How is SCT research carried out?
The x-ray technician positions the patient in a special way, depending on the examination being performed. Next, the gantry (the device on which the tube and receiving sensors are installed) begins to rotate around the scanned area and makes slices of the area under study with certain parameters of power and tube passage step. When scanning the chest and abdominal organs, you will need to hold your breath several times, which the x-ray technician will warn you about. The scanning procedure lasts 2-4 minutes.
What is the essence of the procedure
Spiral computed tomography is a relatively new method. It is based on the procedure of scanning the body of the applicant using X-rays. The X-ray tube and the table with the person on it rotate simultaneously. In this way, it is possible to obtain the required information, which is subsequently transmitted to the monitor and converted into electrical impulses.
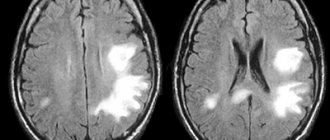
An X-ray emitting source moving in a spiral makes it possible to obtain detailed sections of the problem area in longitudinal and cross sections. The technique is very accurate; it is possible to recognize pathology at the initial stages of development and detect even microscopic-sized (up to 0.1 cm) formations.
The study shows the contours, volume, density, and SCT of the PPN of the area of interest.
What can SKT do?
Computed tomography is simply irreplaceable in diagnosing the conditions of any bone structures, the condition of the lungs, and mediastinum in humans. SCT is also widely used in the study of abdominal organs (liver, spleen, gallbladder, pancreas), adrenal glands, kidneys, and pelvic organs. With the help of CT, it became possible to accurately detect any stones (for example, in the gall bladder, kidneys) and calcifications (for example, those changes that accompany tuberculosis, sclerosis).
Spiral computed tomography is leading in the diagnosis of complex bone injuries , multiple injuries (for example, road accidents) of bones and internal organs, in the diagnosis of complex or multiple injuries of the skull and acute injuries and hemorrhages of the brain.
SCT is also widely used by ENT doctors for a detailed assessment of the condition of the paranasal sinuses, auditory canals and temporal bones, since no other diagnostic method can compare with the accuracy and “depth” of computed tomography.
In studies of the spine using SCT, it is possible to determine the smallest damage in the bone structure, pathological calcifications in the ligamentous apparatus; to diagnose the condition of the intervertebral discs, it is best to use MRI.
The advisability of prescribing SCT in each individual case should be determined by the attending physician, who will subsequently interpret the results obtained from CT taking into account the entire picture and characteristics of the patient.
Indications for KaTe
Tomography is performed in a variety of cases. It is prescribed for initial and repeated examinations, including to confirm an unspecified diagnosis. Most often, CT is performed in the presence of such diseases and injuries:
- osteoporosis;
- pneumonia;
- asthma;
- chronic bronchitis;
- various bone injuries, including the spine;
- scoliosis;
- adenoma;
- aneurysm;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- urolithiasis disease;
- tuberculosis;
- oncological pathologies;
- neoplasms found in the thyroid gland.
In emergency cases, CT is performed for severe injuries, suspected cerebral hemorrhage, damage to large vessels, parenchyma.
What does SKT “dislike”?
First of all, these are movements . Any movements during scanning of the study area distort the resulting images, of course, reducing their information content for the doctor. If in a series of images obtained, even just 1-2 scans are distorted by motion artifacts, then subsequent 3D reconstructions will already have defects and their information content for the doctor, of course, will be reduced.
Secondly, metal. Metal is to X-rays what a mountain is to the sun—it leaves a “shadow.” A large amount of metal in the examination area can significantly distort the resulting images. But if the metal is located in any place other than the area being examined, it cannot in any way affect the quality of the scans.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- speed of research;
- a high resolution;
- reduction of artifacts in images;
- the ability to obtain a three-dimensional image of an entire organ at once;
- ideal for studying blood vessels and the heart;
- increased area of anatomical coverage.
The disadvantages of the study are related to limitations and contraindications, as well as cost and relative inaccessibility, since not all medical institutions have the appropriate expensive equipment in their arsenal.
What do you need to have with you for SCT?
Before the study, you must give your existing medical documentation to the x-ray technician or radiologist (a referral from the attending physician, which indicates the preliminary diagnosis, study area, clinical task, specific comments), data from previous studies (which directly relate to the reason for prescribing SCT to you) and other medical documentation, after analyzing which the radiologist will be able to formulate the most accurate diagnostic conclusion on SCT, taking into account the data of your medical. cards and recommendations of the attending physician. If you do not provide medical documentation in full, then the radiologist will evaluate only the directly obtained SCT scans, without taking into account previous injuries and diseases, any possible consequences that they could entail, and without taking into account possible concomitant pathologies.
Remember, there is no absolute and universal method of medical diagnosis: MRI will never replace SCT, SCT will never replace ultrasound, ultrasound will never replace radiography. All these methods complement each other and sometimes, data from previous studies have the decisive word in the correct interpretation of the resulting picture by a radiologist during computed tomography.
Make an appointment
Make an appointment by calling:
+38 (044) 393 0933
+38 (067) 230 2432
+38 (050) 332 3339
What are the pros and cons of SCT
SCT analysis has both advantages and disadvantages. All of them are listed in the table.
| pros | Minuses |
| • a high resolution; • speed of the procedure; • high throughput; • there are no restrictions on the severity of the condition. | • diagnostics are unsafe and involve receiving a certain dose of radiation; • use of contrast agents to which you may be allergic; • functional studies are limited; • low availability (not all healthcare institutions can afford such a device). |
Who deciphers the results and when they can be obtained.
The resulting SCT images must be examined by a radiologist (a doctor who specializes in CT, MRI, X-ray studies and has the appropriate certificate). It is necessary to “read” all the scans, study the provided medical information. documentation, compare it with the obtained CT image, describe the study, draw a diagnostic conclusion, shoot film with scans. On average it takes about 1-3 hours. At ACMD, we undertake to prepare the results for delivery by the end of the Clinic’s working day.
After the examination, you receive films with scans and a diagnostic report, which will be signed by a radiologist. Also, the diagnostic report may contain recommendations regarding your further actions (which doctor to contact with these results, what types of further examination are recommended, and so on).
How does a tomograph work?
CT scan
The main part of any modern tomograph is the gantry - a ring inside which the beam tube rotates rapidly, opposite which the sensors are located.
The patient lies down on a moving table that moves inside this ring. The movement of the table and the X-ray tube are synchronized so that the resulting information is read in a spiral that goes around the patient's body in the area of the section to be examined from all sides. Such a study is also called multislice computed tomography
(MSCT). The prefix “multi” means that in modern tomographs the sensors are not installed in one row (there can be many such rows). This allows not only to obtain more information per revolution of the radiation tube (which increases the speed of examination and reduces radiation exposure), but also to track the work of dynamic organs and structures (heart, chest, joints in motion).
Consultations and questions regarding your SCT study.
A radiologist is not a clinician (a doctor who treats you) and, as such, cannot provide any advice or recommendations regarding your treatment or diagnostic procedures.
To make objective comments on an SCT study, it is necessary to fully know the patient’s objective data, the picture of his previous studies, the characteristics of his current condition, anamnestic data, and much more.
You can ask all your questions to your attending physician or physician, whose consultation will be recommended to you by a radiologist.
If you still have any specific questions about computed tomography, you can ask them in the specialized MRI and SCT diagnostics section on our Forum.
Check out comprehensive body check packages with up to 30% discount
How is computed tomography performed?
The question of how a computed tomography is done is of concern to everyone who is scheduled for diagnostics carried out at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
A special feature of tomography is that the patient is always in a lying position on the tomograph table, and the layer-by-layer examination of the organ occurs due to the circular movement of the beam tube, due to which X-rays are reflected multiple times, which is recorded by special detectors.
As a rule, the duration of a computed tomography procedure does not exceed 15-30 minutes (depending on the specific diagnostic tasks).
In some cases, to increase efficiency, additional contrast is used (for example, with CT of vessels, it may be necessary to additionally administer a small amount of contrast agent intravenously - usually 100 ml; if indicated, the contrast can be injected into the rectum).
In this case, the duration of the procedure increases, because it is carried out both before and after the administration of contrast. As with an x-ray examination, it is necessary to free the area of the body being examined from clothing. The whole body computer scanning procedure itself is completely painless and well tolerated by patients.
The main inconvenience of the method is the need to maintain maximum immobility during the procedure.
The patient is alone in the office, and the examination is monitored by the doctor via audio communication. At the right moments, the patient is instructed to briefly hold his breath.
A computed tomography scan is usually performed by a radiologist, who also gives a conclusion based on the results of the study. The resulting image is transferred to x-ray film as a series of images.
The time it takes diagnosticians from the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences to evaluate the examination results and prepare a conclusion is 1 hour for a standard examination and 1.5 hours for an examination with contrast. You will be given a final conclusion, and, if necessary, our doctors will advise you on which specialists you should contact. The full set of acquired images can be recorded on a CD or DVD and also given out.
Contrast techniques for SCT.
When examining the abdominal organs, the patient will be asked to drink 500–1000 ml. drinking water with a contrast agent dissolved in it in order to “separate” the stomach and intestines from nearby organs and tissues, as well as to ensure that intestinal loops do not create additional “interference” for the radiologist during the study. This is the so-called oral contrast.
The same technique of intravenous administration of a contrast agent is very often used in order to “highlight” areas with pathological changes, to study the blood flow of tumor formations, or specifically to study blood vessels.
CT with contrast
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography improves the accuracy of the examination. This type of procedure involves the introduction of a radiocontrast substance into the patient’s body, which will enhance the difference in tissue absorption of rays. In the diagnostic department of the Central Clinical Hospital, paid contrast-enhanced computed tomography services are prescribed in the following cases:
- The need to examine the intestines - in this case, the contrast will allow you to visually separate the intestinal loops from adjacent organs;
- Diagnosis of the condition of the bronchopulmonary system;
- Tomographic analysis of the liver with contrast will increase the accuracy of detecting cysts and other neoplasms;
- The method is well suited for examining veins and blood vessels.
Is the SCT procedure painful and is it harmful? What are the contraindications? Where to get a CT scan in Kyiv?
The SCT examination is absolutely painless; the scanner itself does not directly touch your body.
The method is based on X-ray radiation. Naturally, during an SCT study, the patient is exposed to x-rays, therefore, when prescribing this study, the doctor must have fairly compelling reasons and take into account the negative impact of x-rays on the body.
An absolute contraindication for SCT is pregnancy and breastfeeding. Also, SCT is strongly not recommended for children without significant reasons. In other cases, you should consult your doctor.
a computed tomography (CT) scan in Kiev at the ACMD clinic, a 64-slice tomograph (the radiation level is reduced significantly!)
Contraindications
When planning to do a CT scan in Moscow at the clinic of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, you must remember that computed tomography of the entire body or individual internal organs has not only indications, but also contraindications. In particular, computed tomography (both with and without contrast) may be refused in the following cases:
- Body weight more than 150 kg;
- The presence of a metal structure and/or a plaster cast in the area of the organ being examined;
- Pregnancy;
- Childhood;
- The presence of disorders of the central or peripheral nervous system, mental disorders and other pathologies that may affect the patient’s behavior during diagnosis;
- Allergic reactions to iodine (if it is necessary to undergo examination with contrast);
- Also, CT diagnostics is not performed in patients with renal failure.
They've been through it
I recently had an SCT of the brain done in one of the clinics in St. Petersburg, everything went quite quickly, under the supervision of specialists and generally at a high level, the price is acceptable, especially when you realize the importance of this study.
Marina, July 2021
Lately I have been tormented by constant headaches and often had high blood pressure. My doctor advised me to do an MSCT of the brain, thanks to which he was able to see the problems that had arisen and prescribe an effective comprehensive treatment.
I am absolutely satisfied with the examination, I am very glad that I carried it out in a timely manner and eliminated the ailments at their early stages of development.
Mikhail, Nizhny Novgorod, September 2016
Principle of operation
The basis of CT is the ability of tissues to absorb X-rays differently, and the image is obtained from certain sections. Detailed information can be obtained using a sensitive matrix and special sensors inside the device, as well as automatic saving and conversion of data into digital format.
Tomographs of the twenty-first century consist of electronic and mechanical components. X-rays passing through the internal structures of the body are recorded using high-sensitivity detectors. The latter are constantly being modernized, each manufacturer of medical equipment offers its own developments.
The key to the effective functioning of the device is software that allows you to:
- perform research with the required parameters;
- process and transform information;
- analyze the received data.