Magnetic resonance imaging combines high information content, safety and non-invasiveness. MRI of cerebral vessels is the most optimal radiation method for studying the vascular system. The contrast agent used during the study practically does not cause allergic reactions and is well tolerated.
In the absence of contraindications, the procedure is not associated with risks to the patient’s health. Electromagnetic radiation, which provides reading of information about the vascular system, has indicators that do not exceed standard values for humans in any research mode.
MRI of cerebral vessels provides detailed information for making a diagnosis in complex cases and with a confusing clinical picture - many diseases have similar symptoms. The blood supply to the head and brain comes from branches of the aorta passing through the neck. At this level, diseases or damage to the vascular system are often noted that affect cerebral circulation. To accurately determine the cause of painful conditions, an MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck is performed in conjunction with a study of the brain vessels.
The examination allows you to study the condition of the main groups of cerebral vessels:
- internal carotid artery and its branches (ophthalmic, anterior and middle cerebral arteries);
- vertebral arteries located in the cervical spine, basilar, posterior cerebral arteries;
- Circle of Willis - a system of connected arteries at the base of the brain that increases the reliability of the blood supply to the brain;
- veins of the brain and venous sinuses of the dura mater.
Carrying out MRI of the vessels of the head and neck with a contrast agent allows you to visualize the smallest vessels and determine disorders of microcirculation and metabolic processes.
When is the examination carried out?
Before undergoing an MRI of the head and neck vessels, it is advisable to consult a neurologist. The doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms and condition and refer him for the most appropriate study.
The examination is usually carried out if the patient observes the following phenomena for a long time:
- prolonged headaches of unknown cause that cannot be treated with known drugs;
- periodic dizziness, loss of consciousness, fainting, darkening of the eyes, difficulty in spatial orientation;
- unstable blood pressure;
- decreased vision;
- numbness of the arms, shoulder girdle;
- actively developing osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with corresponding symptoms;
- herniated disc in the cervical region;
- subluxation, instability of the cervical vertebrae;
- traumatic brain injury, spinal injury;
- suspicion of cancer or mass formations in the brain.
The value of MRI of the head and neck vessels lies in the possibility of making an early diagnosis. The examination helps to start therapy in a timely manner and prevent the progression of the disease. Having received the necessary treatment, the patient can undergo the procedure again an unlimited number of times without risk to health. The doctor monitors the effectiveness of therapy and, if necessary, makes adjustments or changes tactics.
MRI of cerebral vessels is actively used by neurosurgeons to plan operations. Information about the location and structural features of the vascular system allows you to avoid unforeseen situations and make precise interventions. MRI is important in the postoperative period to monitor recovery processes.
Highly specialized methods
- Doppler ultrasound provides detailed information about blood circulation in the large vessels of the brain and neck. This method allows you to identify pathologies of the vascular system at the initial stages, as well as evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy. The advantages of ultrasound scanning are that you do not need to prepare specially for it, the procedure is painless and has no contraindications.
On the eve of the ultrasound, the patient should stop smoking, drink tea, coffee and other caffeine-containing drinks, so as not to affect vascular tone.
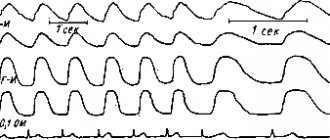
- Electroencephalography is a study of the brain carried out to analyze its functional state, as well as its response to stimuli. With an EEG, the biocurrents of the brain are recorded, and even minor fluctuations are recorded. Data on bioelectrical activity are transferred to a special paper tape or recorded in a file and displayed on a computer monitor. EEG is used to diagnose and treat epilepsy, delayed mental and speech development, and identify the consequences of head injuries.
- Echoencephalography is an examination of the head using ultrasound. A device called an oscilloscope picks up the peculiar echo that is returned when ultrasonic waves are sent to the brain. Thus, an image appears on the display, from which one can judge the presence of tumors in the brain and disorders in its structure after skull injuries.
- Rheoencephalography is the recording of fluctuations in the electrical resistance of tissues in the process of passing a weak high-frequency electric current through them. REG provides accurate information about the condition of blood vessels, allowing one to examine their tone, elasticity, and blood filling. The method allows you to see separately the functioning of the venous and arterial systems of the brain and diagnose intracranial hypertension, atherosclerosis, vascular dystonia, and subdural hematomas. With its help, the effectiveness of treatment of the above pathologies is also assessed.
These rheoencephalograms are obtained by placing electrodes on the surface of the head, having previously lubricated them with a special paste to ensure better contact with the skin. When analyzing information received from the rheograph, organic changes depending on the age of the patients are taken into account.
- Electroneuromyography is a method of studying the brain, which is a recording of its biocurrents. ENMG allows you to identify neuromuscular diseases and dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system.
- Neurosonography – diagnostics of the brain of newborns and infants up to 9-12 months of age. The procedure is absolutely safe, because it is carried out using ultrasound. It is highly informative regarding the identification of pathologies at the earliest stages and can be carried out before the large fontanelle in the child’s skull heals.
- Craniography - in other words, this is a study of the head using X-rays. Allows you to make two projections of the skull (profile and full face) to record the presence of congenital or acquired bone anomalies.
What will the examination show?
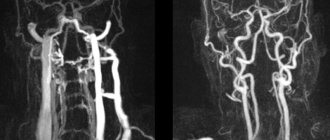
MRI of the vessels of the head and neck is performed in angiography mode - in this case, only areas of the vascular system are visible in the images, without surrounding tissues. The examination makes it possible not only to assess the condition of the arteries and veins, but also to determine the speed of blood flow in the vessels in real time. Based on the scanning results, a three-dimensional 3-D model of the area under study is constructed.
Signs of which diseases will be shown by MRI of cerebral vessels:
- stroke - hemorrhagic (leakage of blood from the vascular system into the brain tissue or meninges) or ischemic (cessation of blood supply to a part of the brain, more common);
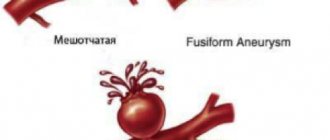
- arterial aneurysm - pathological expansion and thinning of the vascular wall with the risk of rupture;
- arterial dissection as a result of congenital weakness of the arterial wall or damage by a pathological process;
- thrombosis, thromboembolism;
- inflammatory diseases of the vascular system – phlebitis, arthritis, systemic vasculitis;
- vascular tumors – hemangioma, hemangioblastoma, angioreticuloma;
- atherosclerosis;
- narrowing of the lumen of the vessel due to structural features or compression from the outside by a space-occupying formation;
- congenital developmental anomalies and structural features - absence, decrease or increase in diameter, bifurcation of some parts of the vascular system, arteriovenous malformation.
MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck will show structural defects and pathological processes leading to impaired cerebral circulation:
- dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries - damage to the artery wall as a result of injury, bending, with further formation of a hematoma between the walls of the vessel, narrowing of the lumen of the artery and disruption of the blood supply to the brain;
- pathological tortuosity of the carotid artery;
- developmental anomalies and acquired lesions of the vertebral artery;
- neoplasms;
- aneurysm of a section of the vascular system;
- pathologies in the area of the carotid sinus.
What is a diagnostic method
This method of vascular diagnostics provides complete information about the state of the human vascular system. Using ultrasound, you can evaluate and analyze the speed and nature of blood flow, as well as determine the presence of blood clots or other vascular pathologies.
The study usually proceeds in two stages: two-dimensional mode and duplex study.
Content:
- What is a diagnostic method
- Why is the procedure necessary?
- What is the difference between duplex and triplex scanning?
- Who needs the procedure
- Preparation for the procedure and contraindications
- How the procedure works
- Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
In two-dimensional mode, you can see the vessels and adjacent tissues, limited only by this information. It does not provide any information about blood supply.
With a duplex study, the doctor sees a complete picture of what is happening in the vessels, with a detailed description and a color two-dimensional picture.
Contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging of the vascular system of the head and neck
The ban on MRI of head and neck vessels is due to the peculiarities of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with certain metals and magnets. The examination is prescribed with caution in certain patient health conditions.
MRI of cerebral vessels is contraindicated if the patient has the following devices in the body:
- pacemaker and other stimulating implants and pacemakers, cochlear implant - implants may fail under the influence of a magnet;
- metal intravascular stents, artificial heart valves;
- endoprostheses, foreign metal bodies in the body;
- metal clips installed in the vessels of the brain after surgery - under the influence of a magnetic field they can move and cause bleeding.
Not every material prohibits MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and head. Metals that react to a magnetic field by displacement and heating: stainless steel, iron, nickel, cobalt. In other cases, the procedure is not prohibited.
In some patient conditions, examination is allowed by the doctor’s decision on an individual basis:
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks - the fetus is especially sensitive to external factors;
- serious condition of the patient, severe pain;
- epilepsy, seizures, mental illness;
- body weight should not be more than 130 kg - the devices have restrictions on the patient’s weight and waist circumference.
The procedure can be performed in patients who find it difficult to maintain a stationary body position under general anesthesia or in an open-type apparatus. During the entire period of using MRI, there have been no cases of fetal pathology developing after the procedure in the first trimester of pregnancy, however, doctors are careful. If the patient suffers from a mild form of claustrophobia, he may take sedatives before the examination.
MRI of the vessels of the head and neck with the use of contrast agents is contraindicated in pregnant women at any stage, as well as in patients with renal failure.
Preparing for the study
First of all, you should make sure that there are no contraindications, and if there are any, collect all the technical documentation describing the devices and endoprostheses implanted into the body. The examination becomes possible after analyzing the composition of metal implants.
It is advisable to have with you a doctor’s referral, extracts from medical documents, expert advice, as well as the results of previous studies, if any. A patient who is scheduled to receive a contrast agent should undergo a kidney function test in advance. Women should be sure that they are not pregnant.
There is no need for special preparation for MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and head. If an examination with contrast is prescribed, you must arrive on an empty stomach.
Contrast MRI of cerebral vessels
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) creates images based on signals from hydrogen atoms, which are abundant in blood and other fluids. The image on the monitor screen is very clear, so a contrast agent is rarely required. When performing computed tomography, unlike MRI, contrast is used much more often.
In MRI diagnostics, substances based on gadolinium are used. A contrast agent is injected into a vein, changing the magnetic properties of the tissue for a short time, and is excreted through the kidneys. It was possible to create gadolinium compounds that rarely cause unwanted and allergic reactions. There is no evidence that they cause neurological problems after contact with the human body. However, they are used with caution in severe kidney disease.
Before a contrast study, be sure to tell your doctor about:
- pregnancy (confirmed or probable);
- breastfeeding;
- kidney diseases;
- previous allergic reactions to any medications.
Contrast makes it easier to decipher images, as it shows the condition of the vessels in more detail.
Gadolinium-based contrast agent
How is the examination carried out?
First of all, you need to get rid of metal items of clothing, the neck and ears should be free of jewelry. Bags, money, plastic cards, telephones, and electronic devices must be left outside the office. The patient receives disposable comfortable clothing for a comfortable procedure.
The examination without contrast agent lasts about 20 minutes; the introduction of contrast agents doubles the examination time. The patient is positioned on a table, which smoothly slides into the body of the tomograph, where the scanning will take place. During the examination, the neck and head should not make any movements. Fixation is ensured by a special coil.
When performing MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and head, the tomograph operation is accompanied by unusual sounds, so the patient receives earplugs or headphones before the examination. The body of the tomograph is equipped with a fresh air supply system, as well as an intercom through which the doctor can give the command to hold your breath or slightly change the position of your head. If the patient becomes ill, it is possible to urgently contact the staff and stop the scan. After completing the examination, the patient changes clothes and can await the result.
What the results look like
After performing an MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck and head, the doctor receives layer-by-layer images of the vascular pattern with the ability to construct a three-dimensional model. The patient can pick up the images on electronic media or in printed form. The photographs are accompanied by a report from a radiologist.
Normally, the internal carotid arteries are located symmetrically, have clear contours, are not displaced, and are not compressed. The cerebral arteries arise in a typical place, the diameter is not changed, and there is no pathological tortuosity of the vessels. The cerebral veins and sinuses should be of normal diameter, without areas of blood flow disturbance, filling defects or deformations.
On MRI images of the vessels and arteries of the neck you can see signs inherent in certain diseases:
- an aneurysm is a round formation with a high signal intensity; when a thrombus attaches, a layered structure appears;
- vascular malformations appear as linear or tortuous structures with dilated vessels;
- dissection of the arterial wall is characterized by the appearance of a crescent-shaped hematoma located along the vessel, while the lumen of the artery is narrowed evenly or in the form of a rosary;
- atherosclerosis of the vascular system looks like an area of increased intensity on the vessel wall, the lumen is narrowed;
- hemangioma is a high-intensity formation with clear edges and a lobular structure.
Despite a detailed description of all identified pathological formations, the conclusion of a radiologist is not a diagnosis. The MRI result of the area of the cerebral vascular system should be shown to the doctor who ordered the study. Clinics offer the opportunity to consult with the radiologist who performed the procedure. If necessary, he will recommend contacting specialized specialists - a neurologist, oncologist or surgeon.
What is the difference between duplex and triplex scanning?
These diagnostic methods are very similar to each other and have practically no differences, with the only difference being that with triplex scanning the vessels can be viewed in three-dimensional space. Duplex mode presents information in only two planes. In fact, triplex scanning is positioned as an additional procedure when conducting a duplex study.
And if we take into account the fact that the crystal transmitting and receiving the signal is the same, then the resolution of the triplex method is considered slightly worse than the duplex one. The quality of the work will depend entirely on the quality of the apparatus and the qualifications of the doctor conducting the research, and not on the diagnostic method.
Where to get a magnetic resonance imaging scan
The search for a clinical diagnostic center can be significantly speeded up if you use the help of our website. The service contains information about a large number of clinics, ranging from contact details to discount offers. If necessary, our specialist will advise you free of charge over the phone about operating hours, the availability of tomographs of the required type and the time available for making an appointment.
A patient who wants to undergo magnetic resonance imaging of the vascular system of the head and neck can independently filter the list of medical institutions by rating, cost and features of the procedure (24-hour clinics, pediatric MRI).