How does a “heavy” head feel?
It’s not just a headache that can interfere with normal perception of the colors of the world around you and living in peace. Sometimes a tedious heaviness in the head is perceived worse than a migraine attack. After all, a migraine will go away after a certain period of time, and the feeling of a burden in the head can torment a person for a very long time.
How do patients describe their feelings?
- In the morning, my head pulls towards the pillow.
- There is a feeling that the skull has been filled with stones.
- It was as if blood from the whole body had collected in the skull.
- Metal disks move heavily in the brain.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Information is not perceived adequately.
- I want to put my head in my arms and sleep, sleep, sleep.
- Nausea creeps up my throat.
- Lethargy falls on the body, it is difficult to even raise an arm.
Often the headache does not hurt, but it is heavy and cottony. Unpleasant sensations can occur in the morning and do not disappear even after a long sleep.
Symptoms
Experts note the following symptoms that are often encountered in practice:
- cardiac arrhythmia (may be accompanied by palpitations);
- mental abnormalities (expressed in the form of increased excitability or, conversely, passivity bordering on apathy);
- vascular spasms;
- regular headaches and even migraines;
- cloudy head, floating vision, confusion, forgetfulness;
- elevated temperature, fever;
- sleep disturbance;
- constantly cold hands (even in hot weather);
- aching pain in the joints, regardless of whether the person has arthritis or not;
- lack of strength, frequent fainting;
- sudden, short-term loss of the ability to breathe.
Diseases accompanied by heaviness in the head
Heaviness in the head may be a sign of brain damage. Also, unpleasant sensations, a feeling of lethargy and weakness indicate that a person is developing a serious illness.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
With this disease, any unusual load can cause discomfort. The tone of brain vessels is disrupted, the outflow of venous blood is hampered, and the supply of oxygen to brain cells deteriorates. The result is a feeling of overcrowding in the skull.
A person suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia often has panic attacks that worsen the general condition. Depressive thoughts arise that literally make your head explode. If there is no opportunity to rest and relax, the feeling of heaviness is accompanied by a headache: bursting, aching, throbbing.
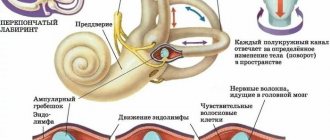
Meniere's disease
Damage to the vestibular system can also cause a person to have a feeling of heaviness in the head. Meniere's disease is an inflammation of the inner ear, labyrinthine dysfunction develops, in which an excess amount of fluid is released. Liquid accumulates in the labyrinth, pressing on the nerve endings. Symptoms of the disease:
- Ear noise, feeling of fullness in the ears.
- Constant dizziness.
- Loss of balance when walking.
- Nausea.
- Hearing loss.
Due to the fact that the vestibular system sends distorted signals to the brain, a person has a feeling of a cotton head. It is difficult for the patient to stand up; when bending over, he is pulled forward.
Osteochondrosis
If the cervical spine is affected by osteochondrosis, then the person’s blood supply to the brain is disrupted. Most often the vertebral artery is compressed. This can provoke an increase in intracranial pressure and lead to oxygen starvation of the brain. A gradual deterioration in blood flow causes the following symptoms:
- Drowsiness, lethargy.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Intrusive headaches.
- Feeling of stiffness in the neck.
- Feeling of heaviness in the skull.
Those at risk include office workers, athletes, people engaged in monotonous work that requires constant repetition of the same actions. Even a nursing mother who regularly falls asleep in an uncomfortable position while breastfeeding may experience a feeling of “fullness” in her head.
Dizziness and heaviness in the head are frequent companions of teachers who spend the entire working day at the blackboard. The static and heaviness of the posture affects the pose - a raised hand with chalk, which performs monotonous movements.
Neurosis-like conditions
Chronic fatigue, constant stress, and depression can lead to a person beginning to develop neurosis. Complaints of patients suffering from neurosis:
- Feeling empty in the head.
- “Muddy” head, like jelly in the skull.
- Tightening, pressing headache.
- The feeling that a heavy hat or a cast-iron helmet was put on your head.
The patient is easily irritated and may start shouting for no apparent reason at his family or just strangers. The patient has difficulty in crowded places where there is a lot of noise and light. They cause increased discomfort; in addition to the symptoms listed above, a feeling of confusion and, at the same time, anger is added.
Sleep disturbances are noted: a person has difficulty falling asleep, often wakes up at night, and lies awake for a long time. The next morning he finds it difficult to get up, even if sleep lasted until lunch, he has a feeling of a “heavy head”, a thick “fog”.
Neoplasms
One of the main symptoms of brain cancer is a daily morning headache. In addition, patients complain of heaviness in the head and drowsiness. Pressing pain occurs in one area of the head due to the fact that the growing tumor puts pressure on the nerve endings and compresses the blood vessels. Due to poor circulation, a feeling of “fullness” and heaviness in the head appears.
The morning nature of the discomfort is due to the fact that when a person changes body position, intracranial pressure rises and cerebral edema increases. Minor physical activity increases the discomfort.
A headache can occur even at night, become stronger in the morning when waking up and subside in the evening. Dizziness, vomiting, feeling of lethargy, apathy are accompanying symptoms of the disease.
Injury
A skull fracture, concussion, neck or head injury can lead to cerebrovascular accident. Heaviness in the skull, accompanied by an annoying bursting headache, is most often a symptom of a complication that develops after a whiplash injury.
Whiplash occurs when unexpected acceleration or deceleration is applied to a person's body. Possible triggering situations:
- Falling from the stairs onto your feet.
- Car accident.
- A quick push from another person when playing football, volleyball, or hockey.
- "Shaking" the baby.
Unpleasant sensations in the head can disappear literally an hour after the injury and appear delayed: after a month, six months, a year, several years. As a result of a whiplash injury, a person experiences dysfunction of the occipital bone and its sutures. In this case, a person develops symptoms such as frequent dizziness, headaches, and heaviness in the head.
Other diseases
Experts identify several other diseases, one of the indirect symptoms of which is a feeling of “fullness” in the head. This type of discomfort does not necessarily appear as the disease progresses, but can sometimes accompany it.
These diseases include:
- Damage to the cardiovascular system.
- Injuries, ruptures of the eardrum.
- Neoplasms in the ocular apparatus, in the middle ear.
- Damage to nerve nodes.
- Migraine.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
- Aneurysm rupture.
- Colds and infectious diseases: flu, rhinitis, otitis media.
- Prolonged lack of oxygen caused by bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, suffocation.
If a person constantly experiences heaviness in the head, the causes of which cannot be determined at home, you should seek help from a doctor.
Comprehensive diagnostics
If fogginess in the head appears constantly, then this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. Therapists, neurologists, and psychotherapists deal with this issue.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must interview the patient and find out what additional symptoms he has, as well as conduct a diagnosis. Here is a list of mandatory tests needed to find out why fuzzy head syndrome occurs:
- General analysis of urine and blood. Exclude the presence of inflammatory reactions and infectious processes.
- Ultrasound of blood vessels in the cervical spine.
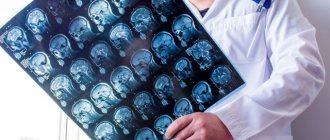
- CT or MRI of the spine and brain. An MRI and CT scan will allow you to exclude malignant processes, determine the condition of blood vessels, identify the presence of chronic diseases of the nervous system, etc.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
The patient may also need to consult other specialists.
If a person experiences a feeling of foggy consciousness, often has a unclear head, or headaches, it is necessary to visit a neurologist. It is this specialist who, after examining the patient and listening to his complaints, suggests undergoing additional examination or refers him to a specialist. Possible diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
- CT and MRI of the head, cervical spine.
If the development of astheno-neurasthenic syndrome is suspected, the person will be referred to see a psychotherapist. If circulatory disorders are caused by neurasthenia, the patient may additionally be advised to undergo rheoencephalography.
Third-party factors that provoke heaviness in the head
Is it hard to raise your head, but you have not been diagnosed with any diseases? Perhaps the cause of discomfort is a person’s lifestyle or some external factors. Unpleasant sensations appear if:
- For a long period of time you don’t sleep enough, go to bed late and get up early.
- Sit at the computer every day, avoiding physical activity.
- Drink alcoholic beverages in large quantities.
- Spend your nights in clubs and sleep during the day.
- Use drugs.
- Use certain medications in large quantities.
Toxic damage to the body (from food, alcohol, drug poisoning) causes oxygen starvation of the brain, and is therefore accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness of the skull. Allergic reactions that occur with cerebral edema can also cause discomfort. When the weather changes, a sudden cold snap, a weather-dependent person may experience heaviness in the head.
How to eliminate discomfort?
Did you get up in the morning with a heavy head and can’t recover? There are several methods you can use to improve your condition.
- When a headache is added to the unpleasant sensations, it makes sense to take a pain reliever (analgesic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug).
- A cool or contrast shower, which should be taken for at least 15 minutes, helps to get rid of discomfort.
- You can conduct a massage or self-massage session, gently rubbing the neck, back of the head, and temple area.
- To alleviate the condition, you can use aromatherapy: apply a couple of drops of mint, rosemary, lavender oil, tea tree oil, lemon.
- Breathing exercises effectively eliminate discomfort.
- Some yoga exercises can reduce discomfort.
- You can try to relax using self-hypnosis: sit or lie down with pleasant music and imagine yourself on the seashore, in a rustling forest, in a meadow.
Sometimes, in order to eliminate discomfort, you just need to get a good night's sleep in a dark room and normalize your working day: if your job is sedentary, periodically take breaks, exercise minutes, and regulate psychological and physical stress. It is advisable to change the pillow and mattress, choosing bedding that helps you relax while sleeping.
Features of treatment
If a patient constantly complains that he has a heavy head, the causes of discomfort are vegetative-vascular dystonia, osteochondrosis or another disease, it is best to entrust treatment to a specialist. The following therapeutic measures are carried out:
- Cerebral circulation is normalized with the help of nootropic and vasotropic drugs.
- Blood circulation is improved with the help of physiotherapy: electropheresis, phonopharesis, and magnetic therapy are used.
- Muscle spasms in cervical osteochondrosis are relieved through massage and manual therapy.
- Nervous tension is eliminated - with the help of tranquilizers, sedatives, sedatives.
- To relieve muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are taken, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory gels and ointments are applied topically.
- Allergic reactions are relieved with antihistamines.
If the cause of discomfort is the growth of a tumor, surgical intervention may be required.
In case of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, it is necessary to strengthen blood vessels and normalize blood pressure. If the discomfort is due to a cold, the patient’s condition will return to normal after recovery.
Regular use of painkillers is required only if the heaviness in the skull is accompanied by a headache. It is advisable not to rely only on medications, but also to change eating habits and give preference to natural products. Spicy, salty, sour foods can increase discomfort, as can caffeinated drinks and chocolate.
Do you want the heaviness in your head to go away? Play sports, preferably swimming. It helps not only to get a feasible load on all muscle groups, but also to relieve accumulated negative emotions, “wash away” stress and a depressive mood. Walking in the fresh air, good sleep and the absence of nervous overload will help avoid unpleasant sensations.
Main etiology
Osteochondrosis is a disease that disrupts blood flow, causing deformation of the vertebrae.
At the same time, it is difficult for the patient to move and regulate his coordination. Often, with age, the vertebral discs change, which provokes weakness, heaviness in the head, drowsiness, and fog in the eyes.
When confirming the diagnosis of osteochondrosis, an integrated approach is used, which consists of taking medications, physiotherapy, and herbal medicine.
If the disease is at an advanced stage, the patient is prescribed acupuncture. If indicated, the patient requires the help of an osteopath.
Intracranial pressure is diagnosed due to the large volume of fluid entering the brain. This is due to the following factors:
- head injury;
- congenital diseases of the central nervous system;
- poisoning of various etiologies;
- brain pathologies;
- oxygen starvation.
Against the background of high intracranial pressure, the brain malfunctions. At the same time, its functions are impaired. The patient complains of weakness, dizziness and heaviness in the head. Additionally, other signs may appear.
Migraine and epilepsy are also characterized by the above symptoms. Migraine is an attack-like pain. More often the disease is hereditary.
In addition to heaviness and pain in the head, the patient complains of lethargy and nausea. Therapy is carried out taking into account the frequency of attacks and the severity of the pathology.
Meniere's syndrome is an inflammation that develops in the inner ear. Against the background of this process, the patient experiences headache, dizziness, and nausea.
Asthenic neurosis or neurasthenia is associated with a pathological state of the nervous system, which manifests itself against the background of prolonged emotional or physical stress.
Neurasthenia develops for the following reasons:
- constant stressful situations;
- experiencing conflict;
- hard work that causes stress;
- conflicts;
- stressful, intense work;
- insufficient sleep;
- work without interruptions.
If this disease is confirmed, the patient requires long-term treatment to eliminate it. To eliminate the disease in question, the patient needs the help of a psychotherapist.
Heaviness in the head, attacks of dizziness, nausea, and other symptoms of neurasthenia are eliminated with sedatives. Drug treatment will significantly improve the patient's condition.
For a complete recovery, it is recommended to rest fully, protecting yourself from stress and conflicts. It is also recommended to change activities: physical to mental work, and vice versa.
If heaviness in the head is caused by a mechanical injury, the help of a neurologist is required. With this etiology, pain receptors, including arteries and nerve endings, are irritated.
Doctors identify light, minor bruises. More often, heaviness in the head, pain, and nausea are provoked by “whiplash injuries” that patients receive in moving vehicles.
Against the background of a sharp jerk during movement, the muscle is easily injured, which leads to stretching of the joints and dislocation of the spine in the cervical region.
Heaviness and other discomfort in the head may appear after diving, with a strong cough.