Today, there are more than 50 million people with epilepsy in the world. This disease is caused by non-infectious brain damage and is chronic. It causes seizures of varying levels of complexity, in which a certain clinical picture is observed: convulsions, fainting, salivation, etc. A single case of such symptoms is not a reason to visit a specialist; every person has experienced a similar condition at least once in their life. If the seizures are constant and prolonged, this becomes a good reason to visit a doctor. In order to find out about the presence of a disease and the extent of brain damage, it is necessary to undergo a lot of diagnostic measures that make it possible to establish the type of disease, as well as its effect on the body. One such method is MRI of epilepsy.
What does an MRI of the brain show in epilepsy?
Magnetic resonance therapy for epilepsy shows the affected areas of the brain and is performed in almost all cases of the disease. This is an excellent way to determine the extent to which the disease has spread to healthy cells and the speed of its development. In terms of its information content and harmlessness, MRI is in many ways superior to even computed tomography. In addition, this technique has an obvious advantage: it does not contain X-ray radiation, and it does not affect the human body in any way. MRI of the brain for epilepsy is performed at any age, since this procedure does not provide for severe clinical consequences, it can be used by patients with a disease of any complexity and degree of development.
It is the deep conviction of international antiepileptic organizations that the process of undergoing MRI or CT scanning is mandatory and should be carried out at the request of a doctor.
Many modern clinics with the latest equipment provide the opportunity to diagnose this disease, so the procedure is mandatory. For a successful examination you need:
- Referral for research with a competent formulation of a possible diagnosis and the need for diagnostics. The referral must indicate possible suspicions of pathology and any of its manifestations. Based on previous examinations, including EEG, the neurologist can assume the possible location and nature of the pathological process.
- Modern MRI scanner with optimal power and amplitude. Such devices conduct research even with minimal sections.
- Radiation therapy specialist with in-depth knowledge of neurology, with a good understanding of the specifics of the nervous system. The doctor must know when to use additional data collection methods that are not provided for in the medical protocol.
Whether an MRI shows epilepsy depends largely on physicians and consultants, as well as MR imaging specialists, who are often unable to meaningfully analyze the collected data to establish a treatment modality and confirm a final diagnosis. However, according to statistics from the Ministry of Health, the number of cryptogenic epilepsies is significantly decreasing, which has a positive effect on further treatment.
Preparation for the procedure
Let's consider the basic rules that a patient should know when going for an MRI:
- If it is necessary to administer contrast, you must come to the medical center on an empty stomach. You should not eat 5-6 hours before the diagnosis.
- If you have previously been diagnosed with epilepsy or had a brain scan done, it is recommended that you take the results of previous examinations with you.
- Remove all metal-based jewelry, glasses and hair clips in advance.
- On the eve of the study, it is forbidden to drink alcohol; it is better to quit smoking a couple of hours before the MRI.
- Go to the toilet in advance before starting the diagnosis so as not to experience discomfort during the examination.
Is it possible to detect epilepsy using MRI?
Epilepsy as a disease has been known for more than 7 thousand years, but instrumental diagnostics began only in 1929. Magnetic resonance imaging in this case is a reliable instrumental method for diagnosing such a pathology, therefore complex procedures are practiced all over the world to determine the spread and development of the disease down to the last small detail. It makes it possible not only to identify the disease, but also to identify the causes that provoked it. A significant advantage of the method is high sensitivity, specificity, and absence of radiation. The Association of Radiologists has developed special protocols for identifying the disease. Thanks to this, it is possible to establish the causes of the pathology, of which there are many:
- defects and anomalies of the brain of various types;
- sclerotic changes;
- oncology and benign tumors;
- changes as a result of impacts and trauma experienced;
- infectious lesions;
- vascular pathologies;
- degenerative changes;
- metabolic disorders.
In other words, diagnostics using modern equipment allows us to examine the pathology from the inside and determine the sources and factors that provoked its development. This method undoubtedly influences the level of treatment, since the final conclusions regarding the patient’s diagnosis are based on MRI or CT readings.
Who prescribes MRI for epilepsy?
Any disease requires the attention of a specialist, and epilepsy is no exception. Especially considering the fact that the most important human organ is affected. After a detailed history, the therapist refers the patient to an appointment with a neurologist, who records the client for an EEG if his suspicions suggest the possibility of damage to tissue cells. This conclusion is required by the radiologist in order to:
- clarify the areas where epileptic activity was detected;
- if necessary, introduce a number of additional programs during the procedure;
- compare the indicators obtained from EEG and MRI, and determine structural changes in tissues.
The use of tomography has several goals pursued by a neurologist. To clarify suspicions and collected data, only those whose history has identified and described a seizure are sent for MRI, since the program allows for a detailed study of possible structural disorders of the areas that are most active during attacks. In addition, the procedure is recommended for patients with an already confirmed diagnosis who cannot get rid of attacks with the help of medications. Drug-resistant epilepsy is not one of the most common pathologies, but its development has certain risks, since drug treatment does not produce results, and the person may not meet the requirements for surgical interventions. MRI is important to clarify the need for surgical intervention for a specific diagnosis.
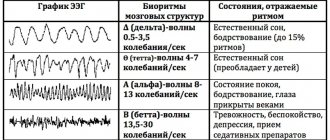
Electroencephalography (EEG)
The electrical activity of the brain can be recorded using electrodes placed on the scalp. The received signals are amplified millions of times and recorded by a computer. During the examination, the patient lies with his eyes closed in a darkened room. In epilepsy, the EEG will show changes called epileptic activity. It should be noted that the presence of epileptic activity on the EEG does not mean that the patient has epilepsy, since in 10% of an absolutely healthy population various electroencephalogram abnormalities can be detected. At the same time, many patients with epilepsy may have a normal EEG between attacks. One way to diagnose epileptic activity in such patients is to provoke pathological electrical impulses in the cerebral cortex. This can be done in various ways. For example, recording an EEG while the patient is sleeping. Sleep provokes increased epileptic activity. The patient is asked to go to bed late the night before the test or not sleep at all. Before the study, the patient falls asleep spontaneously or is given a mild sleeping pill. Other ways to provoke epileptic activity on the EEG are hyperventilation and photostimulation. Hyperventilation is rapid breathing for several minutes, which provokes epileptiform EEG disturbances in children with absence seizures. During photostimulation, the patient looks at flashes of light of a certain frequency. Photostimulation also causes the appearance of epileptiform activity on the electroencephalogram.
CT or MRI - which is better?
Quite a lot depends on the choice of equipment, so random visits to such diagnostic centers are unacceptable. For more detailed diagnostics, the MRI unit is equipped with programs that were created to obtain additional information about the condition of the affected tissues. The absolute coverage of such tissues by the information field of the tomograph greatly simplifies the process of determining therapy and the level of risks for individual cases.
MRI according to the “Epilepsy 3 Tesla” program allows you to create optimal conditions for a patient who can succumb to an epileptic seizure at any moment, and collect the necessary information on the specifics and development of the disease in great detail. The use of modernized equipment in medical institutions has led to first-class diagnostic quality, but thereby increased its duration. However, this method is most in demand in cases where it is difficult to give a final conclusion or determine the damaged areas due to the presence of a tumor or vascular compactions. And whether epilepsy is visible on an MRI of the brain is a rhetorical question.
A CT scan is performed to obtain a detailed cross-sectional picture of the brain. Specialized equipment ensures the safety of the procedure and efficiency, and also guarantees the quality of the results obtained. This is a painless examination option, the only contraindication for which is pregnancy. Both tomography options have their advantages, but the need to use one or another device is determined by the attending physician.
Based on the characteristics, it should be noted that these options are suitable for many patients and do not carry great risks. Precautions and contraindications are always determined before the start of treatment and require general tests and a complete medical history. A detailed study of the pathology allows us to exclude possible complications and additional difficulties during therapy. The patient must provide complete information about the disease, personal intolerance to drugs and allergies, and indicate complications of illness or surgery.
Common symptoms
3.1. Major attacks
Seizures begin with an involuntary contraction or loss of sensation in the hands and feet and spread to other parts of the body, developing into a seizure. The condition is characterized by successive phases:
- Harbingers . A few minutes before the seizure, the patient develops anxiety syndrome. Abnormal neuronal activity increases and covers new sections.
- Toxic seizures . Characterized by sharp tension in all muscle groups. The patient lies down on the floor and arches his back. There is a bluish discoloration of the face due to oxygen deficiency. The duration of the phase is from 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Clinical seizures . Muscles contract involuntarily and quickly. A characteristic sign of the phase is foam at the mouth. Within 5 minutes the patient’s breathing is restored and the bluishness of the face disappears.
- Stupor . After abnormal brain activity, brain inhibition occurs. The phase is characterized by relaxation of all muscle groups. The patient loses control of consciousness. The duration of stupor is 30 minutes.
- Dream . After an attack, a person may suffer from headaches and movement disorders for 2-3 days.
3.2. Minor attacks
The condition is characterized by a vague clinical picture. The patient's muscles in the face and other parts of the body involuntarily contract. During an attack, the person is conscious, but may temporarily experience stupor. He does not notice the neurological changes occurring.
3.3. Status epilepticus
The disease is associated with a series of seizures and requires professional help, since epileptic seizures provoke swelling and hypoxia of the brain. Symptoms come on suddenly and end spontaneously.
How is an MRI performed for epilepsy?
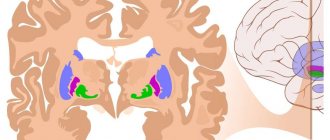
The main obstacle for many is the fact that during the tomography the patient must remain motionless for up to 50 minutes, which is extremely difficult for people with increased irritability or constant anxiety. The procedure itself is carried out according to the same standards as for any other disease that requires a similar diagnosis. Epilepsy is chronic, and it is quite difficult to predict the onset of the next attack. The main object of the search is focal cortical dysplasia, which is a specific sign of true epilepsy, and not symptomatic.
After anamnesis and mandatory tests with established results, the doctor sends you for diagnostics. The patient takes off all metal jewelry, belts, costume jewelry, precious metals and other paraphernalia and sits on the tomograph couch. After this, it enters the center of the ring magnet, and the diagnostic process itself starts. This manipulation does not cause any sensations or discomfort; any complications or inconveniences can arise exclusively in the technical part of the equipment.
The specialist performing the procedure is in another room behind glass and communicates with the patient via a microphone. There should be no foreign objects in the inspection area that could disrupt the operation of the unit. The patient should listen carefully to the doctor and follow his instructions, while remaining as still as possible. A long, but non-traumatic process extracts all the necessary information about the state of the cells and the extent of the spread of the disease.
MRI with contrast for epilepsy
It is known that epilepsy is a disease that has several factors that provoke characteristic seizures. This greatly expands the range of searches for affected tissue areas, which is why different research methods are used. Protocols for diagnosing chronic brain lesions involve the use of a contrast agent, which makes it possible to determine the extent of changes and the functioning of the naked brain during the study.
The procedure itself consists of administering a substance intravenously; it quickly spreads through the vessels and veins, ultimately reaching the brain. The contrast itself contains an acceptable amount of iodine and other compounds that, when released into the blood and under the influence of rays, display their own color. This is how the easily recognizable mesh of the venous system appears. On the computer image, clear contours of all channels and the circulatory system of the head are visible, the smallest changes in the structure of blood vessels are determined, and specialists see where inhibition or fluid accumulation occurs. This is another effective way to determine epilepsy by MRI, caused by vascular pathologies or degenerative changes.
Contraindications
There is no need to take any special measures before the diagnosis itself. The patient can continue medication treatment, adhere to the diet and all the doctor’s requirements. Usually the patient leads a full life, without restrictions and precautions. The main recommendation of doctors is a calm environment at work or at home. An isolated case is a patient who experiences a short interval between seizures. Such people are often kept under the supervision of specialists to establish the intervals between attacks, then acceptable options for examination are prescribed.
Despite all the harmlessness, the procedure still has a number of limitations. This is the presence of any metal implants in the body, implants of the inner and middle ear, as well as pacemakers. In addition, it is not recommended to undergo examination for people whose weight exceeds 130 kg. The first months of pregnancy in women are also contraindications. The procedure is contraindicated for people suffering from claustrophobia. Patients in this category undergo pre-treatment or a similar procedure using adapted devices.
Video-EEG monitoring
Video-EEG combines video monitoring of the patient with simultaneous EEG recording. This type of study allows you to record epileptic activity during an attack, compare the clinical picture of the attack and changes in the encephalogram, and determine the location of the epileptogenic focus. The patient is hospitalized in a special ward for 5-10 days. He is under video camera surveillance 24 hours a day. Electrodes are attached to the patient's head, and EEG recording is carried out continuously in automatic mode. During monitoring, the patient can move freely, watch TV, and receive visitors. At the moment of an attack, the camera records changes in the patient’s behavior, the presence of seizures, etc. The epileptologist then compares the clinical picture of the attack recorded on video and the EEG data. Based on this, he makes a conclusion about the type of epilepsy and the location of the epileptogenic focus.
Video-EEG combines video monitoring of the patient with simultaneous EEG recording. This type of study allows you to record epileptic activity during an attack, compare the clinical picture of the attack and changes in the encephalogram, and determine the location of the epileptogenic focus. The patient is hospitalized in a special ward for 5-10 days. He is under video camera surveillance 24 hours a day. Electrodes are attached to the patient's head, and EEG recording is carried out continuously in automatic mode. During monitoring, the patient can move freely, watch TV, and receive visitors. At the moment of an attack, the camera records changes in the patient’s behavior, the presence of seizures, etc. The epileptologist then compares the clinical picture of the attack recorded on video and the EEG data. Based on this, he makes a conclusion about the type of epilepsy and the location of the epileptogenic focus.
MRI for epilepsy in children
Unfortunately, one of the causes of the disease is a congenital pathology of fetal development. Patients of neurologists and epileptologists often include children of all ages. MRI for epilepsy in children is performed in order to exclude the most dangerous causes that require surgical intervention:
- tumor;
- consequences of injury;
- congenital developmental anomalies;
- cortical dysplasia;
- manifestations of genetic diseases.
It is worth remembering that this examination requires standing still (in the case of examining children) for about 20–30 minutes, so this often becomes a problem. Children are afraid of noise, the absence of adults nearby and unfamiliar sensations. In order for the process itself to proceed quickly and efficiently, a qualified specialist is required who can identify the problem and is well acquainted with the changes in epilepsy. To diagnose all possible changes in brain tissue, the examination must be carried out on a high-field (not
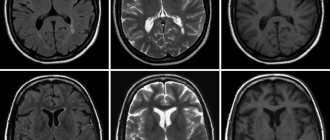
Deciphering MRI for epilepsy
MRI images of the brain are interpreted exclusively by a qualified radiologist. Often this is a specialist who personally performed the diagnosis and works closely with the patient’s attending physician. Correctly interpreting and explaining images requires professional medical training and significant practical experience. At the clinic, the patient can receive tomography results a few hours after completion of the procedure or the next day.
Basic information is transmitted electronically to the attending physician. Specialists conduct a thorough examination of the scanograms, after which they report the results. The images are used to prescribe additional diagnostic measures if the disease causes controversial statements. None of the doctors with a narrow specialization in other areas has the right to interpret the results in any order. Any findings by doctors who are not radiation specialists or the patient's attending physician cannot be considered as a final diagnosis.
4.General and biochemical blood tests.
To timely identify the side effects of AEDs before visiting an epileptologist, it is necessary to conduct a general blood test (with leukocyte count and platelets) and a biochemical blood test (total protein, glucose, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine, urea, amylase, sodium, potassium, calcium). In the first year of taking AEDs, it is advisable to carry out tests at least 3-4 times a year, then 2 times a year (and always before an appointment with an epileptologist).
IDNE specialists recommend conducting these studies at clinical sites:
- Laboratories "EndoMedLab".
- Laboratory Invitro invitro.ru
- Laboratory Gemotest https://www.gemotest.ru/
- Blood tests can also be performed at your place of residence at a local clinic.
Prices for MRI for epilepsy in Moscow
The results of an MRI examination do not constitute a doctor's opinion. This is one of the diagnostic methods, which is largely educational in nature for the doctor, who uses several similar conclusions to determine the diagnosis and prescribe drug or surgical therapy. Therefore, the images and the information obtained appear in the protocols as the main and legal indications for starting and conducting treatment for the patient. This method of examination by specialists is one of the most popular for many diseases. A narrow range of contraindications allows the use of an objective examination of the whole body under any circumstances and in different patients.
The cost of diagnostics in each clinic is determined differently. This depends on the focus and status of the medical institution in which the person is being examined. In addition, the price is also affected by the specifics of the therapy. A patient who is an inpatient in a hospital receives the service free of charge. The cost varies depending on many factors that are often beyond the control of the organization itself. The emergence of modified equipment with the latest developments often affects the pricing of other units already in operation. But even with such price fluctuations, we can say that this is an affordable survey method. 55% of patients use MRI and CT services. Thus, these methods are recognized as one of the most effective, painless and informative methods in examining pathologies of various types and nature.
Determination of drug concentrations in the blood.
Modern approaches to treatment involve not only adequate selection of the dose of the drug, but also monitoring the achievement of the correct concentration of the drug in the blood. This study is necessary in cases where the doctor has reason to assume that the dose received is insufficient (increased metabolism of the drug in the liver, or increased excretion in the urine). The characteristics of enzyme systems in different people can differ significantly, so the doctor must have criteria for individual selection of the dose of the drug.
If the patient receives drugs from the group of valproic acid (Depakine, Konvulex, etc.), carbamazepine (Tegretol, Finlepsin, etc.), phenobarbital, phenytoin - before seeing an epileptologist, it is necessary to determine the concentration of the drug in the blood (in the morning, before taking the drug).
IDNE specialists recommend conducting these studies at clinical sites:
- Determination of the concentration of AEDs (including new AEDs!) can be carried out in our EndoMedLab laboratory.
- Laboratory Invitro invitro.ru
- Laboratory Gemotest https://www.gemotest.ru/