Find out more about other diseases starting with the letter “X”: Huntington’s chorea; Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy; Chronic cerebral ischemia.
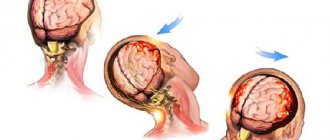
Chronic cerebral ischemia is a failure of the cerebrovascular system that develops against the background of impaired blood circulation in the structures of the brain. Chronic cerebral ischemia is expressed by headaches, dizziness, emotional lability, disorders of cognitive and motor functions.
For diagnostic purposes, CT or MRI of the brain, ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels, and hemostasiogram examination are prescribed. Therapeutic efforts for chronic cerebral ischemia consist of the prescription of antihypertensive drugs, lipid-lowering, antiplatelet measures. In some cases, surgical treatment is provided.
Causes of chronic cerebral ischemia
- The main causes of chronic cerebral ischemia include arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis. Chronic cerebral ischemia caused by a combination of two conditions is common. In addition, among other reasons causing this disease, there will be symptoms of cardiovascular diseases, which are expressed in heart rhythm disturbances (for example, arrhythmia), which, in turn, leads to a decrease in systemic hemodynamics.
- Doctors attach great importance to the study of vascular anomalies, both in the brain and in the vessels of the cervical spine. Such anomalies, like those associated with the aorta or vessels of the shoulder girdle, often do not manifest themselves for a long time, until the development of atherosclerotic and hypertensive processes.
- In recent years, neurologists have identified a number of other reasons that contribute to the development of chronic cerebral ischemia, including venous pathology of an intracranial and extracranial nature. It is possible that the occurrence of chronic ischemia is influenced by compression of arterial and venous vessels. Doctors take into account both the spondylogenic effect and possible compression of blood vessels by muscles, an aneurysm or a tumor. Another possible cause of this pathology is developing cerebral amyloidosis.
Typically, identified encephalopathy manifests itself symptomatically mixed. If factors have been discovered that caused the development of chronic cerebral ischemia, then all other possible causes are considered additional causes. Of course, identifying and accurately identifying additional factors that aggravate the course of the disease will be very necessary, first of all, in order to make the right decision regarding symptomatic or etiopathogenetic treatment.
In medicine in recent years, the occurrence of chronic cerebral ischemia is usually considered in two ways: according to the nature and nature of the damage and according to the usual localization. In the case of bilateral diffuse damage to the brain, more precisely, its white matter, they speak of a leukoencephalopathic type of encephalopathy. The second option is the lacunar type, which has a large number of lacunar foci. If such two options are most often found in theory, then in practice they speak of their mixed type.
Most often, the lacunar variant is caused by a process such as occlusion of small vessels. A significant role in the pathogenesis of diffuse damage is assigned to a decrease in systemic hemodynamics or, as it is also called, arterial hypotension. The reason for the decrease in blood pressure will be improperly administered antihypertensive therapy, as well as a decrease in cardiac output. A significant role is played by severe cough and orthostatic hypotension, which often happens in the case of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
As is known, the main pathogenetic link of this disease is the depletion of the compensation mechanism, as well as a decrease in the energy work of the brain, which leads to the obvious development of functional disorders and such irreversible processes of a morphological nature as a slowdown in blood flow, a decrease in blood glucose levels, a decrease in oxygen levels, and the occurrence of capillary stasis, the appearance of slow cerebral blood flow, thrombus formation, the ability to depolarize cell membranes.
What are the degrees of development?
The disease is dangerous because of its imperceptible onset, which can develop over years, turning into a chronic specific form of cerebrovascular pathological picture.
Processes that cause destruction to the neurons of brain tissue progress. In turn, this leads to a reduction in the flow of blood in the arteries to the parts of the brain.
Prolonged vasoconstriction leads to focal lesions and contributes to the development of microinfarctions.
There are three degrees of the disease:
- 1st degree. Initial, accompanied by headaches, some memory loss, confusion of life events and dates, sleep disturbances, weakness, rapid fatigue, emotional instability;
- 2nd degree. It is characterized by increasing symptoms that noticeably change the personal qualities of the patient, including apathy, depression, and a decrease in former desires and interests; neurological syndromes gradually come to the fore;
- 3rd degree. Neurological disorders are clearly expressed, multiple cortical infarctions develop with the subsequent formation of vascular dementia.
Symptoms of chronic cerebral ischemia
The main symptomatic manifestations of chronic cerebral ischemia include:
- movement disorders of polymorphic type;
- decreased memory and mental abilities;
- changes in the patient's emotional background.
A feature of chronic cerebral ischemia is its progressive course. In addition, the disease is characterized by the presence of stages and syndromes. Doctors note the so-called inverse relationship between present complaints (especially those related to concentration and the ability to remember) and the degree of manifestation of this disease. The more the patient's cognitive functions are weakened, the fewer complaints he will have. As practice shows, the patient’s subjective complaints do not indicate the severity or nature of the disease process.
The main clinical manifestation of dyscirculatory encephalopathy today is considered to be cognitive impairment, which can be detected even at the first stage. Their nature, as a rule, is progressive, which is noticeable already at the third stage of the disease. In parallel with emotional disorders (such as emotional lability, inertia and all kinds of loss of interest), a variety of motor disorders can occur, including the inability to control and perform both simple reflex and complex automated movements).
Mechanism of formation and pathogenesis
The basis of the disease is the weakening of normal nutrition of cerebral structures.
There are several options, but in all known cases there is a slowdown in the movement of liquid connective tissue through the vessels as a result of a mechanical obstruction.
And what was its cause: stenosis (narrowing) of the lumen, blockage with a cholesterol plaque, thrombus, malformation, aneurysm, other anomalies of anatomical development - needs to be clarified.
Without receiving nutrients and oxygen, tissues begin to die. Death or necrosis, however, does not reach a certain critical mass, at which the process becomes an avalanche-like, uncontrollable character - such an emergency condition is called a stroke.
Discirculatory encephalopathy, another name for chronic ischemia (abbreviated as CICI), is considered a precursor to acute necrosis of cerebral tissue.
Recovery is very difficult, but it is necessary to achieve lasting correction. The patient's life is at stake. Requires hospitalization in a neurological hospital.
First stage
At the first stage, there is a combination of classical complaints with a diffuse type of neurological symptoms, which manifests itself as anisoreflexia and a mild type of reflexes. It is also possible that the gait may change (walking may become slow, the patient often moves in small steps). The first stage is characterized by decreased coordination stability and uncertainty when performing movements.
Very often, doctors note emotional disturbances in patients in the form of irritability and anxiety, and depression is often observed. At this stage, minor cognitive deviations of the neurodynamic type occur, which implies exhaustion of the nervous system, decreased attention, and inertia of the intellect. However, in general, patients perform well on memory tests and on routine tasks, but only on tasks that do not require timed performance. Life activity and working abilities at the first stage are not limited for the patient.
Second stage
It is characterized by worsening neurological symptoms, which are characterized by the formation of an invisible syndrome, however, one that subsequently dominates. In addition, various kinds of extrapyramidal disorders can be detected, as well as ataxia, pseudobulbar syndrome, and even CN dysfunction. It is interesting that over time the complaints become less and less pronounced; they are no longer so acutely perceived by the patient himself. However, at this time the emotional background worsens and intensifies. There is an increase in cognitive function, up to the onset of neurodynamic disorders, which can later be supplemented by dysregulatory syndrome.
In addition, at the second stage, the patient’s ability to control his own actions deteriorates, and there are also difficulties in planning what the person wants to do at the next point in time. Although there is a violation in the performance of actions, the ability to compensate remains for a long time. In addition, signs of reduced social adaptation appear.
Third stage
It is distinguished by a clear manifestation of neurological syndromes. In this case, there is a disturbance in walking and the ability to maintain balance (the patient may often fall). Urinary incontinence is observed, and parkinsonian syndrome is also characteristic. Due to the absence or decrease in a sober understanding of what is happening to the patient, the volume of his complaints decreases.
Personality disorders can manifest themselves as inhibited reactions, explosive states, apathetic-abulic symptoms and psychological abnormalities. In addition to neurodynamic (or dysregulatory) disruptions in the cognitive sphere, the manifestation of such operational disorders as speech and memory impairment, decreased thinking ability, etc. is possible. All these symptoms can later develop into dementia. The latter leads to an inability to quickly adapt to a new situation and to a drop in performance in personal, social and professional areas of life. Very often, doctors indicate a person’s inability to work. At a certain point, the patient stops caring for himself.
Cerebral ischemia in newborns
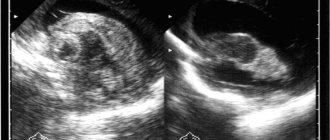
In newborns, cerebral ischemia manifests itself as a result of cerebral hypoxia, that is, insufficient oxygen supply to the baby’s brain during gestation or during childbirth.
Based on the symptoms and results of ultrasound examination of the brain, it is customary to distinguish three degrees of cerebral ischemia. With a mild degree of cerebral ischemia, excessive excitation or depression may occur in the first week of life. With moderate severity of the disease, such disorders last longer, and convulsions may occur periodically. Children with severe cerebral ischemia must be urgently admitted to the intensive care unit. With a mild degree of ischemia, the prognosis is favorable: as a rule, the child recovers completely after a few weeks. For more severe forms of the disease, treatment measures should be determined by a doctor.
Instrumental studies
In order to determine the degree of damage to the blood vessels of the brain, as well as its substance, and to detect any other underlying diseases, doctors recommend undergoing such instrumental studies as:
- ECG;
- echocardiography;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- Doppler ultrasound (primarily, this study is performed for the main arteries of the head);
- cervical spondylography;
- triplex (or duplex) scanning of vessels of intracranial and extracranial types;
- vascular angiography (to detect vascular anomalies).
All patient complaints usually characteristic of the chronic type of cerebral ischemia can also be detected in various somatic pathologies and in some cases in oncology. The symptoms inherent in chronic cerebral ischemia can also be signs of various mental disorders and endogenous disorders. Therefore, differential diagnosis is necessary. But it will be problematic because chronic cerebral ischemia is often confused with neurodegenerative diseases, which share the same cognitive impairments and neurological manifestations.
Diseases with which chronic cerebral ischemia should be differentiated are:
- progressive supranuclear palsy;
- Parkinson's disease;
- corticobasal degeneration;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- multiple system atrophy.
Very often it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of this disease with malignant and benign brain tumors, idiopathic dysplasia, normal pressure hydrocephalus and ataxia.
List of sources
- Gusev E.I. Skvortsova V.I. Cerebral ischemia. M.: Medicine, 2001;
- Suslina Z.A., Varyakin Yu.Ya., Vereshchagin N.V. Vascular diseases of the brain: Epidemiology. Basics of prevention. M.: MEDpress-inform, 2006;
- E.I. Gusev, V.I. Skvortsova “Cerebral Ischemia” - M. Medicine, 2001;
- Stepanchenko A.V., Petukhova N.A., Trushchelev S.A. Dizziness: a guide for doctors. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2006;
- Aronov D.M., Lupanov V.P.. Atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Ed. second, revised. - Moscow, Triada-X, 2009;
- Yakhno N.N., Shtulman D.R. Diseases of the nervous system. M.: Medicine, 2003.
Treatment of chronic cerebral ischemia
The main goal in the treatment of chronic cerebral ischemia is to stabilize the destructive process of cerebral ischemia in order to restore blood circulation in the vessels. Proper treatment will help slow down the rate of disease progression by activating the sanogenetic mechanism of function compensation. Therapy also involves the prevention of this disease and its attendants.
Pathology is not an indication for urgent hospitalization of the patient. Treatment in a hospital is necessary when the course of the disease is complicated by the development of a stroke condition or severe pathology. If a cognitive type of disorder is detected, if the patient is deprived of his usual environment, the condition may worsen.
Treatment of chronic ischemia is usually carried out by a neurologist on an outpatient basis. If the disease develops to stage 3, doctors prescribe patronage.
Cardiac ischemia
Coronary heart disease is a chronic disease that occurs as a result of insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. Cardiac ischemia occurs when the need of the heart muscle for oxygen does not correspond to the amount of oxygen delivered through the coronary arteries.
The occurrence of coronary heart disease is directly related to atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries , arterial spasm , which is sometimes provoked by certain medications and biologically active substances. Also, cardiac ischemia can occur due to increased blood viscosity and the formation of blood clots in the coronary arteries.
But still, the main cause of cardiac ischemia is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. The narrowing of blood vessels occurs due to the formation of plaques on their inner walls.
Mostly, coronary heart disease occurs in males of working age. Clinically, cardiac ischemia can manifest itself in different ways. Most often, this disease is characterized by the occurrence of angina pectoris . In this case, the patient may feel pain in the chest area. Painful sensations mainly occur during times of severe stress , or as a result of physical activity and are of a compressive nature. As cardiac ischemia develops, such attacks become more frequent over time. After all, when under load, the heart requires more oxygen to flow to it. myocardial ischemia may occur , manifested by compressive pain behind the sternum. Cardiac arrhythmia may also occur. Such attacks subside after taking Nitroglycerin . If the attack lasts about half an hour, then it is considered critical, because after some time some of the cells in the myocardium die, and, as a result, a person may develop a serious complication - myocardial infarction . Another form of cardiac ischemia is post-infarction cardiosclerosis . It is a consequence of a previous heart attack.
A complication of coronary heart disease can be heart failure. In this condition, the heart cannot function normally.
The diagnosis of “coronary heart disease” can be made using ECG data, as well as studies using radionuclide methods of studying the heart, echocardiography, daily ECG monitoring, etc. The coronary angiography method is used to detect atherosclerotic plaques.
Treatment of cardiac ischemia is always primarily aimed at normalizing blood flow through the coronary arteries. It is important to prevent all obstacles that interfere with the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle.
Therefore, it is important to properly treat atherosclerosis, prevent the formation of blood clots, restore adequate blood supply to the heart muscle, and correct metabolic processes in the body.
To do this, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors that influence the deterioration of the condition. First of all, you need to fight obesity , lead an active lifestyle, follow a diet , giving up unhealthy foods.
As a rule, the doctor prescribes complex treatment, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the course of the disease. When treating cardiac ischemia, medications are used that reduce the need for myocardial oxygen, drugs that prevent platelet aggregation, heparin , thrombolytics and other drugs.
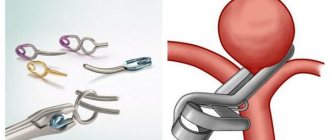
Currently, surgical methods for the treatment of cardiac ischemia are used more and more often. Surgery is especially strongly recommended for patients with severe attacks of angina. The most noticeable effect is brought by surgical interventions aimed at restoring normal blood flow in the coronary artery. Among such operations are the creation of mammary-coronary anastomosis and coronary artery bypass grafting. An angioplasty technique is also used: a catheter with an inflatable balloon is inserted into the coronary artery, allowing the vessel to later expand.
Doctors also prescribe surgery for cardiac aneurysm that develops as a consequence of myocardial infarction. This surgery can prevent heart failure in the future. Sometimes during surgery, thrombotic masses in the aneurysm cavity are removed. All surgical interventions for cardiac ischemia are performed only in special clinics, and artificial circulation is used.
The most favorable prognosis for the treatment of this disease is provided that there are rare attacks of angina pectoris. If the patient has a recurrent heart attack and heart failure, the prognosis is less favorable.
As prevention methods, it is important to eliminate all factors that contribute to the development of coronary heart disease. You should follow a special diet that limits the consumption of foods high in animal fats, too sweet and salty foods. A very important step is to completely quit smoking. Regular exercise is recommended, and if the patient has arterial hypertension or diabetes mellitus , then these diseases must be treated correctly and on time. Patients with cardiac ischemia should be regularly monitored by their physician.
Antihypertensive therapy
Antihypertensive therapy is aimed at maintaining normal blood pressure and stabilizing the state of chronic ischemia. If doctors prescribe antihypertensive drugs, the patient should be careful and monitor for fluctuations in their blood pressure. As is known, in the case of developing chronic ischemia, the mechanism of autoregulation of cerebral blood flow begins to work intermittently.
If we talk directly about antihypertensive drugs prescribed by doctors, then first of all we are talking about medications of two groups:
- angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors;
- angiotensin II receptor antagonists.
Drugs of both the first and second groups are capable of simultaneously exerting two effects: in addition to angiohypertensive, they are also angioprotective, which means protecting the affected organs, which usually include the kidneys, heart and brain. The effect of antihypertensive drugs usually increases significantly when they are combined with antihypertensive drugs such as hydrochlorothiazide and indapamide.
Combination drugs
In addition to the main therapy described above, depending on the mechanism that caused the disease, individual treatment is prescribed, which is designed to normalize the rheological properties of the blood and improve venous blood flow, bringing microcirculation back to normal. Typically, such drugs have neurotrophic and angioprotective properties. For example, a doctor may prescribe one of the following combinations:
- cinnarizine (no more than 75 mg) together with piracetam (1-1.2 g per day);
- piracetam (no more than 1.2 g) with vinpocetine (15 mg per day);
- nicergoline (no more than 30 mg per day) and pentoxifylline (approximately 300 mg per day).
Typically, such combinations of drugs are prescribed no more than twice a year, each course lasting approximately 2 months.
Diet, nutrition for ischemia
Diet for cleansing blood vessels for diseases of the cardiovascular system
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 3 months
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
Diet for coronary heart disease
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 30 days
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
Diet for stroke
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 1 month
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1700-1900 rubles per week
Prognosis and prevention
With timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment, it is most often possible to stop the progressive course of chronic cerebral ischemia. If the disease is quite severe, being aggravated by parallel pathologies (for example, diabetes mellitus or hypertension), there may be a noticeable decrease in the usual ability to work, and sometimes even to the point of complete disability of the patient.
Among the preventive measures that can prevent this disease are the following:
- prevention of obesity in general, and in particular, obesity of cerebral vessels;
- active lifestyle;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- avoidance of stressful situations.
An important preventive measure will be the prevention of hypertension and diabetes. Not everyone knows that atherosclerosis can also contribute to the development of chronic cerebral ischemia, so it must be dealt with in the early stages.
As soon as a person discovers the first symptoms of chronic cerebral ischemia, one should immediately reduce the amount of alcohol consumed (or better yet, give it up altogether), reduce physical activity and avoid direct sunlight.
Causes
The main factor in the development of chronic cerebral ischemia is atherosclerosis. That is, narrowing or blockage of blood vessels in the neck and brain with cholesterol plaques and blood clots.
It develops mainly in smokers, people with metabolic disorders, and bedridden patients.
Another factor is hypertension. Persistent increase in blood pressure.
Possible tumors, hydrocephalus with excessive exposure of cerebrospinal fluid to cerebral tissue, viral and infectious diseases (meningitis, encephalitis) and their consequences, cardiac pathologies with a decrease in the pumping function of the heart, abnormalities in the development of the brain and arteries, congenital and acquired (more often).
Attention:
Assessment of etiology and origin plays a paramount role. Without determining the cause, there is no point in treatment. At best, it will be possible to eliminate the symptoms, but no more. Progression will inexorably go forward and end in the death of a person or severe disability.