CT scan of the brain is an informative and common research method. With its help, various pathological conditions are diagnosed. Accessibility, painlessness, accuracy of the study and quick results are the undoubted advantages of computed tomography. Using CT, a three-dimensional image of the brain is obtained with the ability to study the organ layer by layer. Contrast enhancement increases the diagnostic information content of the method.
Yusupov Hospital conducts all types of computed tomography of the brain. The clinic is equipped with modern equipment that allows diagnostics to be carried out in the shortest possible time.
The essence of the method
Computed tomography of the brain is a research method based on the use of x-rays. Using a series of images, a three-dimensional image of the brain is created. Various pathological conditions are diagnosed in this way. The advantage of CT is the ability to study the organ layer by layer. Tomography is used in various fields of medicine. The method has a small number of contraindications, which allows it to be used for various conditions. To determine damage to the blood vessels of the brain, a computed tomography scan is performed using a contrast agent. This type of study allows you to most accurately determine the affected area.
What does an encephalogram of the brain show?
Electroencephalography in many cases helps to identify the cause of such pathological conditions as:
- headache;
- panic attacks;
- fainting;
- dysfunction of different parts of the brain.
Electroencephalography is informative in the study of epileptic brain activity and allows one to identify foci of epileptic activity.
When prescribing a treatment complex, its effectiveness can be assessed using electroencephalography. Electroencephalography is very important when monitoring patients after neurosurgery: with the help of EEG, not only the effectiveness of surgical treatment is assessed, but also success in the patient’s rehabilitation, and possible complications after surgery.
An encephalogram can be an informative method if the patient continues to exhibit symptoms of central nervous system damage, and other diagnostic methods do not reveal structural defects of the brain. Using electroencephalography, doctors can differentiate the nature of seizures: the picture with a psychiatric diagnosis on the encephalogram looks completely different than with neurogenic disorders.
For patients in a coma or vegetative state, electroencephalography is performed to monitor brain functions and their possible decline. Encephalography confirms or denies brain death.
Advantages
Computed tomography has some advantages over other methods of studying the brain. The main ones include:
- Painless. Some discomfort may occur only after the administration of a contrast agent. This must be reported to your doctor.
- Accuracy. A layer-by-layer study of the brain allows us to detect initial changes in its structure. Contrast enhancement increases the information content of the method.
- Speed of research. The procedure takes on average one hour. Within an hour after diagnosis, the results are delivered to your hands.
- Possible for people suffering from claustrophobia.
How to prepare for encephalography
In order for electroencephalography to be as informative as possible, the patient must properly prepare for the study. In 2-3 days you need:
- give up drinks and foods that stimulate the nervous system: alcohol, coffee, tea, energy drinks, chocolate;
- stop taking (after consulting a doctor) medications: anticonvulsants, sedatives, tranquilizers, so that the medications do not distort the results of electroencephalography.
Before electroencephalography of the brain, it is necessary to wash your hair and not use styling products to ensure close contact of the electroencephalograph sensors with the scalp.
On the day that the electroencephalography is performed, the patient should eat a full breakfast to avoid an increase in blood glucose levels. Smoking is prohibited on the day of the procedure. When visiting a doctor for encephalography, it is better to give preference to loose clothing that does not restrict movement.
In order not to distort the results of the encephalogram, the patient should remove all metal jewelry.
What does a CT scan show?
Computed tomography of the brain is prescribed for various conditions. Depending on the reason for the study, diagnostics are performed with or without a contrast agent. This diagnostic method is prescribed to identify the following conditions:
- bleeding;
- strokes and hemorrhages;
- neoplasms in the head and neck area;
- fractures of the base of the skull;
- hematomas and injuries;
- inflammatory process;
- pathologies of tissue development;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the area being examined.
Specialized methods
The following examination methods exist:
- Doppler ultrasound provides information about blood circulation in important vessels of the neck and brain. In this way, abnormalities of the vascular system are detected in the early stages. The effectiveness of the treatment is analyzed. Meanwhile, the day before you need to stop smoking and drinking caffeine. The above can affect vascular tone.
- Electroencephalography allows you to analyze the functional state of the brain and its irritability. In this case, even minor fluctuations are recorded. The information obtained is transferred to a special paper tape or converted into an image on a computer screen. This method makes it possible to diagnose and treat epilepsy, delayed mental and speech development, and detect the consequences of traumatic brain injuries.
- Echoencephalography diagnoses tumors and disorders of the brain structure, including after injuries. The device works by capturing a kind of echo, which is returned when ultrasonic waves are sent to the brain. The image is displayed on the screen.
- Rheoencephalography uses a weak high-frequency electric current to record fluctuations in the electrical resistance of tissues. This determines the condition of the vessels, their elasticity, blood filling and tone. The functioning of the arterial and venous systems of the brain is also established. Atherosclerosis, intracranial hypertension, subdural hematomas, and vascular dystonia are diagnosed. The effect of therapy for the listed diseases is assessed. The study is carried out using a rheograph apparatus with electrodes connected to it.
- Electroneuromyography. Using this method, brain biocurrents are recorded. The data obtained make it possible to diagnose dysfunctions of the peripheral nervous system and neuromuscular diseases. The procedure does not require lengthy and extensive preparation, and does not take much time, which makes it convenient and comfortable for those being examined.
- Neurosonography allows you to study the condition of babies from birth to 12 months. Ultrasound is used, so the procedure is safe. The equipment is highly accurate, as a result of which diseases are detected at the earliest stages, right up to the overgrowth of a large fontanel in the skull.
- Craniography. The examination is carried out using x-rays. Projections of the skull are made in profile and full face. This is how congenital or acquired bone abnormalities are detected. The value of craniography lies in the ability to quickly assess the presence of large fractures of the bones of the brain and facial skull. Craniography can be performed if there is a suspicion of a tumor of bone structures, brain structures, neuritis of the facial nerve, or if osteomyelitis is suspected.
CT scan
Diagnosis is carried out by calculating the intensity of penetration of X-rays through brain tissue. A detailed image is displayed in cross section. The accuracy of the result is guaranteed even at low levels of radiation.
The examination is used if the patient suffers:
- pain in the head and neck area;
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- speech and memory disorders;
- suffered a stroke;
- visual and auditory impairments.
The examination method under consideration is not applicable to pregnant women and children. If it is necessary to administer intravenously a contrast agent, the following contraindications are added:
- liver and kidney failure;
- heart defects;
- asthma;
- thyroid diseases;
- allergy to iodine;
- diabetes.
Before an examination using a contrast procedure, it is forbidden to consume food or liquid for 4 hours. Other cases do not require special preparation of patients. During the procedure, a person is moved on a moving table into a tomograph, where it is forbidden to move. At certain moments you will need to hold your breath.
In the absence of contraindications, the examination can be carried out as long as necessary to accurately establish the pathology.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is very popular today. Thanks to the action of a magnetic field constantly maintained in the device, the condition of the skull is visualized. Hydrogen atoms present in the cells of the human body repulse the effects of electromagnetic waves. The data obtained is converted into images of brain tissue.
Diagnostics is effective for a wide range of pathologies: from diseases of the vascular system to tumors.
Contraindications to the examination include:
- mental disorders of the patient;
- acute pain syndrome or coma;
- metal and ferromagnetic pins, clips on blood vessels, implants in the patient’s body, permanent crowns on teeth;
- tattoos made with paint containing metallic particles.
The principle of operation is the same as that of computed tomography. The patient lies down on a moving table, the body is secured with straps, and sensory sensors are attached to the head. This is how the signal is sent and read. The table is sent to the tomograph. Duration - up to 40 minutes. The duration depends on the number of programs involved. The patient is required to lie still. The procedure is safe for children and adults.
Magnetic resonance angiography
The examinations are carried out according to the same rules as MRI. This is how pathologies of the vascular system are identified. The data is converted into a three-dimensional image of all brain vessels. The examination also allows the projection of thin sections of individual vessels and nerve trunks.
Positron emission tomography
This method examines the brain to record all ongoing functional processes. With its help, it is possible to distinguish a benign neoplasm from a malignant one in the early stages. The examination allows you to obtain information about abnormalities in the functioning of the brain, the consequences of injuries and bruises, and determine the condition of the organ after a stroke.
Patients are prohibited from eating 4-6 hours before. It is recommended to exclude foods containing protein the day before. The procedure involves intravenous administration of a radiopharmaceutical. The scan lasts 30-75 minutes.
Indications
A CT scan of the brain is possible with or without a contrast agent. Computed tomography without contrast is indicated for the following conditions:
- Head injuries. This group of indications includes bruises, concussions, and damage to the bones of the skull.
- Dental examination. The dentist may prescribe a computed tomography scan to determine developmental disorders of the maxillofacial area. In addition, research is necessary before implantation.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident. If acute cerebrovascular accident is suspected, a CT scan of the brain is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Diseases accompanied by loss of consciousness. Syncope, accompanied by convulsive syndrome, requires a computed tomography scan of the brain.
A CT scan of the brain using a contrast agent is called angiography. It allows you to most accurately examine pathological formations in the brain area. This research method has the following indications:
- Determination of the area of stenosis. Angiography allows you to determine the area of vascular narrowing, as well as the degree of stenosis.
- Diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms.
- Suspicion of ischemic stroke.
- Checking for vascular patency. Using tomography, obstruction is diagnosed due to thrombus formation or blockage of the lumen of the vessel by an embolus.
How to choose an examination technique?
Ultrasound does not require special conditions for placement of equipment. This is the easiest way to diagnose. The purchase and installation of devices for CT, MRI or PET require considerable costs. In this regard, not all medical institutions can afford to carry out such procedures. For this reason, prices for these types of diagnostics will be high.
However, the popularity of the equipment and the price of diagnostics should not be the determining factors. First of all, you need to follow the recommendations of your doctor. The scope of application of the examination method should also be taken into account:
- PET detects a tumor, including a malignant one, with absolute accuracy, long before its manifestation.
- MRI is most effective in neurosurgery and neurology.
- CT is useful in detecting vascular damage and head injuries.
- From the point of view of the absence of ionization and X-ray radiation, MRI is the safest procedure. However, modern equipment for radiography and ultrasound significantly reduces the risk of gene mutations.
It is important not to forget about contraindications. Thus, PET and CT scans are strictly prohibited for pregnant women. MRI is used for expectant mothers if the potential benefit to the woman is higher than the possible risk to the baby.
Children require special preparation for the procedure. Parents should allegorically explain to their children the need to lie still. The youngest require anesthesia.
Only the attending physician can determine the need for a particular diagnosis. In some cases, different types of scanning may be required at the same time.
Indications for CT scan of the head and neck
Computed tomography of the head carries a certain radiation load on the body, so scanning is recommended no more than 3 times a year for emergency indications.
The interval between studies should not be less than 4 weeks. For preventive purposes, experts do not recommend undergoing examination, as the X-ray load on the body increases. The main indications for CT of the head and neck are:
- dizziness and tinnitus, the causes of which have not been established;
- anomalies in the development of bone structures of the head, blood vessels;
- suspicion of the development of a hernia in the cervical spine;
- neck and head injuries;
- suspected tumors of the head and neck;
- headache;
- identifying dilation of blood vessels in the neck and head;
- signs of cerebrovascular insufficiency.
When contacting specialists at the Yusupov Hospital with these signs, patients receive advice on the scope of diagnostic measures to identify the causes of the pathology, after which they are sent for diagnosis.
Make an appointment
General and differences in alternative diagnostic methods
Alternative MRI methods include computed tomography, ultrasound diagnostics, angiography and x-rays. Computed tomography is the closest procedure. The main distinguishing features of MRI are:
- the clearest image in pictures in three-dimensional projection;
- no harm or radiation exposure to the patient’s body;
- there are no restrictions on the number of procedures, that is, this diagnostic method is perfect for monitoring the condition of the organ before surgery and in the postoperative period, as well as for assessing the impact of the prescribed treatment regimen;
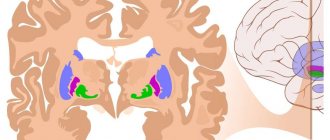
- MRI allows you to see those parts of the brain that are hidden by the bony structures of the skull, for example, the cerebellum (computed tomography does not make it possible to see it);
- the cost of MRI of the brain is significantly higher than the price of other types of examination.
Contraindications
Despite the well-tolerated procedure and its painlessness, computed tomography of the brain has some contraindications. These include:
- Pregnancy. Since the research method is based on the use of X-rays, there is a possibility of negative effects on the fetus. Carrying out a CT scan of the brain in a pregnant woman is justified only in cases of threat to her life.
- Excessively heavy weight. Obesity, in which weight reaches above 200 kg, is a limitation for performing computed tomography of the brain.
- Mental illnesses. During the CT scan, you must remain motionless. Mental illnesses accompanied by inadequate reactions make diagnosis difficult.
- Individual intolerance to the components of the contrast agent.
- The presence of severe renal or liver failure. This contraindication is due to the need to remove the contrast agent. In cases of insufficient liver or kidney function, excretion becomes difficult.
Carrying out the procedure
The procedure is carried out in a research room. The doctor conducting the study connects the electroencephalograph sensors to the amplifier and the patient's head. The electrodes are attached to the head using a special cap with built-in brain activity sensors. The patient is in a reclining position or sitting on a medical couch.
At the beginning of the study, the doctor may ask the patient to blink several times to determine the nature of the technical errors in the study. When performing resting encephalography, the patient is asked not to move during the examination. At the end of this stage of encephalography, encephalography is performed with stress tests (a study that allows us to identify the brain’s reaction to a stimulus). Load tests are of the following types:
- Photostimulation. The test is carried out using a special device - a stroboscopic light source. A light flash with a frequency of 20 times per second makes it possible to record brain reactions in patients predisposed to myoclonic seizures and epilepsy.
- Hyperventilation. During the study, the patient is asked to take deep breaths for 3-4 minutes, and then the brain's response to hyperventilation is recorded. The study is informative in patients predisposed to generalized seizures and absence seizures (a form of epileptic seizure).
When examining patients with epilepsy or patients suffering from sleep disorders, the doctor will prescribe electroencephalography of sleep. EEG sleep monitoring allows us to establish the cause of the disease and differentiate between epileptic and non-epileptic brain activity. Neurologists note that sleep electroencephalography is in some cases more informative than electroencephalography during wakefulness. With EEG sleep monitoring, an electroencephalogram is simultaneously taken and the patient's motor activity is recorded on video. The study can take from 6 hours to a day.
Upon completion of the electroencephalography, the specialist evaluates the result and issues a conclusion that describes the main rhythms and their compliance with the norm, and the brain’s reaction to functional tests. If there is epiactivity of the brain, its localization and the extent of the focus are indicated in conclusion.
Electroencephalography does not cause pain and is an absolutely safe test.
Preparation
No special preparation is required to perform a CT scan of the brain. If it is necessary to use a contrast agent, the last meal should be 5 hours before the examination. Before a CT scan of the brain, it is recommended to consult with your doctor about the need to stop taking medications during the study.
Progress of the study
The procedure for performing a CT scan of the brain consists of the following steps:
- The patient is placed on a conveyor.
- The head is fixed using special devices. This is necessary to ensure maximum immobility during the examination.
- After starting the tomograph, a series of images are taken, with the help of which a three-dimensional image of the brain is formed.
- Computed tomography is a painless diagnostic method. During the examination, the patient hears only clicks. This factor is eliminated with the help of earplugs.
- If contrast enhancement is necessary, a special substance is injected into the body. It stains the blood vessels, which allows for a more accurate diagnosis of the brain. The contrast agent may cause a metallic taste in the mouth, nausea, or headache. This must be reported to the doctor conducting the study.
On average, a CT scan of the brain takes from 30 minutes to an hour. The duration of the study depends on the type of diagnosis and the general condition of the patient. The results are deciphered immediately after the procedure. It takes about 1-1.5 hours depending on the complexity of the tomography.
MRI of the brain, how the procedure works
No preliminary preparation is required before the study. You must come to the procedure in loose clothing without metal accessories. Considering that magnetic fields damage credit cards, flash cards and mechanical watches, they need to be laid out in advance. It is advisable not to use cosmetics, as they may contain metal particles.
The patient is placed on a special movable table that slides inside a magnet. It is very important that the person lies still when the image is taken. The clicks that the magnet makes help you understand that shooting has begun.
The computer on which the images are received is located in the next office.
For greater comfort, the patient is offered headphones with pleasant music. The scanner is air conditioned and well lit.
Decoding the results
After the tomography, the doctor evaluates the resulting layer-by-layer images. The presence or absence of neoplasms, areas of hemorrhage or ischemia are taken into account, and brain structures are assessed. A computed tomography scan is considered normal if there are no signs of pathological neoplasms, brain structures are age-appropriate, there are no areas of fluid accumulation, and there are no violations of the integrity of bone tissue.
Any deviations from the norm are recorded in the conclusion and require further consultation with a specialist. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are deciphering all types of computed tomography of the brain. The latest equipment makes it possible to accurately determine the initial changes in the organ.
Advantages of each type of tomography
To decide between a brain MRI or a CT scan, you need to consider their purpose and benefits for a particular diagnosis, and also take into account the types of tissue that need to be studied.
Benefits of CT
Computed tomography is one of the most accurate ways to study disorders associated with the state of the brain. It is especially effective if it is necessary to identify abnormalities resulting from traumatic brain injury, as well as other problems with the bones and dense tissues of the skull.
This happens because X-rays are reflected in a special way from dense bone tissue. However, the radiation dose that the patient receives is much lower compared to other x-ray studies. In this way, various diseases can be diagnosed without the use of invasive methods, which makes the procedure painless.
Using CT, you can diagnose a stroke, arterial disorders due to atherosclerosis, changes in the structure of the cerebral cortex and lesions of the facial bones. It allows us to examine such disorders in great detail and identify the causes of diseases.
The procedure takes no more than fifteen minutes. There is no risk of distorting the result if the patient accidentally moves.
Patients suffering from claustrophobia can easily tolerate a CT scan because an open machine is used, in which only the head is immersed, and not the whole body.
It is important that the CT result can be seen immediately, although in some cases the image may not have enough contrast.
Benefits of MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is no less accurate than CT, but its scope is somewhat different. It allows you to diagnose diseases of the soft tissues of the brain and shows results in three planes:
- Axial (horizontal projection)
- Frontal (direct projection)
- Sagittal (lateral projection)
MRI allows you to very clearly see problems with soft tissues: benign and malignant (cancer) neoplasms (their shape, location and volume), dysfunction of the pituitary gland, nerve and muscle fibers. You can see and measure the volume of edema, tumors of the nervous system, and more. The bones will be displayed indirectly.
This method is safe, so it can be used to diagnose pregnant patients, but only in the second and third trimesters. It is also allowed to be used for diagnosing children from the age of three. It is necessary to explain to the child how the study will take place so that he is not afraid and tries not to move.
MRI can be done several times over a short period of time.
The procedure lasts about half an hour. During this period, the patient is required to lie still. Otherwise, the image may be distorted and the result may be unreliable or inaccurate.
For patients with a fear of closed spaces, the study can be carried out in a state of medicated sleep.
Price
The cost of a head and neck CT scan varies depending on the qualifications of the specialist, the equipment used and other factors, which include the administration of a contrast agent. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients have access to a wide range of diagnostic services, and also have the opportunity to undergo scanning with contrast.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital guarantee obtaining clear, high-quality images that will allow you to fully evaluate the area under study. If you need a head CT scan, there are many diagnostic centers in Moscow. However, services that meet European standards are provided at the Yusupov multidisciplinary hospital located on Nagornaya Street. If you need a specialist consultation for a head CT scan, please make an appointment by phone.
Make an appointment
In what cases is a CT scan prescribed, and in which MRI?
Because both types of examination rely on different physical and chemical phenomena, the effectiveness of each varies depending on the tissue being analyzed.
When a doctor prescribes a brain MRI or CT scan, he is guided by what exactly needs to be examined. Thus, CT is considered more effective in examining hard tissues, skull bones and their disorders, and MRI is considered more effective for analyzing soft tissues.
Main indications for CT scanning
The study is prescribed in the following cases:
- The patient suffered a traumatic brain injury
- Constant headaches after a stroke
- Pathological change in the bone tissue of the head
- Concussion diagnosed
- It is necessary to confirm or deny the presence of hemorrhage
- Brain structures have shifted
- There is a possibility of a foreign body
Main indications for MRI
Such a study is prescribed in the following cases:
- Suspicion of a tumor
- Regular headaches, dizziness, fainting
- The patient suffered a stroke
- Lost hearing or vision
- Injuries, hematomas and swelling
- Memory loss, problems concentrating
- Inability to perform CT
MRI is also prescribed to evaluate:
- Correctness of treatment
- State of the brain after detection of a malignant tumor
- Pre- and postoperative condition
Magnetic resonance imaging is recommended for a child if:
- He had pathologies during intrauterine development
- He lags behind his peers in various indicators
- The child suffers from convulsions, dizziness, loss of consciousness
- He stutters or has other speech problems