, occurring with attacks of dizziness, ringing and progressive hearing loss.
When the first alarming signs appear: pain and ringing in the ear, congestion, dizziness, the first thing you should do is contact an otolaryngologist. It is possible that one of the pathologies of the hearing aid has developed, which requires immediate, competent therapy.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
In what cases should you immediately consult a doctor if you have ringing in the ears?
The following conditions that complement tinnitus are reasons to immediately seek qualified help:
- Complete or partial hearing loss.
- Vestibular function disorders: difficulty maintaining balance, nausea, dizziness, etc.
- Intense pain in the ear, neck, temple, and back of the head.
- Increased heart rate.
- The appearance of flies before the eyes.
- Increased body temperature.
- Paralysis combined with uncontrolled urination, numbness of the limbs.
- Leakage of fluid from the ear canal.
Causes of noise not related to hearing aids
If there is noise in the ear, and unbearable pain also occurs, the causes of this condition will not necessarily be related directly to the hearing aid. Often the cause of tinnitus and pain is such diagnoses and conditions as:
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- metabolic problems;
- diabetes;
- osteochondrosis;
- side effects from taking certain medications;
- poisoning with alcohol or toxic substances.
If unpleasant symptoms do not go away, but only intensify, the best decision would be to consult an ENT doctor to understand the cause of this pathological condition.
What causes ringing in the ears?
Many adults experience ringing or noise in the ears. This is where the expression came from: which ear is ringing in my ear?
Photo: Depositphotos
Noise is conventionally classified as objective and subjective. In the first case, this is the reaction of the ear to external influences: mechanical damage, disease, external source of noise, increased or abnormal functioning of organs. Objective noise is associated with vibration of certain areas of the body. The doctor can listen to it and prescribe treatment.
Subjective noise is phantom sounds that cannot be heard from the outside. They arise from pathological activity of neurons in the auditory zone in the brain. Unreasonable stimulation of areas of the brain brings chaos to its work - it begins to respond incorrectly to irritation.
If a pathological impulse enters the brain from distant areas, for example, from the ear, it is considered peripheral. Often accompanied by hearing loss. When, due to illness, the source of noise occurs directly in the brain, we are talking about a central mechanism.
With subjective noise, people hear different sounds: crackling, squeaking, whistling, ringing, receiver noise, buzzing. The ringing may occur in one ear, both ears, or the entire head. Prolonged noise leads to insomnia and irritability. Often the sounds are accompanied by headache, weakness, and dizziness. Tinnitus provokes a stressful state, and this further aggravates the symptom - it turns out to be a vicious circle.
Diagnostics
At the initial consultation, the ENT doctor questions the patient for complaints, collects a detailed history and performs an otoscopy or endoscopic examination. An informative study of the degree of hearing impairment is audiometry. In addition, a tympanometric study of the functions of the middle part of the hearing organ (tympanic membrane and auditory ossicles) can be carried out. If there is a suspicion of a disease of the labyrinth (internal part of the hearing organ), special tests are performed to identify vestibular abnormalities. Sometimes an X-ray, CT scan or MRI may be needed.
Sign up for a consultation right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
At the same time, laboratory blood tests and examination of discharge from the ear cavity, if any, are prescribed to determine the causative agent of the disease and sensitivity to antibiotics.
To make a diagnosis, as a rule, a routine examination or questioning of the patient’s complaints is not enough; it is necessary to conduct a set of studies to establish the correct cause of the unpleasant condition.
Prevention
Prevention measures depend on the underlying cause. General recommendations include normalizing your lifestyle:
- Balanced diet, excluding too fatty and spicy foods;
- Drinking enough fluids;
- Maintaining sleep and rest patterns;
- Walks in the open air;
- Regular dosed physical activity;
- Timely treatment of diseases;
- Clinical examination by specialists;
- Adequate intake of medications under the supervision of a physician;
- Use of orthopedic bedding;
- Correct posture while working;
- Quitting smoking and alcohol.
The article is for informational purposes only. If you experience a pressing headache, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment
Treatment of congestion, ringing and noise in the ears is carried out based on the reasons that provoked these symptoms. Inflammatory processes of the hearing organ are treated with antibacterial or antifungal therapy using physiotherapy. If the problem is a sulfur plug, its high-quality removal is carried out in an ENT clinic, after which problems with the hearing organ disappear. A foreign object in the ear canal is also removed in the ENT doctor's office. Some pathologies, such as Meniere's disease and tumors, are treated surgically. For atherosclerosis, atherosclerotic drugs are prescribed. If hearing problems are caused by taking certain medications, you should stop taking this drug and discuss its replacement with your doctor. Sensorineural hearing loss is treated with microcurrent electrical stimulation of hair cells using Transair-07 and Audioton devices. These devices have been successfully used in the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev for a long time and have already helped many patients regain their hearing.
Whatever the cause of tinnitus, the first step towards getting rid of the unpleasant symptom should be a consultation with an otolaryngologist. To make an appointment, please call +7 (926) 384-40-04.
Come! We will definitely help you!
Whistling in the ears in neurological diseases
Neurological pathologies cause tinnitus along with ENT diseases. Let's consider the most common causes of tinnitus, which fall under the competence of neurologists.
Ringing in the ears due to arterial hypertension and hypertensive crisis
With a significant increase in blood pressure (more than 140/90 mm Hg), blood flow to the inner ear becomes uneven. As a result, the nerve endings inside it are excited, and tinnitus occurs. With arterial hypertension, this most often occurs during a hypertensive crisis - an attack of a sharp increase in pressure.
Other manifestations of hypertensive crisis:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the heart area;
- nausea and vomiting;
- convulsions;
- disturbance of consciousness.
During a hypertensive crisis, the patient requires emergency assistance. It is necessary to reduce blood pressure as quickly as possible, otherwise its jump can lead to myocardial infarction, stroke and other serious complications.
If arterial hypertension is accompanied by a chronic disorder of cerebral circulation, then the patient is almost constantly bothered by tinnitus.
Ringing in the ears due to cerebrovascular accident
The most common cause of impaired blood flow in the vessels of the brain is atherosclerosis. This is a disease in which cholesterol plaques form on the walls of the arteries, partially or completely blocking their lumen.
Other causes of cerebrovascular accident:
- arterial hypertension (the main cause of which is also often atherosclerosis);
- increased blood viscosity and blood clot formation;
- diabetes mellitus (with this disease, the vessels of the brain, eyes, and kidneys are primarily affected);
- consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- intracranial tumors, hemorrhages.
The main symptoms of chronic cerebrovascular accident: headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, flashing “spots” before the eyes, increased fatigue, drowsiness, impaired memory and attention. Constant oxygen starvation does not leave its mark on the brain. Nerve cells gradually die, which over time can lead to the development of dementia.
The effect of increased intracranial pressure on tinnitus
Tinnitus as a result of increased intracranial pressure occurs with hydrocephalus, intracranial tumors and hemorrhages, after traumatic brain injuries and infections (meningitis, meningoencephalitis).
Headache and tinnitus - characteristic manifestations of increased intracranial pressure - usually occur in the morning, after a person has been in a horizontal position for a long time. During the day the symptoms disappear. The vertical position of the body helps the excess amount of intracranial fluid flow away and its pressure decreases.
Diseases of the cervical spine
The vertebral arteries, vessels that play an important role in the blood supply to the brain, run along the cervical spine on the right and left. They are not just located on the sides of the spine, but pass through holes in the lateral processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Often, pathological changes in the spine - inflammation, displacement of the intervertebral disc, bone growths that form on the vertebrae - lead to impaired blood flow in the vertebral arteries and neck pain. Blood flow to the head decreases. The brain and other organs experience oxygen starvation.
This condition is called vertebral artery syndrome. Its main manifestations:
- constant burning pain in the back of the head, temples, which intensifies after sleeping in an uncomfortable position, traveling by transport;
- hearing loss and tinnitus;
- blurred vision, “fog before the eyes”;
- dizziness, loss of balance when turning the head suddenly;
- loss of consciousness;
- sleep disturbances, the patient does not feel sleepy and rested, in the afternoon there is severe fatigue and drowsiness.
Noise in the ears is a signal of a tumor
Acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor that leads to tinnitus and other symptoms: decreased hearing on one side, pain and impaired movements of the facial muscles of half the face, and speech impairment. For acoustic neuroma, the doctor prescribes surgical treatment or radiation therapy.
Many intracranial tumors lead to impaired cerebral circulation and increased intracranial pressure. Therefore, tinnitus can also be one of the symptoms of such pathologies.
Multiple sclerosis
This is a chronic disease that most often occurs between the ages of 15 and 40 years. All nerve fibers in the human body are covered with a special myelin sheath. It is necessary for the normal transmission of nerve impulses. In multiple sclerosis, the myelin sheath is destroyed, resulting in slower neuromuscular transmission.
The symptoms of multiple sclerosis are varied. In some people, the disease manifests itself in the form of numbness in a certain part of the body, for example, a limb, while in others severe paralysis develops, including breathing problems.
One possible symptom of multiple sclerosis is tinnitus.
Depression and neuroses
Under certain conditions of the nervous system, the hearing organ becomes hypersensitive to sounds and becomes irritated. This is often caused by depression, neuroses (neurasthenia, hysterical neurosis), and nervous breakdowns. The patient comes to see a doctor and complains of constant tinnitus, but during examination and examination no objective abnormalities are revealed.
For psychogenic tinnitus, psychotherapy and appropriate medications are prescribed.
Taking medications for tinnitus
Some medications are ototoxic—they can harm the nerve endings in the inner ear and cause tinnitus. This side effect is most pronounced with the following drugs:
- antimalarials (quinine) and some antibiotics (for example, streptomycin);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (including aspirin);
- antipsychotics (haloperidol);
- antidepressants;
- digitalis preparations;
- furosemide
If you begin to experience tinnitus while taking one of these medications, you should stop taking it and consult a doctor immediately.
Only a doctor, based on the results of the examination and examinations, will determine what disease led to the occurrence of tinnitus. It is necessary to begin proper treatment of this symptom for any pathology as early as possible - this will help eliminate its root cause and prevent serious complications.
The Yusupov Hospital employs experienced neurologists, therapists, cardiologists, and has all the necessary equipment. This allows us to provide patients with modern, high-quality medical care.
What to do if there is wax in your ears?
Often you want to take a cotton swab and just clean out the earwax. You cannot do this if you feel stuffy. It is necessary to make an appointment with a specialist who will assess the degree of congestion and its cause, and then provide professional medical assistance. The ear plug is washed with special tools; this process takes a couple of minutes and does not cause any pain. After rinsing, it is important to follow the rules of ear care; the doctor may also prescribe drops in the ears.