Of all types of human motor activity, walking is the most common and, at the same time, the most difficult. It involves many parts of the brain, different systems and the skeletal apparatus. In order for a person to walk correctly, all these structures of the body must interact harmoniously with each other. If some kind of failure occurs in the functioning of the central nervous system or it is disrupted, then, accordingly, the way of walking changes.
Gait disturbance has a name from the Greek language - abasia.
Modern medicine applies the name “abasia” to a fairly wide range of gait disorders. These include: hypokinetic, hemiparetic, ataxic, paraspastic, spastic-atactic gait, apraxia of walking, peroneal gait, idiopathic senile dysbasia, dysbasia with mental retardation, duck gait, gait disorders with epilepsy and paroxysmal dyskinesia, gait with diseases of the musculoskeletal system , hyperkinetic gait.
In cases where sensorimotor dysfunction occurs, neurologists use a double name - astasia-abasia. It is used in cases where, along with a gait disorder (abasia), the patient also experiences a balance disorder (i.e., astasia). The most common manifestation of such changes in gait is considered to be frontal dysbasia (normotensive hydrocephalus, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, stroke). There are also such types of dysbasia as psychogenic and senile, dysbasia in neurodegenerative diseases.
What is unsteadiness of movements?
Unstable movements – permanent or temporary loss of coordination. If they occur systematically, this indicates the presence of abnormal disorders in the body. Extra-systemic indicate that inflammatory processes are occurring in the body.
Most often, unsteadiness of walking manifests itself in combination with other symptoms:
- headache;
- unexplained sudden weakness;
- tingling in the legs;
- dizziness.
To better understand, it is necessary to know why a person may stagger when walking and why this is so important.
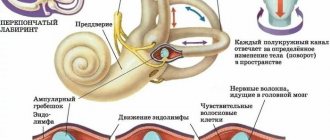
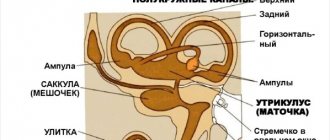
Movement is achieved through a healthy bone structure, developed muscles and healthy joints. The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for coordination; it is also controlled by vision and the vestibular apparatus.
Impulses pass through the spinal cord, sending a signal to the lower parts of the body that a movement needs to be performed. Only after this the muscles begin to work.
When these impulses are disrupted, the entire system is disrupted. This is where the gait disorder comes from. A transmission failure causes the legs to become unresponsive.
Failures in the musculoskeletal system lead to exactly the same result. The legs cannot correctly carry out the necessary “commands”.
If the functioning of the cerebellum is disrupted, the impulse itself does not reach, therefore, the command does not arrive at all. Consequently, a person cannot move, his legs do not obey.
4.Treatment
Gait disturbance is not a disease, but a symptom, so the most important step is timely and accurate diagnosis of the etiopathogenetic factors of dysbasia or astasia-abasia. Therapy is prescribed with the goal of eliminating these factors as much as possible, and it is, of course, impossible to even briefly talk about all possible protocols and schemes for vertebrological, neurological, and neurosurgical treatment. It is more important to emphasize that in some cases, a changed gait may be the first, early and almost the only symptom that will help at the initial stage to identify a developing process that is much more serious and dangerous than dysbasia itself. In this case, timely contact with a doctor is of key importance, and delaying the visit is highly not recommended.
Old age
Often, older people (over 60 years old) experience swaying, as well as “floaters” before the eyes. It is also common to experience tinnitus and dizziness when walking. Headaches appear sharply, and sometimes even fainting occurs. As a rule, all these symptoms are ignored and blamed on age.
In some cases, this may indicate problems with the body, so you should consult a doctor. This way you can ensure your usual full life.
One of the reasons is a malfunction of the cardiovascular system of the brain. Atherosclerosis appears (as mentioned above, a disease of the second category).
With age, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is impaired.
Gait disturbance may also be due to heart disease. For example, ischemia can reduce blood circulation in the area of the ear where the organ responsible for balance is located. Also, insufficient blood circulation leads to uncertain movements. Other diseases also have a detrimental effect (arrhythmia, hypertension).
It has a great influence on gait and blood viscosity, because it supplies oxygen to the organs. How quickly it reaches the desired place, including the cerebellum, depends on its speed.
Injuries and diseases of the spine also make it difficult to transmit signals. Therefore, movement disorders are possible. Elderly people are often susceptible to sleep disorders, which leads to diseases of the third category.
The most common occurrence of maladaptation is observed. The person feels extremely insecure, there is a feeling that no one needs him, inexplicable fears and anxiety. As a result, he may skid when walking, become dizzy, have dark vision, and his condition worsens every day. For treatment, you must definitely contact professionals and it is better not to delay, because the consequences can be disastrous.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that many factors can lead to an unsteady gait and they should not be ignored.
If the cause is eliminated, the consequences will also be eliminated. Life will be familiar, fulfilling and healthy. Therefore, it does not matter how old a person is, treatment is necessary regardless of age.
Feeling of dizziness and unsteadiness of gait when walking in the dark: how to treat?
List of medications for the treatment of dizziness
If you experience unsteadiness in your gait and dizziness only in the dark, it is likely that you have problems with your eyes. In order to confirm or refute such a diagnosis, you will need to contact an ophthalmologist and undergo a full examination.
Typically, this problem is caused by high eye pressure. Also, a similar problem can be provoked by otolaryngological pathologies. Inflammation of the sinuses or ear can provoke vasospasm and against this background unpleasant symptoms may appear. If these pathologies are excluded, you will have to treat neuralgia.
List of medications:
- Betahistine (will help restore cerebral circulation)
- Reklanium
(will establish the correct functioning of the vestibular apparatus) - Nimodipine
(relieves vasospasm and establishes proper oxygen supply to the blood) - Kaviton-forte
(is a mild stimulator of cerebral circulation) - Metacin (helps improve nutrition of cerebral cortex tissue)
- Pilocarpine (a drug to reduce eye pressure)
- Betoptik (reduces fluid flow to the eyeball)
When should you sound the alarm?
Impaired coordination in some cases is a consequence of serious illnesses. It is recommended to consult a specialist if:
- stumbling has become more frequent, often occurring even out of the blue;
- falls due to weakness in the legs;
- impaired control of movements;
- unnatural gait;
- after a long walk there is a sudden stop, then there is a feeling that it is impossible to move your leg;
- feeling of “cotton” legs;
- difficulty walking on stairs;
- when moving, most of the weight increasingly moves to the heel area;
- when trying to get up, a person falls;
- difficulty raising a leg or starting to move after a long rest;
- the appearance of dizziness, pounding in the temples, darkening in the eyes.
Often a person begins to be afraid and panic.
It is absolutely impossible to ignore such symptoms, since they indicate the presence of diseases.
Main manifestations
Various degrees of dyspraxia are diagnosed in 3–6% of children, more often in boys. Many children are clumsy in early childhood, but a child with dyspraxia retains clumsiness even as an adult. Children who have been diagnosed with this disease find it difficult to perform everyday activities: they have difficulty speaking, often fall and stumble when walking, they have difficulty catching a ball in a game, maintaining balance when riding a bicycle, writing or reading something, etc. d.
Activities in which a child with dyspraxia has problems:
- speech – the work of the muscles of the articulatory apparatus is not coordinated, speech breathing is impaired;
- writing, drawing – difficulty holding a pen, brush, pencil, slow writing, long mastery of simple movements;
- reading - it is difficult to control eye movements and hold your gaze, which makes it difficult to follow the line with your eyes;
- performing basic movements when running, walking, jumping, maintaining balance;
- it is difficult to remember and reproduce the sequence of movements;
- games of high and medium mobility - children cannot catch and throw a ball, hold the attributes for the game, or use them.
Although modern medicine, and neuropathology in particular, is constantly developing innovative methods for preventing, treating and preventing disorders, dyspraxia in children is still an insufficiently studied problem.
Doctor's help
It is impossible to make a diagnosis yourself when it sways from one side to the other. This is done exclusively by specialists. To begin with, doctors monitor the patient’s movements using the following methods:
- observation of movements directed forward with the face and forward with the back;
- doctors watch how the patient moves in a straight line with his right and left sides;
- alternate change of step rhythm;
- comparison of walking with eyes closed and with eyes open;
- watching a person climb stairs;
- movement around an object (for example, a chair);
- making turns while driving;
- It is also suggested to walk on your toes and heels.
Based on the results, the doctor prescribes further examination and treatment:
- undergoing magnetic resonance imaging;
- X-ray;
- CT scan;
- blood donation (general analysis and biochemical);
- A biopsy of muscle tissue is performed.
In addition, the patient should be examined by other doctors:
- ENT;
- ophthalmologist;
- endocrinologist
After going through all the stages, the doctor can diagnose the patient and prescribe the necessary treatment.
You should turn to traditional medicine only after examination and consultation with a doctor.
Any medications are prescribed only by a certified specialist! All drugs are prescribed based on the individual characteristics of each organism. Medicines that help one person can cause irreparable harm to another.
Who should I contact?
There are often situations when the patient himself understands that he needs the help of a specialist. However, he has no idea which doctor to see. To do this, you need to carefully monitor the symptoms and act in accordance with them:
- Cardiologist. It is worth contacting him if, along with impaired gait, there is also increased blood pressure or in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Neuropathologist. A neurologist is consulted if a person often experiences stress, nervous or other mental disorders.
- Traumatologist/orthopedist. You have been injured, there is pain in the muscles or joints.
- Surgeon. You should see a surgeon if you receive serious injuries.
If it is impossible to identify the symptoms on your own, you should consult a general practitioner.
Often the cause of symptoms is sought using magnetic resonance imaging. This diagnostic method allows you to identify the cause of the development of pathology, as well as make an accurate diagnosis.
Choosing a clinic is easy to do using the service. A single registration center for MRI or CT allows you to select a medical center based on specified parameters: type of examination, metro station, and also sort the search results by price, rating, work schedule.
Patients have access to online registration through the website or telephone registration with a discount on the study in the amount of up to 1,000 rubles.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
There are numerous types of dis- and abasias, almost each of which is designated by a special term, indicating, as a rule, the cause of the disorders. It is too long to list them all, and it is hardly advisable: cerebellar, spastic-atactic, hemiplegic, psychogenic, hyperkinetic and many others. etc. For example, the “cock step” (a step when the leg bent at the knee is raised high above the floor and then “slammed” back with force) with lesions of the peroneal nerve or multiple sclerosis is fundamentally different from mincing small steps with senile dementia or parkinsonian syndrome.
Regardless of the type of motor function disorder, it is very important to tell the doctor a number of key points that are important for diagnosing the causes: when and after what the disorders developed, did they arise simultaneously, remaining in the same severity, or gradually progress, are they accompanied by other symptoms and disorders ( joint or headaches, dizziness, fainting, disorders of coordination of movements, speech, cognitive functions, etc.). Perhaps the first call will be in the wrong place, and the doctor (for example, an orthopedist or vertebrologist) will redirect the patient to a specialized specialist (neurologist, otolaryngologist, etc.). Next, depending on the suspected etiology, a diagnostic examination will be prescribed, both laboratory (clinical tests, biopsy, bacteriological, immunological or toxicological examination) and instrumental (MRI, CT, electromyography, stabilography, etc.).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!