What is Morton's neuroma disease?
The tendency to develop foot pathology among modern patients is explained by the increased load on this anatomical formation. It consists of muscles, joints, ligaments, bones and the neurovascular system, which must function as a single system when a person performs various movements.
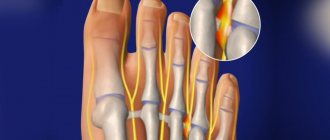
If the functionality of the foot is impaired, we can talk about Morton's neuroma, a disease characterized by the appearance of a benign formation between the tarsal phalanges of the third and fourth toes. This thickening is localized at the level of the nerve passage and has an elongated shape. On average, the width of an interdigital neuroma can reach 0.15-0.50 cm, and its length - 0.95-1.40 cm. In essence, this is one of the signs of tunnel syndrome of the interdigital nerve of the foot, which is one of the pathologies of the peripheral nervous system . The key factor provoking the disease is considered to be repeated microtraumas and compression disorders in the nerve area.
As a rule, women in the age group from 35 to 60 years are susceptible to this pathological process. Moreover, the formation is always localized on one foot.
Features of the course of the disease
Morton's neuroma is caused by pinching or damage to one of the plantar nerves. Typically, a unilateral lesion is at the level of the 3rd interdigital region, less often at the level of the 2nd and even less often at the 1st and 4th. According to statistics, women are much more susceptible to the disease.
Morton's neuroma is not a tumor of the nerve, but only a thickening of its sheath. Terms such as perineural fibrosis, plantar neuroma, metatarsalgia and intermetatarsal neuroma are also often used to refer to the disease.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
Causes of Morton's neuroma formation
In the development of foot neuroma, both endogenous factors and genetic causes are of key importance. The etiological factors involved in the formation of carpal tunnel syndrome include: excessive load on the front of the foot associated with frequent wearing of high-heeled/flat shoes or tight shoes; the presence of hematomas in the area where the nerve is located; flat feet; traumatic lesions of the feet (fractures, bruises); overweight; long walking; various pathological processes in the vascular area; infectious diseases; the presence of benign tumors in the foot area, etc.
Treatment
Non-surgical treatment
Non-surgical treatment can be quite effective, although it requires more time than surgical treatment.
Non-surgical treatment includes the following:
- wearing comfortable shoes
- use of a gel insert that reduces the load on the forefoot.
- reducing activity, which will reduce or eliminate those activities that increase pain. For example, avoid prolonged standing or other activities that place stress on the forefoot.
- local anesthesia can reduce inflammation associated with the nerve.
Steroid injections may temporarily reduce symptoms. Additionally, it was previously hypothesized that injecting alcohol into a nerve would cause controlled death of the nerve and subsequent resolution of symptoms. Currently, there are no successful scientific studies that would show the advantage of this procedure over other standard non-surgical procedures. Additionally, there are concerns that alcohol may cause excessive scarring and damage to other important structures in the area.
Symptoms of Morton's neuroma
Most often, with interdigital neuroma, the patient notes pain. Their intensity and nature are directly related to the size of the formation and its location. At the first signs of the disease, slight itching or a slightly noticeable tingling sensation occurs. Similar symptoms are observed after prolonged standing or increased physical activity. To eliminate discomfort, a night's rest is enough for the patient.
As tunnel neuropathy develops, the pain intensity increases and the toes begin to lose sensation. Over time, the patient indicates a feeling of discomfort in the area between the 3rd and 4th toes, which eliminates the possibility of wearing shoes comfortably.
In advanced stages, the pain syndrome becomes continuous and intense, a person’s gait changes, and other serious complications appear that can impair motor activity.
Clinical manifestations
The initial stages of the disease are characterized by small, mild pain that occurs as a result of mechanical compression of the area between the fingers. Depending on the degree of development of Morton's disease, the following symptoms appear:
- decreased sensitivity of those fingers whose innervating nerve was affected;
- paresthesia - so-called crawling;
- stabbing pain in the fingers as a result of physical activity;
- feeling of burning and/or bloating.
At later stages, a dense formation is determined in the affected area.
Diagnosis of Morton's neuroma
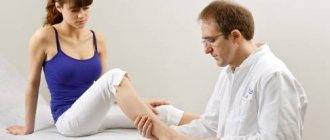
Morton's disease manifests itself against the background of inflammation, and not a malignant process in the tissues. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor asks the patient questions regarding the nature and moment of the onset of discomfort. During the appointment, the specialist examines the shape and outline of the foot, and also pays attention to the presence of anatomical changes. Next, he performs a frontal compression. If the patient notices increased pain in the midfoot area, this sign is characteristic of tunnel neuropathy.
In addition to examining the patient, the following diagnostic measures must be performed:
- X-ray. Allows you to identify the presence of various changes resulting from injury to the foot, as well as judge the development of degenerative processes and deformation of bone tissue;
- MRI is additionally prescribed . It is carried out if after the x-ray the doctor still has doubts about the diagnosis. Based on this method, it is possible to identify the presence of local compaction in the intermetatarsal region;
- Morton's neuroma can be diagnosed by ultrasound . At the same time, it is possible to monitor blood flow and the condition of soft tissues;
- Biopsy. Allows one to judge the presence of a formation under the ligament.
Make an appointment Online booking
- Clinic on Krasnopresnenskaya +7 (499) 252-41-35 Volkov lane, 21
- Clinic on Varshavskaya +7 (499) 610-02-09 Varshavskoe highway, 75, building 1
- Clinic in Annino +7 (495) 388-08-08 Varshavskoe highway, 154, building 1
How is diagnosis done?
Suitable for most patients, doctors work in the field of neurology, orthopedics and traumatology. To make a conclusion, the specialist will need to obtain reliable information about clinical complaints. One of the obvious symptoms of the presence of such an anomaly is a positive response during compression of the foot in the frontal position. The patient begins to experience an increase in pain and its transmission to the fingers that are affected by Morton's disease. In some situations, experts will write referrals for an examination using an X-ray device or CT scanner.
Doctors note that often such methods of checking the patient’s body do not bring results, since they do not provide information about the presence of a neuroma. In the case of an MRI scan, the disease presented appears as an odd region highlighting a high degree of signal. Such disease modeling may give false indications.
The most suitable way to check a patient in modern medicine is the use of an ultrasound machine. Instrumental diagnostic technologies also provide information about the presence of damaged areas, malignant and benign formations, as well as hematomas.
How to treat Morton's neuroma of the foot?
If a patient is diagnosed with Morton's neuroma, treatment begins with reducing the weight on the foot. This is required to slow down the destructive process and prevent pain. As a first step, experts advise purchasing more spacious shoes with heels up to 4 cm or starting to wear an orthopedic model.
Also, for Morton's neuroma, you can use orthopedic insoles , which allow you to restore the optimal position of the transverse arch of the foot. As an additional device, it is recommended to use special pad inserts, which are placed at the base of the metatarsal bones.
If a patient is diagnosed with Morton's neuroma, timely measures can achieve the following effects:
- Minimize the load on the front of the foot and restore the optimal position of the transverse arch;
- Reduce the pressure of ligaments and bones on the nerve;
- Restore biomechanical functions;
- Stop inflammation near the nerve.
Use of medications
In combination with the use of orthopedic devices, Morton's neuroma can be treated with medications:
- In case of a painful attack of increased intensity, the hormonal drug Diprospan or the potent painkiller Novocain are prescribed. The above medications must be used monthly;
- To relieve inflammatory manifestations and eliminate pain, steroid hormones from the subclass of corticosteroids are often prescribed, which are injected into the affected area;
- For pain of moderate intensity, it is recommended to use Baralgin, Nurofen and Ketoprofen;
- To eliminate muscle spasms, the muscle relaxants Mydocalm and Sirdalud are used.
To obtain a prolonged positive effect from the use of the above drugs, they must be used for at least three months.
Physiotherapy for Morton's disease
For Morton's neuroma, additional treatment involving the use of physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed. Due to this, it is possible to increase the effectiveness of the use of drugs, as well as improve metabolic processes in the affected area.
So, for tunnel neuropathy, it is advisable to perform the following procedures:
- Effect on the body of an alternating magnetic field;
- Exposure to shock waves;
- The use of needles inserted into acupuncture points;
- Exposure of the body to direct electric current simultaneously with the introduction of special medicinal compounds through the skin;
- Massotherapy. It is carried out starting from the ankle and ending with the fingertips.
In some situations, there are restrictions on the use of physiotherapeutic methods. These include:
- Presence of wounds on the skin;
- Pustular skin lesions;
- Pathologies of the circulatory system;
- Formations of a malignant nature;
- Cardiovascular failure.
Use of shockwave therapy for Morton's neuroma
As stated earlier, treatment of Morton's neuroma in Moscow begins with the use of special orthopedic devices. These include insoles, which play a key role in Morton's neuroma, as they allow you to restore the optimal position of the transverse arch of the foot. The patient is also recommended to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, injections with steroid hormones, and painkillers.
If conservative methods do not give the desired effect, experts recommend removing Morton's neuroma. However, not all patients with this pathology undergo surgical intervention.
A more gentle and effective way to eliminate the disease is considered to be the SWT , which gives an excellent effect for Morton's neuroma - it improves blood flow in the affected area.
The technique is based on the use of shock waves that affect the nerve trunk. This provides the necessary analgesic effect, helps eliminate the inflammatory process and helps normalize restoration processes in tissues.
The advantages of the procedure also include:
- Increased comfort for the patient;
- Safety;
- Non-invasive nature;
- Quickly achieve the desired result.
In our medical]SWT[/anchor] technique is a priority way to eliminate neuroma. The use of innovative Swiss equipment, an individual approach to the problem and the high professionalism of doctors make it possible to obtain maximum efficiency in its implementation.
Removal of Morton's neuroma
If there is no positive result from conservative methods, the doctor refers the patient to surgery.
Today, the following methods are known for surgical removal of compaction in the area of the frontal part of the foot. These include:
- Resection of the formation. In this case, a small incision is made in the intermetatarsal area and the seal is completely removed. After this, suturing is performed. At the same time, there is no need to implement measures to ensure foot immobility;
- Dissection. It is considered more gentle. In this method, the affected ligament is divided into fibers, which eliminates nerve compression;
- Using a surgical laser. This procedure is famous for its low trauma and does not limit the patient’s motor activity in the future;
- Radiofrequency catheter ablation. The method is minimally invasive. For Morton's neuroma, it is carried out in combination with ultrasound diagnostics . In this case, the seal is destroyed when exposed to electric current;
- Shift of the fourth metatarsal bone. Performed in isolated situations. Using a similar procedure, it is possible to eliminate compression of the nerve. If a patient is diagnosed with Morton's neuroma, bone displacement surgery and subsequent rehabilitation are carried out under x-ray guidance.
By contacting us about seal removal, you will receive a guarantee of a safe and accurate surgical intervention, as well as quick and easy rehabilitation after it. This is due to the presence of highly qualified surgeons in the state, who have hundreds of similar operations behind them.
Treatment of Morton's neuroma with traditional methods at home
Despite the proven effectiveness of the above methods for Morton's neuroma, many patients are interested in how to treat the pathology at home . Their effectiveness with the right approach has also been confirmed. But resorting to these methods is recommended in exceptional situations, with mild forms of the disease. Below we will talk about the most effective of them:
- A bandage on the sore spot, moistened with an infusion of wormwood;
- Burdock root infusion;
- Kalanchoe juice;
- Flax seed infusion;
- A cabbage leaf that is applied to the affected area;
- Dress with an ointment made from lard and baking soda;
- Compress with ointment obtained from laurel leaves (2 tablespoons), pine needles (1 tablespoon) and butter (50 g);
- A bandage soaked in a mixture of sunflower oil, mustard and honey.
With the right approach, the above remedies can be quite effective.
Make an appointment Online booking
- Clinic on Krasnopresnenskaya +7 (499) 252-41-35 Volkov lane, 21
- Clinic on Varshavskaya +7 (499) 610-02-09 Varshavskoe highway, 75, building 1
- Clinic in Annino +7 (495) 388-08-08 Varshavskoe highway, 154, building 1
Features of diagnosing and treating the disease
To diagnose neuromas, use:
- X-ray. It is used to exclude other foot pathologies that have similar clinical manifestations. For example, a stress fracture.
- MRI.
- Ultrasound
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the severity of symptoms. Most often, conservative treatment is sufficient, including the use of arch supports, orthopedic pads and insoles, which reduce pressure on the affected nerve and improve shock absorption of the entire foot. The patient is prescribed ongoing physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as injections of corticosteroids and analgesics.
If there is no adequate effect from conservative treatment, surgical intervention is indicated. The operations are performed using local anesthesia. There are two main types of impact:
- Nerve removal. A radical approach that is used when other methods are ineffective. There is a high risk of loss of sensation in the affected area even if the operation is successful.
- Neuroma ablation. This is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure - an alternative solution to surgical intervention. It involves burning out the neuroma using temperature.
For the purpose of prevention, it is recommended to replace shoes with more comfortable ones, monitor the condition of the feet and promptly treat flat feet and other associated diseases. This group includes diabetes mellitus, chronic infections and obliterating atherosclerosis.
Prevention measures
There are no specific recommendations for preventing the disease. As a preventative measure, it is enough to follow simple rules that will prevent the development of neuroma:
- From an early age, increased stress on the legs should be avoided: do not carry heavy objects, avoid prolonged standing, and often change position during the work process;
- Buy shoes taking into account the anatomy of the foot. At the same time, the presence of a small heel cannot be ruled out - to preserve the arch of the bones;
- Learn how to give a relaxing massage. It should be performed daily when pain occurs;
- Bring your weight back to normal. Excess body weight significantly increases the load on the lower limbs;
- Order orthopedic insoles taking into account the anatomical features of the foot. As mentioned above, such devices are designed to minimize the load on the metatarsal bones;
- Timely contact with a specialist. An experienced doctor will see Morton's neuroma immediately on an x-ray and give recommendations on how to treat this pathology.
How does it manifest itself?
This disease provokes pain in the distal zones of the foot, in particular in the 3rd-4th toe. The manifestation of pain has a burning nature, and at some points it is distinguished by certain lumbago. Many patients report to their doctor about unpleasant discomfort and a constant feeling of a foreign object inside the shoe, although it is not observed there. At the first stage of pathology formation, pain is quite closely associated with wearing shoes. People suffering from the described illness say that they experience positive emotions after its removal. Over time, various problems may disappear and then arise again.
In the event of a complete refusal of qualified medical care, the neuroma begins to develop, which leads to an ongoing pain syndrome, which increases when wearing absolutely any products, and when getting rid of them, the level only decreases. In the following days, a distinct numbness appears in the limbs. Often, most patients visit a specialist’s office already at critical stages of the disease, when standard treatment does not help to get rid of it.
Undesirable consequences of Morton's disease
If a visit to a specialist is delayed or if the orthopedic surgeon’s orders are not followed, the pathological process can provoke the following negative manifestations:
- Pain syndrome of significant intensity, which cannot be relieved even with the help of potent analgesics;
- The appearance of lameness;
- Inability to use stylish modern shoes;
- Scoliosis;
- Mental disorders and depressive conditions.
Types of insoles
All orthopedic insoles differ in purpose and materials of manufacture. They can be:
Serial (non-individual) - produced according to standard parameters, may differ in size, materials, functions. Such orthopedic insoles are prescribed for flat feet in the initial stages or minor pathologies of the foot.
Individual - orthopedic insoles, custom-made for the patient according to his parameters. Suitable for cases where a special approach to correcting the position of the foot is required.
A prescription for serial or custom orthopedic insoles is given by an orthopedic doctor after examining the condition of the feet. Only a competent specialist can choose the right insoles that will be most effective.
There is also a division according to the materials used to make orthopedic insoles:
- Rigid insoles made of plastic, steel, graphite. Indicated for people who are obese and have mild deformities.
- Semi-rigid with plastic instep supports. They provide good arch support.
- Soft insoles with foam insoles. Intended for people suffering from diabetes and other pathologies that lead to the appearance of calluses, corns and trophic ulcers.
The main fabric of the insole can be made of leather, cork, leatherette, and other materials that can adapt to the physiological curves of the foot.
Recovery prognosis
The prognosis is quite favorable. If there is no result from the use of conservative methods, complications can be prevented by removing Morton's neuroma with a laser. This helps prevent further loss of foot function and complete loss of motor activity.
If the patient turns to a specialist at the initial manifestations of the disease, it will be possible to stop the inflammation through physiotherapeutic methods and medications. In the absence of timely treatment measures, this is fraught with serious complications. The affected area expands, and painful attacks become longer and more intense. In advanced stages of the disease, Morton's neuroma can only be treated through surgery, which is confirmed by reviews.
Tests and diagnostics
Clinical diagnosis of neuroma is simple and is based on the presence of pain in a characteristic localization. The presence of sensory disorders is confirmed by neural damage. Regression of the pain syndrome after a therapeutic and diagnostic blockade of the intermetatarsal nerve with a local anesthetic is also a sign of neuroma.
Of the instrumental methods, ultrasound examination of the structures of the foot has the greatest diagnostic value. Also, to clarify the diagnosis, an x-ray of the foot, MRI and CT may be prescribed.
1) and 2) Sonogram of the right/left foot of the 3rd intermetatarsal space. 3) and 5) MRI of Morton's neuroma of the right foot. 4) and 6) MRI of Morton's neuroma of the left foot.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with arthritis of the metatarsophalangeal joints , synovitis of the metatarsophalangeal joint , stress fractures of the metatarsal bones , osteonecrosis of the heads of the metatarsal bones , as well as malignant bone lesions and diseases of the lumbar spinal column with pain radiating to the intermetatarsal spaces.