- Home >
- Symptoms >
- Brain fog
Fog in the head, cloudy consciousness, wobbly head... Today, more and more often, it is with such “vague” complaints that people of different ages turn to the doctor. As practice shows, such a condition can indicate many diseases, but most often it is a manifestation of one of two causes - cerebrovascular accident or neurosis.
At a consultation with a neurologist:
- Conducts an inspection;
- Listens to patient complaints;
- Make a preliminary diagnosis;
- If necessary, he will refer you for additional studies, which can be completed in our center;
- will prescribe an individual course of treatment.
In each of these cases, the feeling of fog in the head is accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms and requires its own treatment method.
Features of treatment
Symptoms such as cloudiness, dizziness, heaviness, a feeling as if the head is in a fog, can accompany a person constantly or appear several times a week.
This condition does not always mean that a person has any disease. Often these signs arise due to the influence of certain factors: changes in weather conditions, excessive physical exertion, lack of sleep, mental work, etc.
The main feature of the brain fog symptom is its sudden appearance. So, a person who felt good a minute ago, almost in an instant feels discomfort, fogginess, dizziness, blurred vision, dullness of consciousness.
The problem is that these symptoms can appear in the workplace or while performing an important task. Due to this, a person is deprived of the opportunity to carry out usual activities.
Brain fog is often accompanied by various symptoms:
- increased or decreased blood pressure;
- drowsiness during the day and sleep disturbance at night;
- weakness;
- headache;
- strong heartbeat;
- excessive sweating, etc.
Often this picture is accompanied by a feeling of unreasonable fear, a feeling of lack of air, and the appearance of a ringing in the head. There are many reasons for this condition.
If a patient constantly complains that he has a heavy head, the causes of discomfort are vegetative-vascular dystonia, osteochondrosis or another disease, it is best to entrust treatment to a specialist. The following therapeutic measures are carried out:
- Cerebral circulation is normalized with the help of nootropic and vasotropic drugs.
- Blood circulation is improved with the help of physiotherapy: electropheresis, phonopharesis, and magnetic therapy are used.
- Muscle spasms in cervical osteochondrosis are relieved through massage and manual therapy.
- Nervous tension is eliminated - with the help of tranquilizers, sedatives, sedatives.
- To relieve muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are taken, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory gels and ointments are applied topically.
- Allergic reactions are relieved with antihistamines.
If the cause of discomfort is the growth of a tumor, surgical intervention may be required.
In case of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, it is necessary to strengthen blood vessels and normalize blood pressure. If the discomfort is due to a cold, the patient’s condition will return to normal after recovery.
Regular use of painkillers is required only if the heaviness in the skull is accompanied by a headache. It is advisable not to rely only on medications, but also to change eating habits and give preference to natural products. Spicy, salty, sour foods can increase discomfort, as can caffeinated drinks and chocolate.
Do you want the heaviness in your head to go away? Play sports, preferably swimming. It helps not only to get a feasible load on all muscle groups, but also to relieve accumulated negative emotions, “wash away” stress and a depressive mood. Walking in the fresh air, good sleep and the absence of nervous overload will help avoid unpleasant sensations.
There are several types of manifestations of brain fog. They are classified based on the primary causes.
Dizziness, cloudiness, heaviness can accompany people constantly or appear periodically. If your head is in a fog, this will not always indicate the development of some kind of disease. Very often, such a symptom is observed due to the influence of certain factors, for example, excessive physical exertion, changes in weather conditions, mental work, lack of sleep and much more.
The main feature of the symptom, when the head is in a fog, is its unexpected appearance. For example, if a person felt very good a minute ago, then almost in an instant he begins to experience discomfort, dizziness, fogginess, dullness of consciousness and blurred vision.
The whole problem with feeling like your head is in a fog is that the symptom can manifest itself while performing some important task or at the workplace. For this reason, the patient is deprived of the opportunity to carry out his usual activities. Dizziness and foggy head may be accompanied by other symptoms, for example:
- Low or high blood pressure.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness during the day and sleep disturbances at night.
- Headache.
- Palpitations.
- Excessive sweating.
Quite often, such a picture is accompanied by unreasonable fear, a feeling of lack of air, and also the formation of ringing in the head. There are many different causes of brain fog. A list of them will be described below.
Heavy and cottony head, reasons, what to do, treatment
It’s not just a headache that can interfere with normal perception of the colors of the world around you and living in peace. Sometimes a tedious heaviness in the head is perceived worse than a migraine attack. After all, a migraine will go away after a certain period of time, and the feeling of a burden in the head can torment a person for a very long time.
How do patients describe their feelings?
- In the morning, my head pulls towards the pillow.
- There is a feeling that the skull has been filled with stones.
- It was as if blood from the whole body had collected in the skull.
- Metal disks move heavily in the brain.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Information is not perceived adequately.
- I want to put my head in my arms and sleep, sleep, sleep.
- Nausea creeps up my throat.
- Lethargy falls on the body, it is difficult to even raise an arm.
Often the headache does not hurt, but it is heavy and cottony. Unpleasant sensations can occur in the morning and do not disappear even after a long sleep.
What to do if you constantly have a heavy head, which causes a lot of discomfort, impairs your ability to work, causes lethargy and adversely affects your well-being? First of all, if possible, free yourself from any work and rest, and at this time find out the reasons why there is heaviness in the head, often accompanied by dizziness.
Let’s immediately deal with the usual factors that can cause problems in any person (fatigue, diets, taking medications, lack of sleep), and then we’ll go through the main diseases, which are not always actively manifested and cause the feeling that the head has become cast iron.
Etiopathogenesis
The brain functions like a constantly running computer. When exposed to discomfort, he will begin to limit some of his actions. One of them is a sense of consciousness, conscious presence. Lack of oxygen, nutrients in the brain, accumulation of metabolic waste, and toxins are factors that lead to fainting, blurred vision, and a foggy state.
When your head is spinning
Dizziness is a rather unpleasant condition in which a person, who is in a motionless state, feels the rotation of surrounding objects around him. This phenomenon is reminiscent of riding a carousel. In medicine, dizziness is called vertigo.
Most often, dizziness is not dangerous for a person. It occurs in response to harmless factors. After eliminating them, the unpleasant sensation completely disappears. But sometimes vertigo can signal serious pathologies that require proper and timely treatment.
Mechanism of development of vertigo
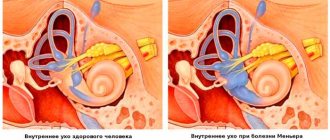
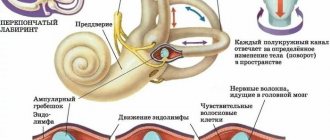
If we consider dizziness from an anatomical point of view, the causes of this condition are quite simple. The vestibular apparatus, responsible for human balance and coordination in space, is located in the inner ear. Vision and muscle reflexes help a person navigate the environment. All received information enters the brain. And it is he who controls the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Sometimes the connection between the inner ear and the brain can become disrupted. A person loses the ability to navigate in space. Dizziness appears. To restore the lost connection, the brain immediately launches several reactions at once. Some of them may affect neighboring centers (for example, emetic). This leads to the appearance of unpleasant accompanying symptoms.
Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome
If there is no clarity in the head, then this may indicate astheno-neurotic syndrome. This pathology, in addition to constant fog in the head, is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Problems falling asleep.
- Superficial sleep.
- Suspiciousness, irritability, hot temper.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Unreasonable anxiety.
- Daytime sleepiness.
- Decreased ability to work.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat.
- Memory problems.
- Stiffness of movements.
- Dizziness.
- Constrictive headaches.
- Tremor of the limbs.
In most cases, this syndrome affects people who are mentally stressed. In addition, this pathology often affects those who have an unstable psyche.
The main causes of astheno-neurotic syndrome are prolonged stress, prolonged nervous tension, anxiety, chronic lack of sleep, and overwork. In addition, pathology can occur in people who have the following diseases and ailments:
- Various chronic diseases.
- Hypertension.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Poisoning.
- Acute viral infection.
- Avitaminosis.
- Head injuries.
- Bad habits.
The syndrome develops over time. At the initial stage of its development, a person feels weak in the morning, restlessness and mild irritability. After this, in the absence of medical intervention, other symptoms appear in the form of sleep disturbances, loss of strength, memory problems, heaviness in the head, a feeling of futility, the appearance of fog in the eyes, as well as decreased ability to work.
After this, pain in the heart sets in, excessive irritability gives way to weakness, appetite disappears, mood and libido decrease, apathy appears, and the patient constantly thinks about the state of his health. As a rule, such people develop a fear of death. Ignoring such symptoms can lead to mental illness.
This disease can be cured using psychotherapeutic methods. However, provoking factors should also be excluded at the initial stage of therapy: lack of sleep, stress, mental stress and excessive physical activity. If you do not reduce the influence of these factors, then drug treatment and psychotherapy will not have the desired effect and will not eliminate the unpleasant symptom.
Medicines are used in severe cases. The most effective are sleeping pills, restoratives, antipsychotics, antidepressants and tranquilizers.
Causes of the symptom
As stated earlier, the causes of brain fog may not always be due to health problems.
Thus, when there are disruptions in the hormonal system, fog in the head is almost always observed. During pregnancy, a woman is often accompanied by this condition, as well as irritability and forgetfulness. The same symptoms may occur during menopause. Other causes of brain fog:
Astheno-neurotic syndrome
If there is no clarity in your head, then most likely we are talking about astheno-neurotic syndrome. This pathology, in addition to brain fog, is accompanied by other symptoms:
- shallow sleep;
- problems falling asleep;
- irritability, suspiciousness, hot temper;
- unreasonable anxiety;
- rapid fatigue;
- drowsiness during the day;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- decreased ability to work;
- stiffness of movements;
- memory problems;
- pressing headaches;
- dizziness;
- tremor of the limbs.
The syndrome mainly affects people whose work involves mental activity and increased responsibility.
In addition, pathology often affects those who have an unstable psyche. The main causes of astheno-neurotic syndrome are prolonged stress, prolonged nervous tension, anxiety, chronic lack of sleep, and overwork. In addition, the pathology occurs in people with:
- chronic diseases;
- hypertension;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- acute viral infections;
- poisoning;
- vitamin deficiency;
- bad habits;
- head injuries.
The syndrome develops gradually.
At the initial stage of neurosis, a person feels weak in the morning, mild irritability, and anxiety. Then, in the absence of medical assistance, other symptoms appear in the form of loss of strength, sleep disturbances, memory problems, a feeling of “vatness,” heaviness in the head, fog in the eyes, decreased ability to work, etc.
Then pain in the heart occurs, severe irritability gives way to weakness, appetite disappears, libido (sexual desire) and mood decrease, apathy appears, the patient constantly thinks about his health, and fear of death appears. Subsequent ignoring of these symptoms leads to mental disorders.
Vegetovascular dystonia
VSD is the most common cause of brain fog. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not a separate disease, but a combination of many symptoms that arise against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for the functioning of all internal organs and systems.
VSD is characterized by the following symptoms:
- fog, heaviness in the head;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- anxiety;
- unreasonable fears;
- nausea, stomach pain;
- tachycardia;
- lack of air;
- tremor of the limbs;
- unsteadiness when walking;
- sleep disorders - insomnia, shallow sleep;
- changes in blood pressure;
- irritability;
- “midges” before the eyes;
- ringing in the ears, etc.
The list of symptoms for VSD can be endless. The main feature of the disease is frequent relapses, manifested in the form of panic attacks.
If you do not take any action - do not take medications, do not strive for changes in lifestyle, do not seek help from doctors (psychotherapist, neurologist) - this can result in the appearance of various phobias and fears.
Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain
If the brain lacks oxygen, this leads to a feeling of brain fog.
The process of hypoxia develops due to compression of the vessels through which the blood carries oxygen and all the substances necessary to nourish the organ. At the same time, in addition to fogginess and “vatness” in the head, a person experiences:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- severe heaviness in the head;
- decreased ability to work;
- memory problems;
- confusion of consciousness;
- problems with perception of information;
- inhibition of reactions;
- severe weakness, fatigue.
With severe oxygen starvation, a person may lose consciousness.
The causes of this condition may be:
- the presence of cervical osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spine;
- use of drugs and alcoholic beverages;
- hypertension, hypotension;
- previous traumatic brain injuries;
- smoking;
- lack of fresh air;
- limited physical activity;
- runny nose.
If this pathology is not treated, then oxygen-starved brain cells gradually lose their functionality, which ultimately leads to serious complications.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Fog in the head is the main symptom that accompanies cervical osteochondrosis. The disease is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical vertebrae.
This process is almost always accompanied by compression of arteries and other vessels in the specified area. This leads to poor circulation and insufficient nutrition of brain cells.
In this regard, a person begins to feel all of the above symptoms, which are accompanied by:
- pain in the neck when bending or turning the head;
- severe heaviness in the head;
- pain in the shoulders, arms;
- a feeling of “dull pain in the head”;
- weakness in the neck;
- stiffness of movement in the shoulder joints.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine develops due to poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, and staying in the same position for a long time.
In advanced cases, the neck and shoulders can be completely immobilized.
Frequent consumption of gluten-containing foods
Not only diseases of the spine, neurosis and VSD can cause a feeling of fog, heaviness and “cottoniness” in the head, but also the consumption of foods containing gluten.
An allergy to this component causes the production of substances that have a negative effect on the brain. If people with a gluten allergy eat a lot of buns, bread, semolina, and pasta made with wheat flour, they will gradually develop the following symptoms:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract - bloating, constipation followed by diarrhea, pain in the stomach and intestines;
- weakness, fatigue, apathy, lethargy;
- brain fog;
- slow reaction;
- mental confusion;
- depression;
- psychological confusion;
- fog.
To find out if you really have a gluten allergy, you should see a doctor and take an allergy test.
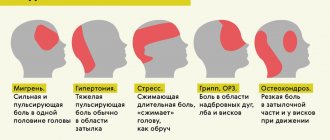
What Causes Brain Fog?
This condition sometimes occurs in healthy people as a result of fear, shock, prolonged standing, or staying in one position. But with a cloudy head, the causes can also be represented by more serious diseases. If such problems occur frequently (more than once a month), consult a doctor.
Causes of brain fog in healthy people:
- Prolonged standing, which can also cause cramps. These symptoms may also indicate chronic venous insufficiency.
- Rapid changes in body position, for example when standing up from a sitting position. We are talking about orthostatic hypotension, which is a drop in blood pressure with a rapid change in posture. This condition can be supported by certain medications.
- Prolonged tilting of the head (for example, when looking at the sky), causing a decrease in blood flow to the head.
- Prolonged stay in a room with “heavy” air.
- Fright.
- Emotional excitement, nervousness.
- Swallowing.
- Defecation.
- Urination.
- Shaving or tying a tie.
- Phobias, looking at unpleasant things (blood, needles, arachnophobia, fear of heights, other phobias).
- Emotional trauma.
- Depression.
- Exhaustion.
- Dehydration.
- Intoxication.
- Sudden or severe pain.
- Severe cough, sneezing.
- Laughter.
- Poor or insufficient sleep.
- Playing sports in high ambient temperatures.
- Hormonal changes.
- Pregnancy (increased cardiac output).
For brain fog, causes may include medications. These include medications for hypertension, allergies, depression, and nausea.
Tablets that may make your head feel cloudy:
- opioid analgesics (at the beginning of use, as a rule, symptoms decrease over time);
- parasympathomimetics (by lowering blood pressure);
- sympatholytics used to reduce blood pressure, tachycardia (blocking norepinephrine receptors);
- antidepressants;
- combinations of antidepressants or their use with opioids - can lead to thought disorders, serotonin syndrome (CNS irritation, tremor, muscle twitching, impaired consciousness, hypertension, rapid heartbeat);
- diuretics.
Sudden dizziness: 5 simple reasons
Typically, loss of communication between the brain and the vestibular system is rare and does not last long.
Dizziness that occurs is not considered a pathology in the following cases:
- Riding on a carousel . Such entertainment creates a serious load on the vestibular apparatus. And if it is naturally weak and untrained, then it may well fail. Such dizziness usually occurs in women, since they also have psycho-emotional experiences added to the load.
- Stress, worries . If dizziness occurs during a speech in front of a large audience or after a reprimand from a boss, then the cause of vertigo is the production of a large amount of adrenaline. This hormone causes vasospasm. And this leads to a temporary deterioration in blood flow in the brain.
- Climbing to heights . In this case, the unpleasant phenomenon is also considered a physiological norm. When rising to a height, a person’s eyes cannot quickly focus on distant and close objects. Abrupt switching between objects causes dizziness.
- Hunger . Similar problems are common to all fans of strict diets. If a person does not receive enough nutrition, then a glucose deficiency occurs in his body. The absence of the main “fuel” leads to deterioration of brain function and the appearance of dizziness.
- Active exercises . Exercise enthusiasts should remember moderation. Excessive exercise can cause low blood pressure. This leads to dizziness and sometimes fainting. The unpleasant condition may be caused by unsuccessful sudden movements of the head, as a result of which the blood supply to the brain is disrupted.
An attack of dizziness may occur in response to taking certain medications. The most common sources of unpleasant symptoms are NSAIDs, antidepressants, antibiotics, and cancer medications. If your head is “turned” by medications, be sure to consult a doctor to change the drug.
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia
This disease is the most common reason for lack of clarity in the head, fog. However, you should pay attention to the fact that vascular dystonia is not a separate disease, but a combination of many symptoms that arise due to disruptions in the functioning of the human autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for the functioning of internal organs and systems. The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Dirty and head, as if in a fog.
- Dizziness.
- Anxiety.
- Headache.
- Stomach pain, nausea.
- Unfounded fears.
- Lack of air.
- Tachycardia.
- Unsteadiness when walking.
- Tremor of the limbs.
- Insomnia and shallow sleep.
- Irritability.
- Changes in blood pressure.
- Floaters before the eyes.
- Severe ringing in the ears.
The list of symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia can be endless. In addition to the fact that a person develops a fog in the head, there is no clarity of thinking with this illness, it should be noted that panic attacks appear. If the patient does not take any measures, does not strive for changes in lifestyle, or does not seek help from a doctor, this can provoke the emergence of various fears and phobias.
So, we figured out that the head is in a fog - this can be a symptom of vegetative-vascular dystonia. To eliminate it, you need to seek help from a doctor. To relieve symptoms, various medications are used: sleeping pills, sedatives, drugs for dizziness, as well as medications to normalize blood pressure.
Also very effective in the fight against this disease are physical procedures, massage, and acupuncture.
Methods for treating cotton head
For osteochondrosis, the patient is prescribed complex treatment. It includes taking medications:
- For pain relief - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- To normalize blood flow - nootropic, vasotropic drugs.
- Locally - gels based on Diclofenac, Ketoprofen to relieve inflammation and reduce pressure on the vertebral artery.
Physiotherapy is also indicated for patients: electrophoresis on the cervical spine, massage, manual therapy.
If a patient complains that he does not have clarity in his head, there is a constant feeling of confusion, vagueness, heaviness, and he is diagnosed with neurasthenia, treatment can take a long time.
First of all, you need to eliminate the factors that provoke the development of discomfort:
- Reduce mental, mental, physical stress.
- Get enough sleep, sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Normalize the work and rest schedule.
- Relieve yourself of some responsibility.
- Eat properly.
Rational psychotherapy is carried out with patients, and autogenic training is also indicated for such patients. Medicines used for treatment:
- Tranquilizers.
- Antidepressants.
- Hypnotic.
- Medicines that have a strengthening effect on blood vessels.
- Vitamins that normalize the functioning of the body.
Increasing immunity, regular walks in the fresh air, and dosed physical activity (swimming, cycling, running) help reduce discomfort.
Many people still experience brain fog once treatment is stopped. Sometimes “being sick” is a way to hide from problems that cannot be resolved. Find the problem with a psychotherapist and fix it. If you can’t do this, you just need to radically change your life: change jobs, decide to vacation in a distant country, forgive all insults.
Lack of oxygen
If the human brain begins to lack oxygen, this can trigger a feeling of brain fog. For this reason, hypoxia develops due to compression of the vessels through which the blood must carry oxygen, as well as all the necessary substances to nourish the organ. In addition to fogginess, a person experiences other symptoms:
- Weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Decreased ability to work.
- Heaviness in the head.
- Bad memory.
- Unclear consciousness.
- Slow reaction.
- Problems with information perception.
- Fatigue, severe weakness.
Diagnostics
A detailed medical history is important for a correct diagnosis. It must contain an accurate description of the event, prodromes, symptoms preceding it and other information. It is also important to find out how often brain fog occurs and whether individual cases have common features.
The history should include the following information:
- type of imbalance, improving and worsening factors;
- provocative moments, the onset of instability (acute, slow);
- duration of progression (minutes, days, months, years);
- course (continuous, progressive, episodic); for episodic manifestations - duration of the attack;
- accompanying symptoms (vegetative, auditory, neurological, others);
- history of somatic and psychiatric comorbidities, medications used.
From the anamnesis and clinical examination we can distinguish:
- signs indicating damage to the vestibular system;
- ataxia as a result of damage to the cerebellum, proprioceptive pathways, and vestibular system;
- disturbances in stability due to damage to the basal ganglia, frontal cortex;
- nonspecific or presyncopic states of imbalance caused by cardiovascular, metabolic, and autonomic causes.
The doctor may also ask about medications you take regularly or occasionally.
Family history includes information about the presence of sudden deaths in the family, especially at a younger age. Cardiac activity is also monitored using ECG and blood pressure is monitored.
If a person experiences a feeling of foggy consciousness, often has a unclear head, or headaches, it is necessary to visit a neurologist. It is this specialist who, after examining the patient and listening to his complaints, suggests undergoing additional examination or refers him to a specialist. Possible diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
- CT and MRI of the head, cervical spine.
If the development of astheno-neurasthenic syndrome is suspected, the person will be referred to see a psychotherapist. If circulatory disorders are caused by neurasthenia, the patient may additionally be advised to undergo rheoencephalography.
If fogginess in the head appears constantly, then this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. Therapists, neurologists, and psychotherapists deal with this issue.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must interview the patient and find out what additional symptoms he has, as well as conduct a diagnosis. Here is a list of mandatory tests needed to find out why fuzzy head syndrome occurs:
- General analysis of urine and blood. Exclude the presence of inflammatory reactions and infectious processes.
- Ultrasound of blood vessels in the cervical spine.
- CT or MRI of the spine and brain. An MRI and CT scan will allow you to exclude malignant processes, determine the condition of blood vessels, identify the presence of chronic diseases of the nervous system, etc.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
The patient may also need to consult other specialists.
How to diagnose?
The only and sure way to determine the cause of poor health is to consult a doctor. As a rule, the patient is referred for examinations:
- taking tests;
- X-ray, CT, MRI;
- consultation of specialized specialists.
The prescription of other measures depends on the severity and frequency of symptoms. In most cases, the diagnosed cause of pressure, wooliness and head fog is damage to the cervical vertebrae.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Patients suffering from osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are faced with various manifestations of the disease. These include pain radiating to the arm and occipital region, and severe headaches. But perhaps one of the most traumatic symptoms is dizziness.
Medicine calls common dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis cochleovestibular symptoms. The main cause of dizziness is insufficient cerebral blood supply due to compression of the vertebral artery.
The vertebral artery supplies blood to the cerebellum, hypothalamus, inner ear and brain stem structures. It arises from the subclavian artery and runs in a canal formed by the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Why does dizziness develop? Initially, due to degenerative processes or injuries, the working structure of a segment of the spinal system in the cervical region is disrupted. Fractures, dislocations and subluxations of the joints in the cervical spine are possible, leading to displacement of the vertebrae and changes in the lumen of the canal formed by the openings of the vertebral processes.
Compression of the artery leads to a decrease in blood flow and, as a result, to oxygen starvation of the tissues of the brain. All of the above leads to the manifestation of symptoms of SPA (symptoms of the vertebral artery) - dizziness, severe throbbing headache (sharp, burning, especially intense in the back of the head and temples), visual disturbances (darkening in the eyes, a feeling of sand, spots in front of the eyes, sparks).
Dizziness is observed in varying degrees, from slight swaying, with a slight disturbance of cerebral circulation, to so-called drop attacks, when a person falls when turning his head sharply, while consciousness remains intact. With severe brain disorders, there may be nausea, vomiting, and tinnitus.
At the moment, treatment of vertebral artery syndrome is a difficult task to solve, as evidenced by the many different treatment methods from different clinics and the lack of a single generally accepted treatment regimen. Here are the main directions in the treatment of vertebral artery syndrome:
- Anti-inflammatory and decongestant treatment.
- The use of drugs that normalize blood circulation in the brain. The use of neuroprotectors and metabolic therapy to protect brain nerve cells under conditions of oxygen starvation.
- In case of severe impairment of cerebral circulation, surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is used to eliminate the causes of compression of the vertebral artery.
- Rehabilitation treatment, involving physical therapy, massage, acupuncture.
Severe headaches with cervical osteochondrosis are somewhat alleviated by painkillers, but this symptom can only be completely eliminated by eliminating osteochondrosis.
Prevention
What can be done to prevent disturbances in the stability of the body, a “drunk” state? First of all, identify the trigger, try to avoid it.
- Get up slowly.
- Tell your doctor if you experience any discomfort during blood draws or other medical procedures. He can take certain measures to prevent it.
- Eat regularly and drink enough water.
What to do if you experience frequent headaches?
It is important to find out the seriousness of the cause of this condition. It can warn of heart rhythm disturbances, narrowing of the aortic valve, heart tumors and other diseases. If discomfort is caused by medications that lower blood pressure, this should be discussed with your doctor and the dosage of the medication adjusted. But it is often enough to increase fluid intake, avoid prolonged standing, and exposure to direct sunlight.
Do you always feel a little drunk or drugged? This condition makes it difficult to concentrate, perform usual work, and may be accompanied by recurring headaches. To get rid of discomfort, it is necessary to establish the cause of its occurrence and try to eliminate it.
As stated earlier, the causes of brain fog may not always be due to health problems. Thus, when there are disruptions in the hormonal system, fog in the head is almost always observed. During pregnancy, a woman is often accompanied by this condition, as well as irritability and forgetfulness. The same symptoms may occur during menopause.
How to get rid of brain fog
1. Determine the cause . It's up to you (or your doctor) to do some self-analysis and come up with a list of possible causes. 2. Come up with a solution . If you can identify the specific cause, it will be much easier for you to find a solution. 3. Treat the cause or eliminate the problem . Simple causes such as poor sleep and diet can be easily corrected in the short term, but eliminating brain fog will require constant "maintenance." 4. Keep trying new things . If you've changed your diet and tried exercise but haven't tried something like meditation, you can see if that helps. If natural treatments don't seem to be helping, you can visit a psychiatrist to have your cognitive function tested.